Dry Type Transformer Cooling Explained: AN vs AF and Advanced Methods| CHBEB
Choosing the right cooling method for your dry-type transformer directly impacts efficiency1, lifespan, and maintenance costs. The three main systems—AN (Air Natural), AF (Air Forced), and ANAF (hybrid)—each have clear advantages depending on your project’s load, environment, and budget. This guide explains how they work, compares their performance, and helps you select the most cost-effective solution for long-term reliability.
Are you struggling to choose the right cooling method for your dry-type transformer? Many engineers find this decision challenging, but understanding your options can lead to optimal performance and longevity.
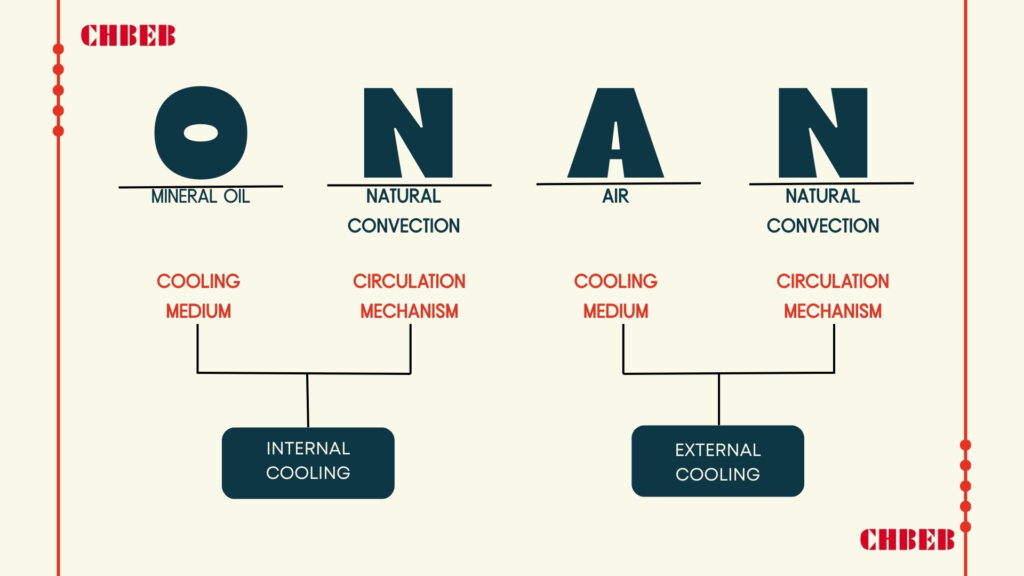
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various cooling methods for dry-type transformers, from basic natural air cooling to advanced hybrid systems. Whether you’re designing a new electrical system or upgrading an existing one, this article will help you make an informed decision about the best cooling method for your transformer.
Why Cooling Efficiency Matters for Transformer Lifespan & Cost
Proper cooling is crucial for the performance and longevity of dry-type transformers. Without effective heat dissipation, transformers can suffer from reduced efficiency, shortened lifespan, and potential failure.
Cooling systems in dry-type transformers manage heat generated during operation. Effective cooling prevents insulation degradation2, maintains efficiency, and extends service life. The choice of cooling method impacts performance, installation options, maintenance needs, and safety compliance.
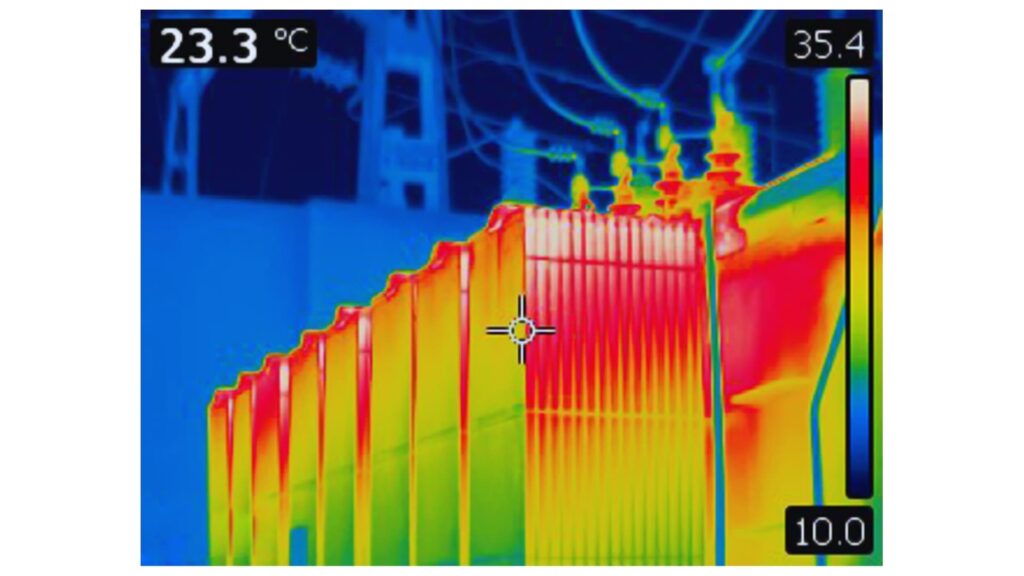
Overheating Transformer Thermal Image
Key Factors Influenced by Cooling Efficiency
- Operational Performance
- Transformer Lifespan
- Installation Flexibility
- Maintenance Requirements
- Safety and Compliance
Impact on Performance and Lifespan
Effective cooling systems:
- Maintain optimal operating temperature
- Prevent hotspots in windings
- Ensure consistent performance under varying loads
💡 Project Insight: In a recent data center upgrade, replacing an undersized cooling system increased transformer efficiency by 15% and extended its projected lifespan by a decade.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
The choice of cooling method affects:
- Space requirements for installation
- Noise levels in the surrounding area
- Maintenance schedules and costs
🔍 Field Example: For a remote industrial site, we chose AN cooling despite its lower capacity because the minimal maintenance requirements were crucial for the location’s limited access.
AN Cooling Explained – How Air Natural Systems Work
AN (Air Natural) cooling is the most basic method for dry-type transformers, relying on passive airflow for heat dissipation.
AN cooling uses natural convection to dissipate heat. Hot air rises from the transformer, creating airflow that cools the unit. This method is ideal for indoor environments with low to medium loads, offering silent operation and minimal maintenance.

AN Cooling Air Flow Diagram
Key Features of AN Cooling
- No fans or moving parts
- Silent operation
- Minimal maintenance requirements
- Suitable for clean, indoor environments
Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Silent operation | Limited cooling capacity |
| Low maintenance | Not suitable for high ambient temperatures |
| Lower initial cost | Requires adequate space for air circulation |
💡 Project Insight: In a multi-story office complex, we installed AN-cooled transformers on each floor. The absence of fans meant zero noise pollution, crucial for the working environment.
AF Cooling Guide – When to Choose Air Forced Systems
AF (Air Forced) cooling enhances heat dissipation in dry-type transformers through the use of fans.
AF cooling uses fans to force air over windings, boosting heat removal for higher load capacity. This method is ideal for compact installations or environments with higher ambient temperatures.

AF Cooling System Diagram
Key Features of AF Cooling
- Active air circulation via fans
- Higher cooling capacity than AN systems
- Ability to handle greater loads and power densities
- Adaptable to varying load conditions
Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Higher cooling capacity | Requires regular maintenance |
| Compact installation possible | Generates operational noise |
| Handles variable loads | Higher energy consumption |
🔍 Field Example: In a manufacturing plant upgrade, replacing AN-cooled transformers with AF units allowed for a 30% increase in production equipment without expanding the electrical room.
Advanced Cooling Systems for Dry Type Transformers (ANAF, ANCF, PCM)
Advanced cooling methods combine the benefits of different approaches to meet complex transformer needs.
ANAF (Air Natural, Air Forced) and ANCF (Air Natural, Closed-loop Forced) are hybrid cooling systems. ANAF switches between passive and active cooling based on load, while ANCF uses sealed air channels for harsh environments. These methods offer enhanced performance and adaptability.
Types of Advanced Cooling Systems
- ANAF (Air Natural, Air Forced)
- ANCF (Air Natural, Closed-loop Forced)
- Heat pipe assisted cooling
- Phase change material (PCM) integration
Advantages of Advanced Cooling Methods
- Adaptability to varying load conditions
- Enhanced protection in harsh environments
- Improved energy efficiency
- Extended transformer lifespan
💡 Project Insight: For a coastal industrial facility, we implemented an ANCF system to protect against corrosive sea air. This solution increased reliability and reduced maintenance costs significantly.
AN vs AF vs ANAF – Comparative Cooling Performance Chart
Choosing the right cooling method requires understanding the key differences between systems.
| Feature | AN (Air Natural) | AF (Air Forced) | ANAF (Air Natural, Air Forced) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Passive airflow | Fan-assisted airflow | Hybrid (passive + active) |
| Cooling Efficiency | Low to Moderate | High | Very High |
| Noise Level | Silent | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Maintenance | Very low | Medium | Medium to High |
| Load Capacity | Low to Medium | High | Very High |
| Ideal Application | Indoor, low load | Industrial, mid-load | Variable load, harsh conditions |
How to Select the Right Transformer Cooling System for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate cooling system is crucial for optimal transformer performance.
Cooling System Selection Checklist
Before choosing a cooling system, evaluate these key parameters for your project:
Checklist for Cooling Selection:
- ✅ Installation environment (indoor/outdoor)
- ✅ Load profile (stable/variable)
- ✅ Ambient conditions (temperature, humidity, contaminants)
- ✅ Noise restrictions
- ✅ Maintenance capabilities
- ✅ Energy efficiency requirements
- ✅ Budget constraints
Decision Matrix for Cooling System Selection
| Factor | Favors AN | Favors AF | Favors ANAF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | Indoor, clean | Outdoor, variable | Harsh, contaminated |
| Load | Stable, low to medium | High, consistent | Variable, high peaks |
| Noise Concern | High | Low | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Minimal available | Regular possible | Specialized available |
💡 Project Insight: For a data center with variable loads and high efficiency requirements, we chose an ANAF system over standard AF. This decision improved cooling performance and resulted in substantial energy savings over time.
From Thermal Risk to Reliable Operation: How CHBEB Solves Dry-Type Pain Points

Real-world dry-type (cast-resin) performance lives or dies on thermal control, installation environment, and the reliability of auxiliary cooling (AN/AF). When fans underperform, ventilation is constrained, or F-class limits (e.g., 60 K temperature rise per GB/T 10228) are exceeded, the result is trips, accelerated insulation aging, and unpredictable lifecycle costs.
What Customers Struggle With → How CHBEB Addresses It
- Unplanned downtime from thermal trips
We design for thermal resilience: optimized ducting, verified airflow paths, and AF packages sized to site conditions—plus optional fan redundancy and alarms to prevent single-point failures. - Reliability uncertainty (insulation aging hard to predict)
We offer condition-based options: winding temperature probes, hotspot estimation, trend logs, and gateway-ready outputs for RUL-style monitoring—turning raw data into actionable maintenance windows. - High TCO from maintenance & certified labor constraints
Service-friendly enclosures place fans, filters, and controls on modular rails for fast swap-outs, cutting service time and reducing specialized labor on site.
Why CHBEB?
- 60+ years manufacturing; two Wenzhou plants + Nanjing plant; Beijing office.
- 100% new, high-grade materials; full-load and routine tests before shipment.
- Compliance-ready (IEC/GB) with documentation to support local approvals.
- Fast delivery (expedited builds) and custom inventory plans for multi-site rollouts.
Plan Your Dry-Type Project with Confidence
Share your kVA, ambient, enclosure, and cooling constraints. We’ll return a specification and TCO view that balances efficiency, uptime, and compliance.
Contact CHBEB for a tailored recommendation
Conclusion: Cooling Efficiency Determines Performance
Choosing the right cooling method for dry-type transformers is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. AN, AF, and ANAF systems each have their strengths for different applications. Consider environmental factors, load profiles, and maintenance capabilities when selecting. The right cooling system ensures efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in your transformer operations.
- Transformer – Cooling and Efficiency. Wikipedia ↩︎
- Insulation Degradation in Dry-Type Transformers. IEEE Xplore ↩︎
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


