Pad Mounted Transformers: The Hidden Heroes of Power Distribution?
Have you ever wondered how electricity reaches your home safely and efficiently? The answer might be hiding in plain sight. Pad mounted transformers are the unsung heroes of our power distribution system, working tirelessly behind the scenes.
Pad mounted transformers are compact, ground-level electrical distribution devices that convert high-voltage electricity to lower voltages suitable for homes and businesses. These hidden powerhouses are essential for safe, reliable, and efficient power distribution in urban and suburban areas, blending seamlessly into our surroundings.

As an electrical engineer with over two decades of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how pad mounted transformers have revolutionized power distribution. Their impact on our daily lives is profound, yet they often go unnoticed. Let’s dive into the world of these hidden heroes and discover why they’re so crucial to our modern power infrastructure.
What is a Pad Mounted Transformer?
Have you ever noticed those green boxes in your neighborhood? They’re not just for decoration. These unassuming structures house powerful electrical equipment that keeps your lights on and your devices running.
A pad mounted transformer is a ground-level electrical distribution device enclosed in a locked, metal cabinet. It’s mounted on a concrete pad, hence the name. These transformers convert high-voltage electricity from utility power lines to lower voltages suitable for use in homes and businesses.
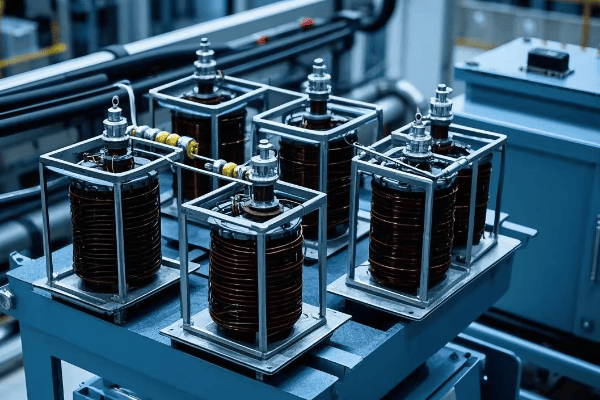
Let’s break down the key components and functions of a pad mounted transformer:
Core Components
-
Transformer Core and Windings:
- Heart of the transformer
- Converts voltage levels through electromagnetic induction
- Made of high-grade electrical steel and copper or aluminum windings
-
Insulating Oil:
- Cools and insulates the core and windings
- Helps prevent electrical arcing
- Often contains additives to improve performance and longevity
-
Bushings:
- Connect the transformer to incoming and outgoing power lines
- Provide insulation where conductors enter the transformer tank
-
Tank and Cabinet:
- Houses all internal components
- Provides weather protection and security
- Often painted green to blend with surroundings
In my early career, I worked on a project to upgrade an older neighborhood’s power distribution. We replaced overhead transformers with pad mounted units. The difference was striking – not only did it improve the area’s aesthetics, but it also significantly reduced power outages during storms.
Comparison of Pad Mounted vs. Pole Mounted Transformers:
| Feature | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Ground level | Elevated on poles |
| Accessibility | Easy for maintenance | Requires bucket truck |
| Aesthetics | Blends with surroundings | More visible |
| Weather Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Safety | Locked enclosure | Exposed components |
| Capacity | Typically larger | Usually smaller |
Key Features of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Are you curious about what makes pad mounted transformers so special? These compact powerhouses pack a punch when it comes to features. Let’s explore what sets them apart from other transformer types.
Pad mounted transformers boast several key features: compact design, enhanced safety through locked enclosures, improved aesthetics, weather resistance, and versatility in power distribution. These features make them ideal for urban and suburban settings where space is at a premium and visual appeal is important.
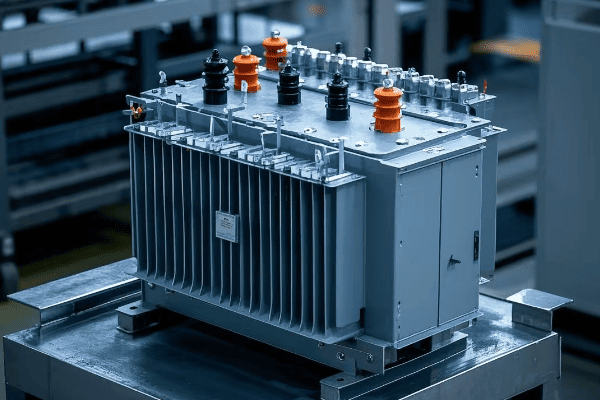
Let’s dive deeper into these features and understand why they’re so important:
Design and Safety Features
-
Compact Design:
- Smaller footprint compared to pole-mounted transformers
- Allows for installation in tight spaces
- Ideal for urban and suburban environments
-
Enhanced Safety:
- Locked metal enclosure prevents unauthorized access
- "Dead-front" design eliminates exposed live parts
- Reduces risk of electrical accidents
-
Weather Resistance:
- Sealed construction protects against rain, snow, and dust
- Can withstand extreme temperatures
- Reduces weather-related outages
-
Improved Aesthetics:
- Low profile blends with landscaping
- Often painted green to match surroundings
- Reduces visual clutter compared to overhead lines
I once worked on a project in a historic district where overhead lines were not permitted. Pad mounted transformers were the perfect solution. Their low profile and ability to blend with the surroundings allowed us to provide modern power distribution without compromising the area’s historic charm.
Feature Comparison Table:
| Feature | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted | Underground Vault |
|---|---|---|---|
| Footprint | Small | Minimal ground space | Large underground |
| Visual Impact | Low | High | Minimal |
| Accessibility | Easy | Difficult | Very Difficult |
| Safety | High | Moderate | High |
| Weather Protection | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Maintenance Ease | High | Moderate | Low |
Safety Aspects of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Worried about the safety of having a transformer in your neighborhood? You’re not alone. Many people have concerns about electrical equipment near their homes. But pad mounted transformers are designed with safety as a top priority.
Pad mounted transformers incorporate multiple safety features to protect both the public and maintenance workers. These include locked enclosures, dead-front design, internal fuses, and protective relays. The goal is to prevent unauthorized access and minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
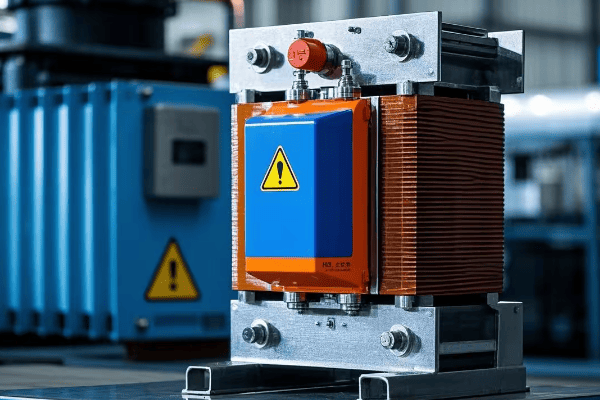
Let’s explore the safety aspects of pad mounted transformers in more detail:
Multi-layered Safety Approach
-
Physical Barriers:
- Locked metal enclosure prevents unauthorized access
- Tamper-resistant hinges and locks
- Warning signs to deter interference
-
Electrical Safety Design:
- Dead-front construction eliminates exposed live parts
- Insulated bushings and cables
- Grounding and bonding to prevent shock hazards
-
Protective Devices:
- Internal fuses to interrupt current in case of faults
- Protective relays to detect abnormal conditions
- Pressure relief devices to prevent tank rupture
-
Maintenance Safety:
- Visible disconnect switches for worker safety
- Oil containment systems to prevent environmental contamination
- Clear labeling of components and hazards
In my years of experience, I’ve seen the evolution of transformer safety. Modern pad mounted transformers are leagues ahead of their predecessors. I recall an incident early in my career where a curious child managed to open an older, poorly secured transformer cabinet. It led to a community-wide initiative to upgrade all transformers with enhanced safety features. Since then, I’ve been a strong advocate for regular safety audits and upgrades.
Safety Feature Effectiveness:
| Safety Feature | Purpose | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Locked Enclosure | Prevent unauthorized access | High |
| Dead-front Design | Eliminate exposed live parts | Very High |
| Internal Fuses | Interrupt fault currents | High |
| Protective Relays | Detect abnormal conditions | Very High |
| Visible Disconnects | Ensure safe maintenance | High |
| Warning Signs | Deter interference | Moderate |
| Grounding | Prevent shock hazards | Very High |
Types and Configurations of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Ever wondered why some pad mounted transformers look different from others? It’s not just about aesthetics. The type and configuration of a pad mounted transformer can significantly impact its performance and application.
Pad mounted transformers come in various types and configurations to suit different power distribution needs. These include single-phase and three-phase designs, loop feed and radial feed configurations, and different kVA ratings. The choice depends on factors like load requirements, system reliability, and future expansion plans.
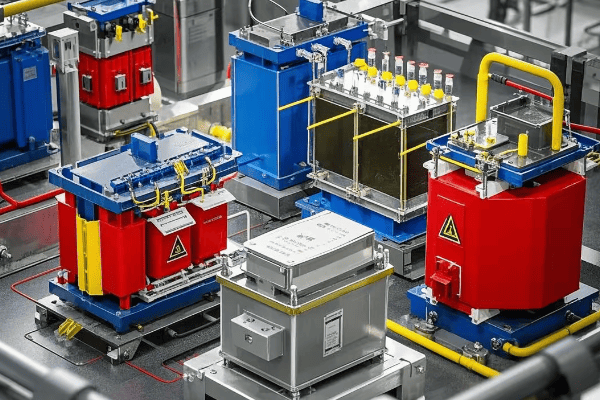
Let’s explore the different types and configurations in more detail:
Diverse Designs for Diverse Needs
-
Phase Configuration:
- Single-phase: For residential and light commercial use
- Three-phase: For industrial and heavy commercial applications
-
Feed Configuration:
- Loop feed: Allows for redundant power supply
- Radial feed: Simpler design for end-of-line applications
-
kVA Ratings:
- Range from 25 kVA to 5000 kVA
- Chosen based on load requirements and future growth
-
Voltage Classes:
- Distribution class: Typically 5 kV to 35 kV
- Sub-transmission class: Up to 69 kV
I once worked on a project for a new industrial park. We had to carefully consider the mix of businesses and their power needs. We ended up using a combination of three-phase loop feed transformers for the larger factories and single-phase radial feed units for smaller offices. This flexible approach allowed us to meet diverse power needs while maintaining system reliability.
Transformer Configuration Comparison:
| Configuration | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-phase | Lower cost, Simpler design | Limited capacity | Residential, Small commercial |
| Three-phase | Higher capacity, Efficient for motor loads | More complex, Higher cost | Industrial, Large commercial |
| Loop feed | Improved reliability, Easier maintenance | More expensive, Complex switching | Critical loads, Urban areas |
| Radial feed | Simpler, Lower cost | Less reliable | Rural areas, End-of-line loads |
Applications of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Curious about where you might find pad mounted transformers in action? These versatile devices are more common than you might think. From residential neighborhoods to industrial complexes, pad mounted transformers play a crucial role in power distribution.
Pad mounted transformers find applications in various settings including residential subdivisions, commercial centers, industrial parks, and institutional campuses. They’re ideal for areas where overhead lines are impractical or undesirable, providing a safe and aesthetically pleasing solution for power distribution.
Let’s explore some specific applications and why pad mounted transformers are chosen for these scenarios:
Versatile Solutions for Diverse Settings
-
Residential Areas:
- Underground power distribution in new subdivisions
- Retrofit projects to replace overhead lines
- Ideal for areas with high aesthetic standards or severe weather
-
Commercial Centers:
- Shopping malls and office complexes
- Hotels and resorts
- Provides reliable power without visual clutter
-
Industrial Parks:
- Manufacturing facilities
- Warehouses and distribution centers
- Handles high power demands and motor loads efficiently
-
Institutional Campuses:
- Universities and schools
- Hospitals and medical centers
- Government facilities
-
Renewable Energy Integration:
- Solar farms
- Wind power installations
- Helps step up voltage for grid connection
I once worked on a project to upgrade the power distribution system for a large university campus. We replaced numerous pole-mounted transformers with strategically placed pad mounted units. This not only improved the campus aesthetics but also significantly enhanced the reliability of the power supply. During a severe storm the following year, the campus maintained power while surrounding areas experienced outages.
Application-Specific Benefits:
| Application | Key Benefits of Pad Mounted Transformers |
|---|---|
| Residential | Improved aesthetics, Increased property values |
| Commercial | Reliable power, Space-saving design |
| Industrial | High capacity, Customizable configurations |
| Institutional | Enhanced safety, Minimal visual impact |
| Renewable Energy | Flexible installation, Scalable capacity |
Advantages of Using Pad Mounted Transformers?
Wondering why pad mounted transformers are becoming increasingly popular? It’s not just a trend. These compact power distribution units offer several compelling advantages over traditional transformer types.
Pad mounted transformers offer numerous advantages including improved safety, better aesthetics, increased reliability, easier maintenance, and flexibility in installation. They’re particularly beneficial in urban and suburban settings where space is limited and visual appeal is important.
Let’s delve deeper into these advantages and understand why they make pad mounted transformers an attractive choice:
Compelling Benefits for Modern Power Distribution
-
Enhanced Safety:
- Locked enclosures prevent unauthorized access
- No climbing required for maintenance, unlike pole-mounted units
- Reduced risk of vehicle collisions compared to pole-mounted transformers
-
Improved Aesthetics:
- Low profile design blends with surroundings
- Eliminates unsightly overhead lines
- Can be easily concealed with landscaping
-
Increased Reliability:
- Protected from weather-related damage
- Less susceptible to wildlife interference
- Reduced outages due to vehicle collisions
-
Easier Maintenance:
- Ground-level access simplifies inspections and repairs
- No need for bucket trucks or climbing equipment
- Safer working conditions for maintenance crews
-
Flexibility in Installation:
- Can be installed in areas unsuitable for overhead lines
- Ideal for underground distribution systems
- Easily scalable for growing power needs
In my career, I’ve overseen numerous projects transitioning from overhead to underground distribution using pad mounted transformers. One particularly memorable project was in a coastal town prone to hurricanes. By replacing the overhead system with pad mounted transformers and underground lines, we reduced storm-related outages by over 70% in the first year alone.
Comparative Advantages:
| Aspect | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted | Underground Vault |
|---|---|---|---|
| Safety | High | Moderate | High |
| Aesthetics | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Reliability | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Maintenance Ease | High | Low | Moderate |
| Installation Flexibility | High | Moderate | Low |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate | High | Low |
| Scalability | High | Moderate | Low |
Design Considerations for Pad Mounted Transformers?
Ever wondered what goes into designing a pad mounted transformer? It’s not as simple as it looks. Engineers must consider a multitude of factors to ensure these units perform efficiently, safely, and reliably.
Designing pad mounted transformers involves careful consideration of factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, safety standards, and aesthetic concerns. Engineers must balance electrical performance with physical constraints, ensuring the transformer meets both technical specifications and practical installation needs.
Let’s explore the key design considerations in more detail:
Balancing Performance, Safety, and Practicality
-
Electrical Design:
- Voltage ratings (primary and secondary)
- kVA capacity
- Impedance
- Efficiency and losses
- Insulation levels
-
Thermal Management:
- Cooling system design (ONAN, ONAF, etc.)
- Temperature rise limits
- Hot spot calculations
-
Mechanical Design:
- Tank strength and rigidity
- Seismic considerations
- Transportation and handling requirements
-
Safety Features:
- Dead-front design
- Interlocking mechanisms
- Pressure relief devices
-
Environmental Considerations:
- Noise levels
- Oil containment
- Corrosion resistance
-
Aesthetics and Size:
- Compact design
- Color and finish options
- Landscaping compatibility
In my experience, one of the most challenging aspects of designing pad mounted transformers is balancing all these factors. I recall a project where we needed to design a high-capacity transformer for a densely populated urban area. We had to innovate to meet the power requirements while keeping the unit compact and quiet enough to satisfy local regulations.
Design Trade-offs:
| Design Aspect | Consideration | Potential Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Higher kVA rating | Larger size, Higher cost |
| Cooling | Better heat dissipation | Increased noise, Larger size |
| Safety | More safety features | Higher cost, Complexity |
| Aesthetics | Improved appearance | Limited design options |
| Environmental | Lower noise, Oil containment | Higher cost, Larger size |
| Maintenance | Easier access | Potential security concerns |
Installation and Maintenance of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Curious about what it takes to install and maintain a pad mounted transformer? It’s not just a matter of dropping a box on a concrete pad. Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring long-term reliability and safety.
Installing pad mounted transformers requires careful site preparation, proper handling, and precise electrical connections. Ongoing maintenance involves regular inspections, oil testing, and occasional repairs or upgrades. Both installationInstalling pad mounted transformers requires careful site preparation, proper handling, and precise electrical connections. Ongoing maintenance involves regular inspections, oil testing, and occasional repairs or upgrades. Both installation and maintenance must adhere to strict safety protocols and industry standards.**
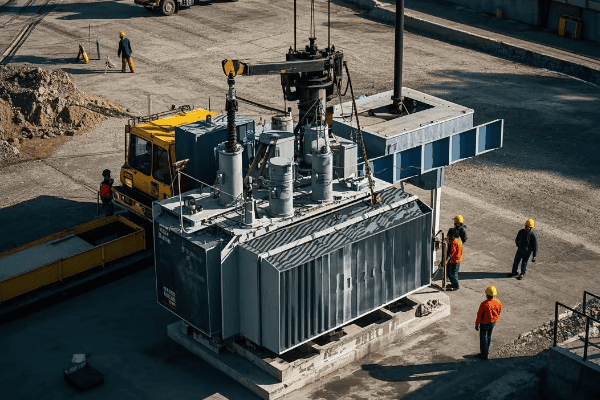
Let’s dive deeper into the installation and maintenance processes:
From Installation to Long-Term Care
-
Installation Process:
- Site preparation (grading, concrete pad installation)
- Transformer placement (usually requires a crane)
- Electrical connections (primary and secondary)
- Grounding and bonding
- Testing and commissioning
-
Regular Maintenance:
- Visual inspections (monthly or quarterly)
- Oil level checks and top-ups
- Insulation resistance tests
- Thermal imaging for hotspot detection
- Cleaning and rust prevention
-
Periodic Maintenance:
- Oil quality testing (annually)
- Bushing inspections and cleaning
- Protective device testing
- Repainting (as needed)
-
Emergency Maintenance:
- Fault diagnosis and repair
- Oil leak containment and repair
- Overload damage assessment and repair
In my career, I’ve overseen countless installations and maintenance operations. One particularly memorable project involved retrofitting an old industrial site with new pad mounted transformers. We had to carefully coordinate the installation to minimize downtime. The precision required during the placement and connection phase was crucial – a misalignment of just a few inches could have caused significant issues down the line.
Maintenance Schedule and Costs:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Estimated Cost | Impact of Neglect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Low | Early problem detection |
| Oil Testing | Annually | Moderate | Prevent insulation failure |
| Thermal Imaging | Bi-annually | Moderate | Identify hotspots early |
| Full Service | Every 3-5 years | High | Extend transformer life |
| Emergency Repair | As needed | Very High | Prevent extended outages |
Comparing Pad Mounted Transformers to Other Types?
Ever wondered how pad mounted transformers stack up against other types? It’s not just about looks – each transformer type has its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these can help you make the right choice for your power distribution needs.
Pad mounted transformers offer unique advantages in terms of safety, aesthetics, and flexibility compared to pole-mounted or vault-type transformers. However, they may have higher initial costs and space requirements. The choice depends on factors like location, power needs, and environmental conditions.
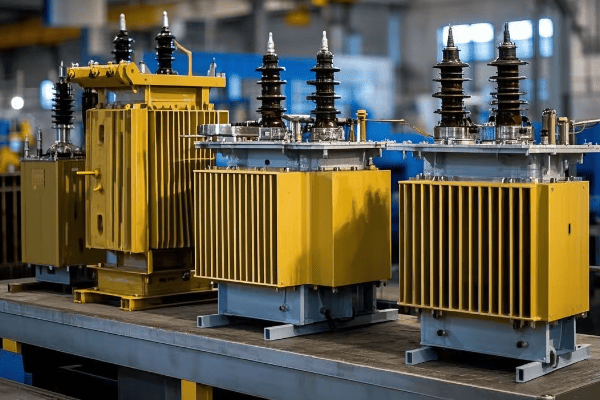
Let’s break down the comparison in more detail:
Weighing the Pros and Cons
-
Pad Mounted vs. Pole Mounted:
- Safety: Pad mounted are safer due to locked enclosures
- Aesthetics: Pad mounted have less visual impact
- Maintenance: Pad mounted are easier to access and maintain
- Cost: Pole mounted typically have lower initial costs
- Space: Pole mounted require less ground space
-
Pad Mounted vs. Vault Transformers:
- Installation: Pad mounted are easier and cheaper to install
- Accessibility: Pad mounted offer better access for maintenance
- Capacity: Vault transformers can often handle higher capacities
- Flooding risk: Pad mounted perform better in flood-prone areas
- Heat dissipation: Vault transformers may struggle with heat in some cases
-
Pad Mounted vs. Dry Type Transformers:
- Location: Pad mounted are for outdoor use, dry type for indoor
- Fire risk: Dry type have lower fire risk (no oil)
- Environmental impact: Pad mounted have potential oil leak risks
- Size: Dry type are often larger for the same capacity
- Cost: Pad mounted are usually more cost-effective for higher capacities
In my experience, the choice often comes down to specific site conditions and requirements. I once worked on a project where we initially planned to use vault transformers for a new commercial development. However, after assessing the high water table and flood risk in the area, we switched to pad mounted units. This decision likely saved millions in potential flood damage over the years.
Comparative Analysis:
| Factor | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted | Vault | Dry Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate | Low | High | Moderate |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Moderate | High | Low |
| Safety | High | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Aesthetics | Good | Poor | Excellent | N/A (Indoor) |
| Capacity Range | Wide | Limited | Very Wide | Moderate |
| Environmental Risk | Moderate (Oil) | Low | Moderate (Oil) | Very Low |
| Space Requirement | Moderate | Low | High | High |
Environmental Impact and Efficiency of Pad Mounted Transformers?
Concerned about the environmental footprint of power distribution? You’re not alone. As we push for greener energy solutions, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact and efficiency of our power infrastructure, including pad mounted transformers.
Pad mounted transformers can be designed for high efficiency, reducing energy losses and operational costs. They also have a smaller environmental footprint compared to some alternatives. However, the presence of oil does present some environmental risks that need to be managed carefully.
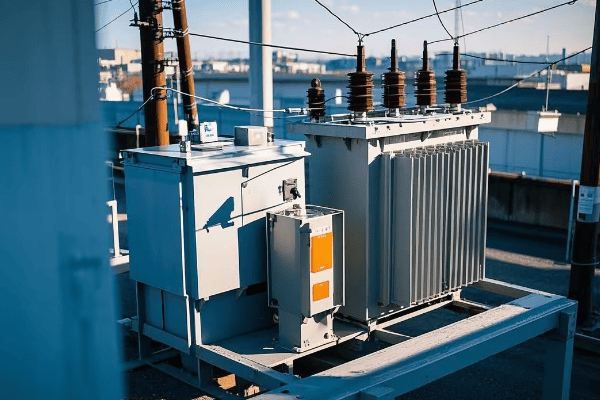

Let’s explore the environmental aspects and efficiency considerations in more detail:
Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Responsibility
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Modern designs minimize core and winding losses
- High-efficiency units can save significant energy over their lifespan
- Proper sizing and load management further improve efficiency
-
Materials and Recycling:
- Many components (steel, copper) are recyclable
- End-of-life disposal must be managed responsibly
- Some manufacturers use recycled materials in production
-
Oil Management:
- Potential for leaks and spills must be mitigated
- Bio-based oils are becoming more common
- Proper containment and regular inspections are crucial
-
Noise Pollution:
- Pad mounted transformers are generally quieter than pole-mounted units
- Noise can be further reduced with special designs and installations
-
Land Use:
- Compact design minimizes land use compared to some alternatives
- Can be integrated into landscaping to reduce visual impact
-
Lifespan and Sustainability:
- Long operational life (30+ years) reduces replacement frequency
- Upgradeable designs can extend useful life further
In my career, I’ve seen a significant shift towards more environmentally conscious transformer designs. I recall a project where we replaced old, inefficient transformers with new high-efficiency pad mounted units. The energy savings were substantial – we calculated a reduction in losses equivalent to powering 50 homes annually.
Efficiency and Environmental Impact Metrics:
| Aspect | Traditional Design | High-Efficiency Design | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Losses | Baseline | 20-30% reduction | Lower energy waste |
| Winding Losses | Baseline | 5-10% reduction | Reduced CO2 emissions |
| Oil Type | Mineral oil | Bio-based oil | Lower environmental risk |
| Noise Level | 60 dB | 50 dB | Reduced noise pollution |
| Lifespan | 25 years | 35+ years | Less frequent replacement |
| Recyclability | 70% | 85% | Less landfill waste |
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers are indeed the hidden heroes of our power distribution system. They offer a unique combination of safety, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal that makes them ideal for modern urban and suburban environments. While they come with their own set of challenges, particularly in terms of initial cost and environmental management, their benefits often outweigh these concerns. As we continue to evolve our power infrastructure to meet growing demands and environmental standards, pad mounted transformers will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a more efficient and reliable electrical grid.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


