Single Phase Power Transformer vs Three Phase: Key Differences Explored?
Are you confused about which type of transformer to choose for your project? The decision between single phase and three phase power transformers can be tricky. But don’t worry, I’m here to help you understand the key differences.
Single phase and three phase power transformers differ in their basic design, application, efficiency, and impact on power systems. Single phase transformers are simpler and used for lower power needs, while three phase transformers are more complex but offer higher efficiency and are ideal for industrial applications and power distribution networks.
In my years of experience working with power systems, I’ve seen how crucial this choice can be. The right transformer can make or break a project’s success. Let’s dive into the key differences between single phase and three phase transformers to help you make an informed decision.
Fundamental Principles: Understanding the Core Differences Between Single and Three Phase Transformers?
Have you ever wondered why some transformers have more wires than others? The answer lies in the fundamental differences between single phase and three phase systems. But what exactly sets them apart?
Single phase transformers work with one alternating current, while three phase transformers handle three currents phase-shifted by 120 degrees. This basic difference affects their design, operation, and applications. Single phase transformers are simpler, while three phase transformers are more complex but offer advantages in power density and efficiency.

In my career, I’ve worked extensively with both types of transformers. Let me break down the fundamental principles for you:
Basic Structure and Operation
The building blocks:
- Single Phase: One primary and one secondary winding.
- Three Phase: Three sets of primary and secondary windings.
- Magnetic Core: Different configurations for each type.
I remember my first hands-on experience with a three phase transformer. The complexity of the winding arrangement compared to a single phase unit was striking. It’s like comparing a simple melody to a three-part harmony.
Power Handling Capacity
Comparing the muscle:
| Aspect | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Power Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Voltage Levels | Typically lower | Can handle higher voltages |
| Current Flow | Pulsating | Constant |
In a recent industrial project, we needed to step up voltage for a large motor. The three phase transformer we used could handle the load with ease, something that would have required multiple single phase units.
Efficiency and Size
More than meets the eye:
- Copper Utilization: Three phase transformers use copper more efficiently.
- Core Material: Three phase designs often require less core material.
- Overall Size: Three phase units are generally more compact for the same power rating.
I once helped redesign a power system for a manufacturing plant. By switching from multiple single phase transformers to a single three phase unit, we reduced the footprint by 30% and improved overall efficiency.
Application Scenarios: When to Choose Single Phase vs Three Phase Power Transformers?
Ever stood in front of two similar products, unsure which to pick? That’s how many feel when choosing between single and three phase transformers. But fear not, there are clear scenarios where each shines.
Single phase transformers are ideal for residential and light commercial applications, powering homes and small businesses. Three phase transformers excel in industrial settings, large commercial buildings, and power distribution networks. The choice depends on the power requirements, available infrastructure, and specific application needs.
Throughout my career, I’ve advised on numerous projects where this choice was crucial. Let’s explore the typical applications for each:
Residential and Small Commercial Use
Where single phase rules:
- Homes: Powering household appliances and lighting.
- Small Shops: Supplying power for basic commercial needs.
- Rural Areas: Often only single phase power is available.
I once worked on a project electrifying a remote village. Single phase transformers were the perfect fit, providing the necessary power for homes and small businesses without the complexity of a three phase system.
Industrial and Large Commercial Applications
The domain of three phase:
| Application | Reason for Three Phase | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Factories | High power machinery | Motor drives, welding equipment |
| Office Buildings | Balanced load distribution | HVAC systems, elevators |
| Data Centers | Efficient power delivery | Server racks, cooling systems |
In a recent project for a new manufacturing plant, we installed a large three phase transformer. It efficiently powered everything from heavy machinery to office equipment, showcasing the versatility of three phase systems.
Special Considerations
Thinking outside the box:
- Renewable Energy: Often uses three phase for grid connection.
- Transportation: Three phase for electric train systems.
- Laboratories: May require both single and three phase power.
I helped design the power system for a cutting-edge research facility. We used a combination of three phase transformers for major equipment and single phase units for sensitive instruments, creating a flexible and efficient power infrastructure.
Efficiency and Performance: Comparing Single and Three Phase Transformer Capabilities?
Worried about energy bills or system performance? The choice between single and three phase transformers can significantly impact both. But how do they really stack up in terms of efficiency and performance?
Three phase transformers generally offer higher efficiency and better performance than single phase units of equivalent power rating. They provide more consistent power delivery, have lower losses, and can handle higher loads more effectively. However, single phase transformers can be more efficient for smaller, specific applications.
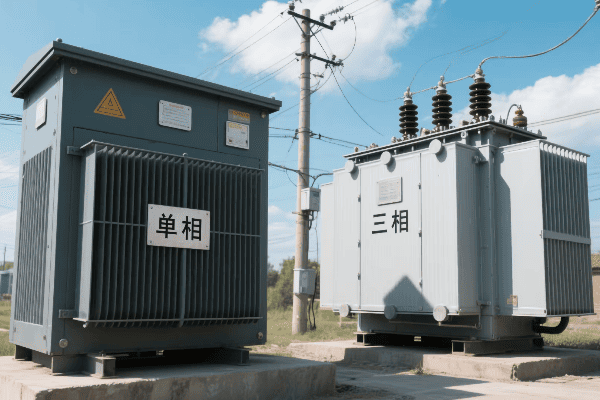

In my years of experience, I’ve seen the real-world impact of these differences. Let’s dive into the details:
Energy Efficiency
The bottom line:
- Core Losses: Three phase transformers typically have lower core losses.
- Copper Losses: More efficient use of copper in three phase designs.
- Overall Efficiency: Three phase usually wins in medium to high power applications.
I once conducted an efficiency study for a large retail chain. By replacing multiple single phase transformers with fewer three phase units, we achieved a 5% increase in overall energy efficiency across their stores.
Power Quality
Keeping it clean:
| Aspect | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Stability | Good | Excellent |
| Harmonics | Can be an issue | Better harmonic cancellation |
| Load Balancing | N/A | Inherently balanced |
In a data center project, we opted for three phase transformers specifically for their superior power quality. The stable, balanced power supply was crucial for the sensitive electronic equipment.
Load Handling Capacity
Meeting demand:
- Overload Capability: Three phase transformers often handle overloads better.
- Power Density: More power in a smaller footprint with three phase.
- Scalability: Easier to scale up with three phase systems.
I advised on a rapidly growing tech company’s power infrastructure. We chose three phase transformers for their main supply, allowing for easy expansion as their power needs grew over time.
Installation and Maintenance: Unique Considerations for Single and Three Phase Systems?
Think installing and maintaining all transformers is the same? Think again. Single and three phase systems have their own quirks when it comes to setup and upkeep. What do you need to know to avoid costly mistakes?
Installation of three phase transformers is generally more complex, requiring careful phase balancing and more sophisticated wiring. Maintenance for three phase units can be more involved due to their complexity. Single phase transformers are simpler to install and maintain, but may require more frequent attention in high-load applications.
Over the years, I’ve overseen numerous transformer installations and maintenance programs. Here’s what you need to know:
Installation Considerations
Getting it right from the start:
- Space Requirements: Three phase units often need more room.
- Wiring Complexity: More connections in three phase systems.
- Phase Balancing: Critical for three phase, not applicable to single phase.
I once managed the installation of a large three phase transformer in a cramped urban substation. The space constraints made the job challenging, but careful planning and a skilled team made it possible.
Maintenance Needs
Keeping things running smoothly:
| Aspect | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | More frequent for high loads | Less frequent but more complex |
| Skill Level Required | Basic to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Common Issues | Overheating in high-load applications | Phase imbalance, harmonics |
In my role overseeing maintenance for a large industrial client, we developed a comprehensive program for their three phase transformers. Regular thermal imaging and oil analysis helped us catch potential issues before they became problems.
Troubleshooting and Repairs
When things go wrong:
- Fault Detection: Often simpler in single phase systems.
- Repair Complexity: Three phase repairs can be more intricate.
- Downtime Impact: Failure in a three phase system can affect more equipment.
I once dealt with a failure in a critical three phase transformer at a manufacturing plant. The complexity of the repair meant longer downtime, but we used the opportunity to upgrade the unit, improving long-term reliability.
Grid Stability and Power Quality: The Impact of Single vs Three Phase Transformers on Electrical Networks?
Ever experienced flickering lights or unexplained power outages? The type of transformer used in your local grid plays a big role in power stability and quality. But how exactly do single and three phase transformers differ in their impact?
Three phase transformers generally provide better grid stability and power quality compared to single phase units. They offer more consistent voltage levels, better load balancing, and improved harmonic suppression. Single phase transformers, while simpler, can lead to phase imbalances in larger networks if not properly managed.
In my work with utility companies and large industrial clients, I’ve seen firsthand how transformer choice affects overall network performance. Let’s break it down:
Voltage Stability
Keeping the power steady:
- Three Phase Advantage: More stable voltage due to balanced loads.
- Single Phase Challenge: Can lead to voltage fluctuations under varying loads.
- Impact on Equipment: Stable voltage means longer life for connected devices.
I once helped a small town upgrade their distribution network from primarily single phase to three phase. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, with fewer complaints about appliance failures and flickering lights.
Load Balancing
Spreading the load:
| Aspect | Single Phase | Three Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Load Distribution | Can be uneven across phases | Inherently balanced |
| Impact on Neutral | Higher neutral currents | Lower neutral currents |
| System Efficiency | Can be lower due to imbalances | Higher due to balanced loads |
In a recent project for a large office complex, we used three phase transformers to ensure even load distribution. This approach significantly reduced neutral currents and improved overall system efficiency.
Harmonic Mitigation
Cleaning up the power:
- Three Phase Advantage: Better cancellation of triplen harmonics.
- Single Phase Issue: More susceptible to harmonic distortion.
- Impact on Power Quality: Cleaner power means less interference with sensitive equipment.
I advised on a power quality improvement project for a hospital. By replacing multiple single phase transformers with a few strategically placed three phase units, we significantly reduced harmonic distortion, improving the reliability of critical medical equipment.
Conclusion
Single and three phase transformers have distinct characteristics suited for different applications. Three phase units offer advantages in efficiency, stability, and power quality for larger systems, while single phase transformers remain ideal for simpler, lower-power needs.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


