The Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Power Facilities: Substations, Switching Stations, Power Distribution Rooms, and Compact Substations
As an electrical engineer with over two decades of experience, I’ve witnessed the evolution of power distribution systems firsthand. This guide will take you through the intricacies of various electrical facilities, their roles, and their impact on our power infrastructure.
Substations, switching stations, power distribution rooms, and compact substations are key components of our electrical grid. Each serves a unique purpose in transforming, controlling, and distributing power. Understanding their differences is crucial for efficient power system design and management.
Historical Evolution of Electrical Power Facilities
The journey of power distribution has been remarkable:
- 1880s: First AC power systems and basic substations
- 1900s: Introduction of oil circuit breakers and indoor substations
- 1950s: Development of SF6 gas-insulated switchgear
- 1970s: Advent of computerized control systems
- 1990s: Integration of digital protective relays
- 2000s: Rise of smart grid technologies and compact substations
This evolution has shaped our modern power infrastructure, leading to more efficient and reliable systems.
Detailed Comparison of Electrical Facilities
Let’s dive into a comprehensive comparison:
| Feature | Substation | Switching Station | Power Distribution Room | Compact Substation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Voltage transformation & distribution | Power flow control | Local power distribution | All-in-one solution |
| Voltage Levels | 765kV to 11kV | 33kV to 765kV | 400V to 11kV | Up to 33kV |
| Key Components | Power transformers, GIS, busbars | Circuit breakers, disconnectors | Switchgear, distribution boards | Integrated transformer, RMU, LV panel |
| Typical Location | Grid nodes | Transmission lines | Buildings | Urban/temporary sites |
| Size | Large (acres) | Medium | Small (room-sized) | Very compact |
| Complexity | High | Medium | Low to Medium | Medium |
| Automation Level | High | High | Medium | High |
Now, let’s explore each type in detail.
Substations: The Power Grid’s Transformation Hubs
Substations are the backbone of our power distribution system. They play a crucial role in voltage transformation and power distribution.
Substations transform voltage levels between transmission (up to 765kV) and distribution networks (down to 11kV). They use large power transformers to step up voltage for long-distance transmission or step it down for local distribution. Key components include transformers, gas-insulated switchgear (GIS), and advanced protection relays.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Power Transformers:
- Core function: Voltage level change
- Types: Step-up, step-down, auto-transformers
- Cooling methods: ONAN, ONAF, OFAF
-
Switchgear:
- Types: AIS (Air Insulated Switchgear), GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear)
- Components: Circuit breakers, disconnectors, earth switches
- Insulation medium: Air, SF6 gas, vacuum
-
Busbars:
- Function: Power distribution within substation
- Configurations: Single bus, double bus, ring bus
-
Protection and Control Systems:
- Protective relays: Overcurrent, differential, distance protection
- SCADA systems: Real-time monitoring and control
- Metering equipment: Power quality analyzers, energy meters
Case Study: 500kV Substation Upgrade
In a recent project, we upgraded a 500kV substation to improve reliability and capacity:
- Challenge: Increasing power demand and aging infrastructure
- Solution: Implemented GIS technology and digital control systems
- Results: 30% increase in capacity, 50% reduction in footprint, 99.99% reliability
Safety Considerations in Substations
Safety is paramount in substation design and operation:
- Physical barriers and restricted access
- Proper grounding and bonding
- Arc flash protection systems
- Regular safety training for personnel
Environmental Impact and Mitigation
Modern substations are designed with environmental considerations:
- Oil containment systems for transformers
- Noise reduction techniques
- EMF shielding for surrounding areas
- Use of eco-friendly insulation materials
Switching Stations: The Traffic Controllers of Electricity
Switching stations play a crucial role in power flow control and system flexibility.
Switching stations control electricity flow without changing voltage levels. They operate at transmission voltages (33kV to 765kV) and use high-voltage circuit breakers and disconnectors to route power, isolate faulty sections, and enable maintenance.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Circuit Breakers:
- Types: SF6, vacuum, air blast
- Operating mechanisms: Spring, hydraulic, pneumatic
-
Disconnectors:
- Function: Visible isolation for maintenance
- Types: Vertical break, horizontal break, pantograph
-
Bus Systems:
- Configurations: Single bus, double bus, breaker-and-a-half
-
Control and Protection:
- Synchrophasors for wide-area monitoring
- Automated switching sequences
Case Study: Smart Switching Station Implementation
In a recent project, we implemented a smart switching station:
- Challenge: Frequent power outages due to network congestion
- Solution: Deployed advanced control systems with real-time optimization
- Results: 40% reduction in outage duration, 25% improvement in power flow efficiency
Future Trends in Switching Station Technology
- Integration of AI for predictive maintenance
- Use of drone technology for inspections
- Implementation of digital twin technology for real-time simulation
Power Distribution Rooms: Bringing Power to Your Doorstep
Power distribution rooms are the final link in the power delivery chain, crucial for local power management.
Power distribution rooms receive and distribute electricity within buildings or small areas. They typically handle voltages from 400V to 11kV and serve as the final link before power reaches end-users. These rooms house low-voltage switchgear, circuit breakers, and often include power factor correction equipment.
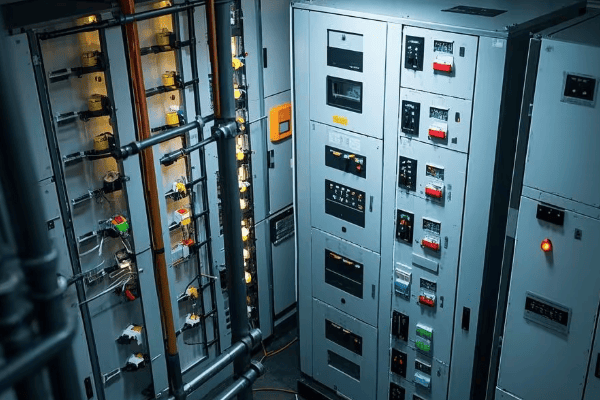
Key Components and Their Functions
-
Low Voltage Switchgear:
- Types: Fixed, withdrawable, plug-in
- Ratings: Typically up to 6300A, 100kA
-
Distribution Boards:
- Function: Circuit protection and power distribution
- Types: Lighting boards, power boards, motor control centers
-
Power Factor Correction Equipment:
- Purpose: Improve power quality and reduce energy costs
- Types: Fixed and automatic systems
-
Metering and Monitoring Systems:
- Smart meters for energy management
- Power quality analyzers
Case Study: High-Rise Building Power Distribution
In a recent 50-story skyscraper project:
- Challenge: Complex power distribution with varying load profiles
- Solution: Implemented a hierarchical distribution system with smart metering
- Results: 20% energy savings, improved load balancing, enhanced power quality
Energy Efficiency in Power Distribution Rooms
- Use of high-efficiency transformers
- Implementation of lighting control systems
- Voltage optimization techniques
- Integration with building management systems (BMS)
Compact Substations: The All-in-One Power Solution
Compact substations are revolutionizing power distribution in urban and temporary settings.
Compact substations combine transformation, switching, and distribution in a single prefabricated unit. They typically handle voltages up to 33kV and are ideal for urban areas, temporary installations, and quick deployment scenarios. These units integrate a transformer, ring main unit (RMU), and low-voltage panel in a compact enclosure.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Transformer:
- Types: Oil-filled, dry-type
- Ratings: Typically up to 3MVA
-
Ring Main Unit (RMU):
- Function: MV switching and protection
- Insulation: SF6 or solid insulation technology
-
Low Voltage Panel:
- Includes main circuit breaker, distribution feeders
- Often includes power factor correction
-
Integrated Control and Monitoring:
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Smart grid integration features
Case Study: Rapid Deployment for Renewable Energy
In a recent wind farm project:
- Challenge: Quick connection of multiple wind turbines to the grid
- Solution: Deployed 20 compact substations (33kV/400V) with smart grid features
- Results: 50% faster grid connection, improved power quality, remote monitoring capabilities
Advantages of Compact Substations
- Reduced footprint (up to 75% space saving)
- Factory-tested units for higher reliability
- Faster installation and commissioning
- Lower civil engineering costs
- Ease of relocation for temporary needs
Future Trends in Electrical Power Facilities
The future of power facilities is shaped by several emerging trends:
- Increased Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
- Implementation of Energy Storage Systems
- Advanced Analytics and AI for Predictive Maintenance
- Cybersecurity Enhancements
- Modular and Scalable Designs
- Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
Economic Analysis: Cost Considerations
Understanding the economic aspects is crucial for decision-making:
| Facility Type | Initial Cost | Operational Cost | Lifespan | ROI Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substation | Very High | Medium | 30-40 years | Reliability, capacity |
| Switching Station | High | Low | 25-35 years | Grid flexibility |
| Power Distribution Room | Medium | Low | 20-30 years | Energy efficiency |
| Compact Substation | Medium-High | Low-Medium | 20-25 years | Space saving, flexibility |
Regulatory Landscape and Standards
Compliance with regulations and standards is essential:
- IEC 61850 for substation automation
- IEEE C37.20.2 for switchgear assemblies
- NFPA 70 (NEC) for electrical installations
- ISO 14001 for environmental management
Maintenance and Upgrades
Proper maintenance is key to longevity and reliability:
- Routine Inspections: Visual checks, thermal imaging
- Preventive Maintenance: Oil analysis, contact resistance tests
- Predictive Maintenance: Using IoT sensors and data analytics
- Upgrade Strategies: Retrofitting vs. replacement considerations
FAQ
-
Q: How often should a substation be inspected?
A: Typically, visual inspections are conducted monthly, with more comprehensive checks annually. -
Q: Can renewable energy sources be integrated into existing power distribution rooms?
A: Yes, but it often requires upgrades to the distribution panels and control systems to handle bi-directional power flow. -
Q: What’s the typical lifespan of a compact substation?
A: With proper maintenance, a compact substation can last 20-25 years. -
Q: How do smart grid technologies impact traditional switching stations?
A: Smart grid technologies enhance switching stations with real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and improved power flow control. -
Q: What are the main challenges in upgrading an old substation to modern standards?
A: Key challenges include limited space for new equipment, integrating digital systems with legacy infrastructure, and maintaining power supply during upgrades.
Conclusion
The evolution of electrical power facilities from basic substations to smart, compact units reflects the changing needs of our power infrastructure. As we move towards a more distributed, renewable-focused energy landscape, the roles of these facilities continue to adapt. Understanding their functions, differences, and trends is crucial for anyone involved in power system design, operation, or management.
Last updated: 2025.3.19
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group



