Types of Transformer Oil Tanks: Which One Is Right for Your Project?
Are you struggling to choose the right oil tank for your transformer? You’re not alone in this complex decision-making process.
Transformer oil tanks come in various types, including open, closed, corrugated, and radiator designs. Each type serves specific purposes and offers unique advantages in terms of cooling efficiency, protection, and maintenance accessibility. The choice depends on factors like transformer size, environmental conditions, and operational requirements.
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in transformer design and maintenance, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial the right oil tank choice can be. Let’s dive into the world of transformer oil tanks and uncover the secrets to selecting the perfect one for your needs.
Open Tank Transformers: When Simplicity Meets Accessibility?
Ever wondered why some transformers look like they’re missing a lid? Welcome to the world of open tank transformers.
Open tank transformers feature a simple design where the core and coils are placed in an open vessel. They offer easy access for monitoring and maintenance but are typically limited to smaller, indoor applications where environmental protection is less critical.
I remember my first encounter with an open tank transformer during my early days as an engineer. Its simplicity was striking, but so were its limitations. Let’s break down the key aspects of open tank transformers:
Design and Construction
-
Basic Structure
- Core and coils exposed at the top
- No sealed enclosure
- Often used in dry-type transformers
-
Materials
- Usually made of steel or stainless steel
- May have reinforced sides for structural integrity
-
Size Range
- Typically used for transformers up to 500 kVA
- Rarely seen in high voltage applications
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Easy access for inspection | Limited environmental protection |
| Simpler cooling system | Not suitable for outdoor use |
| Lower manufacturing cost | Higher risk of contamination |
| Easier maintenance | Limited to smaller capacities |
Applications and Use Cases
-
Indoor Substations
- Where environmental factors are controlled
- In clean, dry environments
-
Industrial Settings
- For powering specific machinery
- Where frequent monitoring is required
-
Educational Institutions
- In laboratories for demonstration purposes
- Where visual inspection of components is beneficial
I once worked on a project for a small manufacturing plant that opted for open tank transformers for their production line power supply. The easy access for regular inspections was a significant factor in their decision, given their stringent maintenance schedules.
Maintenance Considerations
-
Regular Cleaning
- Dust and debris can accumulate on exposed components
- Requires more frequent cleaning than sealed designs
-
Visual Inspections
- Easy to perform without disassembly
- Allows for quick identification of issues like overheating or loose connections
-
Oil Level Monitoring
- Oil levels are easily visible
- Requires more frequent top-ups due to evaporation
Safety Precautions
-
Restricted Access
- Must be installed in areas with limited access to prevent accidental contact
- Clear warning signs and barriers are essential
-
Fire Safety
- Increased fire risk due to exposed components
- May require additional fire suppression systems
While open tank transformers have their place, particularly in controlled environments where frequent access is necessary, their use is becoming less common in modern power systems. The trend towards more sealed and environmentally protected designs reflects the increasing emphasis on safety and reliability in transformer technology.
Closed Tank Transformers: The Workhorses of Power Distribution?
Ever noticed those large, sealed metal boxes humming away in substations? Those are likely closed tank transformers, the backbone of our power distribution system.
Closed tank transformers feature a fully enclosed design that protects the core and windings from environmental factors. They offer superior protection, are suitable for outdoor use, and can handle larger capacities, making them ideal for a wide range of applications in power distribution networks.
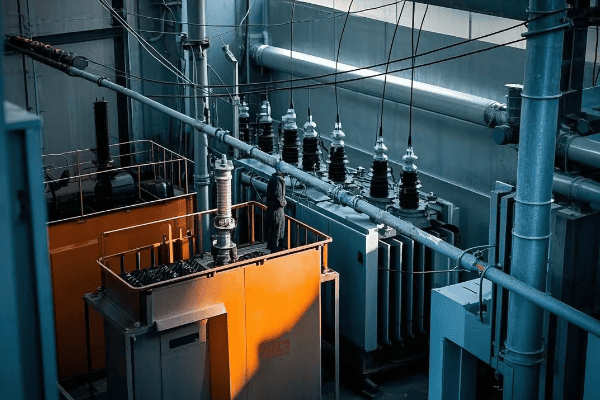

Throughout my career, I’ve worked extensively with closed tank transformers, and their versatility never ceases to impress me. Let’s dive into the details of these powerhouses:
Design and Construction
-
Sealed Enclosure
- Fully enclosed tank with welded or bolted cover
- Often filled with insulating oil or gas
-
Materials
- Heavy-gauge steel construction
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for outdoor use
-
Size Range
- Can range from small distribution transformers to large power transformers
- Capacities from a few kVA to hundreds of MVA
Key Components
-
Tank Body
- Houses the core and windings
- Designed to withstand internal pressure
-
Bushings
- Provide insulated passage for conductors
- High voltage and low voltage bushings
-
Cooling System
- Radiators or fins for oil circulation
- Fans for forced air cooling in larger units
-
Conservator
- Expansion tank to accommodate oil volume changes
- Often equipped with a rubber bag to prevent oil oxidation
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Excellent environmental protection | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Suitable for outdoor installation | More complex maintenance |
| Can handle large capacities | Heavier and bulkier |
| Better cooling efficiency | Requires oil processing equipment |
Applications and Use Cases
-
Utility Substations
- Main step-up and step-down transformers
- Distribution transformers in residential areas
-
Industrial Facilities
- Power supply for large manufacturing plants
- Mining and oil & gas operations
-
Renewable Energy Projects
- Wind farm and solar plant integration
- Grid connection for large-scale renewable installations
I once managed a project to upgrade a city’s aging substation. We replaced several smaller transformers with a large closed tank unit. The improvement in reliability and reduced maintenance needs were remarkable, justifying the higher initial investment.
Maintenance Considerations
-
Oil Testing and Processing
- Regular oil sampling and analysis
- Periodic oil filtration or regeneration
-
Gasket and Seal Inspection
- Critical for maintaining the sealed environment
- Regular checks for leaks or degradation
-
Cooling System Maintenance
- Cleaning of radiators and fans
- Checking for proper oil circulation
Safety Features
-
Pressure Relief Devices
- Prevent tank rupture in case of internal faults
- Buchholz relay for gas accumulation detection
-
Oil Containment
- Bunding or oil pits to contain potential leaks
- Environmental protection measures
-
Thermal Monitoring
- Temperature sensors in oil and windings
- Alarms and automatic shutdown features
Closed tank transformers represent the standard in modern power distribution systems. Their ability to operate reliably in various environments, coupled with their capacity to handle large power ratings, makes them indispensable in our electrical infrastructure. As we continue to see advancements in materials and design, closed tank transformers are evolving to become even more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Corrugated Tank Transformers: The Solution for Compact and Efficient Cooling?
Have you ever noticed transformers with wavy sides and wondered about their unique design? Welcome to the world of corrugated tank transformers.
Corrugated tank transformers feature walls and covers made of corrugated steel. This design increases the surface area for heat dissipation, enhances structural strength, and allows for a more compact footprint. They offer improved cooling efficiency and noise reduction compared to traditional smooth-walled tanks.
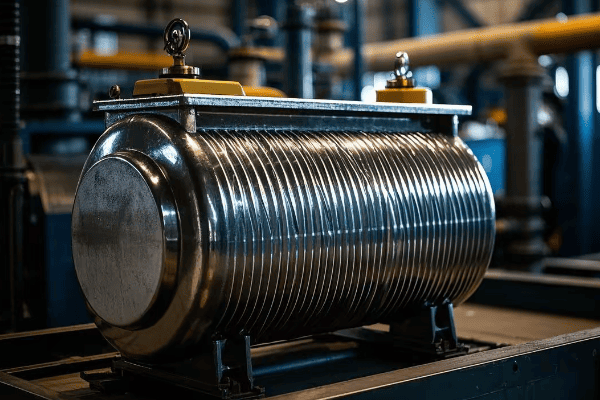
In my years of working with various transformer designs, I’ve come to appreciate the ingenious simplicity of corrugated tanks. Let’s explore why these transformers are gaining popularity:
Design and Construction
-
Corrugated Walls
- Walls and often the top cover are made of corrugated steel
- Corrugations typically run vertically
-
Materials
- High-grade steel with corrosion-resistant coatings
- Thickness varies based on transformer size and voltage rating
-
Size Range
- Commonly used in distribution transformers
- Also applicable in some power transformers up to several MVA
Key Benefits
-
Enhanced Cooling
- Increased surface area improves heat dissipation
- Can reduce or eliminate the need for external cooling fins
-
Structural Strength
- Corrugations provide rigidity and resistance to deformation
- Better withstands internal pressure and external forces
-
Compact Design
- Allows for smaller footprint compared to smooth-walled tanks
- Beneficial in space-constrained installations
-
Noise Reduction
- Corrugations help dampen vibrations
- Reduces audible transformer hum
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved cooling efficiency | More complex manufacturing process |
| Stronger structural integrity | Potential for dirt accumulation in corrugations |
| Compact size | Slightly more challenging to clean |
| Reduced noise levels | May have higher initial cost |
Applications and Use Cases
-
Urban Substations
- Where space is at a premium
- Noise reduction is beneficial in residential areas
-
Industrial Facilities
- Compact design suits cramped factory floors
- Improved cooling benefits high-load industrial applications
-
Renewable Energy Projects
- Used in wind turbine step-up transformers
- Compact design suits offshore wind platforms
I recall a project where we replaced several older transformers in a densely populated urban area with corrugated tank models. The reduction in footprint allowed for better use of limited substation space, while the decreased noise levels significantly reduced complaints from nearby residents.
Maintenance Considerations
-
Cleaning
- Requires special attention to clean between corrugations
- Pressure washing may be necessary for thorough cleaning
-
Corrosion Inspection
- Regular checks for rust or coating damage in corrugation valleys
- Important to maintain protective coatings
-
Thermal Imaging
- Effective for identifying hot spots or cooling issues
- Can reveal any uneven heat distribution across the tank surface
Design Innovations
-
Optimized Corrugation Patterns
- Research into ideal corrugation shapes for maximum cooling
- Some designs incorporate varying corrugation depths
-
Hybrid Designs
- Combination of corrugated and smooth sections
- Tailored to specific cooling and structural needs
-
Advanced Coatings
- Development of coatings that enhance heat dissipation
- Improved corrosion resistance for longer life
Corrugated tank transformers represent an innovative approach to addressing cooling, space, and noise challenges in transformer design. As urban areas become more densely populated and space constraints increase, the compact and efficient nature of corrugated tanks makes them an attractive option for many applications. Their ability to provide effective cooling without external radiators also simplifies maintenance and improves aesthetics, making them a popular choice in modern power distribution systems.
Radiator Tank Transformers: Mastering Heat Dissipation for Optimal Performance?
Ever seen those transformers with what looks like giant fins on the sides? Those are radiator tanks, the cooling champions of the transformer world.
Radiator tank transformers are equipped with external radiators that significantly enhance heat dissipation. This design allows for efficient cooling of the transformer oil, which in turn keeps the core and windings at optimal operating temperatures. They are ideal for high-capacity transformers and applications requiring superior cooling performance.
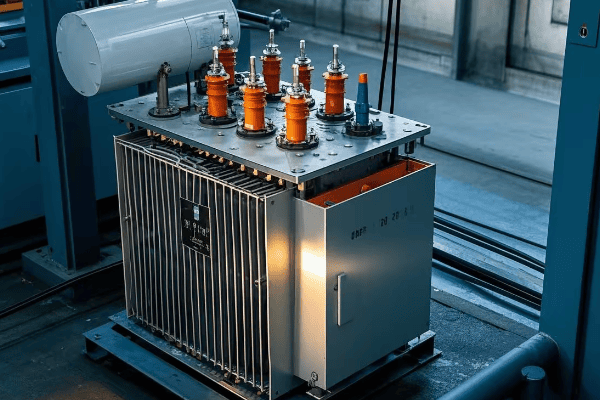
Throughout my career, I’ve worked extensively with radiator tank transformers, and their cooling efficiency never fails to impress. Let’s dive into the details of these cooling powerhouses:
Design and Construction
-
Main Tank
- Houses the core and windings
- Connected to external radiator banks
-
Radiators
- Series of thin, vertical fins attached to the tank
- Increase surface area for heat dissipation
-
Materials
- Tank typically made of high-grade steel
- Radiators often made of lighter materials like aluminum
-
Size Range
- Common in medium to large power transformers
- Capacities ranging from a few MVA to hundreds of MVA
Cooling Mechanisms
-
Natural Oil Circulation (ONAN)
- Hot oil rises, cooled oil sinks
- Creates natural circulation through radiators
-
Forced Oil Circulation (OFAF)
- Pumps circulate oil through radiators
- Used in larger transformers for more efficient cooling
-
Forced Air Cooling (ONAF)
- Fans blow air across radiator surfaces
- Enhances cooling in high load or high ambient temperature conditions
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Excellent cooling efficiency | Larger footprint |
| Suitable for high-capacity transformers | More complex maintenance |
| Flexible cooling options (ONAN, ONAF, OFAF) | Higher initial cost |
| Easier to upgrade cooling capacity | Potential for oil leaks at radiator connections |
Applications and Use Cases
-
Power Generation Plants
- Step-up transformers for large generators
- Able to handle high continuous loads
-
Transmission Substations
- High-voltage transformers for grid interconnections
- Reliable cooling for critical infrastructure
-
Heavy Industrial Applications
- Steel mills, large manufacturing plants
- Where high power demands and continuous operation are common
I once managed a project to upgrade a aging substation near a growing industrial park. We installed a large radiator tank transformer to handle the increased load. The improved cooling efficiency allowed for higher sustained output, meeting the growing energy demands of the area without overheating issues.
Maintenance Considerations
-
Radiator Cleaning
- Regular cleaning of radiator fins to maintain efficiency
- Removal of dust and debris that can impede heat dissipation
-
Oil Flow Checks
- Ensuring proper oil circulation through radiators
- Checking for blockages or restrictions
-
Fan Maintenance (for ONAF systems)
- Regular inspection and servicing of cooling fans
- Replacement of worn bearings or damaged blades
-
Leak Detection
- Careful monitoring of radiator connections for oil leaks
- Prompt repair of any detected leaks to maintain oil levels and prevent environmental issues
Innovations in Radiator Design
-
Detachable Radiators
- Allow for easier transportation and installation
- Facilitate replacement or upgrade of cooling capacity
-
Smart Cooling Controls
- Automated systems adjust cooling based on load and temperature
- Optimize energy efficiency of cooling systems
-
Advanced Materials
- Use of composite materials for lighter, more efficient radiators
- Coatings that enhance heat dissipation properties
-
Compact Radiator Designs
- Development of more efficient radiator shapes
- Aim to reduce overall transformer footprint while maintaining cooling capacity
Radiator tank transformers represent the pinnacle of cooling efficiency in the transformer world. Their ability to handle high loads and maintain optimal operating temperatures makes them indispensable in many critical power applications. As we continue to push the boundaries of power transmission and distribution, innovations in radiator design will play a crucial role in developing more efficient and reliable transformer systems.
Conclusion
Transformer oil tanks come in various designs, each with unique advantages. From open tanks for simplicity to radiator tanks for high-capacity cooling, the choice depends on specific application needs. Understanding these types helps in selecting the most efficient and reliable transformer for any project.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Assess your current transformer cooling needs
B. Explore advanced cooling technologies for your transformers
C. Implement a maintenance plan tailored to your transformer type
D. Review and update your transformer selection criteria for future projects
E. Investigate eco-friendly cooling options for transformers
F. Develop a comprehensive heat management strategy for your transformer fleet
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


