What is a Pad Mounted Transformer: The Hidden Power Behind Your Neighborhood?
Have you ever noticed those green boxes scattered around your neighborhood? They’re not just for decoration. These mysterious containers hold the key to powering your home, but most people walk by without a second glance.
A pad mounted transformer is a ground-level electrical device that converts high voltage power to lower, usable voltages for homes and businesses. These green boxes are safer, more efficient, and less obtrusive than traditional pole-mounted transformers, making them the preferred choice for modern residential areas.
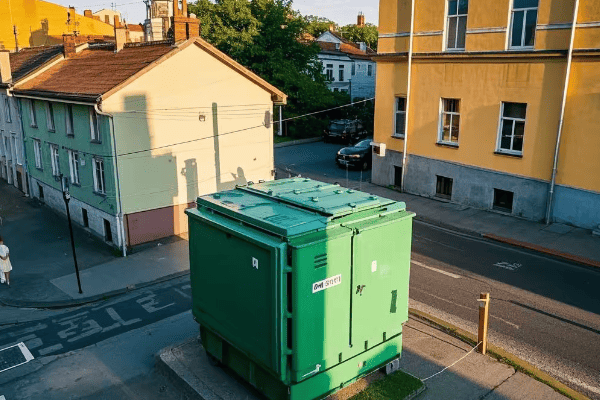

I’ve been working with pad mounted transformers for over 20 years, and I’m always amazed at how these unassuming boxes play such a vital role in our daily lives. In this article, I’ll take you on a journey inside these green powerhouses and reveal why they’re so important for your neighborhood’s electrical supply.
How Do Pad Mounted Transformers Work: The Science Behind Your Street’s Power Supply?
Ever flipped a switch and wondered how electricity magically appears in your home? The secret lies in those green boxes you see around your neighborhood. But how exactly do they work their magic?
Pad mounted transformers work by stepping down high voltage electricity from power lines to lower, safer voltages for home use. They use electromagnetic induction to transfer energy between coils of wire, efficiently converting voltage levels without direct electrical connections.
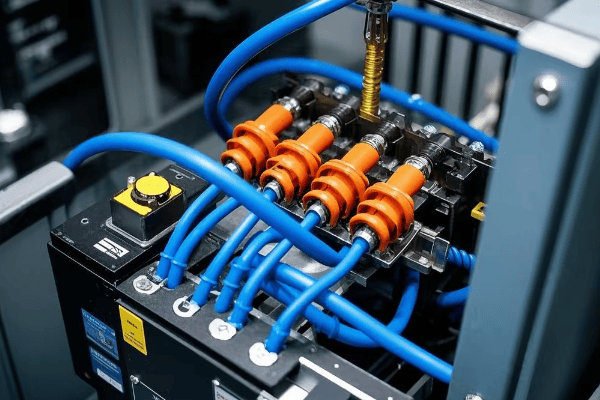
I remember the first time I opened up a pad mounted transformer. The complexity inside that simple green box was astounding. Let me break down how these devices work and why they’re so crucial for our power grid.
The Transformation Process
At its core, a pad mounted transformer operates on a simple yet powerful principle:
-
Input:
- High voltage electricity enters the transformer from underground power lines
- Typically ranges from 4,000 to 34,500 volts
-
Transformation:
- Electricity passes through primary coils wrapped around an iron core
- The changing magnetic field induces current in secondary coils
- The number of windings in each coil determines the voltage change
-
Output:
- Lower voltage electricity exits the transformer
- Usually 120/240 volts for residential use
Key Components
Understanding the parts helps appreciate the whole:
-
Core:
- Made of laminated steel sheets
- Provides a path for magnetic flux
- Designed to minimize energy loss
-
Windings:
- Primary (high voltage) and secondary (low voltage) coils
- Usually made of copper or aluminum wire
- Number of turns determines voltage transformation ratio
-
Insulating Oil:
- Cools and insulates internal components
- Helps prevent arcing and extends transformer life
- Some modern transformers use eco-friendly alternatives
-
Bushings:
- Connect internal wiring to external power lines
- Insulated to prevent short circuits
Efficiency and Load Management
Pad mounted transformers are designed for optimal performance:
-
Load Tap Changers:
- Adjust voltage output based on demand
- Maintain stable voltage during peak and off-peak hours
-
Cooling Systems:
- Oil circulation helps dissipate heat
- Some models include fans for additional cooling
-
Monitoring Equipment:
- Sensors track temperature, oil levels, and electrical load
- Helps prevent overloading and extends transformer life
| Component | Function | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | Reduces energy loss |
| Windings | Voltage conversion | Determines transformation ratio |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Extends lifespan, improves performance |
| Load Tap Changers | Voltage regulation | Optimizes power delivery |
In my years of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial proper design and maintenance are for these transformers. I once visited a neighborhood experiencing frequent power fluctuations. Upon inspection, we found that the pad mounted transformer was undersized for the growing energy demands of the area. Upgrading to a larger capacity transformer solved the issue, highlighting the importance of proper sizing and regular assessments.
It’s fascinating to think about how these relatively small devices handle such enormous amounts of power. A typical residential pad mounted transformer can supply electricity to 10-15 homes, quietly humming away day and night. The efficiency of modern transformers is remarkable, with some models achieving over 98% efficiency in converting voltage.
However, it’s important to note that while pad mounted transformers are highly efficient, they’re not perfect. They still experience some energy loss in the form of heat. That’s why you might notice the area around a transformer is slightly warmer, especially on hot days or during peak usage times.
As we move towards smarter, more connected power grids, pad mounted transformers are evolving too. Some newer models include advanced monitoring systems that can report issues in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and even more efficient power distribution. This integration with smart grid technology is paving the way for a more reliable and responsive electrical infrastructure.
Understanding how pad mounted transformers work isn’t just about satisfying curiosity. It’s about appreciating the complex infrastructure that powers our daily lives. Next time you see one of those green boxes, you’ll know there’s a lot more going on inside than meets the eye.
Key Components of a Pad Mounted Transformer: What’s Inside That Green Box?
Have you ever walked past one of those green boxes in your neighborhood and wondered what’s inside? These pad mounted transformers may look simple on the outside, but they’re packed with sophisticated components that keep your lights on and your appliances running.
A pad mounted transformer contains several key components: a steel core, primary and secondary windings, insulating oil, bushings, and a protective enclosure. Each part plays a crucial role in converting high voltage electricity to the lower voltages used in homes and businesses, ensuring safe and efficient power distribution.
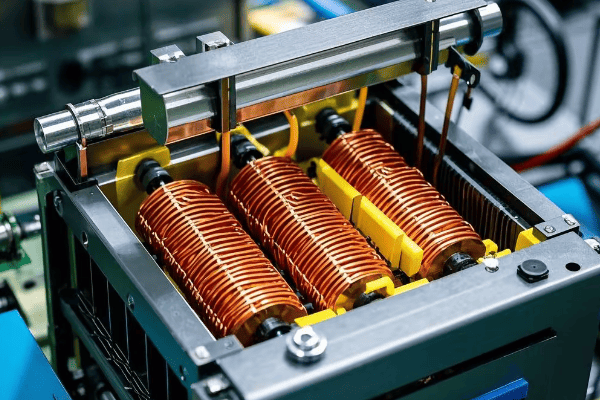
I’ve opened up countless pad mounted transformers over the years, and I’m always impressed by the engineering inside. Let’s take a closer look at what makes these devices tick and why each component is essential for reliable power delivery.
The Heart of the Transformer: Core and Windings
The core and windings are where the magic of voltage transformation happens:
-
Core:
- Made of thin, laminated steel sheets
- Provides a path for magnetic flux
- Designed to minimize energy loss
-
Primary Windings:
- Receive high voltage input
- Usually made of copper wire
- Number of turns determines voltage ratio
-
Secondary Windings:
- Produce lower voltage output
- Also typically copper
- Fewer turns than primary windings
Insulation and Cooling: The Oil Bath
Insulating oil serves multiple crucial functions:
-
Electrical Insulation:
- Prevents arcing between components
- Increases dielectric strength
-
Cooling:
- Absorbs and dissipates heat from windings and core
- Circulates naturally or through forced cooling systems
-
Preservation:
- Protects internal components from oxidation
- Extends the transformer’s lifespan
Connection Points: Bushings and Terminals
Bushings are the transformer’s connection to the outside world:
-
High Voltage Bushings:
- Connect to incoming power lines
- Heavily insulated to prevent flashover
-
Low Voltage Bushings:
- Connect to outgoing distribution lines
- Designed for easier and safer access
Protection and Monitoring: Auxiliary Components
Several additional components ensure safe and efficient operation:
-
Pressure Relief Device:
- Releases pressure in case of internal faults
- Prevents explosive rupture of the tank
-
Temperature Gauge:
- Monitors oil and winding temperatures
- Helps prevent overheating
-
Oil Level Indicator:
- Shows current oil level
- Alerts to potential leaks or low oil conditions
-
Tap Changer:
- Adjusts voltage output
- Maintains stable voltage under varying loads
| Component | Function | Maintenance Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | Check for vibration or unusual noise |
| Windings | Voltage conversion | Monitor for overheating |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Regular testing for contaminants |
| Bushings | Power connections | Inspect for cracks or damage |
| Pressure Relief Device | Safety | Ensure proper operation |
| Temperature Gauge | Monitoring | Verify accuracy periodically |
In my experience, understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. I once encountered a transformer that was running unusually hot. Upon inspection, we found that the oil level was low, reducing its cooling efficiency. A simple top-up of the insulating oil resolved the issue, highlighting the importance of regular checks on all components.
It’s fascinating to see how these parts work together. The core and windings perform the main task of voltage transformation, while the oil keeps everything cool and insulated. The bushings and terminals ensure safe connections, and the auxiliary components provide vital monitoring and protection.
One aspect that often surprises people is the longevity of these devices. With proper maintenance, a pad mounted transformer can last 30 years or more. I’ve worked on transformers that have been quietly serving neighborhoods for decades, a testament to their robust design and the quality of their components.
However, it’s important to note that while pad mounted transformers are designed for long-term reliability, they’re not maintenance-free. Regular inspections and tests are crucial to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Oil tests, for example, can reveal early signs of internal issues before they become major problems.
As technology advances, we’re seeing innovations in transformer components. Some newer models use vegetable-based oils instead of mineral oil, offering better environmental and fire safety properties. Others incorporate smart sensors that can report real-time data on the transformer’s condition, allowing for predictive maintenance.
Understanding the key components of a pad mounted transformer isn’t just for engineers and technicians. It helps everyone appreciate the complexity behind our seemingly simple electrical infrastructure. Next time you pass one of those green boxes, you’ll know there’s a lot more than meets the eye keeping your lights on and your appliances running.
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers are essential components of modern power distribution systems. They efficiently convert high voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses, while offering improved safety and aesthetics compared to traditional pole-mounted transformers. Understanding their inner workings helps us appreciate the complex infrastructure powering our daily lives.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


