Dry Type vs Oil Immersed Transformer: 5 Key Differences in Cost, Safety & Maintenance | CHBEB
Introduction
If you pick the wrong transformer, you could have to pay a lot of money for downtime, safety issues, and maintenance problems. A lot of buyers have trouble figuring out which type is best for their project. This guide explains the distinctions between dry type and oil-immersed transformers1 so you can make a confident choice.

The Main Difference: How They Function
Transformers may seem the same, but the way they deal with heat and insulation is what sets them apart. If you don’t grasp this, things can go wrong, accidents can happen, or things can break down too soon. Let’s go into the main rules for how it works.
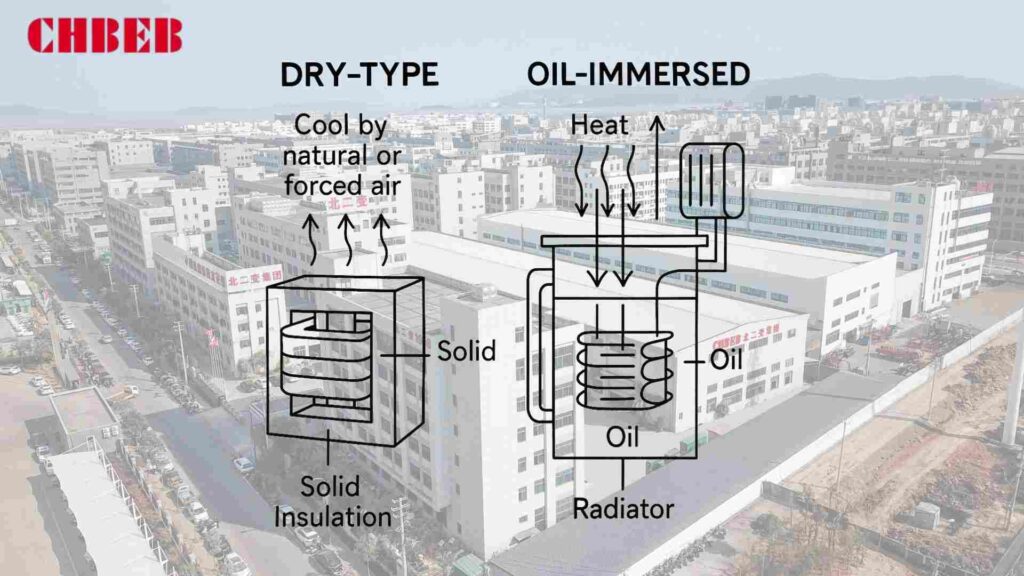
Dry-Type Transformers: Depend on Solid and Air
Instead of liquid, dry-type transformers use air and solid insulation materials.
- Cooling: either by natural means or by forced air.
- Epoxy resin, pressboard, or composite materials are used for insulation.
- Main Benefits: Less chance of fire, less harm to the environment, and can be used indoors.
- Normal Uses: schools, hospitals, commercial buildings, and interior substations.

The Role of Dielectric Fluid in Oil-Immersed Transformers
Mineral or synthetic oil is used to insulate and cool oil-immersed transformers.
- Cooling: Oil takes in heat and moves it to radiators or coolers.
- Insulation: Oil makes dielectric strength stronger and stops electrical arcs.
- Key Benefits: Can handle heavier loads and lasts longer when used heavily.
- Common Uses: Substations in the open air, industrial plants, and utility-scale distribution.
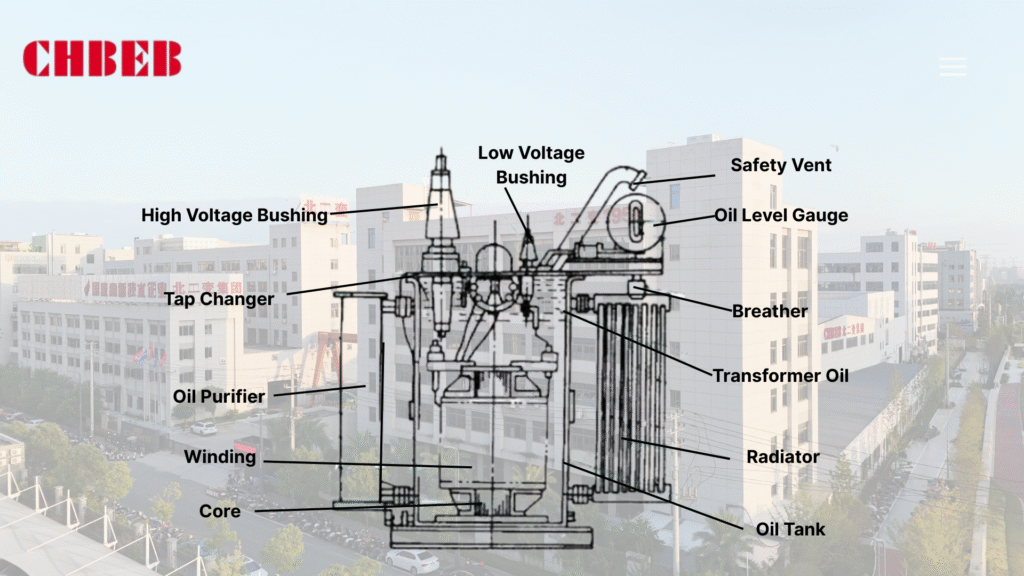
The 5 Key Differences: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Picking the improper type can have an impact on safety, cost, and performance. Here is a full comparison of the five most important things.
1. Safety and Effects on the Environment
Accidents with electricity or oil leaks might be quite bad.
| Feature | Dry-Type | Oil-Immersed |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Risk | Low (no flammable liquid) | Higher (oil is flammable) |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal, non-toxic | Oil spills can contaminate soil/water |
| Indoor Suitability | Ideal | Requires special precautions |
Dry-type transformers work well in small or sensitive spaces, while oil-immersed units need to be kept safe from fire and other hazards.
2. Cost: Initial Investment vs. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)2
The price you pay to buy it is only part of the story.
- Dry-Type: Higher initial cost per kVA, but reduced insurance and maintenance costs.
- Oil-Immersed: Costs less up front, but costs more to maintain, test oil, and clean up spills.
Tip: Don’t simply look at the sticker price; think about the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes things like energy losses, maintenance, and longevity.
3. Upkeep and Longevity
The complexity of maintenance can have an impact on downtime and costs of doing business.
| Feature | Dry-Type | Oil-Immersed |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Maintenance | Minimal (dust removal, visual checks) | Frequent (oil testing, leak checks, cooling system inspection) |
| Lifespan | 20–30 years | 25–40 years with proper care |
| Downtime Risk | Lower | Higher if leaks or faults occur |
If you don’t want to have to do much work on them, dry-type transformers are a good choice. Transformers that are immersed in oil need extra care, but they work well even when there is a lot of weight on them.
4.Load Capacity and Efficiency
Efficiency affects how much it costs to run and how much energy is wasted.
- Dry-Type: Usually has a lower load capacity and may lose a little more power when fully loaded.
- Oil-Immersed: Handles more weight and cools better; works better for big or industrial uses.
Tip: Pick based on what you need to carry. Oil-immersed versions are frequently better for big industrial applications.
5.Putting it together and using it
The installation environment decides what is practical.
| Feature | Dry-Type | Oil-Immersed |
|---|---|---|
| Indoor Use | Excellent | Needs safety measures and containment |
| Outdoor Use | Limited, requires enclosures | Ideal for outdoor substations |
| Space Requirements | Compact | Larger footprint due to cooling equipment |
| Noise | Quiet | Moderate, may need sound reduction |
Transformers that are dry-type work well indoors with little chance of fire, whereas oil-immersed transformers are best for heavy-duty outside use.
Making the Right Choice: A Summary Guide
Choosing the correct transformer will keep you safe, make sure it works, and save you money.
When to Choose Dry-Type:
- Installation within schools, hospitals, or businesses
- Having a low risk of fire is very important.
- It is best if there is little maintenance.
- Environmental sensitivity is a worry
When to Choose Oil-Immersed:
- For use outside or in factories
- You require a lot of load capacity.
- Long longevity under heavy use is needed
- There is extra money in the budget for safety and upkeep.
Conclusion
Dry-type and oil-immersed transformers each have unique strengths, and the right choice depends on your project’s safety requirements, budget, and operating environment.
- Choose a Dry-Type Transformer if your installation is indoors, in sensitive locations such as hospitals, schools, or commercial buildings, where fire safety, low maintenance, and environmental protection are top priorities.
- Choose an Oil-Immersed Transformer if your application demands high load capacity, long service life under heavy operation, and outdoor suitability, such as in substations, industrial facilities, or utility-scale distribution networks.
When evaluating, don’t stop at the purchase price. Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), including energy efficiency, downtime risks, and ongoing maintenance. A well-matched transformer not only ensures safe and reliable operation, but also maximizes your ROI by reducing long-term costs and improving system performance.
👉 Final tip: Align your transformer choice with your installation environment, load requirements, and risk tolerance. This structured approach will help you avoid costly mistakes and secure a solution that is both efficient and sustainable.
- Oil-Immersed Transformer: Construction, Working and Applications ↩︎
- Transformer Total Cost of Ownership ↩︎
Learn More
Looking for the right dry-type transformer for your project? Download our latest product catalog or browse our product categories to find reliable solutions tailored to your needs.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


