Dry Type Transformers Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Operation, Advantages, and Applications
Dry Type Transformers Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Operation, Advantages, and Applications
What is a transformer that is dry? A Look at the Main Ideas and Benefits
If you pick the wrong type of transformer, it could overheat, catch fire, or cost you a lot of money in downtime. Many engineers and procurement managers have a hard time finding the right balance between performance, safety, and maintenance in power distribution. For modern applications, dry-type transformers are a clean, safe, and efficient choice.
The main idea behind how dry-type transformers work
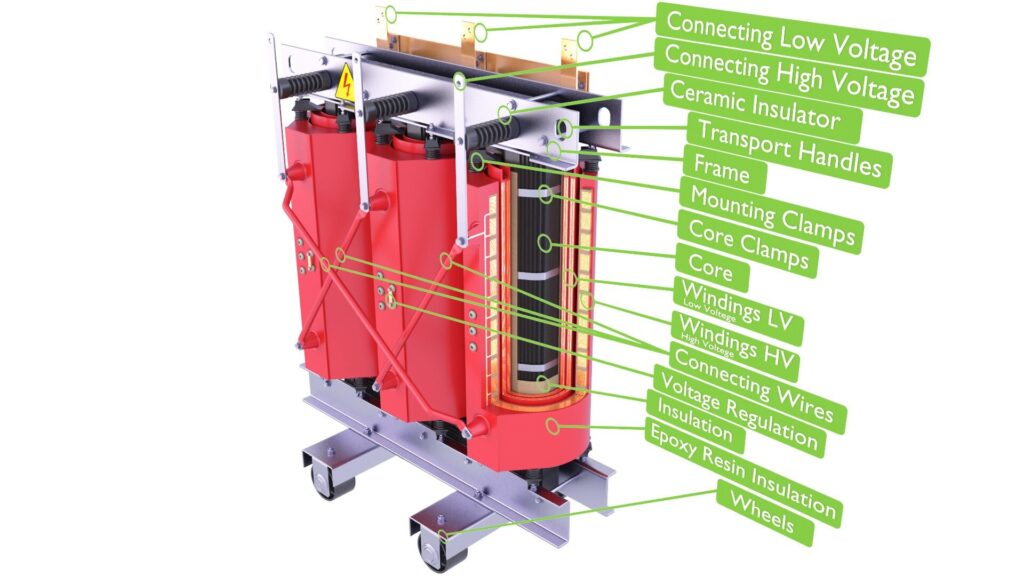
Oil is used for insulation and cooling in traditional transformers. In dry-type transformers, nevertheless, air and solid insulation materials do the trick. This gets rid of the chance of oil leaks, making them perfect for indoor and delicate settings.
The basic idea behind these transformers is electromagnetic induction1. A primary coil gets electrical energy, which causes voltage to flow through a magnetic core to a secondary coil. They stay cool and safe in different ways: with air ventilation and resin insulation instead of oil.
The main difference between dry-type and oil-immersed transformers is

The difference in insulation is huge. Oil-immersed transformers cool and insulate windings by putting them in oil, although this can be dangerous for the environment and for fires. Dry-type transformers get rid of all of these risks: no oil, no flammability, and no poisonous leaks.
| Feature | Dry-Type Transformer | Oil-Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Air/Natural Ventilation or Fan | Oil Circulation |
| Insulation | Epoxy Resin / Varnish | Mineral or Synthetic Oil |
| Fire Risk | Very Low | Medium to High |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires Oil Sampling |
| Indoor Use | Excellent | Limited |
Why Are Dry-Type Transformers Safer?
Safety is a must in high-risk areas like hospitals, schools, and businesses. Because they are flame-resistant and self-extinguishing, dry-type transformers are great for use indoors and in crowded locations.
Also, the fact that there is no flammable oil and that fire-resistant epoxy or varnish is used gives you peace of mind, especially in countries like Europe and North America where there are a lot of rules. A lot of models meet the safety criteria set by IEC 60076-112 and IEEE C57.12.91.
A Detailed Look at the Different Types of Dry-Type Transformers, Their Pros and Cons
Not every dry-type transformer is made the same way. Knowing the distinctions can help you pick the best solution for your project demands and the environment. Let’s look at the different types, their benefits, and any possible drawbacks.
VPI and CRT are the two main types.

Dry-type transformers come primarily in two forms: VPI (Vacuum Pressure Impregnated)3 and CRT (Cast Resin Type).
- VPI Transformers: The windings are soaked in varnish while under pressure and vacuum. Air cools them down, and they are commonly employed in industrial and utility situations with lower humidity.
- CRT Transformers: Coils in CRT transformers are made of solid epoxy resin, which makes them more resistant to moisture and stronger mechanically. This makes them perfect for use in coastal or tropical areas.
| Specification | VPI Transformer | CRT (Cast Resin) Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Varnish-impregnated | Solid Epoxy Resin4 |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Fire Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Application | General Industrial | High Moisture / Indoor Use |
A Look at Core Benefits: Why They Are Commonly Used in Today’s Apps
- Safety: No chance of oil fires or poisonous leaks
- Good for the environment: no oil discharge, smaller environmental footprint
- Low Maintenance: You don’t have to change the oil or sample the fluid.
- Small size makes it easier to install indoors.
- No noise: Great for business spaces because it doesn’t make noise.
- Ready for Compliance: Meets global safety requirements
An Objective Look: Problems and Limitations of Dry-Type Transformers
- Higher Initial Cost: Cast resin models can cost more at first.
- Size and Weight: CRTs are bigger since they are covered in resin
- Efficiency: A little less energy efficient than oil-immersed when fully loaded
- For Use Outside Protection: When used outside, it must be kept in a protective container.
From Theory to Practice: Important Uses and Upkeep
It’s not only about how dry-type transformers work, but also where and how they do their job. Let’s go from technical details to real-world value and maintenance.
Common Use Cases and Examples

- Commercial Buildings: office towers and shopping complexes
- Hospitals and schools: safe, quiet, and clean inside
- Solar farms and wind substations are examples of renewable energy.
- Industrial Plants: This is especially true in places with a lot of humidity or chemicals.
- Transportation Hubs: Subways, airports, tunnels
For example, in 2024, a Dubai-based solar energy EPC put in 75 dry-type transformers in their PV project in the desert. The transformers didn’t need any maintenance for a whole year, even though they had to deal with high temperature changes and sand exposure. This was all because to cast resin insulation.
A Simple and Efficient Guide to Caring for and Maintaining Dry-Type Transformers
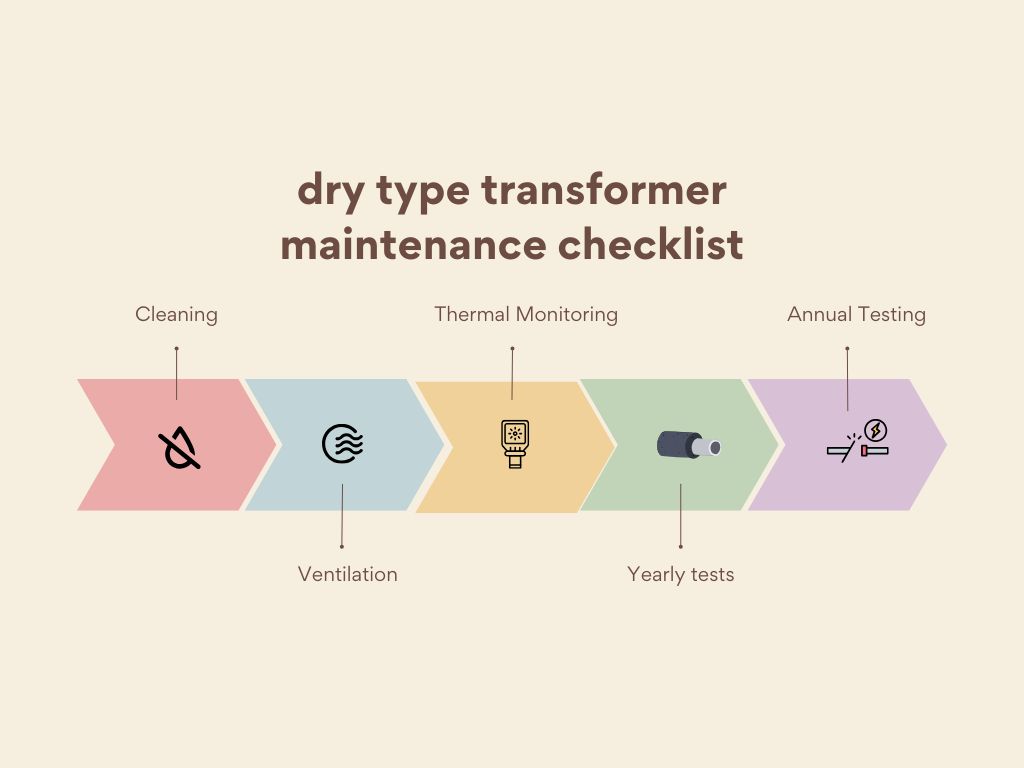
- Check for dust accumulation or signs of overheating once a month by looking at it.
- Cleaning: Don’t get anything wet; use a vacuum or dry cloth.
- Ventilation: Make sure that the cooling ducts are not obstructed.
- Thermal Monitoring: Use sensors that are already in place to keep an eye on temperature fluctuations.
- Yearly tests: IR thermography5 and insulation resistance checksperature changes
- Annual Testing: IR thermography and insulation resistance checks
A dry-type transformer can survive 20 to 30 years with the right maintenance, which is a great return on investment.
Conclusion
Dry-type transformers are safe, reliable, and work well all at the same time. They are a long-term, low-maintenance way to get clean power to people, whether you’re improving city infrastructure or creating renewable systems.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


