The Definitive Guide to Oil-Immersed Distribution Transformers: Selection, Applications, and Maintenance
Introduction
Many projects are plagued by power outages, expensive inefficiencies, and system dangers. Customers sometimes don’t know which transformer to trust, which wastes money and effort. The answer is clear: learn about oil-immersed distribution transformers1, including what they are, how to pick the right one, and how to keep it in good shape for years of reliable operation.
The Basics: What Is an Oil-Immersed Distribution Transformer?
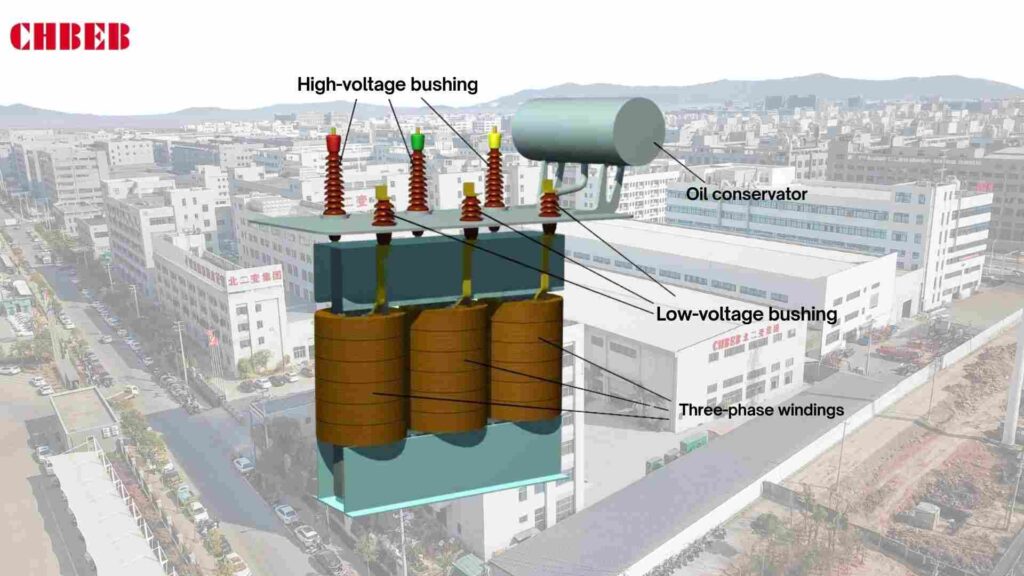
Equipment faults and unstable electricity can stop operations. Many buildings have to deal with high energy expenses and safety problems. Oil-immersed distribution transformers are the answer. They make sure that power is delivered safely, efficiently, and consistently.
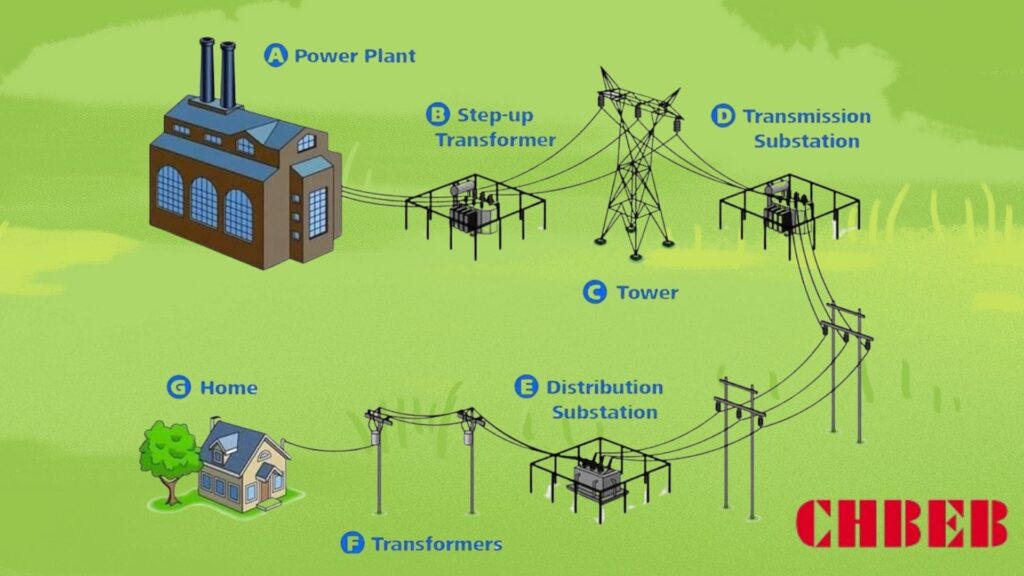
The “Last Mile” in Power Distribution: What It Means and How It Works
Power plants create electricity that is too strong to use directly. This causes problems for homes, businesses, and factories. Oil-immersed distribution transformers fix this by lowering the voltage to levels that may be used. They are the “last mile” in the grid’s distribution chain.
They have a magnetic core and windings that are completely covered in insulating oil. The oil not only keeps things cool, but it also absorbs and spreads heat, which makes sure that the machine works well even when it’s under a lot of stress.
The main difference between distribution transformers and power transformers is
Mistakes that cost a lot of money happen when people mix up power and distribution transformers. Knowing the difference makes sure you buy the right things.
- Power transformers are used in transmission networks to handle very high voltages (≥ 132 kV). Made to work best when fully loaded.
- Distribution transformers work at lower voltages (< 36 kV) and send power straight to end customers. Optimized for efficiency even when not fully loaded.
| Feature | Power Transformer | Distribution Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Level | ≥ 132 kV | ≤ 36 kV |
| Operation | Transmission network | Distribution network (“last mile”) |
| Efficiency Focus | High load efficiency | All-day efficiency at variable load |
| Typical Installation | Power stations, substations | Residential, commercial, industrial |
The Selection Guide: Choosing the Right Transformer for Your Project
Choosing the wrong transformer can lead to overheating, losses, and breakdowns that happen a lot. This not only costs more, but it also makes things last less long. Before selecting a choice, you should look at the most important factors.
Important Factors: Capacity, Voltage, and Cooling Method
Not paying attention to specs can cause problems and cost a lot of money to fix. The best way to go about it is to concentrate on three main factors:
- Capacity (kVA rating): Make sure the capacity of the transformer is big enough to handle your current load and any expansion you expect in the future.
- Voltage (HV/LV levels) should match the needs of the grid supply and the end user.
- Choose a cooling method (ONAN, ONAF, OFWF2, etc.) based on the load and environment in which it will be used.
| Cooling Method | Full Form | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ONAN | Oil Natural Air Natural | Standard distribution transformers |
| ONAF | Oil Natural Air Forced | Industrial projects with higher load |
| OFWF | Oil Forced Water Forced | Large-scale, high-capacity projects |

Structural Comparison: Conservator Tank vs. Hermetically Sealed
People often can’t decide between hermetically sealed and conservator types. Depending on the needs of the project, each structure has its own advantages.
- Transformers that are sealed hermetically
- Small and completely sealed off from damp.
- Less oxidation means less upkeep.
- Best for projects in cities or with limited space.
- Transformers for conservator tanks
- Let the oil expand through the conservator.
- Simple to check and replace oil.
- Best for remote areas or when you need to carry a lot of weight for a long time.
| Feature | Hermetically Sealed | Conservator Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Oxidation | Minimal | Higher risk |
| Maintenance | Low (no oil checks) | Regular oil inspection needed |
| Service Life | 15–25 years | 20–30 years (with care) |
| Best for | Cities, compact installations | Rural, long-term heavy duty |
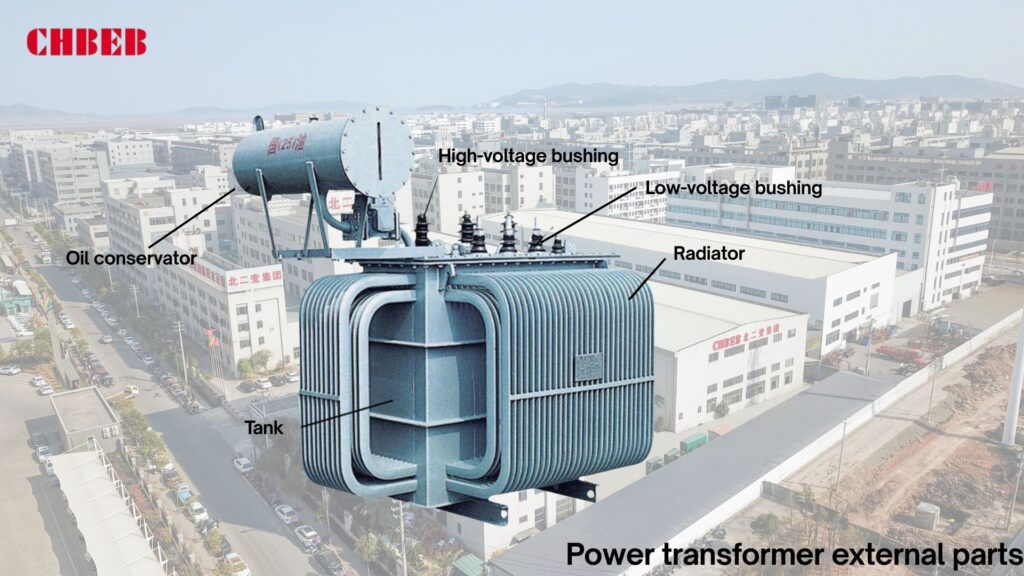
Application & Maintenance: Ensuring Long-Term Reliable Operation
If you don’t take care of it, even the best transformer will break. Improper use or lack of maintenance shortens lifespan. To get good service, you need to use the right tools and have regular checks.
Common Uses: Where Do These Transformers Go?
Oil-immersed distribution transformers are used in many fields, which shows how flexible they are:
- Utilities: Provide steady power to homes and businesses.
- Industrial Plants: These plants provide power to machines and production lines.
- Commercial Centers: Make sure that malls, businesses, and airports always have power.
- Renewable Energy: Reduce the amount of power coming from solar and wind farms.
- Infrastructure includes railroads, subways, hospitals, and data centers.
Key Steps to Keep Your Transformer Running Longer: A Maintenance Checklist
Not keeping things up to date might cause problems and expensive downtime. Long-term performance is guaranteed by regular care:
- Check the dielectric strength and wetness of the oil every 6 to 12 months.
- Check the relay: the Buchholz relay was checked for gas buildup.
- Checks on the cooling system, including servicing fans, pumps, and radiators.
- Visual Checks: Find leaks, rust, or noise early on.
- Thermal Imaging: Find hot spots before they do damage.
- Overhaul: Change the oil, gaskets, and bushings every so often.
| Maintenance Step | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Oil dielectric test | 6–12 months | Ensure insulation quality |
| Relay check | 6 months | Detect faults early |
| Visual inspection | Monthly | Spot leaks, corrosion, noise |
| Cooling system service | Annually | Maintain efficient operation |
| Complete overhaul | 5–10 years | Extend service life |
CHBEB — Reliable Partner for Distribution Transformers

With over 60 years of transformer manufacturing expertise, CHBEB has become one of China’s most trusted distribution transformer suppliers. The company operates two factories in Wenzhou, one in Nanjing, and an office in Beijing, ensuring both strong production capacity and responsive customer support.
What makes CHBEB stand out:
- Strict Quality Commitment: All raw materials are 100% new and high-grade — no recycled or downgraded components.
- Proven Reliability: A qualified supplier for the State Grid Corporation of China, with a spotless record of zero major accidents.
- 100% Product Testing: Every unit is fully tested before delivery to guarantee safety, efficiency, and long service life.
- Fast-Track Orders: Ability to fulfill urgent orders in as little as one week, helping customers meet tight project deadlines.
- Custom Inventory Planning: Flexible stocking and supply strategies designed to align with customer procurement schedules.
- Global Outlook: Rooted in China and expanding worldwide, CHBEB actively supports local agents and partners, including assistance with market-specific certifications.
- Flexible Customization: Tailored transformer designs for utilities, contractors, and industrial clients, with reliable quality and fast delivery.
👉 Looking for a distribution transformer manufacturer that combines Chinese manufacturing strength with international standards?Contact CHBEB for a tailored solution or Download our full transformer catalog here.
Conclusion
Oil-immersed distribution transformers are still the backbone of modern grids, but their long-term value depends on smart choices at the start. To secure reliable performance and lower lifetime costs, buyers should:
- Specify clearly – include kVA rating, cooling method (ONAN/ONAF/OFWF), and tank type (sealed vs. conservator) in every RFQ.
- Plan maintenance – schedule oil dielectric tests every 6–12 months, visual inspections monthly, and overhauls every 5–10 years.
- Check compliance – verify IEC/ANSI standards, loss guarantees, and recent test reports before contract signing.
- Consider environment – for high humidity or dusty regions, sealed tanks reduce oxidation; for rural heavy-duty sites, conservator types offer longer life.
✅ Key takeaway: The right transformer is not just about capacity—it’s about aligning design, standards, and upkeep with your project’s realities. Disciplined selection and proactive care ensure decades of safe and efficient service.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


