In-Depth Analysis of Oil-Immersed Transformers: Core Technology, Working Principles, and Key Selection Guide
Are you having trouble picking the proper oil-immersed transformer for your power distribution needs? These important parts can be very complicated. Don’t worry! This detailed guide will clear up any confusion you may have about oil-immersed transformers, giving you the knowledge you need to make smart choices and improve the operation of your power system.
The Basics: The Main Parts and How Oil-Immersed Transformers Work
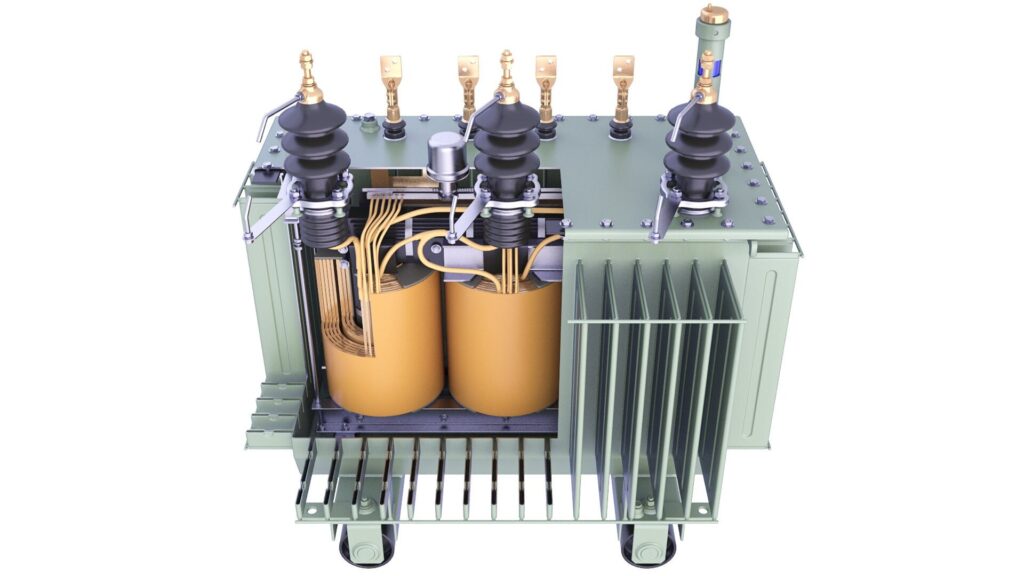

Do you just know what oil-immersed transformers are from books? A lot of specialists don’t pay attention to the small things that make these products work so well. Let’s take a closer look at the main parts and how they work. This will provide you more information that will help you comprehend and make better decisions.
The “Blood” That Can’t Be Missed: How Transformer Oil Keeps Things Cool and Insulated
Oil-immersed transformers rely on transformer oil 1to keep them cold and insulated. This fluid made from mineral oil has great dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. Here’s why it’s important:
- Insulation: The oil fills up the spaces between the windings, which keeps the electricity from breaking down.
- Cooling: It moves heat from the core and windings to the outside of the transformer quickly and easily.
- Diagnostics: Analyzing oil on a regular basis can show problems that could become serious.
Key properties of transformer oil:
| Property | Typical Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 30-50 kV/mm | Prevents electrical breakdown |
| Viscosity | 8-12 cSt at 40°C | Affects cooling efficiency |
| Pour Point | -40°C to -60°C | Ensures fluidity in cold climates |
| Flash Point | >140°C | Safety indicator for fire risk |
A close look at the technology behind key components, from core to casing
To understand how a transformer works as a whole, you need to know how the basic parts work together:
- Core: The core is usually made of grain-oriented silicon steel2, which lets magnetic flux flow through it easily.
- Windings: Primary and secondary coils, which are commonly made of copper or aluminum, move energy through electromagnetic induction.
- Bushings: These insulated openings let conductors safely leave the transformer tank.
- Tank: The sealed container holds all of the internal parts and the insulating oil.
- Cooling system: Radiators or fans help get rid of heat, which is important for keeping everything running smoothly.
Innovations in core materials, like amorphous metal cores3, can cut down on no-load losses by a lot, which makes the whole system more efficient.
Value is based on performance: Learning about the most important technical aspects of oil-immersed transformers
Are you feeling overwhelmed by all the technical details? You’re not the only one. A lot of buyers only look at the power rating and don’t think about other important factors that affect long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. Let’s look at the most significant things to think about.
Cooling Methods: The Key to a Transformer’s “Endurance”
For a transformer to last a long time and work well, it needs to be cooled properly. The way a transformer is cooled has a direct effect on how much load it can handle and how long it will last. Some common ways to cool things down are:
- ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural): Uses natural oil flow and air cooling.
- ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced): Uses fans to make the air cooler.
- OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced): Uses fans and oil pumps to make cooling better.
- ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced): Sends oil through windings to cool things down as much as possible.
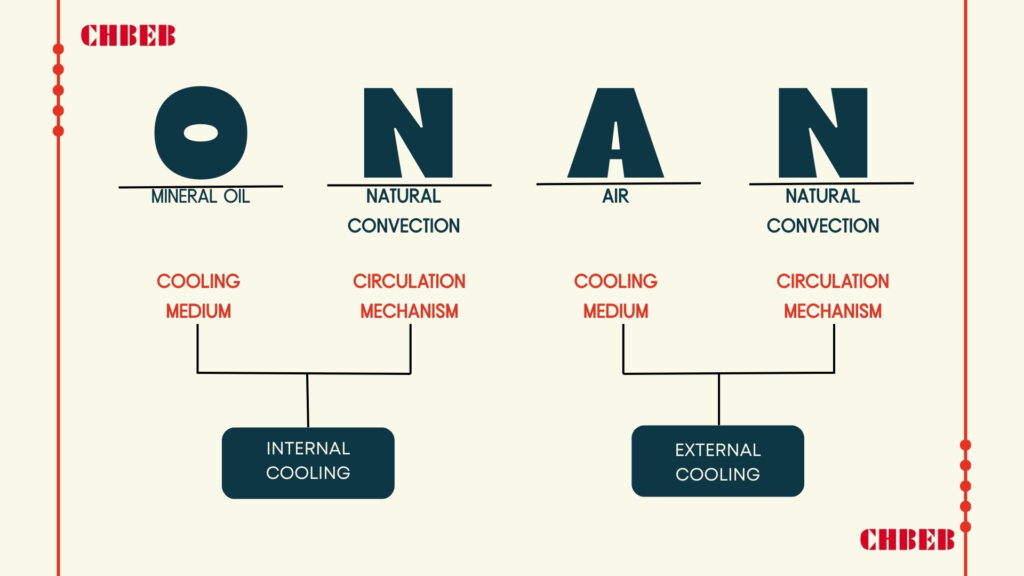
Choosing the right way to cool down depends on things like:
- The temperature outside
- Profile of the load
- Setting up the environment
- Ability to do maintenance
Windings and Core: The Best Way to Balance Loss and Impedance
To get the most performance out of a transformer, it’s important to balance losses and impedance:
- No-load losses happen in the core because of hysteresis and eddy currents.
- Load losses happen because of resistance in the windings and stray losses.
- Impedance voltage: affects the current and voltage regulation in a short circuit.
Think about these trade-offs:
- Lower impedance makes voltage regulation better, but it also makes short-circuit current higher.
- Cutting down on losses usually means higher material costs and bigger transformers.
To make a smart choice, think about what you really need:
- Load profile (fixed vs. changing)
- Life expectancy
- Costs of energy
- Limited space
Operation, Maintenance, and Safety: Making Sure Transformers Work Well for a Long Time
Have you thought about how your choice of transformer would affect you in the long run? To get the best performance and longest life out of something, it needs to be used and cared for properly. Let’s look at some important ways to make sure your transformer runs well and safely for a long time.
Using oil analysis to check health: finding and fixing common problems
Regularly checking the oil in a transformer is the best way to tell how healthy it is. It can show:
- Moisture content: Too much moisture might damage insulation.
- Acidity: Shows that oil is breaking down and may be corroding.
- Dissolved gas analysis (DGA)4 finds problems inside the system, such as partial discharge or overheating.
Common signs of a problem:
- High hydrogen: Partial discharge
- High acetylene: Arcing
- More carbon monoxide: Paper insulation breaks down
Things you can do to stop it:
- Set up a consistent timetable for taking oil samples
- Use online systems to keep an eye on important transformers.
- When necessary, do oil filtering or regeneration on time.
Fire Protection and Environmental Safety: Keeping Oil-Immersed Transformers Safe
Never put safety off till later. Think about these important things:
- Protection from fire:
- Put up fire barriers and deluge systemss5
- In places where there is a lot of risk, use fluids that don’t catch fire as easily, like silicone or ester-based oils.
- Environmental protections:
- Set up the right systems to hold oil in place
- Use oils that break down in nature when you can
- Things to think about when it comes to earthquakes:
- Make sure the anchors are in the right place in areas that are likely to have earthquakes.
- Think about bushings and accessories that are rated for seismic activity.
Regular safety checks and drills can help find and fix possible problems before they become big ones.
Conclusion
Oil-immersed transformers are complex yet crucial components in power systems. You can make smart choices to improve performance, efficiency, and safety if you know their fundamental technology, important parameters, and maintenance needs. Keep in mind that the appropriate option today will make sure that power is distributed safely for years to come.
- Transformer oil. Wikipedia. Available at: ↩︎
- Grain-oriented electrical steels. ScienceDirect. Available at: ↩︎
- Amorphous metal transformer cores. IEEE Xplore. Available at: ↩︎
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) for Transformers. All About Circuits. Available at: ↩︎
- Fire protection solutions for transformers. Schneider Electric. Available at: ↩︎
Want to explore detailed specifications and models? You can download our product catalog or browse our website to learn more about CHBEB’s transformer solutions.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


