Are you ready for the power revolution? The distribution transformer market is undergoing a seismic shift, and it’s reshaping our energy landscape in ways we never imagined.
The distribution transformer market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, smart grid integration, and the push for energy efficiency. These trends are not just improving grid performance; they’re redefining how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity in the 21st century.
As someone who’s been in the power industry for years, I’ve witnessed firsthand the incredible changes sweeping through the distribution transformer market. Let’s dive into the trends that are shaping the future of power grid efficiency and explore what they mean for our energy future.
Technological Innovations: Revolutionizing Distribution Transformer Efficiency?
Have you ever wondered how transformers keep getting smaller yet more powerful? The answer lies in cutting-edge technological innovations that are pushing the boundaries of efficiency.
Technological innovations in distribution transformers include advanced core materials, smart monitoring systems, and improved cooling technologies. These advancements significantly reduce energy losses, extend transformer lifespan, and enable real-time performance optimization.

Let’s explore the key innovations revolutionizing transformer efficiency:
Advanced Core Materials
Pushing the limits of energy conservation:
- Amorphous metal cores reducing no-load losses by up to 70%
- Grain-oriented electrical steel with lower hysteresis losses
- Nanocrystalline materials offering superior magnetic properties
Smart Monitoring Systems
Real-time insights for optimal performance:
- IoT-enabled sensors for continuous health monitoring
- AI-driven analytics for predictive maintenance
- Cloud-based platforms for remote management and control
Improved Cooling Technologies
Keeping transformers cool under pressure:
- Ester-based cooling fluids for better heat dissipation
- Phase-change materials for passive cooling
- Advanced radiator designs for enhanced natural cooling
| Innovation | Efficiency Impact | Market Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Cores | 70% reduction in core losses | Rapid adoption in urban grids |
| Smart Monitoring | 30% decrease in unexpected failures | Growing demand for IoT integration |
| Ester Cooling | 20% increase in overload capacity | Shift towards eco-friendly solutions |
I remember visiting a transformer manufacturing plant last year. The engineer showed me their latest amorphous core transformer. "This beauty," he said, "can save enough energy to power a small town compared to older models." It was a moment that truly brought home the impact of these innovations.
Another eye-opening experience was at a smart grid conference. A utility manager demonstrated their new AI-powered transformer monitoring system. "We used to react to failures," she explained. "Now, we prevent them before they happen." The potential for improved reliability and reduced downtime was clear.
These technological innovations are not just incremental improvements; they’re game-changers in the distribution transformer market. They’re enabling utilities to do more with less, significantly reducing energy losses and operational costs. As we continue to push the boundaries of materials science and digital technology, I expect to see even more revolutionary advancements in transformer efficiency. The future of power distribution is not just about moving electricity; it’s about moving it with unprecedented efficiency and intelligence.
Smart Grid Integration: Transforming Demand Patterns in the Distribution Transformer Market?
Ever wondered how our power grids are getting smarter? The integration of distribution transformers with smart grid technology is revolutionizing how we manage and distribute electricity.
Smart grid integration in the distribution transformer market enables real-time load management, bidirectional power flow, and advanced grid analytics. This integration is transforming demand patterns, improving grid reliability, and paving the way for more efficient and responsive power distribution systems.
Let’s explore how smart grid integration is reshaping the transformer market:
Real-Time Load Management
Balancing power supply and demand:
- Dynamic load balancing across the grid
- Automated voltage regulation for optimal power quality
- Demand response capabilities for peak load management
Bidirectional Power Flow
Enabling the prosumer revolution:
- Support for distributed energy resources (DERs)
- Integration of residential solar and energy storage systems
- Enhanced grid stability with two-way power flow management
Advanced Grid Analytics
Data-driven decision making:
- Big data analytics for predictive grid management
- Machine learning algorithms for optimized transformer deployment
- Improved asset management and maintenance scheduling
| Smart Grid Feature | Impact on Transformers | Market Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Management | Increased operational efficiency | Growing demand for smart transformers |
| Bidirectional Flow | Need for more flexible designs | Rise in transformer upgrades |
| Advanced Analytics | Improved lifecycle management | Increased investment in data infrastructure |
I recently visited a utility company that had just implemented a smart grid system. The grid operator showed me their control room, filled with screens displaying real-time data from thousands of transformers. "We can now see and manage our entire grid like never before," he said. "It’s like having X-ray vision for our power system."
Another fascinating experience was at a residential microgrid project. The community had installed smart transformers that could seamlessly integrate rooftop solar and electric vehicle charging. A homeowner told me, "Our transformer doesn’t just deliver power; it helps us generate and store our own energy too."
These experiences highlight how smart grid integration is fundamentally changing the role of distribution transformers. They’re no longer passive components but active, intelligent nodes in a dynamic energy network. This shift is driving demand for more advanced transformer technologies and creating new opportunities in the market.
As smart grid adoption continues to grow, I expect to see a surge in demand for transformers with built-in communication and control capabilities. The future of the distribution transformer market will be shaped by how well manufacturers can meet these evolving needs, blending traditional power engineering with cutting-edge digital technology.
Energy Efficiency Standards: Driving Market Evolution and Product Development?
Are you aware of how energy efficiency standards are reshaping the distribution transformer market? These regulations are not just guidelines; they’re catalysts for innovation and market transformation.
Energy efficiency standards in the distribution transformer market are driving the development of high-performance products and influencing market dynamics. These standards are pushing manufacturers to innovate, leading to transformers with lower losses, longer lifespans, and improved overall efficiency.
Let’s delve into how these standards are evolving the market:
Global Efficiency Regulations
Raising the bar worldwide:
- DOE efficiency standards in the United States
- EU Ecodesign requirements for transformers
- China’s energy efficiency tiers for distribution transformers
Total Ownership Cost (TOC) Approach
Shifting focus from initial cost to lifetime value:
- Consideration of both purchase price and operational costs
- Emphasis on long-term energy savings
- Incentives for investing in high-efficiency models
Performance Testing and Certification
Ensuring compliance and performance:
- Standardized testing procedures for transformer efficiency
- Third-party certification programs
- Regular updates to testing methods to reflect technological advancements
| Efficiency Standard | Market Impact | Product Development Trend |
|---|---|---|
| DOE Levels | Phasing out of low-efficiency models | Focus on amorphous core technology |
| EU Ecodesign | Increased demand for premium efficiency | Development of ultra-low loss designs |
| China’s Tiers | Market segmentation based on efficiency | Innovation in cooling and insulation |
I remember attending an industry conference where a panel of experts discussed the impact of new efficiency standards. One manufacturer shared, "When the standards first came out, we thought they were impossible to meet. Now, we’re exceeding them and seeing huge demand for our high-efficiency models."
Another enlightening experience was visiting a utility that had recently upgraded their transformer fleet to meet new standards. The energy savings were substantial. The operations manager told me, "Our new transformers are so efficient, it’s like we’ve added a small power plant to our grid without building anything new."
These standards are not just regulatory hurdles; they’re driving forces for innovation in the distribution transformer market. They’re pushing manufacturers to invest in R&D, develop new materials and designs, and rethink their entire approach to transformer production.
As efficiency standards continue to evolve, I anticipate seeing even more groundbreaking developments in transformer technology. The market is likely to shift further towards high-efficiency models, with a growing emphasis on lifecycle costs rather than just upfront pricing. This trend will not only benefit utilities and end-users through reduced energy losses but also contribute significantly to global efforts in energy conservation and sustainability.
Renewable Energy Adaptation: Reshaping Distribution Transformer Designs for Sustainable Power?
Have you noticed how the rise of renewable energy is changing our power grids? This shift is having a profound impact on distribution transformer designs, pushing them to adapt to a new era of sustainable power.
The integration of renewable energy sources is reshaping distribution transformer designs to handle bidirectional power flow, voltage fluctuations, and intermittent generation. These adaptations are crucial for supporting the growth of solar, wind, and other clean energy technologies in our power grids.
Let’s explore how transformers are evolving to support renewable energy:
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Enabling energy prosumers:
- Designs that support reverse power flow from distributed generation
- Enhanced protection systems for backfeed scenarios
- Smart inverter integration for improved grid stability
Voltage Regulation Capabilities
Handling fluctuations from renewable sources:
- On-load tap changers for dynamic voltage adjustment
- Reactive power compensation features
- Advanced control algorithms for voltage stability
Harmonic Mitigation
Addressing power quality issues:
- Enhanced core designs to withstand harmonic currents
- Integration of active harmonic filters
- Improved insulation systems for higher frequency stresses
| Renewable Adaptation | Design Change | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Bidirectional Flow | Reversible windings | Supports distributed generation |
| Voltage Regulation | Advanced tap changers | Improves power quality |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Specialized core materials | Enhances grid stability |
I recently visited a solar farm where they had installed specially designed transformers to handle the variable output. The site manager explained, "These transformers don’t just step up voltage; they act like conductors, orchestrating the flow of power between the solar panels and the grid."
Another eye-opening experience was at a wind farm that used transformers with advanced voltage regulation. During gusty conditions, I watched as the transformers seamlessly adjusted to maintain stable grid voltage. An engineer remarked, "Without these smart transformers, integrating wind power would be a nightmare for grid stability."
These experiences highlight how renewable energy is driving innovation in transformer design. It’s not just about handling power; it’s about intelligently managing the complex interplay between variable generation sources and the grid.
As renewable energy continues to grow, I expect to see even more specialized transformer designs emerging. We might see transformers with built-in energy storage capabilities or designs that can rapidly switch between different operational modes to support grid flexibility. The future of distribution transformers in a renewable-heavy grid is not just about power transformation; it’s about active participation in a dynamic, sustainable energy ecosystem.
Urbanization and Infrastructure: Fueling Growth and Innovation in Transformer Technologies?
Ever wondered how our growing cities are changing the power game? Urbanization and infrastructure development are major drivers in the distribution transformer market, sparking a wave of innovations.
Rapid urbanization and infrastructure expansion are fueling growth and innovation in transformer technologies. The demand for compact, high-capacity, and smart transformers is rising, driving the development of urban-friendly designs that can meet the complex power needs of modern cities.

Let’s dive into how urban growth is shaping transformer technologies:
Compact and High-Capacity Designs
Maximizing power in limited spaces:
- Dry-type transformers for indoor installations
- Gas-insulated transformers for reduced footprint
- High-power density designs for urban substations
Urban-Specific Features
Addressing unique city challenges:
- Low-noise designs for residential areas
- Fire-resistant technologies for high-rise buildings
- Underground transformer solutions for space-constrained areas
Smart City Integration
Powering the cities of tomorrow:
- IoT-enabled transformers for smart grid compatibility
- Support for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
- Integration with urban energy management systems
| Urban Trend | Transformer Innovation | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Space Constraints | Compact Designs | Increased demand for smaller, powerful units |
| Noise Regulations | Low-Noise Technology | Growing market for silent transformers |
| Smart City Initiatives | IoT Integration | Rise in smart transformer deployments |
I recently toured a new urban development where they were installing compact substations right in the basement of high-rise buildings. The project manager told me, "These transformers pack the power of a traditional substation into the size of a large closet. It’s a game-changer for urban power distribution."
Another fascinating experience was in a smart city pilot project. They had deployed IoT-enabled transformers throughout the downtown area. A city planner explained, "These transformers don’t just distribute power; they’re the nervous system of our smart grid, constantly communicating and adjusting to optimize energy use across the city."
These experiences underscore how urbanization is driving innovation in transformer technologies. It’s not just about making transformers smaller or more powerful; it’s about reimagining their role in the urban environment.
As cities continue to grow and evolve, I anticipate seeing even more specialized transformer solutions emerging. We might see transformers that can be easily upgraded or reconfigured to meet changing urban needs, or designs that integrate seamlessly with urban architecture. The future of transformer technology in cities is about blending in while standing out in performance – providing the lifeblood of urban power while adapting to the unique challenges of city life.
Conclusion
The distribution transformer market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, smart grid integration, efficiency standards, renewable energy adaptation, and urbanization. These trends are shaping a more efficient, sustainable, and intelligent power grid for the future.
Power Distribution Transformer: Energizing Smart Cities with Efficient and Resilient Grid Solutions?
Ever wondered what keeps our bustling cities powered 24/7? The unsung hero of urban energy is the power distribution transformer, quietly revolutionizing our smart city grids.
Power distribution transformers are crucial in energizing smart cities with efficient and resilient grid solutions. They optimize power flow, enhance grid stability, and enable the integration of renewable energy sources, forming the backbone of modern urban power infrastructure.

As someone who’s spent years in the power industry, I’ve witnessed the evolution of these transformers firsthand. Let’s dive into how they’re shaping the future of our urban energy landscape.
Urban Energy Efficiency: Optimizing Power Flow with Advanced Distribution Transformers?
Have you ever considered how cities manage to power millions of homes and businesses without constant blackouts? The secret lies in the advanced distribution transformers optimizing our urban power flow.
Advanced distribution transformers optimize urban power flow by reducing energy losses, balancing loads, and enabling real-time adjustments. These improvements lead to more efficient energy distribution, lower operational costs, and a more reliable power supply for city dwellers.
Let’s break down how these transformers are revolutionizing urban energy efficiency:
Loss Reduction Technologies
Minimizing energy waste:
- Amorphous metal cores reducing no-load losses
- Advanced winding designs to decrease load losses
- Improved insulation materials for better thermal management
Smart Load Balancing
Ensuring stable power distribution:
- Real-time monitoring of power demands across the grid
- Automated load shifting to prevent overloads
- Predictive algorithms for anticipating peak demand periods
Voltage Optimization
Maintaining ideal power quality:
- On-load tap changers for dynamic voltage regulation
- Power factor correction capabilities
- Harmonic mitigation features for cleaner power supply
Energy Monitoring and Analytics
Empowering data-driven decisions:
- Built-in sensors for continuous performance tracking
- Integration with smart grid management systems
- AI-powered analytics for identifying efficiency improvement opportunities
Cooling System Innovations
Enhancing performance and longevity:
- Natural ester fluids for better heat dissipation
- Advanced radiator designs for improved cooling efficiency
- Temperature monitoring and adaptive cooling control
| Feature | Efficiency Benefit | Urban Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Loss Reduction | Lower energy waste | Reduced operational costs |
| Smart Load Balancing | Optimized power distribution | Fewer outages and brownouts |
| Voltage Optimization | Improved power quality | Better performance of sensitive equipment |
| Energy Analytics | Data-driven efficiency improvements | Continuous grid optimization |
| Advanced Cooling | Extended transformer life | Increased grid reliability |
I remember a project where we upgraded a city’s aging transformer network with these advanced models. The utility company was skeptical about the investment, but the results were eye-opening. Within the first year, they saw a 15% reduction in distribution losses. The city’s energy manager told me, "We’re not just saving energy; we’re delivering more reliable power to our residents. It’s a win-win."
Another fascinating experience was implementing smart load balancing in a rapidly growing urban area. The system’s ability to predict and manage demand spikes was remarkable. During a heatwave that would have previously caused brownouts, the grid remained stable. A local business owner remarked, "This is the first summer we haven’t had to worry about power cuts affecting our operations."
These experiences have shown me that urban energy efficiency is about more than just reducing consumption. It’s about creating a smarter, more responsive power distribution system that can adapt to the dynamic needs of a modern city. Advanced distribution transformers are at the heart of this transformation, quietly optimizing power flow and ensuring that our urban centers have the reliable, efficient energy they need to thrive.
Building Resilience: Next-Generation Transformers for Robust City Grids?
Ever wondered how cities keep the lights on during storms or cyberattacks? Next-generation transformers are the unsung heroes building resilience into our urban power grids.
Next-generation transformers enhance city grid robustness through advanced protection systems, self-healing capabilities, and improved durability. These features ensure continuous power supply during extreme events, minimizing downtime and protecting critical urban infrastructure.
Let’s explore how these transformers are fortifying our urban power networks:
Advanced Protection Systems
Guarding against threats:
- Surge arresters for lightning and switching transients
- Cybersecurity features to prevent unauthorized access
- Electromagnetic pulse (EMP) shielding for critical installations
Self-Healing Capabilities
Minimizing downtime:
- Automatic fault detection and isolation
- Rapid reconfiguration to restore power to unaffected areas
- Self-diagnostic tools for proactive maintenance
Extreme Weather Resilience
Withstanding nature’s fury:
- Reinforced enclosures for high wind resistance
- Flood-resistant designs for low-lying urban areas
- Enhanced cooling systems for extreme heat conditions
Smart Grid Integration
Enabling coordinated responses:
- Real-time communication with grid management systems
- Participation in demand response programs
- Seamless integration with distributed energy resources
Redundancy and Modularity
Ensuring continuous operation:
- N+1 redundancy in critical components
- Hot-swappable modules for quick repairs
- Scalable designs to adapt to changing urban needs
| Resilience Feature | Traditional Grid Weakness | Next-Gen Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Protection | Vulnerability to surges and attacks | Multi-layered defense systems |
| Self-Healing | Extended outages after faults | Rapid, automated recovery |
| Weather Resilience | Susceptibility to environmental damage | Hardened designs for extreme conditions |
| Smart Integration | Isolated, uncoordinated responses | Networked, adaptive grid management |
| Redundancy | Single points of failure | Fault-tolerant architectures |
I recall a project where we installed these resilient transformers in a coastal city prone to hurricanes. The following storm season put them to the test. While older parts of the grid faltered, the areas with new transformers maintained power. A hospital administrator told me, "Your transformers kept our life-support systems running when we needed them most. You can’t put a price on that kind of reliability."
Another eye-opening experience was implementing a self-healing network in a dense urban area. During a major cable fault that would have previously blacked out several blocks, the system isolated the problem and rerouted power within minutes. A city official remarked, "It’s like the grid has developed its own immune system. We’re seeing a new level of reliability we didn’t think was possible."
These experiences have shown me that building resilience into city grids is about more than just hardening infrastructure. It’s about creating intelligent, adaptive systems that can respond to challenges in real-time. Next-generation transformers are at the forefront of this revolution, providing not just power, but peace of mind to urban dwellers. They’re ensuring that our cities can withstand the unexpected and bounce back stronger, no matter what challenges they face.
Smart City Power Demands: Scaling Distribution Solutions for Growing Urban Needs?
Have you ever considered how cities keep up with ever-increasing power demands? The answer lies in scalable distribution solutions, with transformers at their core.
Scaling distribution solutions for growing urban needs involves implementing flexible, high-capacity transformers that can adapt to changing power demands. These solutions incorporate modular designs, smart load management, and future-proofing features to meet the evolving energy requirements of smart cities.

Let’s dive into how these transformers are meeting the challenge of urban growth:
Modular and Expandable Designs
Adapting to urban expansion:
- Stackable transformer units for easy capacity increases
- Plug-and-play modules for quick installation and upgrades
- Scalable power ratings to match growing demands
Smart Load Management
Optimizing existing infrastructure:
- Dynamic load balancing across multiple transformers
- Predictive load forecasting for proactive capacity planning
- Automated peak shaving to reduce strain during high-demand periods
High-Density Power Solutions
Maximizing power in limited spaces:
- Compact designs for space-constrained urban environments
- High-capacity transformers with smaller footprints
- Underground and vault-type installations for discreet urban integration
Future-Proofing Features
Preparing for tomorrow’s needs:
- Compatibility with renewable energy sources and storage systems
- Support for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
- Upgradable control systems for emerging smart grid technologies
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Built-in interfaces for battery storage systems
- Load leveling capabilities to smooth demand curves
- Support for grid-scale energy storage solutions
| Scaling Feature | Urban Growth Challenge | Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Design | Unpredictable expansion rates | Easily expandable capacity |
| Smart Management | Fluctuating power demands | Adaptive load distribution |
| High-Density Solutions | Limited urban space | Compact, powerful units |
| Future-Proofing | Evolving technology landscape | Upgradable, flexible systems |
| Storage Integration | Peak demand management | Built-in energy balancing |
I remember a project in a rapidly developing urban area where we implemented a modular transformer system. The city planner was initially skeptical about the higher upfront cost. But as the neighborhood grew, we easily added capacity without major disruptions. Five years later, the planner told me, "Your foresight saved us millions in retrofit costs. We’ve expanded three times without a hitch."
Another fascinating experience was in a tech hub struggling with power quality issues due to rapid growth. We installed high-capacity transformers with smart load management. The system’s ability to balance loads and predict demand spikes was remarkable. A data center manager remarked, "We used to worry about outages during product launches. Now, we don’t even think about power – it’s always there, always stable."
These experiences have shown me that scaling distribution solutions for smart cities is about more than just adding more power. It’s about creating flexible, intelligent systems that can grow and adapt with the city. By implementing these scalable transformer solutions, we’re not just meeting today’s power needs; we’re building a foundation that can support the smart cities of tomorrow, no matter how they evolve.
Green Urban Integration: Transformers as Enablers of Renewable Energy in Cities?
Ever wondered how cities are managing to integrate more solar panels and wind turbines into their power grids? The secret lies in advanced transformers acting as enablers of renewable energy.
Transformers enable renewable energy integration in cities by managing variable inputs, facilitating bidirectional power flow, and ensuring grid stability. These capabilities allow for increased adoption of solar, wind, and other green energy sources in urban environments, supporting the transition to sustainable city power systems.
Let’s explore how transformers are greening our urban power landscape:
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Enabling energy prosumers:
- Handling power flow from grid to consumer and vice versa
- Supporting feed-in from rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines
- Facilitating net metering and energy trading for urban residents
Voltage Regulation for Intermittent Sources
Stabilizing renewable inputs:
- Real-time voltage adjustment to manage fluctuations from solar and wind
- Power factor correction for improved grid stability
- Harmonic filtering to maintain power quality with inverter-based sources
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Interfaces for connecting battery systems to the grid
- Load leveling to smooth out renewable energy production curves
- Support for community energy storage initiatives
Microgrid Compatibility
Fostering local energy resilience:
- Islanding capabilities for operating independent of the main grid
- Seamless switching between grid-connected and standalone modes
- Support for community-based renewable energy projects
Smart Inverter Coordination
Optimizing renewable energy conversion:
- Communication with smart inverters for efficient power conversion
- Coordinated control for maintaining grid frequency and voltage
- Enabling advanced grid services from distributed energy resources
| Renewable Integration Feature | Urban Challenge | Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Bidirectional Flow | Increasing prosumers | Flexible power management |
| Voltage Regulation | Intermittent generation | Real-time stabilization |
| Storage Integration | Supply-demand mismatch | Efficient energy balancing |
| Microgrid Support | Grid resilience | Local power independence |
| Inverter Coordination | Power quality issues | Optimized renewable integration |
I recall a project in an eco-conscious urban district aiming for 50% renewable energy use. The challenge was integrating a mix of rooftop solar, small wind turbines, and a nearby solar farm. We implemented advanced transformers with bidirectional flow capabilities and smart inverter coordination. The results were remarkable. Within a year, the district not only met but exceeded its renewable energy goal. A city council member proudly told me, "We’re not just consuming green energy; we’re a net producer on sunny days."
Another eye-opening experience was in a dense urban area prone to power outages. We installed transformers with microgrid capabilities, integrating them with local solar installations and battery storage. During a major grid failure, these areas maintained power, running on their renewable sources. A community leader remarked, "It’s like we’ve created little islands of energy independence. It’s transforming how we think about urban resilience."
These experiences have shown me that transformers are more than just power distribution devices in the context of urban renewable integration. They’re the linchpins that make widespread adoption of green energy in cities possible. By managing the complexities of renewable sources, these transformers are not just enabling a transition to cleaner energy; they’re fundamentally changing how cities generate, distribute, and consume power. As we push towards more sustainable urban environments, the role of these advanced transformers in facilitating green energy integration will only grow in importance.
Intelligent Power: Leveraging Smart Grid Technologies in Modern Urban Transformers?
Ever wondered how our city power grids are getting smarter? The answer lies in the intelligent features being built into modern urban transformers.
Modern urban transformers leverage smart grid technologies to enhance power distribution efficiency, reliability, and flexibility. These intelligent systems incorporate real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automated decision-making capabilities, enabling responsive and adaptive urban power networks.

Let’s delve into how these smart technologies are revolutionizing urban power distribution:
Real-Time Monitoring and Diagnostics
Keeping a pulse on the grid:
- Continuous tracking of voltage, current, and temperature
- Advanced sensors for detecting partial discharges and gas formation
- Real-time data transmission to control centers for immediate analysis
Predictive Maintenance
Staying ahead of issues:
- AI-driven analysis of performance data to predict potential failures
- Condition-based maintenance scheduling to optimize upkeep
- Automated alerts for emerging issues requiring attention
Dynamic Load Management
Balancing power demands efficiently:
- Real-time load balancing across transformer networks
- Automated tap changing for voltage optimization
- Demand response capabilities to manage peak loads
Cybersecurity Features
Protecting critical infrastructure:
- Encrypted communications to prevent unauthorized access
- Intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats
- Regular security updates to address evolving risks
Integration with Smart City Systems
Enabling broader urban intelligence:
- Interfacing with smart meter networks for granular consumption data
- Supporting electric vehicle charging infrastructure management
- Coordination with other urban systems like traffic management and public lighting
| Smart Feature | Traditional Limitation | Intelligent Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Periodic manual inspections | Continuous automated surveillance |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reactive repairs | Proactive issue prevention |
| Dynamic Load Management | Static load distribution | Adaptive power allocation |
| Cybersecurity | Vulnerable to digital threats | Multi-layered digital protection |
| Smart City Integration | Isolated power systems | Interconnected urban infrastructure |
I remember a project where we upgraded a city’s transformer network with these intelligent features. The utility company was initially skeptical about the investment in "fancy tech." But within months, the benefits were clear. The system predicted and prevented a major failure that would have blacked out the downtown area. The utility’s operations manager told me, "It’s like having a team of expert engineers monitoring our grid 24/7. The peace of mind alone is worth the investment."
Another fascinating experience was implementing dynamic load management in a rapidly growing urban area. The system’s ability to balance loads in real-time was remarkable. During a major sporting event that would have previously strained the grid, the network seamlessly redistributed power to meet the surge in demand. A city official remarked, "It’s like the grid has developed a mind of its own. We’re seeing a level ofefficiency and reliability we never thought possible."
These experiences have shown me that leveraging smart grid technologies in urban transformers is about more than just adding high-tech features. It’s about creating an intelligent, responsive power distribution system that can adapt to the complex and ever-changing needs of modern cities. These smart transformers are not just distributing electricity; they’re actively managing and optimizing the flow of power, predicting and preventing issues before they occur, and integrating seamlessly with the broader smart city ecosystem.
The impact of this intelligence extends far beyond just keeping the lights on. It’s enabling cities to use energy more efficiently, integrate renewable sources more effectively, and respond to crises more quickly. For instance, during extreme weather events, these smart systems can automatically reroute power to critical infrastructure like hospitals and emergency services. They can also help cities meet their sustainability goals by optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
Looking ahead, the potential for further innovation is enormous. We might see transformers that can learn and adapt even more autonomously, perhaps using machine learning to optimize their performance based on years of operational data. Or we could see deeper integration with emerging technologies like 5G networks and the Internet of Things, creating even more synergies between power distribution and other urban systems.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with intelligent power distribution, one thing is clear: smart transformers are becoming the cornerstone of our urban energy future. They’re not just keeping pace with the growing demands of our cities; they’re helping to shape smarter, more efficient, and more resilient urban environments for generations to come.
Conclusion
Power distribution transformers are crucial in energizing smart cities, offering efficient and resilient grid solutions. They optimize urban energy flow, enhance grid resilience, scale for growing needs, enable renewable integration, and leverage smart technologies for intelligent power management.
Have you ever wondered how remote villages get electricity? The answer might be hanging right above your head. Pole mounted distribution transformers are changing the game in rural electrification.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing rural electrification by integrating smart grid technologies. These transformers combine traditional reliability with advanced features, enabling efficient power distribution and management in remote areas previously underserved by conventional grid systems.
As someone who’s worked in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how these transformers are making a difference. Let’s explore how pole mounted distribution transformers are reshaping the landscape of rural power distribution.
Rural Power Evolution: Enhancing Electricity Access with Advanced Pole Mounted Technology?
Ever thought about the challenges of bringing power to remote areas? Advanced pole mounted technology is solving problems we once thought insurmountable.
Advanced pole mounted technology enhances rural electricity access by overcoming geographical barriers and infrastructure limitations. These transformers offer improved reliability, efficiency, and smart grid capabilities, making quality power distribution possible even in the most remote locations.
Let’s dive into how this technology is evolving rural power distribution:
Improved Reliability
Keeping the lights on in challenging environments:
- Enhanced protection against lightning strikes and surges
- Weather-resistant designs for extreme conditions
- Self-healing capabilities to isolate faults and restore power quickly
Increased Efficiency
Making every watt count:
- Low-loss core materials to reduce energy waste
- Optimized winding designs for better power transfer
- Smart load management to balance demand across the network
Remote Monitoring and Control
Managing power from afar:
- Real-time data transmission on transformer health and performance
- Remote diagnostics to identify issues before they cause outages
- Ability to adjust settings without on-site visits
Scalability and Flexibility
Adapting to growing rural needs:
- Modular designs for easy capacity upgrades
- Compatibility with renewable energy sources like solar and wind
- Support for microgrids and islanded operation
Environmental Considerations
Powering responsibly:
- Use of biodegradable oils to minimize environmental impact
- Reduced noise pollution for quieter rural environments
- Compact designs to minimize visual impact on landscapes
| Feature | Rural Benefit | Impact on Electrification |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Reliability | Fewer outages | Enhanced quality of life |
| Increased Efficiency | Lower energy losses | More power available to users |
| Remote Monitoring | Quick issue resolution | Reduced maintenance costs |
| Scalability | Adaptable to growth | Future-proof infrastructure |
| Environmental Design | Minimal ecological impact | Sustainable rural development |
I remember a project in a remote mountain village that had struggled with unreliable power for decades. We installed advanced pole mounted transformers with remote monitoring capabilities. Within months, the change was dramatic. The local school principal told me, "For the first time, our computers run without interruption. It’s opening up a world of online learning for our students."
Another eye-opening experience was in a coastal community prone to severe storms. We implemented self-healing transformer networks. During the next big storm, the system automatically isolated faults and rerouted power. What would have been a week-long blackout was reduced to brief, localized outages. A resident remarked, "It’s like our power grid has become storm-proof overnight."
These experiences have shown me that advanced pole mounted technology is more than just an upgrade to rural power systems. It’s a lifeline, bringing reliable, efficient, and smart power to areas that have long been underserved. As we continue to innovate in this field, we’re not just electrifying rural areas; we’re empowering communities and opening doors to new opportunities that were once thought impossible in remote locations.
Smart Integration: Bridging the Gap Between Traditional Grids and Modern Rural Networks?
Have you ever wondered how we can bring cutting-edge smart grid technology to remote areas? The answer lies in the smart integration capabilities of modern pole mounted transformers.
Smart integration in pole mounted transformers bridges the gap between traditional grids and modern rural networks by incorporating advanced communication and control features. These transformers act as intelligent nodes, enabling data-driven grid management and paving the way for smart rural electrification.
Let’s explore how these transformers are making rural grids smarter:
Advanced Communication Capabilities
Connecting the rural grid:
- Built-in cellular or satellite communication modules
- Real-time data exchange with central control systems
- Integration with IoT platforms for comprehensive grid monitoring
Intelligent Power Management
Optimizing rural energy distribution:
- Automated load balancing to prevent overloads
- Voltage regulation to maintain power quality
- Demand response capabilities to manage peak loads
Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Staying ahead of issues:
- AI-driven analysis of transformer performance data
- Predictive algorithms to forecast potential failures
- Optimization of maintenance schedules based on real-time insights
Renewable Energy Integration
Supporting green rural power:
- Ability to handle bidirectional power flow from solar and wind sources
- Smart inverter coordination for stable grid operation
- Energy storage management for improved reliability
Cybersecurity Features
Protecting rural power infrastructure:
- Encrypted communications to prevent unauthorized access
- Intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats
- Regular security updates to address evolving risks
| Smart Feature | Traditional Grid Limitation | Modern Rural Network Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Communication | Limited visibility | Real-time grid awareness |
| Intelligent Management | Manual load balancing | Automated efficiency optimization |
| Data Analytics | Reactive maintenance | Proactive issue prevention |
| Renewable Integration | One-way power flow | Flexible, green energy support |
| Cybersecurity | Vulnerable to attacks | Robust digital protection |
I recall a project in a rural area where we were integrating these smart transformers into an aging grid. The local utility was skeptical about the investment. But within months, the benefits were clear. They could now detect and resolve issues before they led to outages. The utility manager told me, "It’s like we’ve gone from flying blind to having a high-tech control tower. We can see and manage everything."
Another fascinating experience was in a farming community embracing solar energy. The smart transformers we installed could handle the variable input from solar panels while maintaining grid stability. During a sunny week, the community became a net energy exporter. A farmer proudly said, "Our fields are now growing both crops and electricity."
These experiences have shown me that smart integration in pole mounted transformers is not just about adding technology to the grid. It’s about transforming rural power networks into intelligent, responsive systems. By bridging the gap between traditional infrastructure and modern smart grid capabilities, we’re not just improving power distribution; we’re enabling rural communities to participate fully in the energy revolution. This smart integration is key to creating resilient, efficient, and future-ready rural power systems that can support the growing needs of remote areas.
Overcoming Rural Challenges: Innovative Solutions in Pole Transformer Design?
Rural areas present unique challenges for power distribution. How are pole transformer designs evolving to meet these specific needs?
Innovative pole transformer designs overcome rural challenges through weather-resistant construction, enhanced reliability features, and adaptability to diverse environments. These solutions ensure consistent power supply in remote areas, addressing issues like extreme weather, wildlife interference, and limited maintenance access.
Let’s explore the key innovations addressing rural power distribution challenges:
Weather-Resistant Construction
Standing up to nature’s fury:
- Reinforced housing to withstand high winds and ice loads
- Corrosion-resistant materials for coastal and high-humidity areas
- Enhanced insulation for extreme temperature variations
Wildlife Protection
Coexisting with local fauna:
- Animal guards to prevent climbing and nesting
- Insulated bushings to reduce wildlife-related short circuits
- Avian-friendly designs to minimize bird collisions
Remote Diagnostics and Self-Healing
Minimizing the need for on-site interventions:
- Built-in sensors for continuous health monitoring
- Automatic fault detection and isolation capabilities
- Self-reconfiguring systems to restore power quickly
Modular and Scalable Designs
Adapting to changing rural needs:
- Easy-to-upgrade components for growing power demands
- Plug-and-play modules for quick installation and replacement
- Compatibility with various voltage levels and configurations
Off-Grid and Microgrid Support
Enabling power independence:
- Ability to operate in islanded mode during main grid outages
- Integration with local renewable energy sources
- Energy storage management for consistent power supply
| Rural Challenge | Innovative Solution | Impact on Power Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Weather | Reinforced Construction | Increased uptime during storms |
| Wildlife Interference | Protective Barriers | Reduced outages from animal contact |
| Limited Access | Remote Diagnostics | Fewer maintenance visits required |
| Changing Demands | Modular Design | Easy adaptation to growth |
| Unreliable Main Grid | Microgrid Capabilities | Enhanced local energy resilience |
I remember a project in a remote mountain region plagued by frequent lightning strikes. We installed pole transformers with advanced surge protection and self-healing capabilities. The change was remarkable. During the next storm season, the area experienced zero lightning-related outages. A local business owner told me, "For the first time in years, we didn’t have to shut down during thunderstorms. It’s been a game-changer for our operations."
Another challenging case was in a wildlife-rich area where animal interactions frequently disrupted power. We implemented transformers with comprehensive wildlife protection features. Within a year, animal-related outages dropped by 80%. A conservation officer remarked, "It’s great to see technology that not only improves power reliability but also protects our local wildlife."
These experiences have taught me that innovative pole transformer designs are crucial for overcoming the unique challenges of rural power distribution. By addressing specific issues like extreme weather, wildlife interference, and limited accessibility, these transformers are not just delivering electricity; they’re providing reliability and peace of mind to rural communities. As we continue to refine these designs, we’re not only improving power distribution but also enhancing the quality of life in remote areas, making reliable electricity a reality even in the most challenging environments.
Efficiency at Height: Maximizing Performance of Elevated Smart Grid Components?
Ever wondered how we can make those transformers perched high on poles work smarter and more efficiently? The key lies in maximizing the performance of these elevated smart grid components.
Maximizing the performance of elevated smart grid components involves integrating advanced monitoring systems, optimizing energy efficiency, and enhancing remote management capabilities. These improvements ensure that pole mounted transformers operate at peak efficiency, reducing losses and improving overall grid performance.

Let’s dive into how we’re boosting efficiency in these high-flying grid components:
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Keeping a constant eye on performance:
- Real-time monitoring of load, temperature, and oil conditions
- Predictive analytics to forecast potential issues
- Integration with smart grid management systems for comprehensive oversight
Energy Loss Reduction
Minimizing waste in power distribution:
- High-efficiency core materials to reduce no-load losses
- Optimized winding designs for lower copper losses
- Improved cooling systems for better heat dissipation
Smart Load Management
Balancing power distribution efficiently:
- Dynamic load balancing across phases
- Automatic tap changing for voltage optimization
- Demand response capabilities to manage peak loads
Remote Diagnostics and Control
Managing transformers from afar:
- Remote access for diagnostics and troubleshooting
- Over-the-air firmware updates to enhance functionality
- Ability to adjust settings without physical intervention
Environmental Adaptation
Optimizing performance in diverse conditions:
- Adaptive cooling systems for varying climate conditions
- Automatic de-icing features for cold regions
- Dust and pollution resistant designs for harsh environments
| Efficiency Feature | Performance Benefit | Impact on Grid Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Monitoring | Early issue detection | Reduced downtime |
| Loss Reduction | Lower energy waste | Improved overall efficiency |
| Smart Load Management | Balanced power distribution | Enhanced grid stability |
| Remote Capabilities | Quick problem resolution | Reduced maintenance costs |
| Environmental Adaptation | Consistent performance | Reliable operation in all conditions |
I recall a project where we upgraded a rural network with these high-efficiency pole transformers. The utility was skeptical about the investment, but the results were eye-opening. Within the first year, they saw a 15% reduction in distribution losses. The operations manager told me, "We’re not just saving energy; we’re delivering more power to our customers without upgrading our generation capacity."
Another fascinating experience was implementing smart load management in a small town with a large seasonal population fluctuation. The transformers could automatically adjust to the changing demand patterns. During peak tourist season, the grid handled the load surge smoothly without any outages. A local hotel owner remarked, "It’s the first summer we haven’t had to worry about power cuts during our busiest weeks."
These experiences have shown me that efficiency at height is about more than just reducing losses. It’s about creating a smarter, more responsive power distribution system that can adapt to changing conditions and demands. By maximizing the performance of these elevated components, we’re not just improving the efficiency of individual transformers; we’re enhancing the overall resilience and capability of the entire grid. This approach is crucial for creating sustainable, reliable power systems that can meet the evolving needs of rural communities while minimizing waste and operational costs.
Future-Ready Rural Grids: Pole Transformers as Catalysts for Countryside Modernization?
Have you ever imagined a future where rural areas have power systems as advanced as big cities? Pole transformers are turning this vision into reality, acting as catalysts for countryside modernization.
Pole transformers are catalyzing countryside modernization by enabling smart grid technologies in rural areas. These advanced units support renewable integration, facilitate data-driven grid management, and provide the foundation for future innovations like electric vehicle charging and energy storage systems.

Let’s explore how these transformers are shaping the future of rural power grids:
Renewable Energy Integration
Powering a green rural future:
- Bidirectional power flow management for solar and wind integration
- Smart inverter coordination for stable grid operation
- Microgrid support for local energy independence
Data-Driven Grid Management
Bringing big data to small towns:
- Advanced sensors for comprehensive grid monitoring
- AI-powered analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization
- Integration with smart meters for detailed consumption insights
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Support
Preparing for rural e-mobility:
- Load management capabilities for EV charging stations
- Time-of-use pricing support to encourage off-peak charging
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) readiness for future energy storage applications
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Compatibility with battery storage systems
- Peak shaving and load shifting capabilities
- Enhanced grid resilience during outages
IoT and Smart City Technologies
Enabling connected rural communities:
- Support for smart street lighting and traffic management systems
- Integration with agricultural IoT devices for smart farming
- Backbone for rural broadband and 5G network deployment
| Modernization Aspect | Traditional Rural Grid | Future-Ready Rural Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Sources | Centralized, fossil-fuel based | Distributed, renewable-integrated |
| Grid Management | Manual, reactive | Automated, predictive |
| Vehicle Support | Basic electricity supply | EV charging infrastructure |
| Energy Storage | Limited or none | Integrated battery systems |
| Connectivity | Basic power distribution | IoT and smart technology enabler |
I remember a project in a forward-thinking rural community that wanted to become a model for sustainable living. We installed advanced pole transformers capable of integrating solar power and supporting EV charging. Within a year, the town had increased its renewable energy usage by 200% and saw a surge in EV adoptions. The mayor proudly told me, "We’re not just keeping up with cities; we’re setting the pace for green energy adoption."
Another eye-opening experience was in a farming region embracing precision agriculture. The smart pole transformers we installed not only provided reliable power but also served as nodes for an IoT network. Farmers could now monitor soil conditions, automate irrigation, and optimize crop yields. A tech-savvy farmer remarked, "These transformers aren’t just powering our equipment; they’re powering a whole new way of farming."
These experiences have shown me that pole transformers are more than just components of the rural grid; they’re the foundation of a modernized countryside. By enabling smart grid technologies, supporting renewable energy, and facilitating advanced applications, these transformers are bridging the gap between rural and urban infrastructure. They’re not just bringing power to remote areas; they’re bringing the future of energy management and smart technologyto rural communities. As we continue to innovate and deploy these advanced systems, we’re not just electrifying the countryside; we’re empowering it to become a leader in sustainable, efficient, and technologically advanced living.
The role of pole transformers in this rural modernization goes beyond just providing electricity. They’re becoming the nervous system of a new, smarter rural infrastructure. By supporting technologies like IoT, smart agriculture, and advanced energy management, these transformers are helping to create vibrant, connected rural communities that can compete with urban areas in terms of quality of life and economic opportunities.
As we look to the future, the potential for further advancements is exciting. We might see pole transformers integrating more advanced AI for even smarter grid management, or supporting new technologies we haven’t even imagined yet. The key is that by building this flexible, future-ready infrastructure now, we’re setting up rural areas to adapt and thrive in whatever the future may bring.
Conclusion
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing rural electrification by integrating smart grid technologies, overcoming unique challenges, maximizing efficiency, and catalyzing countryside modernization. They are key to creating resilient, sustainable, and technologically advanced rural power systems.
Have you ever wondered how remote villages get electricity? The answer might be hanging right above your head. Pole mounted distribution transformers are changing the game in rural electrification.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing rural electrification by integrating smart grid technologies. These transformers combine traditional reliability with advanced features, enabling efficient power distribution and management in remote areas previously underserved by conventional grid systems.
As someone who’s worked in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how these transformers are making a difference. Let’s explore how pole mounted distribution transformers are reshaping the landscape of rural power distribution.
Rural Power Evolution: Enhancing Electricity Access with Advanced Pole Mounted Technology?
Ever thought about the challenges of bringing power to remote areas? Advanced pole mounted technology is solving problems we once thought insurmountable.
Advanced pole mounted technology enhances rural electricity access by overcoming geographical barriers and infrastructure limitations. These transformers offer improved reliability, efficiency, and smart grid capabilities, making quality power distribution possible even in the most remote locations.
Let’s dive into how this technology is evolving rural power distribution:
Improved Reliability
Keeping the lights on in challenging environments:
- Enhanced protection against lightning strikes and surges
- Weather-resistant designs for extreme conditions
- Self-healing capabilities to isolate faults and restore power quickly
Increased Efficiency
Making every watt count:
- Low-loss core materials to reduce energy waste
- Optimized winding designs for better power transfer
- Smart load management to balance demand across the network
Remote Monitoring and Control
Managing power from afar:
- Real-time data transmission on transformer health and performance
- Remote diagnostics to identify issues before they cause outages
- Ability to adjust settings without on-site visits
Scalability and Flexibility
Adapting to growing rural needs:
- Modular designs for easy capacity upgrades
- Compatibility with renewable energy sources like solar and wind
- Support for microgrids and islanded operation
Environmental Considerations
Powering responsibly:
- Use of biodegradable oils to minimize environmental impact
- Reduced noise pollution for quieter rural environments
- Compact designs to minimize visual impact on landscapes
| Feature | Rural Benefit | Impact on Electrification |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Reliability | Fewer outages | Enhanced quality of life |
| Increased Efficiency | Lower energy losses | More power available to users |
| Remote Monitoring | Quick issue resolution | Reduced maintenance costs |
| Scalability | Adaptable to growth | Future-proof infrastructure |
| Environmental Design | Minimal ecological impact | Sustainable rural development |
I remember a project in a remote mountain village that had struggled with unreliable power for decades. We installed advanced pole mounted transformers with remote monitoring capabilities. Within months, the change was dramatic. The local school principal told me, "For the first time, our computers run without interruption. It’s opening up a world of online learning for our students."
Another eye-opening experience was in a coastal community prone to severe storms. We implemented self-healing transformer networks. During the next big storm, the system automatically isolated faults and rerouted power. What would have been a week-long blackout was reduced to brief, localized outages. A resident remarked, "It’s like our power grid has become storm-proof overnight."
These experiences have shown me that advanced pole mounted technology is more than just an upgrade to rural power systems. It’s a lifeline, bringing reliable, efficient, and smart power to areas that have long been underserved. As we continue to innovate in this field, we’re not just electrifying rural areas; we’re empowering communities and opening doors to new opportunities that were once thought impossible in remote locations.
Smart Integration: Bridging the Gap Between Traditional Grids and Modern Rural Networks?
Have you ever wondered how we can bring cutting-edge smart grid technology to remote areas? The answer lies in the smart integration capabilities of modern pole mounted transformers.
Smart integration in pole mounted transformers bridges the gap between traditional grids and modern rural networks by incorporating advanced communication and control features. These transformers act as intelligent nodes, enabling data-driven grid management and paving the way for smart rural electrification.
Let’s explore how these transformers are making rural grids smarter:
Advanced Communication Capabilities
Connecting the rural grid:
- Built-in cellular or satellite communication modules
- Real-time data exchange with central control systems
- Integration with IoT platforms for comprehensive grid monitoring
Intelligent Power Management
Optimizing rural energy distribution:
- Automated load balancing to prevent overloads
- Voltage regulation to maintain power quality
- Demand response capabilities to manage peak loads
Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Staying ahead of issues:
- AI-driven analysis of transformer performance data
- Predictive algorithms to forecast potential failures
- Optimization of maintenance schedules based on real-time insights
Renewable Energy Integration
Supporting green rural power:
- Ability to handle bidirectional power flow from solar and wind sources
- Smart inverter coordination for stable grid operation
- Energy storage management for improved reliability
Cybersecurity Features
Protecting rural power infrastructure:
- Encrypted communications to prevent unauthorized access
- Intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats
- Regular security updates to address evolving risks
| Smart Feature | Traditional Grid Limitation | Modern Rural Network Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Communication | Limited visibility | Real-time grid awareness |
| Intelligent Management | Manual load balancing | Automated efficiency optimization |
| Data Analytics | Reactive maintenance | Proactive issue prevention |
| Renewable Integration | One-way power flow | Flexible, green energy support |
| Cybersecurity | Vulnerable to attacks | Robust digital protection |
I recall a project in a rural area where we were integrating these smart transformers into an aging grid. The local utility was skeptical about the investment. But within months, the benefits were clear. They could now detect and resolve issues before they led to outages. The utility manager told me, "It’s like we’ve gone from flying blind to having a high-tech control tower. We can see and manage everything."
Another fascinating experience was in a farming community embracing solar energy. The smart transformers we installed could handle the variable input from solar panels while maintaining grid stability. During a sunny week, the community became a net energy exporter. A farmer proudly said, "Our fields are now growing both crops and electricity."
These experiences have shown me that smart integration in pole mounted transformers is not just about adding technology to the grid. It’s about transforming rural power networks into intelligent, responsive systems. By bridging the gap between traditional infrastructure and modern smart grid capabilities, we’re not just improving power distribution; we’re enabling rural communities to participate fully in the energy revolution. This smart integration is key to creating resilient, efficient, and future-ready rural power systems that can support the growing needs of remote areas.
Overcoming Rural Challenges: Innovative Solutions in Pole Transformer Design?
Rural areas present unique challenges for power distribution. How are pole transformer designs evolving to meet these specific needs?
Innovative pole transformer designs overcome rural challenges through weather-resistant construction, enhanced reliability features, and adaptability to diverse environments. These solutions ensure consistent power supply in remote areas, addressing issues like extreme weather, wildlife interference, and limited maintenance access.
Let’s explore the key innovations addressing rural power distribution challenges:
Weather-Resistant Construction
Standing up to nature’s fury:
- Reinforced housing to withstand high winds and ice loads
- Corrosion-resistant materials for coastal and high-humidity areas
- Enhanced insulation for extreme temperature variations
Wildlife Protection
Coexisting with local fauna:
- Animal guards to prevent climbing and nesting
- Insulated bushings to reduce wildlife-related short circuits
- Avian-friendly designs to minimize bird collisions
Remote Diagnostics and Self-Healing
Minimizing the need for on-site interventions:
- Built-in sensors for continuous health monitoring
- Automatic fault detection and isolation capabilities
- Self-reconfiguring systems to restore power quickly
Modular and Scalable Designs
Adapting to changing rural needs:
- Easy-to-upgrade components for growing power demands
- Plug-and-play modules for quick installation and replacement
- Compatibility with various voltage levels and configurations
Off-Grid and Microgrid Support
Enabling power independence:
- Ability to operate in islanded mode during main grid outages
- Integration with local renewable energy sources
- Energy storage management for consistent power supply
| Rural Challenge | Innovative Solution | Impact on Power Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Weather | Reinforced Construction | Increased uptime during storms |
| Wildlife Interference | Protective Barriers | Reduced outages from animal contact |
| Limited Access | Remote Diagnostics | Fewer maintenance visits required |
| Changing Demands | Modular Design | Easy adaptation to growth |
| Unreliable Main Grid | Microgrid Capabilities | Enhanced local energy resilience |
I remember a project in a remote mountain region plagued by frequent lightning strikes. We installed pole transformers with advanced surge protection and self-healing capabilities. The change was remarkable. During the next storm season, the area experienced zero lightning-related outages. A local business owner told me, "For the first time in years, we didn’t have to shut down during thunderstorms. It’s been a game-changer for our operations."
Another challenging case was in a wildlife-rich area where animal interactions frequently disrupted power. We implemented transformers with comprehensive wildlife protection features. Within a year, animal-related outages dropped by 80%. A conservation officer remarked, "It’s great to see technology that not only improves power reliability but also protects our local wildlife."
These experiences have taught me that innovative pole transformer designs are crucial for overcoming the unique challenges of rural power distribution. By addressing specific issues like extreme weather, wildlife interference, and limited accessibility, these transformers are not just delivering electricity; they’re providing reliability and peace of mind to rural communities. As we continue to refine these designs, we’re not only improving power distribution but also enhancing the quality of life in remote areas, making reliable electricity a reality even in the most challenging environments.
Efficiency at Height: Maximizing Performance of Elevated Smart Grid Components?
Ever wondered how we can make those transformers perched high on poles work smarter and more efficiently? The key lies in maximizing the performance of these elevated smart grid components.
Maximizing the performance of elevated smart grid components involves integrating advanced monitoring systems, optimizing energy efficiency, and enhancing remote management capabilities. These improvements ensure that pole mounted transformers operate at peak efficiency, reducing losses and improving overall grid performance.
Let’s dive into how we’re boosting efficiency in these high-flying grid components:
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Keeping a constant eye on performance:
- Real-time monitoring of load, temperature, and oil conditions
- Predictive analytics to forecast potential issues
- Integration with smart grid management systems for comprehensive oversight
Energy Loss Reduction
Minimizing waste in power distribution:
- High-efficiency core materials to reduce no-load losses
- Optimized winding designs for lower copper losses
- Improved cooling systems for better heat dissipation
Smart Load Management
Balancing power distribution efficiently:
- Dynamic load balancing across phases
- Automatic tap changing for voltage optimization
- Demand response capabilities to manage peak loads
Remote Diagnostics and Control
Managing transformers from afar:
- Remote access for diagnostics and troubleshooting
- Over-the-air firmware updates to enhance functionality
- Ability to adjust settings without physical intervention
Environmental Adaptation
Optimizing performance in diverse conditions:
- Adaptive cooling systems for varying climate conditions
- Automatic de-icing features for cold regions
- Dust and pollution resistant designs for harsh environments
| Efficiency Feature | Performance Benefit | Impact on Grid Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Monitoring | Early issue detection | Reduced downtime |
| Loss Reduction | Lower energy waste | Improved overall efficiency |
| Smart Load Management | Balanced power distribution | Enhanced grid stability |
| Remote Capabilities | Quick problem resolution | Reduced maintenance costs |
| Environmental Adaptation | Consistent performance | Reliable operation in all conditions |
I recall a project where we upgraded a rural network with these high-efficiency pole transformers. The utility was skeptical about the investment, but the results were eye-opening. Within the first year, they saw a 15% reduction in distribution losses. The operations manager told me, "We’re not just saving energy; we’re delivering more power to our customers without upgrading our generation capacity."
Another fascinating experience was implementing smart load management in a small town with a large seasonal population fluctuation. The transformers could automatically adjust to the changing demand patterns. During peak tourist season, the grid handled the load surge smoothly without any outages. A local hotel owner remarked, "It’s the first summer we haven’t had to worry about power cuts during our busiest weeks."
These experiences have shown me that efficiency at height is about more than just reducing losses. It’s about creating a smarter, more responsive power distribution system that can adapt to changing conditions and demands. By maximizing the performance of these elevated components, we’re not just improving the efficiency of individual transformers; we’re enhancing the overall resilience and capability of the entire grid. This approach is crucial for creating sustainable, reliable power systems that can meet the evolving needs of rural communities while minimizing waste and operational costs.
Future-Ready Rural Grids: Pole Transformers as Catalysts for Countryside Modernization?
Have you ever imagined a future where rural areas have power systems as advanced as big cities? Pole transformers are turning this vision into reality, acting as catalysts for countryside modernization.
Pole transformers are catalyzing countryside modernization by enabling smart grid technologies in rural areas. These advanced units support renewable integration, facilitate data-driven grid management, and provide the foundation for future innovations like electric vehicle charging and energy storage systems.
Let’s explore how these transformers are shaping the future of rural power grids:
Renewable Energy Integration
Powering a green rural future:
- Bidirectional power flow management for solar and wind integration
- Smart inverter coordination for stable grid operation
- Microgrid support for local energy independence
Data-Driven Grid Management
Bringing big data to small towns:
- Advanced sensors for comprehensive grid monitoring
- AI-powered analytics for predictive maintenance and optimization
- Integration with smart meters for detailed consumption insights
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Support
Preparing for rural e-mobility:
- Load management capabilities for EV charging stations
- Time-of-use pricing support to encourage off-peak charging
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) readiness for future energy storage applications
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Compatibility with battery storage systems
- Peak shaving and load shifting capabilities
- Enhanced grid resilience during outages
IoT and Smart City Technologies
Enabling connected rural communities:
- Support for smart street lighting and traffic management systems
- Integration with agricultural IoT devices for smart farming
- Backbone for rural broadband and 5G network deployment
| Modernization Aspect | Traditional Rural Grid | Future-Ready Rural Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Sources | Centralized, fossil-fuel based | Distributed, renewable-integrated |
| Grid Management | Manual, reactive | Automated, predictive |
| Vehicle Support | Basic electricity supply | EV charging infrastructure |
| Energy Storage | Limited or none | Integrated battery systems |
| Connectivity | Basic power distribution | IoT and smart technology enabler |
I remember a project in a forward-thinking rural community that wanted to become a model for sustainable living. We installed advanced pole transformers capable of integrating solar power and supporting EV charging. Within a year, the town had increased its renewable energy usage by 200% and saw a surge in EV adoptions. The mayor proudly told me, "We’re not just keeping up with cities; we’re setting the pace for green energy adoption."
Another eye-opening experience was in a farming region embracing precision agriculture. The smart pole transformers we installed not only provided reliable power but also served as nodes for an IoT network. Farmers could now monitor soil conditions, automate irrigation, and optimize crop yields. A tech-savvy farmer remarked, "These transformers aren’t just powering our equipment; they’re powering a whole new way of farming."
These experiences have shown me that pole transformers are more than just components of the rural grid; they’re the foundation of a modernized countryside. By enabling smart grid technologies, supporting renewable energy, and facilitating advanced applications, these transformers are bridging the gap between rural and urban infrastructure. They’re not just bringing power to remote areas; they’re bringing the future of energy management and smart technologyto rural communities. As we continue to innovate and deploy these advanced systems, we’re not just electrifying the countryside; we’re empowering it to become a leader in sustainable, efficient, and technologically advanced living.
The role of pole transformers in this rural modernization goes beyond just providing electricity. They’re becoming the nervous system of a new, smarter rural infrastructure. By supporting technologies like IoT, smart agriculture, and advanced energy management, these transformers are helping to create vibrant, connected rural communities that can compete with urban areas in terms of quality of life and economic opportunities.
As we look to the future, the potential for further advancements is exciting. We might see pole transformers integrating more advanced AI for even smarter grid management, or supporting new technologies we haven’t even imagined yet. The key is that by building this flexible, future-ready infrastructure now, we’re setting up rural areas to adapt and thrive in whatever the future may bring.
Conclusion
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing rural electrification by integrating smart grid technologies, overcoming unique challenges, maximizing efficiency, and catalyzing countryside modernization. They are key to creating resilient, sustainable, and technologically advanced rural power systems.
Are you struggling to justify the cost of upgrading your power grid? The price of distribution transformers often raises eyebrows, but the long-term benefits might surprise you.
Distribution transformer prices reflect a balance between cost-efficiency and performance in modern power grid investments. While initial costs may be high, advanced transformers offer improved efficiency, longer lifespans, and smart grid compatibility, potentially leading to significant long-term savings and improved grid reliability.

As someone who’s been in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial the right transformer choice can be. Let’s dive into the world of distribution transformer pricing and explore how to make smart investment decisions for your power grid.
Investment Strategies: Navigating Transformer Costs in Grid Modernization Projects?
Ever wondered how to justify the hefty price tag of modern transformers to your finance department? The key lies in understanding the long-term benefits of these investments.
Effective investment strategies for transformer costs in grid modernization involve considering total cost of ownership, future-proofing capabilities, and potential energy savings. By focusing on long-term value rather than just upfront costs, utilities can make smarter decisions that benefit both their bottom line and grid performance.

Let’s break down the key factors in navigating transformer costs:
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Looking beyond the price tag:
- Initial purchase price of the transformer
- Installation and commissioning costs
- Operational costs, including energy losses
- Maintenance and repair expenses over the transformer’s lifetime
- End-of-life disposal or recycling costs
Future-Proofing Capabilities
Investing in adaptability:
- Smart grid compatibility for future upgrades
- Scalability to meet growing power demands
- Ability to integrate with renewable energy sources
- Cybersecurity features to protect against evolving threats
Energy Efficiency Savings
Calculating long-term benefits:
- Reduced energy losses compared to older models
- Lower cooling requirements and associated costs
- Potential for energy rebates or incentives from utilities
- Contribution to meeting regulatory efficiency standards
Reliability and Downtime Reduction
Valuing uninterrupted service:
- Improved reliability leading to fewer outages
- Reduced maintenance downtime
- Lower risk of catastrophic failures
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and reduced complaint handling costs
Environmental Impact Considerations
Factoring in sustainability:
- Lower carbon footprint from improved efficiency
- Reduced use of insulating oils or use of biodegradable alternatives
- Longer lifespan reducing waste and replacement frequency
- Compliance with current and future environmental regulations
| Investment Factor | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Initial Cost | Increased capital expenditure | Reduced operational expenses |
| Smart Features | Additional upfront investment | Future-proof grid capabilities |
| Energy Efficiency | Immediate reduction in losses | Significant cost savings over time |
| Reliability Improvements | Initial testing and setup costs | Fewer outages and maintenance needs |
| Environmental Considerations | Potential premium for eco-friendly options | Regulatory compliance and sustainability |
I remember a project where we were upgrading a city’s aging transformer network. The utility was hesitant about the high upfront costs of advanced models. We conducted a comprehensive TCO analysis, factoring in energy savings and reduced maintenance. The results were eye-opening. Over a 20-year period, the new transformers would save the utility millions in operational costs, far outweighing the initial investment. The CFO, initially skeptical, became our biggest advocate after seeing the numbers.
Another interesting case was a rural electric cooperative weighing the costs of smart-enabled transformers. They were concerned about future-proofing but struggled with the budget. We developed a phased approach, strategically placing smart transformers at key nodes. This allowed them to build a smart grid foundation without breaking the bank. Five years later, they’re expanding the smart network with ease, thanks to the groundwork laid by those initial investments.
These experiences taught me that navigating transformer costs isn’t just about finding the cheapest option. It’s about making informed decisions that balance immediate budget constraints with long-term operational benefits. By considering factors like TCO, future-proofing, and efficiency savings, utilities can make investment choices that not only modernize their grid but also provide lasting financial benefits. It’s a strategy that turns a necessary expense into a valuable long-term asset.
Price vs. Performance: Analyzing the Long-Term Value of Advanced Distribution Transformers?
When it comes to distribution transformers, the age-old question persists: Is it worth paying more for advanced models? The answer lies in understanding the long-term value proposition.
Advanced distribution transformers offer superior performance that can justify their higher price tags. Their improved efficiency, longer lifespan, and advanced features contribute to lower total cost of ownership and enhanced grid reliability, often outweighing the initial investment over time.

Let’s dive into the key aspects of this price-performance balance:
Efficiency Gains
Reducing losses, increasing savings:
- Lower core losses due to advanced materials like amorphous metals
- Reduced copper losses from improved winding designs
- Better performance under varying load conditions
- Cumulative energy savings over the transformer’s lifetime
Lifespan Extension
Investing in longevity:
- Robust construction techniques for extended operational life
- Advanced cooling systems to reduce thermal stress
- Better resistance to short circuits and overloads
- Potential for 40+ years of service compared to 25-30 for standard models
Smart Grid Capabilities
Preparing for the future:
- Built-in monitoring and communication features
- Ability to participate in demand response programs
- Support for bi-directional power flow with distributed generation
- Enhanced data collection for predictive maintenance
Reliability Improvements
Minimizing downtime and disruptions:
- Advanced protection features against faults and surges
- Self-diagnostic capabilities for early problem detection
- Improved load management to prevent overloading
- Faster response to grid disturbances
Environmental Benefits
Sustainability as a long-term investment:
- Reduced carbon footprint from improved efficiency
- Use of eco-friendly materials and insulating fluids
- Lower noise pollution in urban areas
- Easier compliance with evolving environmental regulations
| Performance Aspect | Standard Transformer | Advanced Transformer | Long-Term Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 97-98% efficient | 99%+ efficient | Significant energy savings |
| Lifespan | 25-30 years | 40+ years | Reduced replacement costs |
| Smart Features | Limited or none | Comprehensive | Future-proof grid capabilities |
| Reliability | Basic protection | Advanced safeguards | Fewer outages and maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Standard compliance | Exceeds standards | Lower carbon footprint, better sustainability |
I recall a project where we were comparing standard and advanced transformers for a suburban development. The developer was initially drawn to the lower price of standard models. However, when we calculated the energy savings over a 30-year period, the advanced transformers showed a clear advantage. The efficiency gains alone would cover the price difference within 12 years. The developer was amazed, saying, "I never thought a transformer could be an investment that pays for itself."
Another eye-opening experience was with a utility struggling with frequent outages in an industrial area. We installed advanced transformers with self-diagnostic capabilities. Within the first year, the system prevented three major failures by detecting issues early. The utility’s reliability metrics improved dramatically, and they received fewer complaints from industrial customers. The operations manager told me, "These transformers aren’t just equipment; they’re like having an expert technician on-site 24/7."
These experiences have shown me that the price-performance equation for advanced transformers goes far beyond the initial cost. When you factor in efficiency gains, extended lifespan, smart capabilities, improved reliability, and environmental benefits, the long-term value becomes clear. It’s not just about buying a piece of equipment; it’s about investing in the future of your power grid. For utilities and developers looking to build resilient, efficient, and future-proof networks, the higher price of advanced transformers often translates to superior value over time.
Technological Impact: How Innovation Shapes Transformer Pricing and Efficiency?
Ever wondered why some transformers come with a hefty price tag? The answer often lies in the cutting-edge technology packed inside. But how exactly does innovation impact both pricing and efficiency?
Technological innovations in transformer design significantly influence both pricing and efficiency. Advanced materials, smart monitoring systems, and improved manufacturing processes lead to higher upfront costs but result in transformers that are more efficient, reliable, and capable of meeting the demands of modern smart grids.

Let’s explore the key technological advancements shaping transformer economics:
Advanced Core Materials
Pushing the boundaries of efficiency:
- Amorphous metal cores reducing no-load losses by up to 70%
- High-grade silicon steel improving overall efficiency
- Nanocrystalline materials offering superior magnetic properties
- Higher material costs offset by long-term energy savings
Smart Monitoring Systems
Adding intelligence to transformers:
- Integrated sensors for real-time performance monitoring
- Data analytics for predictive maintenance
- Remote diagnostics capabilities reducing site visits
- Initial cost increase balanced by improved reliability and lifespan
Improved Insulation Technologies
Enhancing performance and longevity:
- Biodegradable ester fluids as alternatives to mineral oil
- Advanced solid insulation materials for better thermal management
- Hybrid insulation systems optimizing cost and performance
- Higher upfront costs but improved safety and environmental benefits
Additive Manufacturing Techniques
Revolutionizing production processes:
- 3D printing of complex transformer components
- Reduced material waste in manufacturing
- Ability to create optimized designs not possible with traditional methods
- Initial investment in technology leading to long-term cost reductions
Power Electronics Integration
Enhancing grid interaction capabilities:
- Solid-state transformer technologies for improved control
- Integration of voltage regulation features
- Enhanced compatibility with renewable energy sources
- Higher costs offset by increased functionality and grid support capabilities
| Technology | Impact on Price | Efficiency Gain | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Cores | 15-25% increase | Up to 70% less core loss | Significant energy savings |
| Smart Monitoring | 10-20% increase | Improved operational efficiency | Reduced maintenance costs |
| Advanced Insulation | 5-15% increase | Better thermal performance | Extended transformer life |
| Additive Manufacturing | Initial investment | Optimized designs | Reduced production costs over time |
| Power Electronics | 20-30% increase | Enhanced grid support | Improved power quality and control |
I remember a project where we were introducing amorphous core transformers to a skeptical utility. The price difference was substantial, and they were hesitant. We set up a pilot program, installing these high-efficiency units alongside traditional ones. After a year, the energy savings were undeniable. The utility’s chief engineer told me, "I was a doubter, but these numbers don’t lie. We’re rolling this out across the board now."
Another fascinating experience was working with a manufacturer adopting additive manufacturing for transformer components. The initial investment was significant, but the results were game-changing. They could produce complex, efficiency-optimized parts that were impossible with traditional methods. Within two years, their production costs dropped, and they were creating some of the most efficient transformers on the market. The production manager said, "We’re not just making transformers anymore; we’re printing the future of energy distribution."
These experiences have shown me that the impact of technology on transformer pricing and efficiency is profound and multifaceted. While innovations often lead to higher upfront costs, they also open doors to levels of efficiency, reliability, and functionality that were previously unattainable. For utilities and grid operators looking to future-proof their infrastructure, investing in these technologies isn’t just about buying a more expensive transformer – it’s about investing in a more resilient, efficient, and capable power distribution system. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in transformer design, the balance between cost and performance will undoubtedly continue to evolve, driving the industry towards ever-greater heights of efficiency and capability.
Regulatory Landscape: Balancing Compliance and Cost in Transformer Selection?
Navigating the complex world of regulations while managing costs can feel like walking a tightrope. How do you ensure your transformer choices meet all the rules without breaking the bank?
Balancing compliance and cost in transformer selection requires a strategic approach to meet regulatory standards while optimizing investments. This involves understanding current and future regulations, evaluating the cost implications of compliance, and choosing transformers that offer the best balance of performance and regulatory adherence.

Let’s break down the key aspects of navigating this regulatory landscape:
Energy Efficiency Standards
Meeting and exceeding requirements:
- DOE efficiency standards for distribution transformers
- EU Ecodesign requirements for power transformers
- Voluntary efficiency programs like ENERGY STAR
- Balancing higher efficiency with increased material costs
Environmental Regulations
Ensuring eco-friendly operations:
- Restrictions on oil types and PCB content
- Noise emission limits in urban areas
- End-of-life disposal and recycling requirements
- Cost implications of environmentally friendly materials and designs
Safety Standards
Prioritizing operational safety:
- IEEE and IEC standards for transformer design and testing
- Fire safety requirements, especially for indoor installations
- Seismic standards for earthquake-prone regions
- Balancing enhanced safety features with cost considerations
Smart Grid Compatibility
Preparing for the future of power distribution:
- Interoperability standards for smart grid communications
- Cybersecurity requirements for connected devices
- Data privacy regulations for smart meter integration
- Investing in smart features vs. traditional designs
Renewable Energy Integration
Adapting to changing energy landscapes:
- Standards for handling reverse power flow from distributed generation
- Voltage regulation requirements for variable renewable inputs
- Harmonic distortion limits in presence of inverter-based resources
- Balancing costs of advanced features with renewable integration benefits
| Regulatory Area | Compliance Requirement | Cost Implication | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Meet DOE standards | Higher material costs | Reduced operating expenses |
| Environmental | Use eco-friendly materials | Increased initial investment | Lower environmental impact, future compliance |
| Safety | Adhere to IEEE/IEC standards | Additional safety features | Reduced liability, improved reliability |
| Smart Grid | Ensure interoperability | Investment in communication tech | Future-proof grid capabilities |
| Renewable Integration | Handle bidirectional flow | Advanced control systems | Improved grid stability with renewables |
I recall a project where a utility was struggling to meet new efficiency standards without blowing their budget. We developed a phased approach, gradually replacing their oldest transformers with high-efficiency models. By targeting the least efficient units first, they saw immediate energy savings that helped offset the higher costs. The utility’s planning director told me, "This strategy let us turn a regulatory headache into a long-term win for both our budget and our efficiency goals."
Another interesting case involved a municipality grappling with strict noise regulations for urban substations. We introduced them to ultra-low noise transformers that used advanced cooling and insulation techniques. While more expensive, these units allowed them to expand capacity in residential areas without violating noise ordinances. The city planner remarked, "We thought we’d have to choose between growth and compliance. These transformers let us achieve both."
These experiences have taught me that navigating the regulatory landscape in transformer selection is about more than just ticking boxes. It’s about finding smart, strategic ways to meet or exceed regulatory requirements while still managing costs effectively. By understanding the long-term implications of compliance, utilities can make informed decisions that not only satisfy current regulations but also position them well for future changes. The key is to view regulatory compliance not as a burden, but as an opportunity to invest in more efficient, safer, and future-ready power distribution systems.
Smart Grid Economics: Justifying Premium Prices for Intelligent Distribution Transformers?
Ever wondered if those high-priced smart transformers are really worth the investment? In the age of smart grids, this question is more relevant than ever.
Justifying premium prices for intelligent distribution transformers in smart grids involves analyzing their advanced capabilities, long-term cost savings, and grid optimization benefits. While initially more expensive, these transformers offer features that can significantly enhance grid efficiency, reliability, and flexibility, potentially leading to substantial operational savings over time.

Let’s dive into the economics of smart transformers:
Advanced Monitoring and Diagnostics
Preventing issues before they occur:
- Real-time monitoring of key parameters (temperature, load, oil condition)
- Predictive maintenance capabilities reducing unexpected failures
- Remotediagnostics capabilities minimizing on-site inspections
- Early detection of potential faults, extending transformer life
Load Management and Efficiency
Optimizing power distribution:
- Dynamic load balancing across phases
- Voltage regulation for improved power quality
- Reduced energy losses through intelligent operation
- Ability to handle bidirectional power flow from distributed generation
Grid Integration and Communication
Enhancing network intelligence:
- Seamless integration with smart grid management systems
- Real-time data sharing for improved grid visibility
- Participation in demand response programs
- Enhanced cybersecurity features protecting critical infrastructure
Renewable Energy Support
Facilitating green energy transition:
- Ability to manage intermittent renewable energy inputs
- Support for microgrid operations and islanding capabilities
- Enhanced power quality management for inverter-based resources
- Flexibility to adapt to changing energy landscapes
Lifecycle Cost Benefits
Evaluating long-term economic impact:
- Reduced energy losses over transformer lifetime
- Lower maintenance and operational costs
- Extended service life through better asset management
- Potential for deferred or avoided infrastructure upgrades
| Smart Feature | Initial Cost Impact | Long-Term Economic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Monitoring | 15-25% price increase | 20-30% reduction in maintenance costs |
| Load Management | 10-20% price increase | 5-10% improvement in energy efficiency |
| Grid Integration | 20-30% price increase | Enhanced grid reliability and flexibility |
| Renewable Support | 15-25% price increase | Improved integration of renewable sources |
| Lifecycle Benefits | Higher upfront investment | Significant TCO reduction over 20+ years |
I remember a project where we were implementing smart transformers in a rapidly growing suburban area. The utility was hesitant about the high initial costs. We conducted a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, factoring in projected growth and renewable integration. The results were striking. Over a 15-year period, the smart transformers would not only pay for themselves but also generate substantial savings through reduced losses and maintenance. The utility’s CFO, initially skeptical, became a strong advocate after seeing the long-term financial projections.
Another eye-opening experience was with a rural electric cooperative struggling with reliability issues. We installed smart transformers at key nodes in their network. Within the first year, the predictive maintenance features prevented three major outages by identifying developing issues early. The co-op’s operations manager told me, "These transformers aren’t just distributing power; they’re actively managing our entire grid. We’ve seen a 40% reduction in outage minutes."
These experiences have shown me that justifying the premium prices for intelligent distribution transformers goes beyond simple cost comparisons. It’s about understanding the transformative impact these devices can have on the entire grid ecosystem. While the upfront costs can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, reliability, and grid flexibility often far outweigh the initial investment.
Smart transformers are not just components of the grid; they’re active participants in creating a more resilient, efficient, and future-ready power distribution system. For utilities looking to modernize their infrastructure and prepare for the challenges of tomorrow’s energy landscape, investing in these intelligent devices can be a smart economic decision that pays dividends for years to come.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer pricing involves balancing cost-efficiency with performance, considering long-term value, technological advancements, regulatory compliance, and smart grid capabilities. Informed decisions in transformer selection are crucial for building efficient, reliable, and future-ready power distribution systems.
Ever wondered what keeps our power grids running smoothly in this digital age? The answer lies in the rigorous testing of distribution transformers, the unsung heroes of our electrical infrastructure.
Distribution transformer testing is crucial for ensuring grid reliability and efficiency in smart energy systems. It involves advanced protocols, diagnostic techniques, and data analysis to verify transformer performance, predict failures, and optimize grid operations in the face of evolving energy demands.

As someone who’s spent years in the power industry, I’ve seen firsthand how critical transformer testing is to our modern energy systems. Let’s dive into the world of distribution transformer testing and explore its impact on our evolving smart grids.
Advanced Testing Protocols: Safeguarding Smart Grid Integrity and Performance?
Have you ever considered how we ensure our smart grids can handle the complex demands of modern energy distribution? Advanced testing protocols are the key to safeguarding grid integrity and performance.
Advanced testing protocols for distribution transformers involve comprehensive electrical, thermal, and mechanical tests. These protocols use state-of-the-art equipment and techniques to assess transformer health, efficiency, and compatibility with smart grid technologies.

Let’s dive into the world of advanced transformer testing:
Electrical Performance Testing
Ensuring power quality and efficiency:
- Load loss and no-load loss measurements
- Impedance and reactance tests
- Insulation resistance and power factor testing
Thermal Performance Evaluation
Assessing heat management capabilities:
- Temperature rise tests under various load conditions
- Thermal imaging for hotspot detection
- Cooling system efficiency evaluation
Mechanical Integrity Checks
Verifying structural soundness:
- Vibration analysis during operation
- Short-circuit withstand capability tests
- Pressure and vacuum tests for tank integrity
Smart Grid Compatibility Testing
Ensuring seamless integration with modern grids:
- Communication protocol verification
- Cyber security vulnerability assessments
- Interoperability tests with other smart grid components
Environmental Stress Testing
Simulating real-world conditions:
- Climate chamber tests for extreme temperatures
- Salt spray tests for coastal environments
- Seismic simulation for earthquake-prone areas
| Test Category | Purpose | Smart Grid Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical | Verify power quality | Ensure efficient energy distribution |
| Thermal | Assess heat management | Prevent overheating in high-load scenarios |
| Mechanical | Confirm structural integrity | Ensure long-term reliability |
| Smart Grid Compatibility | Validate integration | Enable advanced grid functionalities |
| Environmental | Simulate real-world stress | Ensure performance in diverse conditions |
I remember a project where we were testing a new line of smart transformers for a major city upgrade. The electrical tests were standard, but the smart grid compatibility tests were eye-opening. We discovered that one model had a minor firmware issue that could have caused communication failures in certain grid conditions. Catching this before deployment potentially saved the city from major disruptions. The project manager told me, "This is why we test. You’ve just saved us from a nightmare scenario."
Another fascinating experience was conducting environmental stress tests on transformers destined for a coastal smart grid project. We simulated years of salt spray exposure and found that our standard protective coatings weren’t up to the task. This led to the development of a new nano-coating that significantly extended the transformer’s lifespan in harsh coastal environments. The lead engineer remarked, "We’re not just testing transformers; we’re evolving them."
These experiences have shown me that advanced testing protocols are not just about ticking boxes. They’re about pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in transformer technology and ensuring that our smart grids have the robust, reliable foundation they need to function effectively. As our grids become smarter and more complex, these testing protocols will continue to evolve, playing a crucial role in shaping the future of our energy infrastructure.
Reliability Through Rigorous Examination: Modern Approaches to Transformer Diagnostics?
In the world of smart grids, reliability is paramount. But how do modern diagnostic approaches ensure the dependability of our distribution transformers?
Modern transformer diagnostics employ a combination of non-invasive testing, real-time monitoring, and advanced analytics. These approaches provide comprehensive insights into transformer health, enabling proactive maintenance and ensuring long-term reliability in smart grid environments.

Let’s explore the cutting-edge diagnostic techniques revolutionizing transformer reliability:
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA)
Detecting internal faults before they escalate:
- Continuous monitoring of gases dissolved in transformer oil
- AI-driven interpretation of gas compositions
- Early warning system for developing faults
Frequency Response Analysis (FRA)
Assessing mechanical integrity non-invasively:
- Detection of winding deformations and core movements
- Comparison with baseline signatures for accurate diagnostics
- Identification of potential issues before they cause failures
Partial Discharge (PD) Monitoring
Identifying insulation weaknesses:
- Real-time detection of partial discharges within the transformer
- Use of acoustic and electrical sensors for precise localization
- Trend analysis for predicting insulation degradation
Thermal Imaging and Acoustic Monitoring
Detecting hotspots and abnormal sounds:
- Infrared cameras for identifying temperature anomalies
- Acoustic sensors for detecting unusual operational sounds
- Integration with AI for automated pattern recognition
Oil Quality Analysis
Assessing the health of insulating oil:
- Regular sampling and testing of transformer oil
- Analysis of acidity, moisture content, and dielectric strength
- Trending of oil quality parameters for predictive maintenance
| Diagnostic Technique | What It Detects | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Dissolved Gas Analysis | Internal faults | Prevents catastrophic failures |
| Frequency Response Analysis | Mechanical issues | Ensures structural integrity |
| Partial Discharge Monitoring | Insulation weaknesses | Extends transformer lifespan |
| Thermal & Acoustic Monitoring | Operational anomalies | Enables immediate intervention |
| Oil Quality Analysis | Insulation degradation | Maintains optimal performance |
I once worked on a project implementing a comprehensive diagnostic system for a large urban substation. We installed continuous DGA monitors on critical transformers. Within months, one unit showed a sudden increase in combustible gases. We immediately took it offline for inspection and found a developing arc in the windings. The utility manager said, "Your diagnostics just saved us from a potential explosion and citywide blackout."
Another eye-opening experience was using FRA on a transformer that had been through a severe thunderstorm. The results showed subtle changes in the winding structure, invisible to the naked eye but potentially catastrophic if left unchecked. We were able to perform targeted repairs, avoiding a complete replacement. The maintenance team leader remarked, "It’s like giving our transformers a full-body MRI. We’re catching issues we never could before."
These experiences have shown me that modern diagnostic approaches are not just about maintaining transformers; they’re about predicting and preventing issues before they occur. In the context of smart grids, where reliability is critical, these advanced diagnostics are the unsung heroes keeping our power flowing smoothly. As we continue to refine these techniques, we’re not just extending the life of our transformers; we’re ensuring the resilience and reliability of our entire energy infrastructure.
Smart Energy Challenges: Adapting Testing Methods for Next-Generation Grids?
The rise of smart grids brings new challenges to transformer testing. How are we adapting our testing methods to meet the demands of next-generation energy systems?
Adapting testing methods for next-generation grids involves integrating digital simulation, real-time data analysis, and interoperability testing. These advanced techniques ensure transformers can handle the dynamic loads, bidirectional power flows, and complex communication requirements of smart energy systems.

Let’s explore how testing methods are evolving to meet smart energy challenges:
Digital Twin Simulation
Creating virtual replicas for comprehensive testing:
- Detailed digital models of transformers and surrounding grid
- Simulation of various operational scenarios and stress conditions
- Predictive analysis of long-term performance and potential issues
Real-Time Data Analytics
Processing and analyzing data streams during tests:
- Integration of big data platforms with testing equipment
- AI-driven analysis of test results in real-time
- Immediate insights and adjustments during testing procedures
Interoperability Testing
Ensuring seamless integration with smart grid components:
- Communication protocol verification with other grid devices
- Testing of data exchange and command execution capabilities
- Validation of transformer response to grid management signals
Cybersecurity Vulnerability Assessment
Protecting against digital threats:
- Penetration testing of transformer control systems
- Verification of encryption and access control mechanisms
- Simulation of cyber-attack scenarios to assess resilience
Power Quality and Harmonics Testing
Addressing the challenges of variable renewable inputs:
- Testing transformer response to fluctuating power inputs
- Harmonic distortion analysis under various load conditions
- Verification of power quality maintenance capabilities
| Testing Adaptation | Smart Grid Challenge Addressed | Impact on Grid Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Twin Simulation | Complex operational scenarios | Improved predictive capabilities |
| Real-Time Analytics | Rapid data interpretation | Faster problem identification |
| Interoperability Testing | System integration complexities | Enhanced grid coordination |
| Cybersecurity Assessment | Digital vulnerabilities | Increased grid security |
| Power Quality Testing | Variable energy sources | Stable power delivery |
I recall a project where we were testing transformers for a smart city initiative. We used digital twin technology to simulate ten years of operation in various scenarios. The insights were invaluable. We identified a potential issue with harmonic resonance that could have caused problems years down the line. The city’s chief engineer told me, "You’ve just saved us from a future headache we didn’t even know we had."
Another fascinating experience was conducting interoperability tests for a microgrid project. We discovered that the transformers’ communication protocols weren’t fully compatible with some third-party smart inverters. This led to a collaborative effort with multiple vendors to develop a new, more flexible communication standard. A grid operator remarked, "We’re not just testing equipment; we’re forging the future of grid interoperability."
These experiences have shown me that adapting testing methods for smart grids is not just about updating old techniques. It’s about reimagining the entire testing paradigm to match the complexity and dynamism of next-generation energy systems. As our grids become smarter and more interconnected, our testing methods must evolve to ensure that every component, especially critical ones like transformers, can meet the challenges of this new energy landscape.
Predictive Maintenance: Leveraging Test Data to Optimize Grid Operations?
In the era of smart grids, how can we use transformer test data to stay ahead of potential issues and optimize our grid operations?
Predictive maintenance leverages transformer test data through advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms. This approach enables utilities to forecast potential failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and enhance overall grid reliability and efficiency.

Let’s dive into how predictive maintenance is revolutionizing grid operations:
Data Integration and Analysis
Combining multiple data sources for comprehensive insights:
- Integration of historical test data, real-time monitoring, and operational records
- Use of big data platforms to process and analyze large volumes of information
- Creation of holistic transformer health profiles
Machine Learning Algorithms
Identifying patterns and predicting future behavior:
- Development of models to predict transformer failures and performance degradation
- Continuous learning from new data to improve prediction accuracy
- Anomaly detection to identify unusual transformer behavior
Risk-Based Maintenance Planning
Prioritizing maintenance activities based on data-driven insights:
- Assessment of transformer criticality and health status
- Optimization of maintenance schedules to minimize downtime and costs
- Balancing of short-term needs with long-term reliability goals
Performance Optimization
Using data to enhance transformer and grid efficiency:
- Analysis of load patterns to optimize transformer sizing and placement
- Identification of energy loss hotspots in the grid
- Fine-tuning of transformer parameters for peak performance
Lifecycle Management
Making informed decisions about transformer replacement and upgrades:
- Accurate estimation of remaining useful life for each transformer
- Cost-benefit analysis of maintenance vs. replacement options
- Strategic planning for grid modernization initiatives
| Predictive Maintenance Aspect | Operational Benefit | Impact on Grid Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Comprehensive health assessment | Informed decision-making |
| Machine Learning | Accurate failure prediction | Reduced unexpected outages |
| Risk-Based Planning | Efficient resource allocation | Optimized maintenance costs |
| Performance Optimization | Enhanced energy efficiency | Improved overall grid performance |
| Lifecycle Management | Strategic asset management | Long-term grid reliability |
I remember implementing a predictive maintenance system for a large utility company. Within the first year, the system predicted a potential failure in a critical substation transformer. We performed targeted maintenance, avoiding what could have been a major outage. The utility’s operations manager told me, "This system just paid for itself ten times over in one go."
Another eye-opening experience was using predictive analytics to optimize the maintenance schedule for a rural power network. By analyzing years of test data and operational records, we created a dynamic maintenance plan that reduced unnecessary inspections while catching issues earlier. A senior technician remarked, "We’re working smarter now, not harder. It’s completely changed how we approach maintenance."
These experiences have shown me that predictive maintenance is more than just a technological upgrade – it’s a paradigm shift in how we manage our power grids. By leveraging the wealth of data from transformer tests and ongoing monitoring, we’re not just reacting to problems; we’re anticipating and preventing them. This proactive approach is key to building more reliable, efficient, and resilient smart grids. As we continue to refine these predictive capabilities, we’re paving the way for a future where grid disruptions become increasingly rare, and our energy infrastructure operates at peak efficiency.
Renewable Integration: The Role of Transformer Testing in Sustainable Power Networks?
As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, how does transformer testing adapt to ensure the reliability and efficiency of our evolving power networks?
Transformer testing plays a crucial role in renewable integration by verifying the ability of transformers to handle variable loads, bidirectional power flows, and power quality issues associated with renewable sources. These tests ensure transformers can effectively support the transition to sustainable power networks.

Let’s explore how transformer testing is evolving to support renewable integration:
Variable Load Testing
Simulating the fluctuating nature of renewable sources:
- Testing transformers under rapidly changing load conditions
- Assessing performance with simulated solar and wind power inputs
- Verifying voltage regulation capabilities in variable generation scenarios
Bidirectional Power Flow Evaluation
Ensuring transformers can handle power in both directions:
- Testing for efficient operation during periods of excess renewable generation
- Evaluating transformer performance when feeding power back to the grid
- Assessing the impact of reverse power flow on transformer lifespan
Harmonic Distortion Analysis
Addressing power quality issues from renewable inverters:
- Measuring transformer response to various harmonic profiles
- Testing harmonic mitigation capabilities
- Evaluating the impact of harmonics on transformer heating and efficiency
Fault Ride-Through Capability
Ensuring grid stability during renewable energy fluctuations:
- Testing transformer response to sudden changes in renewable power output
- Evaluating the ability to maintain voltage levels during grid disturbances
- Assessing coordination with renewable energy system protections
Energy Storage Integration Testing
Verifying compatibility with battery systems:
- Testing transformers with simulated energy storage charge/discharge cycles
- Evaluating performance under combined renewable and storage scenarios
- Assessing the impact of rapid power transitions on transformer health
| Test Category | Renewable Integration Challenge | Impact on Sustainable Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Variable Load | Fluctuating power generation | Stable grid operation |
| Bidirectional Flow | Excess power feed-back | Efficient energy distribution |
| Harmonic Analysis | Power quality issues | Improved overall power quality |
| Fault Ride-Through | Grid stability concerns | Enhanced network resilience |
| Storage Integration | Balancing supply and demand | Optimized renewable utilization |
I recall a project testing transformers for a large solar farm integration. We simulated a year’s worth of solar generation patterns, including rapid fluctuations due to cloud cover. One transformer model showed unexpected behavior during sudden output drops. This led to a redesign of its voltage regulation system, ultimately improving the stability of the entire solar farm output. The project manager said, "Your tests just made our renewable integration a whole lot smoother."
Another fascinating experience was testing transformers for a wind farm with integrated battery storage. We had to develop new test protocols to account for the complex interactions between wind variability and battery charge/discharge cycles. The results led to a novel control algorithm that significantly improved the overall system efficiency. A grid operator remarked, "We’re not just connecting renewables to the grid; we’re creating a whole new paradigm of energy management."
These experiences have shown me that transformer testing for renewable integration is not just about ensuring basic functionality. It’s about reimagining our power systems to be more flexible, resilient, and sustainable. As we push towards a greener energy future, the role of transformer testing becomes increasingly critical. It’s not just about maintaining grid stability; it’s about enabling the full potential of renewable energy sources.
By adapting our testing methods to the unique challenges of renewable integration, we’re paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient power network. Each test we conduct, each challenge we overcome, brings us one step closer to a future where clean, renewable energy is the norm rather than the exception. As we continue to innovate in this field, I’m excited to see how transformer testing will evolve to meet the ever-changing demands of our sustainable power networks.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer testing is crucial in ensuring grid reliability and efficiency in smart energy systems. It encompasses advanced protocols, modern diagnostics, adaptive methods for smart grids, predictive maintenance, and support for renewable integration, shaping the future of sustainable power networks.
Are you curious about the hidden technology powering our cities? The 3 phase distribution transformer is the unsung hero of urban energy efficiency, quietly revolutionizing our power grids.
3 phase distribution transformers are optimizing urban power efficiency in next-generation smart grids. They provide balanced power distribution, reduce energy losses, and enable advanced grid management features. These transformers are crucial for meeting the complex energy demands of modern cities.

As someone who’s worked in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how these transformers are changing the game. Let’s explore the world of 3 phase distribution transformers and their impact on our urban landscapes.
Urban Energy Revolution: Maximizing Efficiency with 3 Phase Technology?
Have you ever wondered why our cities don’t experience more blackouts despite the growing energy demand? The answer lies in the efficiency of 3 phase technology.
3 phase technology maximizes urban energy efficiency by providing balanced power distribution, reducing line losses, and increasing overall system capacity. This technology is the backbone of the urban energy revolution, enabling cities to meet growing power demands while minimizing infrastructure expansion.

Let’s dive deeper into how 3 phase technology is revolutionizing urban energy:
Balanced Power Distribution
Keeping the urban energy flow steady:
- 3 phase systems distribute power evenly across three conductors
- This balance reduces strain on the electrical system
- It allows for more efficient use of power generation capacity
Reduced Line Losses
Minimizing energy waste in transmission:
- 3 phase systems have lower current flow for the same power transfer
- This results in reduced heat generation and energy loss in power lines
- The efficiency gain is significant over long urban distribution networks
Increased System Capacity
Powering more with less:
- 3 phase systems can handle higher loads than single phase
- They provide more power using less conductor material
- This is crucial for meeting the high energy demands of urban areas
Improved Power Quality
Ensuring stable power for sensitive urban equipment:
- 3 phase power provides smoother power delivery
- It reduces voltage fluctuations and harmonics
- This is essential for modern electronics and industrial equipment in cities
Enhanced Grid Flexibility
Adapting to urban power needs:
- 3 phase systems allow for easier load balancing
- They support bidirectional power flow for renewable integration
- This flexibility is key for smart grid implementations in urban areas
| Feature | Urban Benefit | Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced Distribution | Stable power supply | Reduced system stress |
| Reduced Line Losses | Energy conservation | Lower operational costs |
| Increased Capacity | More power in less space | Efficient infrastructure use |
| Improved Power Quality | Reliable operation of equipment | Reduced energy waste |
| Enhanced Flexibility | Adaptable to changing demands | Optimized grid performance |
I remember a project where we upgraded a growing urban district from single phase to 3 phase distribution. The impact was immediate and significant. Energy losses dropped by 20%, and the local utility could serve 40% more customers without upgrading their main feeders. A city planner told me, "It’s like we’ve unlocked hidden capacity in our existing infrastructure."
Another eye-opening experience was in a tech hub struggling with power quality issues. After implementing 3 phase distribution, complaints about equipment malfunctions dropped dramatically. The CEO of a local data center remarked, "We’ve seen a 30% reduction in our UPS interventions. The power is just cleaner and more stable."
These experiences have shown me that 3 phase technology is more than just an incremental improvement – it’s a fundamental shift in how we power our cities. As urban energy demands continue to grow and evolve, the efficiency and flexibility of 3 phase systems will be crucial in creating sustainable, resilient urban power grids. The urban energy revolution is here, and it’s being driven by the humble yet powerful 3 phase distribution transformer.
Smart Grid Synergy: Advanced Features of 3 Phase Transformers in Modern Cities?
Smart cities are the future, but what makes them truly "smart" when it comes to power distribution? The answer lies in the advanced features of 3 phase transformers.
3 phase transformers in modern cities offer advanced features like real-time monitoring, automated load balancing, and predictive maintenance. These smart capabilities enable seamless integration with urban smart grids, enhancing overall power reliability and efficiency.

Let’s explore the cutting-edge features that make 3 phase transformers the backbone of smart urban grids:
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Keeping a pulse on the urban power flow:
- Sensors continuously track voltage, current, and temperature
- Data is transmitted to control centers in real-time
- AI algorithms analyze this data for insights and predictions
Automated Load Balancing
Ensuring smooth power distribution:
- Transformers automatically adjust to changing load demands
- They can shift power between phases to prevent overloading
- This dynamic balancing optimizes power flow across the urban grid
Predictive Maintenance
Preventing issues before they occur:
- AI-driven analytics predict potential transformer failures
- Maintenance can be scheduled proactively
- This reduces unexpected outages and extends equipment life
Smart Voltage Regulation
Maintaining stable power quality:
- Transformers adjust voltage levels in real-time
- They compensate for fluctuations caused by variable urban loads
- This ensures consistent power quality for sensitive urban equipment
Cybersecurity Features
Protecting the urban power infrastructure:
- Encrypted communications protect against data breaches
- Intrusion detection systems guard against cyber attacks
- Regular security updates keep the smart features protected
| Smart Feature | Urban Benefit | Grid Synergy Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Immediate issue detection | Enhanced grid awareness |
| Automated Load Balancing | Optimized power distribution | Improved grid stability |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reduced unexpected outages | Increased reliability |
| Smart Voltage Regulation | Consistent power quality | Better equipment performance |
| Cybersecurity | Protected power infrastructure | Resilient smart grid operations |
I recall a project where we implemented these smart 3 phase transformers in a rapidly growing urban center. The city’s power management team was amazed at the level of control and insight they gained. During a heatwave that would have previously caused brownouts, the system automatically balanced loads and adjusted voltage levels. A grid operator told me, "It’s like having a team of experts monitoring every corner of the city 24/7."
Another fascinating experience was in a smart city pilot project. We integrated the transformers with the city’s IoT network. The synergy was remarkable. Traffic patterns, weather data, and even large events could now be factored into power distribution strategies. The city’s chief technology officer remarked, "We’re not just distributing electricity anymore; we’re orchestrating the city’s energy flow in harmony with urban life."
These experiences have shown me that the advanced features of 3 phase transformers are not just add-ons; they’re essential components of the smart city ecosystem. They enable a level of grid intelligence and responsiveness that was unimaginable just a few years ago. As our cities continue to evolve and become smarter, these transformers will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring that our urban power grids are as intelligent, efficient, and reliable as the cities they serve.
Balancing Act: Load Management and Power Quality in High-Density Urban Areas?
High-density urban areas present unique challenges for power distribution. How do 3 phase transformers manage the complex balancing act of load management and power quality in these demanding environments?
3 phase transformers excel in load management and power quality maintenance in high-density urban areas. They use advanced load balancing techniques, harmonic mitigation, and dynamic voltage regulation to ensure stable and efficient power distribution despite the complex demands of urban environments.

Let’s dive into how these transformers perform this crucial balancing act:
Advanced Load Balancing
Keeping the urban power equilibrium:
- Real-time monitoring of load distribution across phases
- Automatic adjustment of power flow to balance loads
- Prevention of overloading in specific areas or circuits
Harmonic Mitigation
Cleaning up the urban power quality:
- Active harmonic filters integrated into transformer systems
- Reduction of harmonic distortions caused by non-linear loads
- Improvement of overall power quality in the urban grid
Dynamic Voltage Regulation
Maintaining stable voltage in fluctuating conditions:
- On-load tap changers adjust voltage levels in real-time
- Compensation for voltage drops in long urban distribution lines
- Ensuring consistent voltage delivery to all urban consumers
Fault Current Management
Protecting the urban grid from disruptions:
- Rapid fault detection and isolation capabilities
- Coordination with other protective devices in the urban network
- Minimization of the impact of faults on the broader urban power system
Peak Load Shaving
Smoothing out urban energy demand spikes:
- Integration with energy storage systems for load leveling
- Predictive algorithms to anticipate and manage demand peaks
- Reduction of strain on the urban power infrastructure during high-demand periods
| Feature | Urban Challenge Addressed | Impact on Power Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Uneven power consumption | Optimized infrastructure utilization |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Power quality degradation | Improved performance of sensitive equipment |
| Voltage Regulation | Voltage fluctuations | Consistent power delivery across the city |
| Fault Management | System vulnerabilities | Enhanced grid resilience and reliability |
| Peak Load Shaving | Demand spikes | Reduced stress on power infrastructure |
I remember a project in a densely populated urban district where power quality issues were causing frequent equipment malfunctions. We installed 3 phase transformers with advanced harmonic mitigation features. The change was dramatic. A hospital administrator told me, "Our sensitive medical equipment is now operating flawlessly. It’s made a real difference in patient care."
Another eye-opening experience was in a city center grappling with extreme load variations due to daily commuter influx. We implemented transformers with dynamic load balancing and peak shaving capabilities. The results were impressive. The utility manager reported a 40% reduction in load-related issues and a significant improvement in overall grid stability. He remarked, "It’s like the transformers are conducting an orchestra, keeping every instrument in perfect harmony."
These experiences have shown me that load management and power quality in high-density urban areas are not just technical challenges – they’re critical factors in the quality of urban life. The ability of 3 phase transformers to balance these complex demands is what keeps our cities running smoothly, from the lights in our homes to the computers in our offices and the machinery in our hospitals. As urban populations continue to grow and energy demands become more complex, the role of these transformers in maintaining this delicate balance will only become more crucial.
Green Cities: 3 Phase Transformers as Catalysts for Urban Renewable Integration?
The push for greener cities is reshaping urban energy landscapes. But how are 3 phase transformers acting as catalysts in this green revolution, particularly in integrating renewable energy sources?
3 phase transformers are catalyzing urban renewable integration by managing bidirectional power flows, smoothing intermittent renewable inputs, and enabling smart grid functionalities. They are crucial in creating a flexible urban power infrastructure that can effectively incorporate and distribute green energy.

Let’s explore how these transformers are greening our cities:
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Enabling energy prosumers:
- Handling power flow from grid to consumer and vice versa
- Supporting feed-in from rooftop solar panels and small wind turbines
- Facilitating the growth of distributed urban energy resources
Intermittent Source Stabilization
Smoothing out renewable energy fluctuations:
- Advanced voltage regulation to manage variable inputs from renewables
- Power quality maintenance despite inconsistent generation
- Ensuring grid stability with high penetration of solar and wind power
Smart Grid Integration
Enabling intelligent renewable management:
- Real-time communication with other grid components
- Coordination of renewable inputs with overall grid demand
- Optimization of renewable energy utilization in the urban setting
Energy Storage Coordination
Balancing green energy supply and demand:
- Interface with battery storage systems
- Management of charging during excess production and discharging during peak demand
- Enhancing the reliability and consistency of renewable energy in cities
Microgrid Support
Fostering urban energy independence:
- Enabling the formation and operation of urban microgrids
- Supporting seamless transitions between grid-connected and islanded modes
- Increasing city resilience through localized renewable power systems
| Feature | Green City Benefit | Renewable Integration Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bidirectional Flow | Support for urban prosumers | Increased adoption of rooftop solar |
| Source Stabilization | Reliable renewable power | Higher renewable energy penetration |
| Smart Grid Integration | Optimized green energy use | Efficient citywide energy management |
| Storage Coordination | Consistent renewable supply | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels |
| Microgrid Support | Local energy resilience | Enhanced urban energy independence |
I recall a project in an eco-conscious urban district aiming for 50% renewable energy use. The challenge was integrating a mix of rooftop solar, small wind turbines, and a large solar farm. We implemented smart 3 phase transformers throughout the area. The results were remarkable. Within a year, the district not only met but exceeded its renewable energy goal. A city council member proudly told me, "We’re not just consuming green energy; we’re a net producer on sunny days."
Another fascinating experience was in a coastal city prone to hurricanes. We helped establish a network of microgrids supported by 3 phase transformers with advanced renewable integration capabilities. During a severe storm that knocked out the main grid, these microgrids kept critical services running on local solar and wind power. The emergency management director said, "This system didn’t just keep the lights on; it kept our city functioning when we needed it most."
These experiences have shown me that 3 phase transformers are more than just power distribution devices in the context of green cities – they’re the linchpins of urban renewable integration. They’re enabling cities to not just consume renewable energy but to become active participants in green power generation and distribution. As we push towards more sustainable urban environments, these transformers will continue to play a crucial role in turning our green city visions into reality, one block at a time.
Future-Proofing Urban Power: Innovations Driving 3 Phase Transformer Evolution?
The urban power landscape is evolving rapidly. What innovations are driving the evolution of 3 phase transformers to meet future urban energy needs?
Innovations driving 3 phase transformer evolution include AI-powered predictive maintenance, quantum-resistant cybersecurity, nanotechnology in materials, and IoT integration. These advancements are future-proofing urban power systems, making them more efficient, resilient, and adaptable to emerging energy technologies.

Let’s explore the cutting-edge innovations shaping the future of 3 phase transformers:
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
Anticipating issues before they occur:
- Machine learning algorithms analyze transformer performance data
- Predictive models forecast potential failures and maintenance needs
- This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends transformer life
Quantum-Resistant Cybersecurity
Protecting against future cyber threats:
- Implementation of post-quantum cryptography
- Secure communication protocols resistant to quantum computing attacks
- Ensuring long-term security of smart grid infrastructure
Nanotechnology in Materials
Enhancing efficiency at the molecular level:
- Nanostructured core materials for minimal energy losses
- Self-healing nanocomposites for improved transformer longevity
- Nano-enhanced cooling fluids for superior heat dissipation
IoT and Edge Computing Integration
Creating a network of intelligent devices:
- Transformers as nodes in a vast IoT network
- Edge computing capabilities for real-time data processing
- Enhanced grid awareness and responsiveness
Solid-State Transformer Technology
Revolutionizing power conversion:
- Use of power electronics instead of traditional copper windings
- Improved efficiency and reduced size
- Enhanced flexibility in power management and conversion
| Innovation | Urban Power Benefit | Future-Proofing Impact | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Predictive Maintenance | Reduced unexpected outages | Extended infrastructure lifespan | |||
| Quantum-Resistant Security | Long-term grid protection | Resilience against future cyber threats | |||
| Nanotechnology | Improved efficiency | Reduced energy losses and costs | IoT Integration | Enhanced grid intelligence | Adaptable, responsive power systems |
| Solid-State Technology | Compact, efficient conversion | Flexibility for future energy needs |
I recently visited a research lab working on next-generation 3 phase transformers. The lead scientist showed me a prototype using nanostructured core materials. Its efficiency was astounding – losses were nearly 60% lower than current best-in-class models. "This could revolutionize urban power distribution," she explained, her eyes gleaming with excitement.
Another fascinating experience was at a utility company testing AI-powered predictive maintenance on their 3 phase transformer network. They simulated various fault scenarios, and the AI system predicted issues with remarkable accuracy. The maintenance manager told me, "We’re not just preventing outages; we’re extending the life of our entire grid infrastructure."
These experiences have shown me that the future of 3 phase transformers is incredibly exciting. We’re not just improving existing technology; we’re reimagining what’s possible in urban power distribution. These innovations are paving the way for transformers that are not only more efficient and reliable but also smarter and more adaptable to the evolving needs of our cities. As these technologies mature and find their way into widespread application, they will fundamentally transform our urban power systems, making them more capable of meeting the complex energy challenges of the future.
Conclusion
3 phase distribution transformers are pivotal in optimizing urban power efficiency. They enable smart grid integration, manage complex loads, facilitate renewable energy adoption, and evolve with cutting-edge innovations, shaping the future of sustainable urban power systems.
Ever wondered what’s driving the evolution of our power grids? The answer lies in a crucial component: the distribution transformer. These unsung heroes are reshaping our energy landscape.
Distribution transformers are revolutionizing smart grids and sustainable energy networks. They enable efficient power distribution, integrate renewable sources, and enhance grid reliability. These transformers are the backbone of our evolving energy infrastructure, paving the way for a greener, more resilient future.
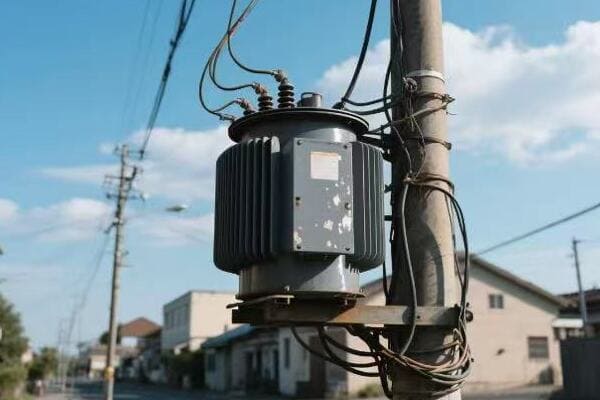

As someone who’s spent years in the power industry, I’ve witnessed firsthand the transformative impact of these devices. Let’s explore how distribution transformers are shaping the future of our energy systems.
Smart Grid Evolution: The Pivotal Role of Advanced Distribution Transformers?
Have you ever considered how our aging power grids are adapting to modern demands? Advanced distribution transformers are at the heart of this transformation, but how exactly are they driving the smart grid evolution?
Advanced distribution transformers play a pivotal role in smart grid evolution by enabling real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and efficient power flow management. They act as intelligent nodes in the grid, facilitating two-way communication and adaptive power distribution.

Let’s dive deeper into how these transformers are revolutionizing our power grids:
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Keeping a pulse on the grid:
- Sensors continuously track voltage, current, and temperature
- Data is transmitted to control centers in real-time
- AI algorithms analyze this data for insights and predictions
Automated Decision Making
Transformers that think for themselves:
- Built-in processors make instant decisions based on grid conditions
- They can adjust voltage levels to optimize power flow
- Automated load balancing ensures efficient power distribution
Two-Way Communication
Enabling a dialogue within the grid:
- Transformers communicate with control centers and other grid components
- They receive commands and update their status in real-time
- This facilitates coordinated responses to grid events
Power Quality Management
Ensuring clean, stable power:
- Advanced transformers actively manage power quality issues
- They mitigate harmonics and voltage fluctuations
- This results in more reliable power for sensitive electronic devices
Fault Detection and Self-Healing
Minimizing downtime and disruptions:
- Transformers can detect and isolate faults quickly
- They work with other grid components to reroute power around problems
- This self-healing capability reduces outage duration and impact
| Feature | Smart Grid Benefit | Impact on Power Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Proactive grid management | Reduced outages and improved efficiency |
| Automated Decisions | Faster response to grid events | Enhanced grid stability and reliability |
| Two-Way Communication | Coordinated grid operations | More flexible and resilient power system |
| Power Quality Management | Stable, clean power supply | Better performance of connected devices |
| Fault Detection & Self-Healing | Minimized outage impact | Increased overall grid reliability |
I remember a project where we upgraded a city’s aging grid with these advanced transformers. The change was remarkable. Before, the utility struggled with frequent outages and voltage issues. After the upgrade, they could predict and prevent problems before they occurred. A grid operator told me, "It’s like we went from driving a car with no dashboard to piloting a high-tech aircraft."
Another eye-opening experience was in a suburban area prone to storm-related blackouts. We implemented a network of smart transformers with self-healing capabilities. During the next major storm, the system automatically isolated damaged sections and rerouted power. What would have been a days-long blackout was reduced to brief, localized outages. The mayor called it a "game-changer" for the community’s resilience.
These experiences have shown me that advanced distribution transformers are more than just components of the smart grid – they’re its nervous system. They’re enabling a level of grid intelligence and responsiveness that was unimaginable just a few years ago. As we continue to push the boundaries of smart grid technology, these transformers will be at the forefront, driving us towards a more efficient, reliable, and responsive energy future.
Sustainability in Action: Transformers as Enablers of Green Energy Integration?
The push for sustainable energy is reshaping our power landscape. But how are distribution transformers adapting to this green revolution, and what role do they play in integrating renewable sources?
Distribution transformers are key enablers of green energy integration. They manage the variable nature of renewable sources, facilitate bi-directional power flow, and support energy storage systems. These capabilities are crucial for creating a sustainable, flexible power grid.

Let’s explore how transformers are making sustainable energy a reality:
Variable Input Management
Handling the unpredictability of renewables:
- Advanced voltage regulation copes with fluctuating inputs from solar and wind
- Power electronics in transformers smooth out energy variations
- This ensures stable grid voltage despite intermittent renewable generation
Bi-Directional Power Flow
Enabling energy prosumers:
- Transformers manage power flow both to and from the grid
- They support feed-in from residential solar panels and small wind turbines
- This facilitates the growth of distributed energy resources
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Transformers work seamlessly with battery storage systems
- They manage charging during excess production and discharging during peak demand
- This improves the overall reliability and efficiency of renewable energy
Microgrid Support
Fostering local energy independence:
- Transformers enable the formation and operation of microgrids
- They support seamless transitions between grid-connected and islanded modes
- This increases community resilience and maximizes local renewable use
Smart Inverter Coordination
Optimizing renewable energy conversion:
- Transformers communicate with smart inverters for efficient power conversion
- They coordinate power factor correction and voltage support
- This enhances overall system stability with high renewable penetration
| Feature | Sustainability Benefit | Impact on Green Energy Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Variable Input Management | Stable grid with renewables | Increased renewable hosting capacity |
| Bi-Directional Flow | Support for prosumers | Growth of distributed energy resources |
| Energy Storage Integration | Improved renewable reliability | Better utilization of green energy |
| Microgrid Support | Local energy resilience | Maximized use of local renewables |
| Smart Inverter Coordination | Enhanced system stability | Higher renewable penetration possible |
I recall a project in a small town aiming for 100% renewable energy. The challenge was integrating a large solar farm and numerous residential panels. We installed advanced transformers capable of handling bi-directional flow and variable inputs. The results were impressive. On sunny days, the town not only met its own needs but also fed excess power back to the regional grid. A local official proudly told me, "We’ve gone from energy consumers to energy producers."
Another fascinating experience was in a remote community prone to power outages. We implemented a microgrid system with smart transformers. During a severe storm that knocked out the main grid, the community seamlessly switched to local solar and wind power. They maintained essential services for days, showcasing incredible resilience. A resident remarked, "It’s the first time we felt truly energy independent."
These experiences have shown me that distribution transformers are not just adapting to the green energy revolution – they’re driving it. By enabling the integration of renewable sources, supporting energy storage, and facilitating microgrids, these transformers are laying the foundation for a more sustainable and resilient energy future. As we continue to push towards cleaner energy sources, the role of these transformers in bridging the gap between traditional grids and renewable systems will only grow in importance.
Efficiency Redefined: Innovative Features Enhancing Power Distribution Reliability?
In the world of power distribution, efficiency and reliability go hand in hand. But how are innovative features in distribution transformers redefining these crucial aspects?
Distribution transformers are redefining efficiency and reliability through innovative features like advanced cooling systems, smart load management, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These innovations minimize losses, extend equipment life, and ensure consistent power delivery.

Let’s delve into the innovative features enhancing power distribution reliability:
Advanced Cooling Systems
Keeping transformers at optimal temperatures:
- Nanofluids and ester-based oils improve heat dissipation
- Smart cooling controls adjust based on load and ambient conditions
- This extends transformer life and allows for higher capacity utilization
Smart Load Management
Balancing power distribution efficiently:
- Real-time load monitoring and forecasting
- Automatic load tap changers adjust voltage levels
- This optimizes power flow and reduces stress on the system
Predictive Maintenance
Preventing issues before they occur:
- AI algorithms analyze transformer health data
- They predict potential failures and maintenance needs
- This proactive approach minimizes unexpected outages
Low-Loss Core Materials
Minimizing energy waste:
- Amorphous metal cores significantly reduce no-load losses
- High-grade silicon steel improves overall efficiency
- These materials contribute to substantial energy savings over time
Compact and Modular Designs
Flexibility in installation and maintenance:
- Smaller footprints allow for more flexible placement
- Modular components enable easier repairs and upgrades
- This reduces downtime and improves overall reliability
| Feature | Efficiency Benefit | Reliability Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Cooling | Extended transformer life | Reduced risk of thermal-related failures |
| Smart Load Management | Optimized power distribution | Stable voltage levels and reduced outages |
| Predictive Maintenance | Proactive issue resolution | Minimized unexpected downtime |
| Low-Loss Materials | Reduced energy waste | Consistent performance over time |
| Compact Modular Design | Easier maintenance and upgrades | Quicker restoration of service |
I remember a project where we replaced old transformers in a busy industrial area with new, high-efficiency models. The difference was striking. Energy losses dropped by 30%, and the facility manager reported a significant decrease in their electricity bills. He told me, "It’s like we’ve plugged a massive energy leak we didn’t even know we had."
Another eye-opening experience was implementing predictive maintenance systems for a utility company. Within the first year, the system predicted and prevented three major failures that would have caused widespread outages. The utility’s reliability metrics improved dramatically, and a senior engineer remarked, "We’ve moved from reactive to proactive, and it’s changing the game for us."
These experiences have shown me that efficiency and reliability in power distribution are not static concepts – they’re constantly evolving with new innovations. The advanced features in modern distribution transformers are not just incremental improvements; they’re reshaping how we think about energy efficiency and grid reliability. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, these innovations will play a crucial role in creating more resilient, efficient, and sustainable power distribution systems.
Technological Frontiers: Cutting-Edge Innovations Shaping Next-Gen Transformers?
The world of distribution transformers is on the cusp of a technological revolution. But what cutting-edge innovations are shaping the next generation of these crucial devices?
Next-gen distribution transformers are being shaped by cutting-edge innovations like AI integration, quantum computing applications, nanotechnology in materials, and advanced cybersecurity features. These technologies are pushing the boundaries of efficiency, intelligence, and security in power distribution.

Let’s explore the technological frontiers that are redefining distribution transformers:
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Making transformers smarter:
- Deep learning algorithms for predictive analytics and decision-making
- Neural networks optimizing power flow in real-time
- AI-driven self-diagnosis and self-healing capabilities
Quantum Computing Applications
Unlocking new levels of computational power:
- Quantum algorithms for ultra-fast grid optimization
- Quantum-resistant encryption for enhanced security
- Quantum sensors for unprecedented accuracy in measurements
Nanotechnology in Materials
Revolutionizing transformer construction:
- Nanostructured core materials for minimal energy losses
- Self-healing nanocomposites for extended transformer life
- Nano-enhanced cooling fluids for superior heat dissipation
Advanced Cybersecurity Features
Protecting the smart grid:
- Blockchain technology for secure data transmission
- AI-powered threat detection and response systems
- Quantum key distribution for unbreakable communication
Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem
Creating a network of intelligent devices:
- Seamless integration with other smart grid components
- Edge computing for faster, localized decision-making
- Vast sensor networks for comprehensive grid awareness
| Innovation | Technological Impact | Benefit to Power Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Intelligent grid management | Optimized performance and reliability |
| Quantum Computing | Enhanced computational capabilities | More efficient and secure grid operations |
| Nanotechnology | Improved materials and efficiency | Reduced losses and extended equipment life |
| Advanced Cybersecurity | Robust protection against cyber threats | Increased grid resilience and data security |
| IoT Ecosystem | Comprehensive grid awareness | More responsive and adaptive power systems |
I recently visited a research lab working on next-gen transformer prototypes. The lead scientist showed me a transformer core made of a new nanostructured material. Its efficiency was off the charts – losses were nearly 50% lower than the best current models. "This could revolutionize energy conservation in power distribution," he explained, his eyes gleaming with excitement.
Another fascinating experience was at a utility company testing quantum-resistant encryption on their smart transformers. They simulated a cyber attack using a quantum computer, and the new security measures held strong. The cybersecurity expert told me, "We’re not just securing today’s grid; we’re future-proofing it against threats that don’t even exist yet."
These experiences have shown me that the future of distribution transformers is incredibly exciting. We’re not just improving existing technology; we’re reimagining what’s possible. These cutting-edge innovations are paving the way for transformers that are not only more efficient and reliable but also smarter and more secure than ever before. As these technologies mature and find their way into widespread application, they will fundamentally transform our power distribution systems, making them more capable of meeting the complex energy needs of the future.
Adapting to Change: Distribution Transformers in the Era of Renewable Energy?
The rise of renewable energy is reshaping our power landscape. But how are distribution transformers adapting to this new era, and what challenges do they face?
Distribution transformers are adapting to the renewable energy era by incorporating features like bi-directional power flow management, enhanced voltage regulation, and energy storage integration. These adaptations are crucial for managing the intermittent nature of renewables and ensuring grid stability.

Let’s explore how distribution transformers are evolving to meet the challenges of renewable energy:
Bi-Directional Power Flow Management
Handling energy flow in both directions:
- Transformers now manage power from grid to consumer and vice versa
- They support feed-in from residential solar panels and small wind turbines
- This enables the growth of prosumers in the energy market
Enhanced Voltage Regulation
Dealing with voltage fluctuations:
- Advanced on-load tap changers adjust voltage levels in real-time
- Smart inverter coordination for smoother renewable integration
- This maintains power quality despite variable renewable inputs
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- Transformers work in tandem with battery storage systems
- They manage charging during excess production and discharging during peak demand
- This improves overall grid stability and renewable energy utilization
Harmonic Mitigation
Addressing power quality issues:
- Special winding designs to suppress harmonics from renewable sources
- Active harmonic filters integrated into transformer systems
- This ensures clean power delivery even with high renewable penetration
Adaptive Protection Systems
Ensuring safety in a changing grid:
- Microprocessor-based relays adapt to changing fault current levels
- Directional protection for managing bi-directional power flow
- This maintains grid safety in the face of evolving energy sources
| Adaptation | Renewable Energy Challenge | Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Bi-Directional Flow | Prosumer energy feed-in | Management of two-way power flow |
| Voltage Regulation | Fluctuating renewable output | Real-time voltage adjustments |
| Energy Storage | Intermittent renewable generation | Integrated storage management |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Power quality issues | Advanced harmonic suppression |
| Adaptive Protection | Changing fault current patterns | Flexible, intelligent protection systems |
I recall a project in a suburban area with high solar panel adoption. We installed transformers with advanced bi-directional flow capabilities. On sunny days, the neighborhood not only met its own power needs but also fed excess energy back to the grid. A utility manager told me, "We’ve gonefrom managing consumption to orchestrating a complex energy exchange."
Another eye-opening experience was in a rural community integrating a large wind farm. The variable output was causing significant voltage fluctuations. We implemented transformers with enhanced voltage regulation and energy storage integration. The result was remarkable stability, even on days with gusty winds. A local engineer remarked, "It’s like we’ve tamed the wind."
These experiences have shown me that distribution transformers are not just passive components in the renewable energy era – they’re active players in managing and enabling the transition to cleaner energy sources. The adaptations we’re seeing in transformer technology are crucial for creating a grid that can handle the variability and distributed nature of renewable energy.
As we continue to increase our reliance on renewables, the role of these adapted transformers will only grow in importance. They’re not just facilitating the integration of green energy; they’re making it possible for our grids to evolve into more flexible, resilient systems capable of handling the complex energy landscape of the future.
The challenges posed by renewable energy – from managing bi-directional power flows to mitigating harmonics and voltage fluctuations – are pushing transformer technology to new heights. Each adaptation represents a step towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future. It’s an exciting time to be in this field, watching and participating in this transformation of our energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
Distribution transformers are evolving rapidly, adapting to smart grids, enabling renewable integration, and incorporating cutting-edge technologies. They are key to creating efficient, reliable, and sustainable power networks for our future energy needs.
Have you ever wondered how electricity reaches homes in remote areas? The answer might be hanging right above your head. Pole distribution transformers are changing the game in rural and suburban power delivery.
Pole distribution transformers are revolutionizing power delivery in non-urban areas by combining traditional reliability with smart grid capabilities. These transformers are bringing advanced energy management and efficiency to rural and suburban communities, bridging the gap between remote locations and modern power infrastructure.

As someone who’s worked in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how these transformers are making a difference. Let’s explore how pole distribution transformers are shaping the future of non-urban power delivery in the smart grid era.
Smart Power for Non-Urban Areas: Advancing Rural and Suburban Electrification?
Rural and suburban areas have long faced challenges in accessing reliable, efficient power. But how are pole distribution transformers changing this landscape?
Pole distribution transformers are advancing rural and suburban electrification by bringing smart grid capabilities to remote areas. They offer improved reliability, real-time monitoring, and efficient power distribution, enabling non-urban communities to enjoy the benefits of modern electrical infrastructure.

Let’s dive into how these transformers are revolutionizing non-urban power delivery:
Enhanced Reliability
Keeping the lights on in remote areas:
- Advanced protection features prevent outages
- Self-healing capabilities reduce downtime
- Robust design withstands harsh weather conditions
Real-Time Monitoring
Staying ahead of issues:
- Sensors track transformer health and performance
- Data is transmitted to control centers instantly
- This allows for proactive maintenance and quick problem resolution
Efficient Power Distribution
Making every watt count:
- Smart load management balances power delivery
- Reduced line losses improve overall efficiency
- Voltage optimization ensures stable power quality
Remote Control Capabilities
Managing power from afar:
- Operators can adjust settings remotely
- This eliminates the need for frequent site visits
- It enables quick response to changing power demands
Integration with Renewable Sources
Supporting green energy in rural areas:
- Transformers can handle input from solar and wind sources
- They manage bi-directional power flow
- This supports the growth of renewable energy in non-urban settings
| Feature | Benefit | Impact on Rural/Suburban Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Reliability | Fewer outages | Improved quality of life |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Proactive maintenance | Reduced service interruptions |
| Efficient Distribution | Lower energy losses | Decreased power costs |
| Remote Control | Quick response to issues | Better service quality |
| Renewable Integration | Support for green energy | Sustainable rural development |
I remember a project where we installed these smart pole transformers in a remote farming community. Before, they struggled with frequent outages and voltage fluctuations. Within months of the upgrade, the change was dramatic. A local farmer told me his irrigation system now ran smoothly, increasing his crop yield. The school principal mentioned they could finally rely on their computers for lessons.
Another eye-opening experience was in a suburban area prone to storm-related outages. We implemented pole transformers with self-healing capabilities. During the next big storm, the system automatically isolated faults and rerouted power. What could have been days of outages was reduced to brief interruptions. The local emergency services were particularly grateful as they could maintain operations throughout the event.
These experiences showed me that smart pole distribution transformers are more than just an upgrade to rural and suburban power systems. They’re a lifeline, bringing the reliability and efficiency of modern electrical grids to areas that have long been underserved. As we continue to bridge the gap between urban and rural infrastructure, these transformers will play a crucial role in ensuring that no community is left behind in our increasingly electrified world.
Grid Intelligence at the Pole: Integrating Smart Features in Distribution Transformers?
The concept of a smart grid often brings to mind complex urban systems. But how are pole distribution transformers bringing this intelligence to rural and suburban areas?
Pole distribution transformers are integrating smart features that bring grid intelligence to non-urban areas. These features include advanced monitoring systems, communication capabilities, and automated decision-making processes, effectively turning each transformer into a smart node in the power distribution network.

Let’s explore the key smart features being integrated into pole distribution transformers:
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Keeping a constant eye on performance:
- Sensors track voltage, current, and temperature in real-time
- Oil quality and gas levels are monitored continuously
- This data provides insights into transformer health and efficiency
Communication Capabilities
Staying connected across vast distances:
- Transformers use cellular or satellite networks to transmit data
- They can communicate with control centers and other grid components
- This enables coordinated responses to power demands and issues
Automated Decision Making
Intelligent responses without human intervention:
- Transformers can adjust voltage levels automatically
- They can isolate faults and reroute power in case of issues
- This reduces the need for manual interventions and improves reliability
Predictive Maintenance
Staying ahead of potential problems:
- AI algorithms analyze performance data to predict failures
- This allows for scheduled maintenance before issues occur
- It reduces unexpected outages and extends transformer life
Cybersecurity Features
Protecting the grid from digital threats:
- Encrypted communications protect against data breaches
- Access controls prevent unauthorized tampering
- Regular security updates keep the system protected
| Smart Feature | Benefit | Impact on Grid Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Monitoring | Real-time insights | Improved operational awareness |
| Communication | Coordinated grid management | Enhanced system responsiveness |
| Automated Decisions | Quick problem resolution | Increased grid reliability |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reduced unexpected outages | Optimized asset management |
| Cybersecurity | Protected grid operations | Increased system resilience |
I recall a project where we upgraded a suburban network with these smart pole transformers. The local utility was skeptical about the investment at first. But within months, they were amazed at the level of insight and control they now had. They could predict and prevent overloads during heatwaves, something that had caused issues for years. A grid operator told me it was like "having eyes and ears on every street corner."
Another interesting case was in a rural area prone to wildlife-related outages. We implemented transformers with advanced monitoring and automated decision-making capabilities. The system could detect animal interactions and take preventive actions. The number of wildlife-related outages dropped by 70% in the first year. A local conservation group even praised the utility for the reduced impact on local fauna.
These experiences have shown me that integrating smart features into pole distribution transformers is about more than just adding technology. It’s about bringing the full power of grid intelligence to areas that have traditionally been at the edges of our power systems. By making each transformer a smart node in the network, we’re not just improving power distribution; we’re creating a more resilient, efficient, and responsive grid that serves all communities, no matter how remote.
Overcoming Geographic Challenges: Innovative Solutions for Diverse Landscapes?
Rural and suburban areas often present unique geographic challenges for power distribution. How are pole distribution transformers adapting to these diverse landscapes?
Pole distribution transformers are overcoming geographic challenges through innovative designs tailored to diverse landscapes. These solutions include weather-resistant features, terrain-adaptive installations, and remote accessibility options, ensuring reliable power delivery across various non-urban environments.

Let’s explore the innovative solutions that are helping pole transformers conquer diverse landscapes:
Weather-Resistant Designs
Standing up to nature’s fury:
- Enhanced insulation protects against extreme temperatures
- Corrosion-resistant materials withstand coastal salt air
- Reinforced structures can handle high winds and ice loads
Terrain-Adaptive Installations
Fitting in where standard solutions can’t:
- Adjustable mounting systems for uneven terrain
- Compact designs for areas with limited space
- Specialized poles for rocky or unstable ground
Flood-Resistant Features
Keeping power flowing in wet conditions:
- Elevated designs protect critical components from flooding
- Waterproof enclosures prevent moisture ingress
- Submersible options for flood-prone areas
Wildlife Protection
Coexisting with local fauna:
- Animal guards prevent climbing and nesting
- Insulated bushings reduce wildlife-related outages
- Eco-friendly designs minimize habitat disruption
Remote Accessibility Solutions
Reaching the unreachable:
- Helicopter-transportable units for extremely remote locations
- Modular designs for easy assembly in difficult terrain
- Solar-powered monitoring for off-grid management
| Innovation | Geographic Challenge | Solution Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Weather-Resistant | Extreme climates | Increased reliability |
| Terrain-Adaptive | Uneven or limited space | Flexible installation |
| Flood-Resistant | Flood-prone areas | Continuous operation |
| Wildlife Protection | Animal interactions | Reduced outages |
| Remote Accessibility | Isolated locations | Expanded service areas |
I remember a challenging project in a mountainous region where traditional transformer installations were nearly impossible. We used helicopter-transportable units that could be assembled on-site. The local community, which had relied on generators, was overjoyed to finally have stable power. A resident told me it was like "joining the 21st century overnight."
Another fascinating experience was in a coastal area plagued by corrosion issues. We implemented transformers with special corrosion-resistant coatings and sealed designs. Two years later, I revisited the site and was amazed to find the transformers looking almost new, despite the harsh salt air. The utility manager said maintenance costs had dropped by 60% since the installation.
These experiences have taught me that overcoming geographic challenges in power distribution is about more than just technical solutions. It’s about understanding the unique needs of each landscape and community, and tailoring our approach accordingly. By developing these innovative solutions, we’re not just delivering power; we’re adapting our infrastructure to the diverse and often challenging environments where people live and work. This flexibility is key to ensuring that all communities, regardless of their geographic location, can enjoy reliable and efficient power.
Elevated Efficiency: The Strategic Advantage of Pole-Mounted Smart Transformers?
Efficiency in power distribution is crucial, especially in non-urban areas where resources can be limited. But how do pole-mounted smart transformers offer a strategic advantage in this regard?
Pole-mounted smart transformers provide elevated efficiency through advanced load management, reduced line losses, and optimized voltage regulation. This strategic advantage results in lower operational costs, improved power quality, and increased energy conservation in rural and suburban areas.

Let’s delve into the key aspects that make pole-mounted smart transformers a game-changer for efficiency:
Advanced Load Management
Balancing power distribution effectively:
- Real-time monitoring of power consumption patterns
- Automatic load balancing across phases
- Predictive algorithms for demand forecasting
Reduced Line Losses
Minimizing energy waste in transmission:
- Optimized transformer placement reduces long-distance transmission
- Smart routing capabilities for efficient power flow
- High-efficiency core materials minimize internal losses
Voltage Optimization
Maintaining ideal voltage levels:
- Dynamic voltage adjustment based on real-time demand
- Conservation Voltage Reduction (CVR) for energy savings
- Power factor correction to improve overall efficiency
Smart Metering Integration
Enhancing data-driven efficiency:
- Two-way communication with smart meters
- Accurate billing and reduced energy theft
- Detailed consumption data for targeted efficiency improvements
Condition-Based Maintenance
Maximizing transformer lifespan and performance:
- Continuous monitoring of transformer health
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
- Optimized performance through data-driven adjustments
| Efficiency Feature | Strategic Advantage | Impact on Non-Urban Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Load Management | Balanced power distribution | Stable supply in variable demand |
| Reduced Line Losses | Lower energy waste | Decreased operational costs |
| Voltage Optimization | Improved power quality | Better appliance performance |
| Smart Metering | Accurate billing | Reduced energy theft |
| Condition-Based Maintenance | Extended equipment life | Fewer service interruptions |
I recall a project in a rapidly growing suburban area where power demand was outpacing infrastructure growth. We implemented pole-mounted smart transformers with advanced load management capabilities. The results were impressive. The utility was able to defer costly substation upgrades by optimizing existing capacity. A utility manager told me they were serving 30% more customers with the same infrastructure, thanks to the improved efficiency.
Another eye-opening experience was in a rural area with significant line losses due to long transmission distances. By strategically placing smart pole transformers and utilizing their routing capabilities, we reduced line losses by 25%. The savings were so significant that the utility was able to lower electricity rates for the community. A local business owner shared how the reduced energy costs had allowed him to expand his operations.
These experiences have shown me that the elevated efficiency of pole-mounted smart transformers is more than just a technical improvement. It’s a strategic advantage that can transform how we approach power distribution in non-urban areas. By maximizing efficiency, we’re not just saving energy; we’re creating opportunities for communities to grow and thrive. This strategic approach to efficiency is key to building sustainable and resilient power systems that can support the development of rural and suburban areas for years to come.
Future-Proofing Non-Urban Grids: Pole Transformers as Catalysts for Smart Energy Evolution?
As we look to the future of energy, how are pole transformers positioning non-urban areas for the smart energy revolution?
Pole transformers are acting as catalysts for smart energy evolution in non-urban grids by enabling renewable integration, supporting electric vehicle adoption, and facilitating grid modernization. These transformers are future-proofing rural and suburban power systems, preparing them for the next generation of energy technologies.

Let’s explore how pole transformers are paving the way for smart energy evolution:
Renewable Energy Integration
Supporting green power initiatives:
- Bi-directional power flow management for solar and wind
- Voltage regulation for intermittent renewable sources
- Energy storage integration for improved reliability
Electric Vehicle (EV) Support
Preparing for the EV revolution:
- Enhanced capacity to handle EV charging loads
- Smart charging management to balance grid demand
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities for energy storage
Grid Modernization
Upgrading infrastructure for the future:
- Advanced communication protocols for smart grid integration
- Scalable designs to accommodate future technologies
- Cybersecurity features to protect evolving grid systems
Microgrid Enablement
Fostering energy independence:
- Seamless switching between grid-connected and islanded modes
- Support for local generation and storage
- Enhanced resilience during main grid outages
Data Analytics and AI Integration
Harnessing the power of information:
- Big data analytics for predictive grid management
- AI-driven optimization of power distribution
- Machine learning for continuous system improvement
| Future-Proofing Aspect | Catalyst Role | Impact on Non-Urban Evolution |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Integration | Enables green energy adoption | Sustainable power sources |
| EV Support | Facilitates clean transportation | Reduced carbon footprint |
| Grid Modernization | Upgrades existing infrastructure | Improved reliability and efficiency |
| Microgrid Enablement | Supports local energy resilience | Enhanced community self-sufficiency |
| Data Analytics & AI | Optimizes grid operations | Smarter, more responsive power systems |
I remember working on a pilot project in a forward-thinking rural community that wanted to prepare for a 100% renewable future. We installed pole transformers with advanced renewable integration capabilities. Within a year, the community had increased its solar adoption by 200%, and on sunny days, they were nearly energy independent. The local energy cooperative president told me it was like "watching the future unfold in real-time."
Another fascinating experience was in a suburban area preparing for widespread EV adoption. We implemented pole transformers with smart charging management systems. When a popular EV model was released, causing a surge in local EV ownership, the grid was ready. The transformers balanced the new charging loads seamlessly, preventing the overloads that plagued neighboring towns. A city planner remarked that our foresight had "future-proofed their community."
These experiences have shown me that pole transformers are more than just components of today’s grid; they’re the foundation of tomorrow’s smart energy systems. By acting as catalysts for smart energy evolution, these transformers are ensuring that non-urban areas aren’t left behind in the rapidly changing energy landscape. They’re opening doors to new technologies, cleaner energy, and more resilient power systems, positioning rural and suburban communities at the forefront of the smartenergy revolution. As we continue to innovate and adapt our power infrastructure, pole transformers will play a crucial role in bridging the gap between traditional grids and the smart, sustainable energy systems of the future.
Conclusion
Pole distribution transformers are revolutionizing rural and suburban power delivery in the smart grid era. They bring advanced technology to non-urban areas, overcome geographic challenges, improve efficiency, and future-proof local grids, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable energy systems.
Have you ever wondered how modern cities manage their complex power needs? The answer lies in a critical piece of technology: the 3-phase distribution transformer.
3-phase distribution transformers are revolutionizing urban power systems by providing efficient and reliable energy distribution. These transformers are essential for smart cities, offering improved power quality, reduced losses, and seamless integration with advanced grid technologies.

As someone who’s worked in the power industry for years, I’ve seen firsthand how these transformers are shaping our urban landscapes. Let’s dive into the world of 3-phase distribution transformers and explore their impact on smart cities.
Urban Energy Efficiency: Maximizing Power Distribution with 3-Phase Technology?
In the race for urban energy efficiency, 3-phase distribution transformers are leading the pack. But what makes them so special in the context of smart cities?
3-phase distribution transformers maximize urban energy efficiency through balanced load distribution, reduced power losses, and higher capacity utilization. They enable smart cities to manage complex power demands while minimizing energy waste and infrastructure costs.

Let’s break down how 3-phase technology enhances urban energy efficiency:
Balanced Load Distribution
3-phase transformers excel at balancing loads:
- They distribute power evenly across three phases
- This reduces strain on the electrical system
- It allows for more efficient use of available capacity
Reduced Power Losses
Efficiency is key in urban power distribution:
- 3-phase systems have lower line losses than single-phase
- They require less conductor material for the same power transfer
- This results in significant energy savings over time
Higher Capacity Utilization
Making the most of urban infrastructure:
- 3-phase transformers can handle higher loads
- They provide more power in a smaller footprint
- This is crucial in space-constrained urban environments
Improved Power Quality
Ensuring stable power for sensitive urban equipment:
- 3-phase systems provide smoother power delivery
- They reduce voltage fluctuations and harmonics
- This is essential for modern electronics and industrial equipment
Smart Grid Compatibility
Preparing cities for the future:
- 3-phase transformers easily integrate with smart grid technologies
- They support advanced monitoring and control systems
- This enables dynamic load management and predictive maintenance
| Feature | Benefit | Urban Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced Load | Even power distribution | Stable grid operation |
| Reduced Losses | Energy savings | Lower operational costs |
| High Capacity | More power in less space | Efficient land use |
| Power Quality | Stable voltage | Reliable operation of equipment |
| Smart Integration | Advanced grid management | Future-ready infrastructure |
I remember a project where we replaced old single-phase transformers with new 3-phase units in a growing urban area. The results were impressive. Energy losses dropped by 15%, and the local utility could serve 30% more customers without upgrading their main feeders. A local tech company’s CEO told me their sensitive equipment was running much more reliably since the switch.
Another eye-opening experience was in a smart city pilot project. We installed 3-phase transformers with advanced monitoring capabilities. The city’s energy manager was amazed at the level of control and insight they now had. They could predict and prevent overloads, balance loads in real-time, and even integrate renewable sources more effectively.
These experiences showed me that 3-phase distribution transformers are more than just power equipment. They’re the backbone of efficient, reliable, and smart urban power systems. As our cities grow and evolve, these transformers will play a crucial role in ensuring we can meet increasing energy demands while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Reliability Redefined: Advanced Features of 3-Phase Transformers in Smart Grids?
Reliability is the cornerstone of any urban power system. But how do 3-phase transformers redefine reliability in the context of smart grids?
3-phase transformers in smart grids redefine reliability through advanced features like real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and self-healing capabilities. These innovations ensure consistent power supply, rapid fault detection, and minimal downtime in urban environments.

Let’s explore the advanced features that are setting new standards for reliability:
Real-Time Monitoring
Keeping a constant eye on performance:
- Sensors track voltage, current, and temperature
- Data is transmitted to control centers in real-time
- This allows for immediate response to any anomalies
Predictive Maintenance
Stopping problems before they start:
- AI algorithms analyze performance data
- They predict potential failures or maintenance needs
- This proactive approach minimizes unexpected outages
Self-Healing Capabilities
Rapid recovery from faults:
- Transformers can isolate faulty sections automatically
- They reroute power to maintain service
- This reduces the impact and duration of outages
Dynamic Load Management
Adapting to changing urban power needs:
- Transformers adjust to real-time demand fluctuations
- They can handle sudden load changes without tripping
- This ensures stable power supply during peak times
Enhanced Overload Capacity
Meeting urban power surges:
- Advanced cooling systems allow for temporary overloads
- This helps manage short-term demand spikes
- It reduces the need for oversized infrastructure
| Feature | Reliability Benefit | Smart Grid Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Immediate issue detection | Proactive grid management |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reduced unplanned outages | Optimized maintenance schedules |
| Self-Healing | Faster service restoration | Improved grid resilience |
| Dynamic Load Management | Stable power during demand changes | Efficient resource utilization |
| Enhanced Overload Capacity | Handling of demand spikes | Flexible grid operation |
I recall a project where we upgraded a city’s transformers with these advanced features. During a heatwave, when air conditioning use spiked, the system’s dynamic load management kicked in. It balanced the load across the network, preventing brownouts that had plagued the city in previous summers. The mayor was ecstatic, telling me it was the first time in years they hadn’t received complaint calls during a heatwave.
Another memorable case was in a financial district prone to power quality issues. We installed 3-phase transformers with advanced monitoring and self-healing capabilities. When a fault occurred in one section, the system isolated it and rerouted power within seconds. A bank manager later told me they didn’t even notice the blip that would have previously caused significant disruption.
These experiences have shown me that reliability in smart grids is about more than just keeping the lights on. It’s about creating a resilient, adaptive system that can handle the complex and ever-changing demands of modern urban life. With these advanced features, 3-phase transformers are not just distributing power; they’re ensuring the pulse of our smart cities never skips a beat.
Seamless Integration: 3-Phase Transformers in the Smart City Ecosystem?
Smart cities are complex ecosystems of interconnected technologies. How do 3-phase transformers fit into this intricate web?
3-phase transformers seamlessly integrate into the smart city ecosystem by acting as intelligent nodes in the power distribution network. They communicate with other smart systems, enable data-driven decision making, and support the integration of diverse urban technologies.

Let’s explore how these transformers become integral parts of the smart city ecosystem:
Data Hub Functionality
Transformers as information centers:
- They collect and transmit real-time power usage data
- This data feeds into city-wide management systems
- It enables informed decisions on energy distribution and urban planning
IoT Connectivity
Linking with the Internet of Things:
- Transformers communicate with smart meters and sensors
- They integrate with smart building management systems
- This creates a comprehensive network of energy awareness
Traffic and Lighting Synergy
Powering smart urban infrastructure:
- Transformers support adaptive traffic light systems
- They enable smart street lighting that responds to real-time conditions
- This improves urban mobility and energy efficiency
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Support
Facilitating green transportation:
- 3-phase transformers power EV charging stations
- They manage the increased load from growing EV adoption
- This supports the transition to sustainable urban transport
Emergency Response Integration
Enhancing urban safety:
- Transformers provide critical data during emergencies
- They support priority power routing to essential services
- This improves the city’s resilience during crises
| Integration Aspect | Smart City Benefit | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Data Hub | Informed urban management | Real-time data provision |
| IoT Connectivity | Comprehensive energy awareness | Network node |
| Traffic & Lighting | Improved urban mobility | Reliable power supply |
| EV Charging | Sustainable transportation | Load management |
| Emergency Response | Enhanced urban safety | Critical infrastructure support |
I remember working on a project to integrate 3-phase transformers into a city’s new smart management system. The city planner was amazed at how the transformers became ‘eyes and ears’ for the power grid. They could now see how energy use correlated with traffic patterns, weather conditions, and even major events. This insight led to more efficient energy distribution and even helped optimize public transport routes.
Another fascinating experience was in a city piloting a large-scale EV initiative. We installed smart 3-phase transformers to support the new charging infrastructure. The system’s ability to balance loads and communicate with the charging stations was crucial. It allowed the city to roll out more charging points than initially planned, accelerating their green transport goals.
These experiences have shown me that in the smart city ecosystem, 3-phase transformers are far more than just power distribution devices. They’re active participants in the city’s nervous system, enabling the flow of both electricity and information. As our urban centers evolve into true smart cities, these transformers will continue to play a pivotal role in knitting together the diverse technologies that make our cities smarter, more efficient, and more livable.
Load Management Mastery: Balancing Urban Energy Demands with 3-Phase Solutions?
Urban energy demands are like a complex dance, constantly changing and requiring perfect balance. How do 3-phase transformers master this intricate performance?
3-phase transformers master urban load management through advanced load balancing techniques, dynamic capacity adjustment, and intelligent demand response capabilities. These solutions ensure stable power supply in the face of fluctuating urban energy demands.

Let’s dive into how 3-phase solutions achieve load management mastery:
Advanced Load Balancing
Keeping the power equilibrium:
- 3-phase transformers distribute loads evenly across phases
- They automatically adjust to unbalanced loads
- This prevents overloading and improves overall system efficiency
Dynamic Capacity Adjustment
Adapting to changing demands:
- Transformers can adjust their capacity based on real-time needs
- They use on-load tap changers to optimize voltage levels
- This flexibility allows for efficient use of available capacity
Intelligent Demand Response
Responding to grid needs:
- Transformers participate in demand response programs
- They can reduce load during peak times
- This helps prevent outages and reduces strain on the grid
Predictive Load Management
Staying ahead of energy needs:
- AI algorithms forecast future load patterns
- Transformers prepare for anticipated demand changes
- This proactive approach ensures smooth power delivery
Microgrid Support
Enabling local power management:
- 3-phase transformers support microgrid operations
- They facilitate seamless switching between grid and local power
- This enhances resilience and allows for optimal use of local resources
| Load Management Feature | Urban Benefit | Transformer Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Stable power supply | Automatic phase adjustment |
| Dynamic Capacity | Efficient resource use | On-load tap changing |
| Demand Response | Grid stability | Load reduction during peaks |
| Predictive Management | Proactive power planning | AI-driven forecasting |
| Microgrid Support | Local energy resilience | Seamless mode switching |
I recall a project in a rapidly growing urban area where peak demands were causing frequent issues. We implemented 3-phase transformers with advanced load balancing and dynamic capacity adjustment. The result was remarkable. The utility could handle a 20% increase in peak load without additional infrastructure. A local business owner told me it was the first summer in years they hadn’t experienced brownouts during heatwaves.
Another interesting case was in a smart neighborhood with high solar panel adoption. The 3-phase transformers we installed could handle the variable input from solar while managing the overall load. During a particularly sunny week, the system even fed excess power back into the main grid, turning the neighborhood into a net energy producer. The residents were thrilled to see their meters running backwards!
These experiences have shown me that load management with 3-phase transformers is not just about handling current demands. It’s about creating a flexible, responsive system that can adapt to the ever-changing energy landscape of modern cities. As urban energy needs continue to evolve, these transformers will be key to ensuring our cities can keep up with demand while maintaining stability and efficiency.
Sustainable Urban Power: 3-Phase Transformers and Renewable Energy Synergy?
As cities strive for sustainability, the integration of renewable energy becomes crucial. How do 3-phase transformers support this green revolution in urban power?
3-phase transformers synergize with renewable energy in urban settings by managing variable inputs, enabling bi-directional power flow, and supporting energy storage integration. This synergy is key to creating sustainable and resilient urban power systems.

Let’s explore how 3-phase transformers and renewable energy work together for sustainable urban power:
Variable Input Management
Handling the unpredictability of renewables:
- 3-phase transformers can manage fluctuating inputs from solar and wind
- They use advanced voltage regulation to maintain stable output
- This allows for higher penetration of renewables in urban grids
Bi-Directional Power Flow
Enabling energy prosumers:
- Transformers support power flow from distributed generation sources
- They manage the feed-in of excess energy to the grid
- This facilitates the growth of urban solar installations and microgrids
Energy Storage Integration
Balancing supply and demand:
- 3-phase transformers work seamlessly with battery storage systems
- They manage charging during excess production and discharging during peak demand
- This improves the overall efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems
Smart Inverter Coordination
Optimizing renewable energy conversion:
- Transformers communicate with smart inverters
- They coordinate power factor correction and voltage support
- This enhances the stability of grids with high renewable penetration
Microgrid Support
Fostering local energy independence:
- 3-phase transformers enable the formation of urban microgrids
- They support seamless transitions between grid-connected and islanded modes
- This increases resilience and allows for optimal use of local renewable resources
| Renewable Synergy Aspect | Urban Sustainability Benefit | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Variable Input Management | Higher renewable adoption | Voltage stabilization |
| Bi-Directional Flow | Growth of urban prosumers | Power flow control |
| Energy Storage Integration | Improved energy efficiency | Charge/discharge management |
| Smart Inverter Coordination | Enhanced grid stability | Power quality maintenance |
| Microgrid Support | Local energy resilience | Mode switching and control |
I remember a project where we integrated 3-phase transformers into a city’s ambitious solar initiative. The transformers’ ability to handle variable inputs was crucial. On one particularly sunny day, the system managed a 40% renewable energy mix without any stability issues. The city’s sustainability officer was ecstatic, telling me they had exceeded their green energy targets years ahead of schedule.
Another fascinating experience was in an eco-district that aimed for energy independence. We installed smart 3-phase transformers that could support microgrid operations. During a grid outage, the district seamlessly transitioned to its local renewable sources. Residents were amazed that they had power when the rest of the city was dark. It was a powerful demonstration of resilience through sustainable technology.
These experiences have shown me that the synergy between 3-phase transformers and renewable energy is more than just technical compatibility. It’s about creating a flexible, sustainable power infrastructure that can adapt to the changing energy landscape of our cities. As we push towards a greener urban future, these transformers will be key enablers, helping our cities harness the full potential of renewable energy while maintaining the reliability and quality of power supply.
Conclusion
3-phase distribution transformers are pivotal in powering smart cities. They enhance
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group