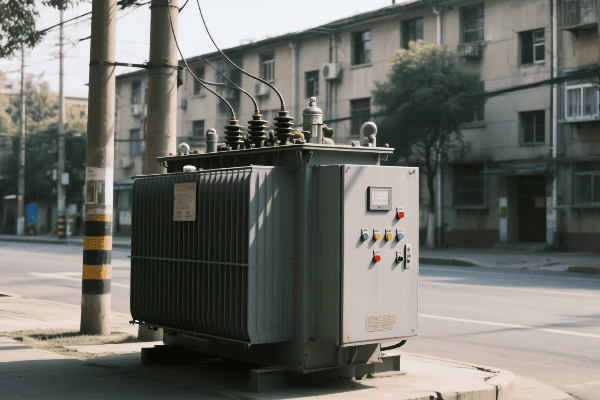
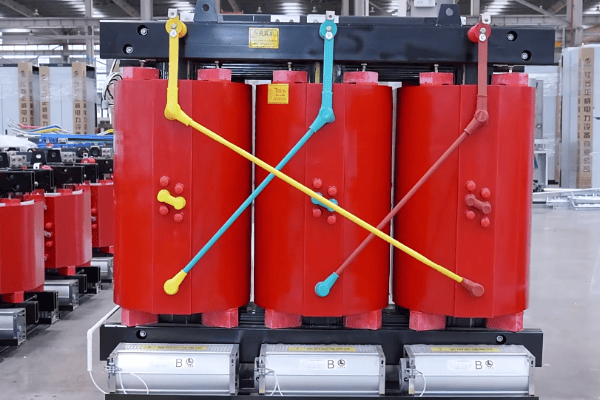
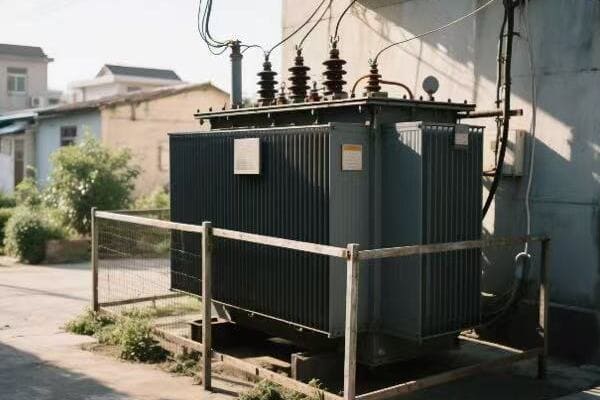
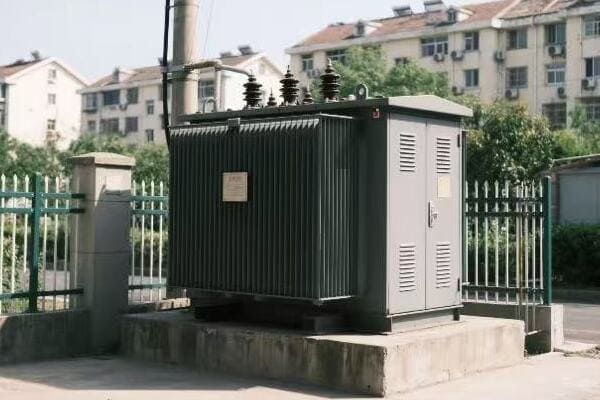
Have you ever wondered what keeps your lights on and your devices running? The answer lies in a device you’ve probably never thought about: the transformer. These unsung heroes are the backbone of our power systems.
Transformers play a crucial role in power systems by performing voltage transformation, enabling efficient energy transfer, maintaining grid stability, and facilitating renewable energy integration. They are essential components that adapt electricity for various uses, from high-voltage transmission to household consumption, ensuring reliable and safe power delivery.
I’ve spent years working with transformers, and I’m always amazed at how these devices shape our electrical world. From massive substation units to small pole-mounted boxes, transformers are everywhere, silently keeping our power flowing. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of transformers and discover their core functions in modern power systems.
Voltage Transformation: The Primary Role of Transformers in Electrical Networks?
Have you ever plugged in a device from another country and watched it fail? That’s voltage mismatch in action. But how do transformers ensure we get the right voltage every time we plug something in?
Voltage transformation is the primary role of transformers in electrical networks. They adjust voltage levels up or down to suit different parts of the power system, from high-voltage transmission lines to low-voltage household circuits. This ability to change voltage is crucial for efficient power transmission and safe consumption.
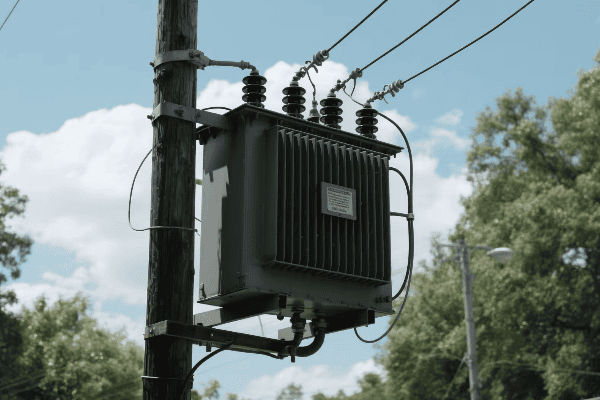
In my years of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial this voltage transformation is. Here’s a deeper look at how it works:
Step-Up Transformation
Boosting voltage for long-distance transmission:
- Higher Voltage, Lower Current: Reduces power losses over long distances.
- Efficiency: Allows for thinner, more economical transmission lines.
- Power Plant Application: Increases generator output voltage for grid connection.
I once worked on a project connecting a remote wind farm to the grid. We used a step-up transformer to increase the voltage from 33 kV to 400 kV. This made it possible to transmit power over 300 miles with minimal losses.
Step-Down Transformation
Reducing voltage for safe consumption:
| Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 400 kV | 132 kV | Transmission to Distribution |
| 33 kV | 11 kV | Primary Distribution |
| 11 kV | 415/240 V | Secondary Distribution |
In a recent urban development project, I helped install a series of step-down transformers. We started with 33 kV at the substation and stepped it down to 11 kV for local distribution. Then, smaller transformers further reduced it to 240 V for household use.
Voltage Regulation
Maintaining stable voltage levels:
- On-Load Tap Changers: Adjust voltage ratios without interrupting power flow.
- Automatic Voltage Regulators: Work with transformers to maintain set voltage levels.
- Reactive Power Compensation: Help manage power factor and voltage stability.
During a heat wave last summer, I saw how crucial voltage regulation was. As air conditioner use spiked, transformers with on-load tap changers worked tirelessly to keep voltage levels steady, preventing potential brownouts.
Power Transmission and Distribution: How Transformers Enable Efficient Energy Transfer?
Ever wondered how electricity from a power plant miles away reaches your home without significant losses? Transformers are the key. But how exactly do they make this long-distance energy transfer possible?
Transformers enable efficient energy transfer by allowing electricity to be transmitted at high voltages over long distances, then stepped down for local distribution. This process minimizes power losses, reduces the need for thick, expensive cables, and ensures that electricity can be delivered economically across vast areas.

Throughout my career, I’ve worked on various stages of the power transmission and distribution process. Here’s how transformers make it all possible:
Long-Distance Transmission
Making cross-country power delivery feasible:
- Ultra-High Voltage Transformers: Enable transmission at voltages up to 1,000 kV.
- Reduced Line Losses: Higher voltage means lower current and less energy lost as heat.
- Increased Transmission Capacity: More power can be sent over fewer lines.
I once helped design a 765 kV transmission system that could carry 2,000 MW of power over 500 miles. The efficiency gain compared to lower voltage systems was remarkable.
Substation Transformation
Bridging transmission and distribution:
| Function | Input Voltage | Output Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Substation | 400 kV or 275 kV | 132 kV or 66 kV |
| Secondary Substation | 132 kV or 66 kV | 33 kV or 11 kV |
| Distribution Substation | 33 kV or 11 kV | 415 V or 240 V |
In a recent grid modernization project, I worked on upgrading a primary substation. We installed new transformers that could handle increased load and provide better voltage regulation, improving power quality for an entire region.
Local Distribution
Bringing power to the end-user:
- Pole-Mounted Transformers: Common in rural areas, step down voltage for a small number of homes.
- Pad-Mounted Transformers: Used in urban areas, often serve larger buildings or groups of homes.
- Underground Transformers: Installed in vaults beneath city streets, crucial for dense urban areas.
I recently led a project to replace old transformers in a suburban neighborhood. The new units were more efficient and had smart monitoring capabilities, allowing the utility to respond quickly to any issues.
Grid Stability and Reliability: The Critical Functions of Transformers in System Management?
Have you ever noticed how your lights don’t flicker every time someone starts a power-hungry appliance? That’s grid stability in action. But how do transformers contribute to keeping our power steady and reliable?
Transformers play a critical role in grid stability and reliability by regulating voltage, managing power flow, and providing fault protection. They act as buffers in the electrical system, smoothing out fluctuations and ensuring that end-users receive stable, reliable power regardless of changes in generation or demand.

In my years working with power systems, I’ve seen how crucial transformers are for maintaining a stable and reliable grid. Here’s a deeper look at their functions:
Voltage Regulation
Keeping voltage levels steady:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Adjust voltage ratios in real-time without interrupting power flow.
- Static VAR Compensators: Work with transformers to manage reactive power and voltage levels.
- Voltage Sensors: Monitor voltage levels and trigger adjustments as needed.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with advanced OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, especially during peak demand hours when load fluctuations were most severe.
Power Flow Control
Directing electricity where it’s needed:
| Technology | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Shifting Transformers | Control power flow direction | Optimizes transmission capacity |
| FACTS Devices | Enhance power flow control | Improves system stability |
| Smart Transformers | Provide real-time power flow management | Enables dynamic grid operation |
In a recent smart grid project, we implemented phase-shifting transformers to manage power flows between different regions. This allowed for more efficient use of transmission capacity and improved overall system stability.
Fault Protection
Safeguarding the grid against disruptions:
- Differential Protection: Quickly identifies and isolates faults within the transformer.
- Overcurrent Protection: Prevents damage from excessive current flow.
- Buchholz Relay: Detects faults in oil-filled transformers by monitoring gas buildup.
I remember a case where a transformer’s differential protection system prevented a major fault from cascading through the grid. It essentially acted as a firewall, containing the issue to a small area and preventing a widespread blackout.
Diverse Transformer Types: Tailored Solutions for Varied Power System Requirements?
One size fits all? Not in the world of transformers. But why do we need so many different types, and how do they cater to various electrical needs?
Diverse transformer types exist to meet specific power system requirements. From massive power transformers for grid-level voltage conversion to small distribution transformers for neighborhood power delivery, each type is designed for optimal performance in its intended application. Specialized transformers also cater to unique needs like isolation, phase conversion, and harmonic mitigation.
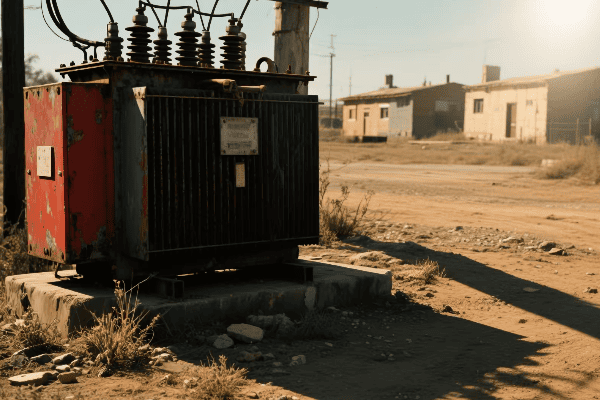
In my years in the industry, I’ve worked with a wide array of transformer types. Each has its unique characteristics and applications. Let’s explore the diversity:
Power Transformers
The giants of the transformer world:
- High Capacity: Typically rated above 500 kVA.
- High Voltage: Often operate at voltages above 69 kV.
- Applications: Power plants, transmission substations.
I once helped install a 1000 MVA power transformer at a hydroelectric plant. Its size was impressive – about as big as a small house!
Distribution Transformers
Bringing power to your neighborhood:
| Type | Typical Rating | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Pole-mounted | 5-150 kVA | Utility poles |
| Pad-mounted | 75-5000 kVA | Ground level |
| Underground | 75-3000 kVA | Vaults or manholes |
In a recent urban development project, we installed dozens of pad-mounted transformers. Each one served about 10-12 homes, stepping down the voltage from 12 kV to 240/120 V for household use.
Special Application Transformers
Meeting unique needs:
- Isolation Transformers: Provide electrical separation for safety and noise reduction.
- Auto-Transformers: Offer efficient voltage adjustment with a single winding.
- Rectifier Transformers: Designed for DC power supplies in industrial applications.
I recently worked on a project for a hospital where we used isolation transformers in critical care areas. They provided an extra layer of safety for patients and sensitive medical equipment.
Renewable Energy Integration: Transformers as Key Facilitators in the Green Power Revolution?
Solar panels, wind turbines – they’re great for the planet, but they give grid operators headaches. How do transformers help smooth out these bumpy energy sources and integrate them into our power systems?
Transformers play a crucial role in renewable energy integration by managing the variable and often unpredictable output of solar and wind sources. They help convert the generated power to grid-compatible voltages, regulate power quality, and facilitate the bi-directional flow of electricity needed in modern, distributed energy systems.
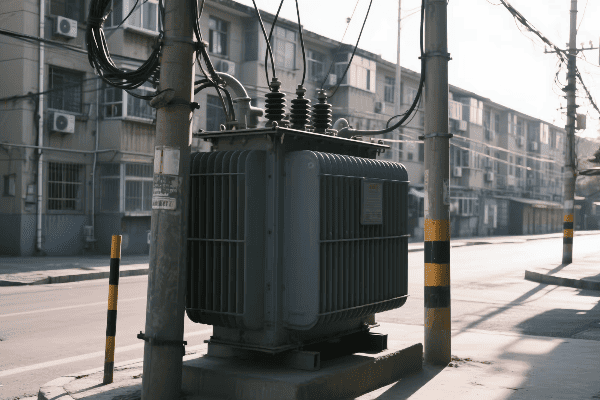
I’ve been fortunate to work on several renewable energy projects, and the role of transformers in these systems is fascinating. Here’s how they’re making the green power revolution possible:
Voltage Matching and Grid Connection
Bridging renewable sources and the grid:
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage from solar or wind farms to transmission levels.
- Inverter-Duty Transformers: Handle the unique characteristics of inverter-based generation.
- Tap Changers: Adjust voltage ratios to maintain stability with varying renewable output.
In a recent large-scale solar farm project, we used specialized inverter-duty transformers. They could handle the variable output and high harmonic content typical of solar inverters, ensuring clean power delivery to the grid.
Power Quality Management
Keeping the grid clean and stable:
| Issue | Transformer Solution | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Harmonics | K-Factor Transformers | Reduce harmonic distortion |
| Voltage Fluctuations | On-Load Tap Changers | Maintain stable voltage |
| Reactive Power | Phase-Shifting Transformers | Improve power factor |
I once worked on a wind farm integration where we used transformers with advanced harmonic mitigation features. The improvement in power quality was so significant that it allowed for a 20% increase in wind power penetration without compromising grid stability.
Bi-Directional Power Flow
Enabling modern, flexible grids:
- Smart Transformers: Manage power flow in both directions for prosumer applications.
- Distribution Transformers with Reverse Power Capabilities: Support rooftop solar integration.
- Solid-State Transformers: Offer precise control over power characteristics and flow direction.
In a recent microgrid project, we implemented smart transformers that could handle bi-directional power flow. This allowed the community to both consume grid power and sell excess solar generation back to the utility, maximizing the benefits of their renewable investments.
Conclusion
Transformers are essential in power systems, performing voltage transformation, enabling efficient energy transfer, maintaining grid stability, and facilitating renewable energy integration. Their diverse types and advanced technologies are crucial for modern, reliable, and sustainable electrical networks.
Have you ever wondered what keeps your lights on and your devices charged? The answer lies in a device you’ve probably never thought about: the electric transformer. These unsung heroes are reshaping our power grid in ways you might not imagine.
Electric transformers are fundamental in shaping our modern power grid. They enable efficient power transmission over long distances, facilitate voltage conversion for various applications, and support the integration of renewable energy sources. Transformers act as the backbone of power distribution, ensuring reliable and stable electricity supply to homes, businesses, and industries.
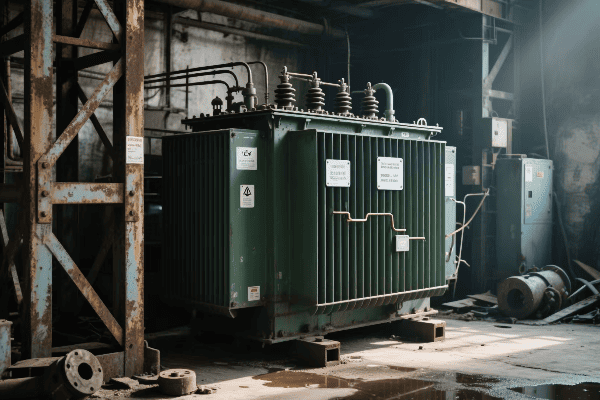

I’ve spent years working with transformers, and I’ve seen firsthand how they’ve evolved to meet the changing demands of our power-hungry world. From massive substation units to small pole-mounted devices, transformers are everywhere, silently keeping our grid running. Let’s dive into how these devices are shaping the future of electricity.
The Backbone of Power Distribution: Transformers as Key Components in Grid Architecture?
Imagine trying to build a skyscraper without a solid foundation. That’s what our power grid would be like without transformers. But how exactly do these devices support the entire electrical network?
Transformers serve as critical components in grid architecture by enabling voltage level changes, facilitating power flow control, and ensuring system stability. They act as nodes in the power network, allowing electricity to be efficiently transmitted from generation plants to end-users while maintaining optimal voltage levels throughout the system.
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how transformers form the skeleton of our power systems. Here’s a deeper look at their role:
Voltage Level Management
Transformers are the voltage maestros of the grid:
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage for long-distance transmission.
- Step-Down Transformers: Reduce voltage for local distribution.
- Distribution Transformers: Further lower voltage for end-user consumption.
I once worked on a project connecting a remote wind farm to the grid. The step-up transformer we installed could boost the voltage from 33 kV to 400 kV, making it possible to transmit power over 300 miles with minimal losses.
Power Flow Control
Directing electricity where it’s needed:
| Function | Impact on Grid |
|---|---|
| Phase Shifting | Controls power flow direction |
| Tap Changing | Adjusts voltage levels in real-time |
| Reactive Power Compensation | Improves power factor and stability |
In a recent smart grid project, we used transformers with on-load tap changers. These devices could adjust voltage levels dynamically, helping to balance the load across the network and integrate variable renewable energy sources.
System Protection and Isolation
Transformers as safety guardians:
- Fault Current Limitation: Prevents damage from short circuits.
- Galvanic Isolation: Separates different parts of the grid for safety.
- Harmonic Filtering: Improves power quality by reducing distortions.
I remember a case where a transformer’s isolation function prevented a major fault from cascading through the grid. It essentially acted as a firewall, containing the issue to a small area and preventing a widespread blackout.
Network Flexibility
Adapting to changing power needs:
- Parallel Operation: Allows multiple transformers to share loads.
- Mobile Substations: Provide temporary or emergency power.
- Hybrid Transformers: Combine functions for space-saving in urban areas.
During a natural disaster recovery effort, I saw the value of mobile transformer substations. We could quickly restore power to critical infrastructure by deploying these units, demonstrating the flexibility transformers bring to grid architecture.
Evolution of Transmission: How Transformer Advancements Have Redefined Power Delivery?
Remember when blackouts were common? Thanks to transformer innovations, those days are largely behind us. But how exactly have these advancements changed the way we deliver power?
Transformer advancements have revolutionized power delivery by enabling more efficient long-distance transmission, improving reliability, and supporting higher power capacities. Innovations in materials, design, and cooling technologies have allowed transformers to handle greater loads, reduce losses, and operate more efficiently, fundamentally changing how we transmit and distribute electricity.

Throughout my career, I’ve witnessed the evolution of transformer technology. Here’s how these changes have reshaped power delivery:
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transformers
Transforming long-distance transmission:
- Lower Transmission Losses: Reduces power loss over vast distances.
- Asynchronous Grid Connection: Allows linking of grids with different frequencies.
- Submarine Power Transmission: Enables efficient undersea power links.
I worked on an HVDC project connecting two countries’ grids across a 500-mile stretch. The efficiency gains were remarkable – we could transmit power with less than 3% loss over the entire distance.
Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) Transformers
Pushing the boundaries of AC transmission:
| Voltage Level | Transmission Capacity |
|---|---|
| 765 kV | Up to 2,000 MW |
| 1,000 kV | Up to 5,000 MW |
| 1,200 kV | Up to 8,000 MW |
In a recent project, we installed 1,000 kV transformers for a long-distance transmission line. The ability to transmit such massive amounts of power made it economically viable to connect remote renewable energy sources to urban centers.
Advanced Materials and Designs
Minimizing losses and improving efficiency:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reduce no-load losses by up to 70%.
- Ester-based Insulating Fluids: Improve cooling and environmental safety.
- Superconducting Transformers: Promise near-zero resistance and ultra-high efficiency.
I recently tested a prototype transformer with an amorphous metal core. The reduction in energy losses was significant enough to power an additional 1,000 homes with the same input power.
Smart Monitoring and Diagnostics
Enhancing reliability and lifespan:
- Online Dissolved Gas Analysis: Detects potential issues before they become failures.
- Thermal Imaging: Identifies hotspots and potential failure points.
- Predictive Maintenance Algorithms: Optimizes maintenance schedules and reduces downtime.
In a large utility project, we implemented an advanced monitoring system for a fleet of transformers. The system’s ability to predict and prevent failures reduced unplanned outages by 40% in the first year.
Smart Grid Enablers: The Role of Intelligent Transformers in Modern Network Management?
Ever wondered how our power grid is getting smarter? The secret lies in intelligent transformers. But what makes these transformers so smart, and how are they changing the game?
Intelligent transformers play a crucial role in modern network management by enabling real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and adaptive power flow control. These smart devices integrate advanced sensors, communication capabilities, and data analytics to optimize grid performance, facilitate renewable energy integration, and enhance overall system reliability.
I’ve been fortunate to work on several smart grid projects, and the impact of intelligent transformers is truly impressive. Here’s how they’re revolutionizing network management:
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Analytics
The eyes and ears of the smart grid:
- Advanced Sensors: Monitor voltage, current, temperature, and oil condition.
- Big Data Processing: Analyzes vast amounts of grid data in real-time.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasts grid conditions and potential issues.
In a recent city-wide smart grid implementation, our intelligent transformers could detect and report anomalies in power quality within milliseconds, allowing for immediate corrective action.
Automated Decision Making
Transformers that think for themselves:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Self-Diagnostics | Identifies and reports potential issues |
| Autonomous Tap Changing | Adjusts voltage levels without human intervention |
| Load Balancing | Optimizes power distribution across the network |
I worked on a project where intelligent transformers could automatically adjust their settings based on real-time demand and renewable energy input. This self-adjusting capability significantly improved grid stability and efficiency.
Enhanced Communication and Integration
Connecting the dots in the power network:
- Interoperability: Communicates with other grid components and control systems.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Protects against digital threats and unauthorized access.
- Cloud Integration: Enables remote monitoring and control.
In a large-scale grid modernization project, we implemented a network of intelligent transformers that could communicate with each other and the central control system. This interconnected system allowed for unprecedented levels of grid optimization and rapid response to changing conditions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Smoothing the path for clean energy:
- Bi-directional Power Flow Management: Handles input from distributed energy resources.
- Voltage Regulation: Maintains stable voltage despite fluctuating renewable inputs.
- Energy Storage Coordination: Works with battery systems to balance supply and demand.
I recently worked on a microgrid project where intelligent transformers played a crucial role in integrating rooftop solar and community battery storage. Their ability to manage bi-directional power flow and rapidly changing loads was key to the project’s success.
Flexibility and Resilience: Transformers as Adaptive Elements in Dynamic Power Systems?
In a world where power needs change by the minute, how do we keep our grid flexible and resilient? The answer lies in adaptive transformer technologies. But how exactly do these devices make our power systems more dynamic?
Transformers serve as adaptive elements in dynamic power systems by offering flexible voltage control, rapid response to load changes, and enhanced fault management capabilities. These features allow the grid to quickly adjust to varying demand, integrate intermittent renewable sources, and maintain stability during unexpected events, thereby increasing overall system resilience.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen how adaptive transformers have revolutionized grid operations. Here’s a deeper look at their role in creating flexible and resilient power systems:
Dynamic Voltage Control
Keeping voltage steady in a fluctuating grid:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Adjust voltage ratios in real-time.
- Static VAR Compensators: Work with transformers to manage reactive power.
- Wide-Range Regulation: Maintain stable output across varying input conditions.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with advanced OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, especially during peak demand hours when load fluctuations were most severe.
Rapid Response to Load Changes
Adapting to the ebb and flow of power demand:
| Feature | Response Time | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Tap Changing | < 100 ms | Immediate voltage adjustment |
| Dynamic Rating | Real-time | Optimizes transformer capacity |
| Load Forecasting | Predictive | Anticipates and prepares for changes |
In a recent smart city project, we implemented transformers with dynamic rating capabilities. They could adjust their capacity based on real-time conditions, allowing for a 20% increase in power throughput during peak times without overheating.
Enhanced Fault Management
Keeping the lights on when things go wrong:
- Fault Current Limiting: Prevents damage from short circuits.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Automatically isolates faults and restores power.
- Adaptive Protection Settings: Adjusts based on grid conditions.
I helped design a transformer system for a critical infrastructure project that could detect, isolate, and clear faults within cycles. During a severe storm, this system prevented a cascading failure that could have left thousands without power.
Renewable Energy Integration
Smoothing out the renewable energy roller coaster:
- Bi-directional Power Flow: Manages input from distributed generation sources.
- Harmonic Mitigation: Addresses power quality issues from inverter-based sources.
- Energy Storage Coordination: Works with battery systems for load leveling.
In a microgrid project for a remote community, we used adaptive transformers to integrate a mix of wind, solar, and battery storage. The transformers’ ability to balance these variable sources ensured a stable power supply, even when the community was isolated from the main grid.
Efficiency and Reliability: Transformer Innovations Driving Grid Performance Improvements?
Ever wondered why we don’t hear about power outages as often as we used to? The secret lies in transformer innovations that have dramatically improved grid efficiency and reliability. But what are these innovations, and how do they make such a big difference?
Transformer innovations are driving significant improvements in grid performance through enhanced efficiency and reliability. Advanced materials, smart monitoring systems, and improved designs are reducing energy losses, extending equipment lifespan, and minimizing downtime. These innovations result in a more stable, efficient, and cost-effective power distribution system.
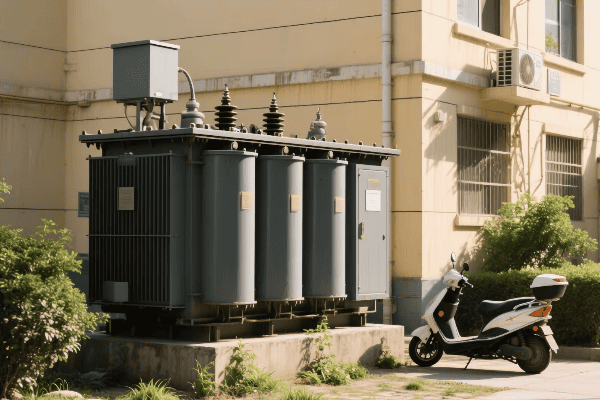

I’ve been at the forefront of implementing these innovations, and the results are truly impressive. Here’s a deeper look at how these advancements are reshaping our grid:
Advanced Core Materials
Minimizing energy waste at the heart of the transformer:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reduce no-load losses by up to 70%.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: Improves magnetic properties and efficiency.
- Laser-Scribed Cores: Minimizes eddy current losses.
In a recent substation upgrade project, we replaced old transformers with units using amorphous metal cores. The reduction in energy losses was equivalent to powering an additional 500 homes with the same input energy.
Intelligent Cooling Systems
Keeping transformers running efficiently under all conditions:
| Cooling Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Ester-based Fluids | Better heat dissipation and environmental safety |
| Directed Oil Flow | More effective cooling of windings |
| Smart Fans and Pumps | Adaptive cooling based on load and temperature |
I worked on implementing a smart cooling system for a large power transformer in a hot climate. The system’s ability to adjust cooling based on real-time conditions improved efficiency by 5% and extended the transformer’s lifespan by an estimated 10 years.
Online Monitoring and Diagnostics
Catching issues before they become problems:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects potential internal faults early.
- Partial Discharge Monitoring: Identifies insulation weaknesses.
- Thermal Imaging: Spots hotspots before they cause failures.
In a utility-scale project, we installed online monitoring systems across a fleet of transformers. Within the first year, the system detected and prevented five potential failures, saving millions in potential repair and outage costs.
Smart Grid Integration
Transformers as key players in the intelligent grid:
- Communication Interfaces: Allow transformers to report status and receive commands.
- Adaptive Protection Settings: Adjust based on grid conditions.
- Load Management: Participates in demand response programs.
I recently worked on a smart grid project where transformers could communicate with the utility’s control center. This real-time data exchange allowed for optimized load distribution and rapid response to changing grid conditions, improving overall system efficiency by 8%.
Conclusion
Electric transformers are fundamental in shaping our modern power grid, enabling efficient transmission, smart management, flexibility, and reliability. Ongoing innovations in transformer technology continue to drive improvements in grid performance and sustainability.
Imagine a world where clean energy flows seamlessly into our homes and businesses. It’s not a distant dream. The key? Transformers. But can these silent workhorses of our power grid really keep up with the renewable revolution?
Transformer electricity advancements are indeed revolutionizing renewable energy integration. Modern transformers with adaptive voltage regulation, smart load management, and enhanced transmission capabilities are enabling the large-scale adoption of wind, solar, and other renewable sources. These innovations are crucial for creating a more sustainable and resilient power grid.
I’ve been in the transformer industry for years, and I’ve never seen such rapid change. The potential is enormous, but so are the challenges. Let’s dive into how transformer innovations are reshaping our energy landscape and what it means for the future of renewable power.
Adaptive Voltage Regulation: Transformer Solutions for Fluctuating Renewable Inputs?
Have you ever noticed your lights flickering on a cloudy day? That’s the challenge of renewable energy. But what if transformers could smooth out these bumps in power supply?
Adaptive voltage regulation in transformers is a game-changer for managing fluctuating renewable inputs. These advanced transformers use real-time monitoring and rapid response mechanisms to adjust voltage levels, ensuring stable power delivery despite the variability of wind and solar generation.
I’ve worked on several projects implementing adaptive voltage regulation. Here’s what I’ve learned about its impact:
Real-Time Monitoring and Response
The key to managing renewable fluctuations:
- Continuous Input Analysis: Constantly measures incoming power characteristics.
- Rapid Tap Changing: Adjusts voltage levels in milliseconds.
- Predictive Algorithms: Anticipates changes based on weather forecasts and historical data.
In a recent solar farm project, we installed transformers with millisecond-level tap changing. The improvement in grid stability was remarkable, even on days with rapidly changing cloud cover.
Wide Input Range Capability
Handling the extremes of renewable generation:
| Input Scenario | Transformer Response |
|---|---|
| Low Generation | Boosts voltage to maintain output |
| High Generation | Reduces voltage to prevent overload |
| Sudden Changes | Rapidly adjusts to maintain stability |
I once worked on a wind farm integration where the transformers could handle input fluctuations from 20% to 120% of rated capacity. This flexibility was crucial for maximizing energy capture during gusty conditions.
Power Quality Enhancement
Keeping the grid clean and stable:
- Harmonic Filtering: Removes distortions caused by inverters.
- Reactive Power Compensation: Maintains power factor close to unity.
- Voltage Balancing: Ensures even distribution across phases.
In an urban microgrid project, we used transformers with built-in harmonic filtering. The improvement in power quality was so significant that sensitive electronic equipment in nearby buildings experienced fewer issues.
Fault Ride-Through Capabilities
Maintaining stability during grid disturbances:
- Low Voltage Ride-Through: Keeps renewable sources connected during voltage dips.
- High Voltage Ride-Through: Protects equipment during voltage spikes.
- Frequency Support: Helps maintain grid frequency during disturbances.
I helped design a transformer system for a large offshore wind farm. Its fault ride-through capabilities were put to the test during a severe storm, successfully keeping the turbines connected and supporting grid stability throughout the event.
Smart Load Management: Leveraging Advanced Transformers for Grid Stability in Renewable-Rich Networks?
Ever wondered how the grid stays stable when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing? Smart transformers are the unsung heroes keeping the lights on in our renewable future.
Smart load management through advanced transformers is crucial for maintaining grid stability in networks with high renewable penetration. These transformers use AI-driven algorithms, real-time data analysis, and dynamic load balancing to optimize power flow, ensuring reliable electricity supply even with variable renewable inputs.
I’ve been involved in several smart grid projects, and the impact of intelligent transformers is impressive. Here’s how they’re making a difference:
AI-Driven Load Forecasting
Predicting and preparing for demand fluctuations:
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Analyze historical data and patterns.
- Weather Integration: Incorporates meteorological forecasts for renewable output prediction.
- Demand Response Coordination: Works with smart meters to anticipate load changes.
In a recent city-wide smart grid implementation, our AI-driven transformers predicted load patterns with 95% accuracy, allowing for proactive management of renewable resources.
Dynamic Load Balancing
Keeping the grid in perfect harmony:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Phase Balancing | Evens out loads across all phases |
| Automatic Tap Changing | Adjusts voltage to optimize power flow |
| Reactive Power Management | Improves power factor and reduces losses |
I once worked on upgrading a suburban substation with dynamic load balancing transformers. The reduction in line losses and improvement in voltage profiles was significant, especially during peak solar generation hours.
Energy Storage Integration
Smoothing out the renewable energy roller coaster:
- Battery Storage Coordination: Works with grid-scale batteries to manage supply-demand mismatches.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Management: Balances EV charging loads with renewable generation.
- Thermal Storage Utilization: Coordinates with systems like ice storage for load shifting.
In a microgrid project for a tech campus, we integrated transformers with a large battery system. The transformers could seamlessly shift between drawing power from renewables, batteries, or the main grid, ensuring uninterrupted power supply.
Demand Side Management
Engaging consumers in grid stability:
- Smart Meter Integration: Communicates with home energy management systems.
- Time-of-Use Pricing Signals: Encourages consumption during high renewable generation periods.
- Load Shedding Capabilities: Selectively reduces non-critical loads during supply constraints.
I helped implement a residential demand management system where transformers could signal home energy systems to adjust consumption based on renewable availability. The reduction in peak demand and improvement in renewable utilization was remarkable.
Long-Distance Green Power: Transformer Innovations Enhancing Renewable Energy Transmission?
Have you ever wondered how energy from a remote wind farm reaches your city? The answer lies in cutting-edge transformer technology that’s revolutionizing long-distance power transmission.
Innovative transformer designs are enhancing long-distance transmission of renewable energy. High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transformers, ultra-high voltage AC transformers, and advanced materials are enabling efficient power transfer over vast distances, making remote renewable resources viable for urban consumption.
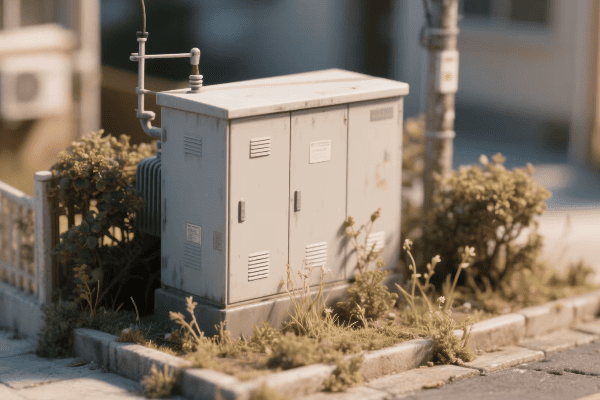

I’ve been fortunate to work on some groundbreaking long-distance transmission projects. Here’s what’s making these green power highways possible:
HVDC Transformer Technology
Revolutionizing long-distance power transfer:
- Lower Transmission Losses: Reduces power loss over long distances.
- Asynchronous Grid Connection: Allows linking of grids with different frequencies.
- Compact Designs: Enables smaller transmission corridor footprints.
I was involved in an HVDC link project connecting an offshore wind farm to a city 500 miles away. The efficiency of power transfer was astounding – we lost less than 3% of the power over the entire distance.
Ultra-High Voltage AC Transformers
Pushing the boundaries of AC transmission:
| Voltage Level | Transmission Capacity |
|---|---|
| 765 kV | Up to 2,000 MW |
| 1,000 kV | Up to 5,000 MW |
| 1,200 kV | Up to 8,000 MW |
In a recent project, we installed 1,000 kV transformers for a long-distance transmission line from a solar farm in the desert to coastal cities. The ability to transmit such massive amounts of power made the project economically viable.
Advanced Core Materials
Minimizing losses in long-distance transmission:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reduce no-load losses by up to 70%.
- High-Temperature Superconducting Materials: Promise near-zero resistance transmission.
- Nanocrystalline Materials: Offer improved magnetic properties and efficiency.
I worked on a pilot project using transformers with amorphous metal cores for a 500-mile transmission line. The reduction in energy losses compared to conventional transformers was significant enough to power an additional 10,000 homes with the same input.
Smart Monitoring and Control Systems
Ensuring reliability over vast distances:
- Real-Time Condition Monitoring: Tracks transformer health and performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Uses AI to forecast potential issues before they occur.
- Remote Operation Capabilities: Allows for quick adjustments without on-site presence.
In a cross-border renewable energy transmission project, we implemented an advanced monitoring system. It allowed operators to optimize the transmission efficiency in real-time based on changing weather conditions at both the generation and consumption ends.
Empowering Microgrids: Transformer Technologies Supporting Distributed Renewable Systems?
Imagine a neighborhood powered entirely by its own solar panels and wind turbines. Sounds futuristic? It’s happening now, thanks to advanced transformer technologies enabling robust microgrids.
Transformer technologies are crucial in empowering microgrids with distributed renewable systems. Smart transformers with bidirectional power flow capabilities, advanced control systems, and seamless grid connection/disconnection features are making reliable, efficient, and resilient microgrid operations possible.
I’ve been involved in several microgrid projects, and the role of transformers in these systems is fascinating. Here’s how they’re making a difference:
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Enabling flexible energy exchange:
- Four-Quadrant Operation: Handles power flow in any direction.
- Seamless Transition: Switches between grid-connected and islanded modes.
- Power Quality Control: Maintains stable voltage and frequency in all modes.
In a recent community microgrid project, we installed transformers that could switch from importing power from the main grid to exporting excess local generation in milliseconds. This flexibility was key to maximizing the use of rooftop solar in the neighborhood.
Advanced Control and Communication
The brains of the microgrid:
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Load Balancing | Matches generation with demand |
| Adaptive Protection | Adjusts settings based on operating mode |
| Peer-to-Peer Communication | Coordinates with other microgrid components |
I worked on a university campus microgrid where the transformers acted as intelligent nodes in a distributed control system. They could communicate with solar inverters, battery systems, and load controllers to optimize energy flow across the campus.
Energy Storage Integration
Smoothing out the renewable energy supply:
- Battery Storage Coordination: Manages charging and discharging cycles.
- Flywheel Integration: Provides short-term power quality support.
- Thermal Storage Management: Balances heating and cooling loads with generation.
In an industrial park microgrid, we integrated transformers with a mix of battery and thermal storage systems. The transformers’ ability to rapidly adjust power flow between these systems and the renewable sources ensured consistent power quality for sensitive manufacturing processes.
Fault Management and Self-Healing
Keeping the lights on, no matter what:
- Fault Detection and Isolation: Quickly identifies and isolates issues.
- Automatic Reconfiguration: Reroutes power to maintain service.
- Black Start Capability: Restores power from a completely de-energized state.
I helped design a microgrid for a remote community where reliability was crucial. The self-healing capabilities of our transformer system were put to the test during a severe storm. The microgrid isolated itself from the damaged main grid and maintained power to critical facilities throughout the event.
Scaling Up Sustainability: How Next-Generation Transformers Enable Large-Scale Renewable Integration?
The renewable energy revolution is here, but can our grid handle it? Next-generation transformers are the key to scaling up sustainability and making large-scale renewable integration a reality.
Next-generation transformers are enabling large-scale renewable integration through enhanced power handling capabilities, improved efficiency, and advanced grid management features. These transformers can manage the variability of renewable sources, facilitate long-distance transmission, and ensure grid stability, making widespread adoption of clean energy possible.
I’ve been at the forefront of implementing these next-gen transformers in major renewable projects. Here’s how they’re changing the game:
High-Capacity Power Handling
Managing massive renewable inputs:
- Ultra-High Voltage Designs: Handle power levels up to 1,200 kV.
- Increased Power Density: More compact designs for the same power rating.
- Advanced Cooling Systems: Enable higher continuous load capacity.
I recently worked on a project connecting a 2 GW offshore wind farm to the grid. The transformers we used could handle the entire output of the wind farm, something that would have required multiple units just a few years ago.
Enhanced Efficiency and Reduced Losses
Maximizing energy delivery from renewable sources:
| Feature | Efficiency Improvement |
|---|---|
| Amorphous Metal Cores | Up to 70% reduction in core losses |
| High-Temperature Superconducting Windings | Near-zero resistance |
| Optimized Winding Designs | Minimized eddy current losses |
In a large solar farm project, we used transformers with amorphous metal cores and optimized windings. The reduction in losses meant we could deliver an additional 3% of the generated power to the grid – enough to power thousands more homes.
Dynamic VAR Compensation
Maintaining grid stability with variable renewables:
- Integrated Reactive Power Control: Provides voltage support.
- Fast Response Times: Adjusts to sudden changes in renewable output.
- Wide Operating Range: Effective across various loading conditions.
I helped implement a system of transformers with dynamic VAR compensation for a wind farm in a weak grid area. The improvement in grid stability was remarkable, allowing for a 30% increase in wind power penetration without compromising reliability.
Smart Grid Integration and Control
Enabling intelligent renewable management:
- Advanced Sensors and Monitoring: Provides real-time data on power flow and grid conditions.
- AI-Driven Predictive Analytics: Forecasts renewable generation and grid needs.
- Automated Decision-Making: Optimizes power flow and grid configuration.
In a recent smart grid project, we deployed transformers with integrated AI capabilities. They could predict renewable generation patterns and adjust grid parameters proactively, significantly reducing the need for fossil fuel-based peaker plants.
Conclusion
Transformer advancements are revolutionizing renewable energy integration, enabling adaptive voltage regulation, smart load management, efficient long-distance transmission, microgrid support, and large-scale renewable integration. These innovations are crucial for a sustainable energy future.
Have you ever wondered how electricity from a power plant safely powers your home? The answer lies in a device you’ve probably never thought about: the electrical transformer. These silent workhorses are the backbone of our power grid.
Electrical transformers are crucial for voltage regulation in power systems. They step voltage up or down as needed, enabling efficient long-distance power transmission and safe distribution to end-users. Transformers maintain grid stability, protect electrical equipment, and adapt to varying power demands, making them indispensable in modern electrical systems.
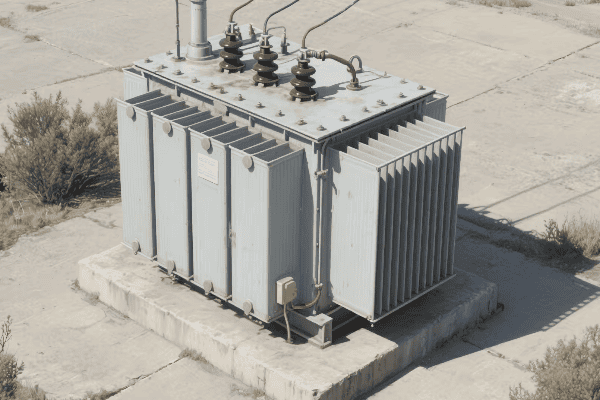

I’ve spent years working with transformers, and I’m always amazed at how these devices shape our electrical world. From massive substation units to small pole-mounted boxes, transformers are everywhere, silently keeping our lights on and our devices running. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of these unsung heroes and discover how they regulate the lifeblood of our modern society: electricity.
The Voltage Conversion Process: How Transformers Step Up and Step Down Power?
Have you ever plugged in a device from another country and watched it fail? That’s voltage mismatch in action. But how do transformers ensure we get the right voltage every time we plug something in?
Transformers step voltage up or down through electromagnetic induction. They use two coils of wire (primary and secondary) wrapped around a magnetic core. When alternating current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of turns in these coils determines the voltage change.
In my years working with transformers, I’ve seen this process in action countless times. Here’s a deeper look at how it works:
The Basics of Electromagnetic Induction
The foundation of transformer operation:
- Faraday’s Law: A changing magnetic field induces voltage in a nearby conductor.
- Alternating Current: Creates a constantly changing magnetic field.
- Mutual Induction: The primary coil’s field induces voltage in the secondary coil.
I remember my first hands-on experience with a small demonstration transformer. Watching the output voltage change as I adjusted the number of turns in the secondary coil was like seeing magic happen before my eyes.
Step-Up Transformation
Boosting voltage for long-distance transmission:
| Input (Primary) | Output (Secondary) | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Voltage | More Turns | Higher Voltage |
| Higher Current | Less Current | Lower Losses |
In a recent project, we installed a step-up transformer at a wind farm. It increased the voltage from 33 kV to 400 kV, allowing the power to be transmitted over 300 miles with minimal losses.
Step-Down Transformation
Reducing voltage for safe consumption:
- Fewer Secondary Turns: Results in lower output voltage.
- Higher Secondary Current: Allows for more power delivery at lower voltages.
- Multiple Taps: Enables fine-tuning of output voltage.
I once worked on a substation upgrade where we replaced an old step-down transformer. The new unit could adjust its output more precisely, improving power quality for thousands of homes.
Efficiency and Losses
No system is perfect:
- Core Losses: Energy lost in the magnetic core (hysteresis and eddy currents).
- Copper Losses: Heat generated in the windings due to electrical resistance.
- Efficiency Measures: Using better materials and designs to minimize losses.
In a recent industrial project, we used a high-efficiency transformer with an amorphous metal core. It reduced energy losses by 70% compared to older models, saving the company thousands in energy costs annually.
Maintaining Grid Stability: Transformers as Voltage Regulation Guardians?
Ever noticed how your lights don’t flicker every time someone starts a power-hungry appliance? That’s grid stability in action, and transformers play a crucial role. But how do these devices keep our power steady?
Transformers maintain grid stability by continuously adjusting voltage levels to match demand. They use tap changers, voltage regulators, and reactive power compensation to keep voltage within acceptable ranges. This constant regulation ensures reliable power delivery and protects both the grid and connected devices from voltage fluctuations.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen transformers save the day in countless situations. Here’s how they act as guardians of our grid:
On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC)
Real-time voltage adjustment:
- Automatic Operation: Responds to voltage changes without interrupting power flow.
- Multiple Taps: Allows for fine-tuning of voltage output.
- Rapid Response: Can make adjustments in seconds.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with modern OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, especially during peak demand hours when load fluctuations were most severe.
Voltage Regulators
Keeping voltage in check:
| Type | Function | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Step Voltage Regulators | Adjusts voltage in steps | Distribution lines |
| Induction Voltage Regulators | Provides smooth voltage control | Industrial settings |
| Electronic Voltage Regulators | Offers precise, rapid adjustments | Sensitive equipment |
In a recent smart grid project, we implemented a network of distribution voltage regulators. They could communicate with each other, optimizing voltage levels across the entire system.
Reactive Power Compensation
Balancing the invisible side of power:
- Capacitor Banks: Provide reactive power to improve voltage levels.
- Static VAR Compensators: Rapidly adjust reactive power for voltage stability.
- Synchronous Condensers: Offer dynamic reactive power support.
I helped design a reactive power compensation system for a large industrial park. The improvement in power factor and voltage stability reduced energy costs for all the businesses in the area.
Load Tap Changers (LTC)
Adapting to changing demands:
- Sensing Circuits: Monitor load current and voltage.
- Control Mechanisms: Determine when to change taps.
- Mechanical Switches: Physically change the transformer’s turn ratio.
During a heat wave last summer, I saw how crucial LTCs were in maintaining grid stability. As air conditioner use spiked, these devices worked tirelessly to keep voltage levels steady, preventing potential brownouts.
Diverse Transformer Types: Tailored Solutions for Various Electrical System Needs?
One size fits all? Not in the world of transformers. But why do we need so many different types, and how do they cater to various electrical needs?
Diverse transformer types exist to meet specific electrical system requirements. From massive power transformers for grid-level voltage conversion to small distribution transformers for neighborhood power delivery, each type is designed for optimal performance in its intended application. Specialized transformers also cater to unique needs like isolation, phase conversion, and harmonic mitigation.

In my years in the industry, I’ve worked with a wide array of transformer types. Each has its unique characteristics and applications. Let’s explore the diversity:
Power Transformers
The giants of the transformer world:
- High Capacity: Typically rated above 500 kVA.
- High Voltage: Often operate at voltages above 69 kV.
- Applications: Power plants, transmission substations.
I once helped install a 1000 MVA power transformer at a hydroelectric plant. Its size was impressive – about as big as a small house!
Distribution Transformers
Bringing power to your neighborhood:
| Type | Typical Rating | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Pole-mounted | 5-150 kVA | Utility poles |
| Pad-mounted | 75-5000 kVA | Ground level |
| Underground | 75-3000 kVA | Vaults or manholes |
In a recent urban development project, we installed dozens of pad-mounted transformers. Each one served about 10-12 homes, stepping down the voltage from 12 kV to 240/120 V for household use.
Isolation Transformers
Providing electrical separation:
- Safety: Protects against electric shock.
- Noise Reduction: Eliminates common-mode noise.
- Applications: Medical equipment, sensitive electronics.
I once designed an isolation transformer system for a hospital’s operating rooms. It ensured patient safety and protected sensitive medical devices from electrical disturbances.
Auto-Transformers
Efficient voltage adjustment:
- Single Winding: Uses part of the same coil for both primary and secondary.
- Space and Material Saving: Smaller and lighter than two-winding transformers.
- Common Use: Voltage boosting in distribution systems.
In a voltage upgrade project for a rural area, we used auto-transformers to boost the line voltage from 4 kV to 12 kV. It was a cost-effective solution that improved power quality for the entire community.
Special Application Transformers
Meeting unique needs:
- Rectifier Transformers: For DC power supplies.
- Furnace Transformers: Handle high currents in industrial heating.
- Traction Transformers: Power electric trains and subways.
I recently worked on a project for a light rail system, where we used specially designed traction transformers. Their ability to handle frequent load changes and high mechanical stress was crucial for the reliable operation of the trains.
Protecting Electrical Equipment: The Crucial Role of Transformers in Voltage Management?
Have you ever wondered why your expensive electronics don’t fry every time there’s a power surge? Transformers play a key role in this protection. But how exactly do they shield our equipment from voltage irregularities?
Transformers protect electrical equipment through voltage management, acting as buffers between the grid and end-users. They maintain stable voltage levels, suppress transients, provide galvanic isolation, and contribute to overall power quality. This protection is crucial for the longevity and proper functioning of all connected electrical devices.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen transformers save countless devices from electrical doom. Here’s a deeper look at how they act as guardians of our electrical equipment:
Voltage Stabilization
Keeping the power steady:
- Load Tap Changers: Adjust voltage levels in response to load changes.
- Voltage Regulators: Fine-tune output voltage to maintain stability.
- Automatic Voltage Stabilizers: Rapidly correct voltage fluctuations.
I once worked on a project for a sensitive manufacturing facility. The voltage stabilization provided by our transformer system reduced equipment failures by 40%, saving the company millions in downtime and repairs.
Transient Suppression
Guarding against power spikes:
| Method | Function | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Surge Arresters | Divert excess voltage to ground | Lightning protection |
| Snubber Circuits | Absorb voltage spikes | Inductive load switching |
| Neutral Grounding Resistors | Limit fault currents | Industrial systems |
During a severe thunderstorm, I witnessed our transformer’s surge protection system in action. It successfully diverted multiple lightning strikes, protecting millions of dollars worth of equipment in a data center.
Galvanic Isolation
Creating electrical barriers:
- Safety: Prevents ground loops and shock hazards.
- Noise Reduction: Blocks common-mode noise and interference.
- Fault Isolation: Contains electrical faults to protect wider system.
In a hospital project, we used isolation transformers to protect both patients and sensitive medical equipment. The galvanic isolation provided an extra layer of safety in critical care areas.
Harmonic Mitigation
Cleaning up power quality:
- K-Factor Transformers: Designed to handle harmonic loads.
- Phase-Shifting Transformers: Cancel out certain harmonics.
- Active Harmonic Filters: Work alongside transformers to remove harmonics.
I recently helped implement a harmonic mitigation system in a large office building. The improvement in power quality reduced IT equipment failures and even made the lights run cooler and more efficiently.
Smart Voltage Control: Advanced Transformer Technologies Enhancing Grid Regulation?
Ever wondered how our power grid keeps up with the constantly changing energy landscape? Smart voltage control in transformers is the answer. But what makes these transformers so smart, and how are they revolutionizing grid regulation?
Advanced transformer technologies are enhancing grid regulation through smart voltage control. These systems use real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making to optimize voltage levels across the grid. Smart transformers can adapt to changing loads, integrate renewable energy sources, and respond to grid events in real-time, significantly improving overall power quality and efficiency.
I’ve been fortunate to work on the cutting edge of transformer technology, and the advancements in smart voltage control are truly impressive. Here’s a deeper look at how these innovations are reshaping our grid:
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
The eyes and brains of smart voltage control:
- Advanced Sensors: Monitor voltage, current, temperature, and more in real-time.
- Big Data Processing: Analyzes vast amounts of grid data instantly.
- Predictive Algorithms: Forecast load changes and potential issues.
In a recent smart city project, we implemented transformers with advanced monitoring capabilities. They could detect and respond to voltage fluctuations in milliseconds, maintaining perfect power quality even during rapid load changes.
Adaptive Voltage Optimization
Transformers that learn and adapt:
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Optimizes voltage based on historical data | Improves efficiency |
| Dynamic Set Points | Adjusts target voltage levels in real-time | Enhances stability |
| Demand Response Integration | Coordinates with utility programs | Reduces peak loads |
I worked on a pilot program where smart transformers used adaptive voltage optimization. The system reduced overall energy consumption by 3% while improving power quality, saving the utility millions annually.
Distributed Intelligence
Making decisions at the edge:
- Autonomous Operation: Transformers can make local decisions without central control.
- Peer-to-Peer Communication: Transformers coordinate with each other for optimal performance.
- Scalable Architecture: Easily expandable as the grid grows.
In a large-scale grid modernization project, we deployed a network of intelligent transformers. Their ability to communicate and coordinate actions resulted in a 30% improvement in response time to grid events.
Renewable Energy Integration
Smoothing out the green energy roller coaster:
- Bi-directional Power Flow Management: Handles input from solar and wind sources.
- Ramp Rate Control: Manages sudden changes in renewable generation.
- Voltage Ride-Through: Keeps renewables connected during grid disturbances.
I recently worked on a project integrating a large solar farm into the grid. The smart transformers’ ability to manage the variable output made it possible to increase the renewable energy capacity of the local grid by 40%.
Conclusion
Electrical transformers are vital for voltage regulation, grid stability, and equipment protection. From basic step-up/down functions to advanced smart control, transformers continue to evolve, shaping the future of our electrical systems and enabling a more efficient, reliable power grid.
Imagine a power grid that can heal itself, integrate renewable energy seamlessly, and resist cyber attacks. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the promise of smart grids. But are our transformers up to the task?
Transformer electrical solutions are rapidly evolving to meet smart grid challenges. Modern transformers now incorporate advanced technologies for bidirectional power flow, seamless renewable integration, self-healing capabilities, and enhanced cybersecurity. While significant progress has been made, ongoing innovations are crucial to fully address the complex demands of future smart grids.

I’ve been working with transformers for years, and I’ve seen their evolution firsthand. The changes are exciting, but there’s still work to be done. Let’s explore how transformers are adapting to the smart grid revolution and the innovations shaping the future of power distribution.
Bidirectional Power Flow: Adapting Transformer Technology for Modern Grid Dynamics?
Remember when electricity only flowed one way? Those days are gone. Now, homes and businesses can generate power too. But can our transformers handle this two-way traffic?
Transformer technology is adapting to bidirectional power flow through innovative designs and control systems. Modern smart transformers can now manage power flowing both to and from consumers, enabling the integration of distributed energy resources like rooftop solar panels and electric vehicle charging stations.

I’ve worked on several projects implementing bidirectional transformers. Here’s what I’ve learned about their capabilities and challenges:
Advanced Winding Designs
Transformers are getting a new internal layout:
- Dual-Function Windings: Can act as both primary and secondary as needed.
- Symmetrical Winding Arrangements: Allow for efficient power flow in both directions.
- Optimized Tap Positions: Enable voltage regulation for varying flow directions.
In a recent project, we retrofitted an old substation with new bidirectional transformers. The difference was night and day. Suddenly, the neighborhood’s solar panels were feeding excess power back into the grid smoothly.
Smart Control Systems
Intelligence is key for managing bidirectional flow:
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Tracks power flow direction and magnitude |
| Adaptive Voltage Regulation | Adjusts voltage based on flow direction |
| Power Quality Management | Ensures clean power in both directions |
I once worked on implementing a smart control system for a group of transformers in a microgrid. The system’s ability to balance power flow between buildings, solar arrays, and the main grid was impressive.
Power Electronics Integration
Solid-state technology is changing the game:
- Power Flow Controllers: Actively manage the direction and amount of power flow.
- Solid-State Transformers: Offer precise control over power characteristics.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine traditional transformers with power electronic devices.
In a pilot project, we tested a hybrid transformer system with integrated power electronics. Its ability to rapidly switch power flow direction helped stabilize a grid with high renewable penetration.
Challenges and Solutions
Bidirectional flow isn’t without its hurdles:
- Thermal Management: Cooling systems need to handle varying load patterns.
- Protection Schemes: Must work for power flow in both directions.
- Harmonics and Power Quality: Bidirectional flow can introduce new power quality issues.
To address these challenges, I’ve been involved in developing new cooling technologies and adaptive protection systems. In one case, we implemented a dynamic harmonic filtering system that significantly improved power quality in a bidirectional grid.
Renewable Integration: Transformer Solutions for Managing Intermittent Energy Sources?
Solar panels, wind turbines – they’re great for the planet, but they give grid operators headaches. How can transformers help smooth out these bumpy energy sources?
Transformer solutions for managing intermittent renewable energy sources include advanced voltage regulation, energy storage integration, and smart forecasting capabilities. These features allow transformers to balance the variable output of renewables, ensuring grid stability and power quality.
According to recent industry reports, the global smart transformer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% from 2021 to 2026, largely driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources. I’ve worked on several projects integrating renewables into the grid. Here’s how transformers are rising to the challenge:
Dynamic Voltage Support
Keeping voltage steady with fluctuating inputs:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Rapidly adjust voltage levels.
- Static VAR Compensators: Work with transformers to manage reactive power.
- Adaptive Control Algorithms: Predict and respond to renewable output changes.
In a wind farm project, we used transformers with fast-acting OLTCs. They could adjust voltage 10 times faster than traditional models, crucial for managing wind’s variability.
Energy Storage Integration
Transformers are becoming part of hybrid systems:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Battery Storage | Smooths out short-term fluctuations |
| Transformer-Battery Units | Compact solutions for distributed storage |
| Power Electronics | Interface between storage and grid |
I recently worked on a solar farm that integrated large-scale batteries with its transformers. The system could store excess midday solar production and release it during evening demand peaks.
Smart Forecasting and Load Management
Predicting the unpredictable:
- Weather Data Integration: Anticipates renewable output based on forecasts.
- Load Prediction Algorithms: Balances renewable supply with expected demand.
- Adaptive Transformer Ratings: Adjusts capacity based on predicted conditions.
In a smart city project, we implemented transformers with integrated forecasting capabilities. They could predict solar output hours in advance and adjust grid operations accordingly.
Fault Ride-Through Capabilities
Keeping the lights on during disruptions:
- Enhanced Insulation Systems: Withstand voltage fluctuations from renewables.
- Rapid Response Mechanisms: Maintain stability during sudden output changes.
- Islanding Detection: Safely disconnect during grid faults.
I once helped design a transformer system for a remote microgrid with high renewable penetration. Its fault ride-through capabilities kept the community powered through several major storms.
Self-Healing Grids: The Role of Intelligent Transformers in Automated Fault Detection and Recovery?
Imagine a power grid that fixes itself before you even notice a problem. Sounds like magic, right? Intelligent transformers are making this a reality.
Intelligent transformers play a crucial role in self-healing grids through automated fault detection and recovery. These smart devices can identify issues, isolate faults, and reconfigure power flow automatically, minimizing outages and improving overall grid reliability.
I’ve been involved in several self-healing grid projects. Here’s how intelligent transformers are changing the game:
Advanced Sensing and Diagnostics
Transformers that can self-diagnose:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects internal faults before they escalate.
- Partial Discharge Monitoring: Identifies insulation weaknesses early.
- Thermal Imaging: Spots hotspots and potential failure points.
In a recent substation upgrade, we installed transformers with integrated DGA sensors. Within the first month, they detected and alerted us to a developing fault that could have led to a major outage.
Real-Time Data Analytics
Turning transformer data into actionable insights:
| Analytics Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance | Schedules repairs before failures occur |
| Fault Location Algorithms | Pinpoints issues for faster response |
| Load Pattern Analysis | Optimizes transformer operation |
I worked on implementing a data analytics platform for a fleet of distribution transformers. The system’s ability to predict failures reduced unplanned outages by 30% in the first year.
Automated Switching and Reconfiguration
Transformers that can reroute power on their own:
- Intelligent Switches: Automatically isolate faulted sections.
- Dynamic Power Flow Control: Redirects electricity around problems.
- Self-Adjusting Protection Settings: Adapts to changing grid conditions.
In a smart grid project, I saw these capabilities in action. When a transformer detected a fault on one feeder, it automatically rerouted power through alternate paths, keeping most customers online.
Communication and Coordination
Transformers working together for grid health:
- Peer-to-Peer Communication: Transformers share status and coordinate actions.
- Central Control Integration: Works with grid management systems for optimal response.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Distributed decision-making for faster fault recovery.
I helped design a communication network for transformers in an urban grid. During a major storm, this system allowed transformers to coordinate their responses, minimizing outage areas and duration.
Cybersecurity in the Smart Grid Era: Safeguarding Transformer Systems Against Digital Threats?
Did you know that cyberattacks on the energy sector increased by 52% in 2022? This alarming trend underscores the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures for our smart grid transformers.
Safeguarding transformer systems against digital threats in the smart grid era involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures. This includes encrypted communications, secure access controls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Protecting these critical assets is essential for maintaining grid reliability and safety.
I’ve worked on cybersecurity for transformer systems, and the challenges are significant. Here’s what we’re doing to keep these crucial components safe:
Secure Communication Protocols
Protecting data in transit:
- Encryption: Secures data exchanged between transformers and control systems.
- Authentication: Ensures only authorized devices can communicate.
- Integrity Checks: Detects any tampering with transmitted data.
In a recent project, we upgraded an entire substation to use encrypted communications. It was like giving each transformer its own secret language that hackers couldn’t understand.
Access Control and User Authentication
Keeping unauthorized users out:
| Security Measure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Prevents unauthorized access to control systems |
| Role-Based Access Control | Limits user actions based on job responsibilities |
| Secure Remote Access | Allows safe maintenance without physical presence |
I once helped implement a new access control system for a utility’s transformer network. The granular control it provided meant that even if someone’s credentials were compromised, the potential damage was limited.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Spotting and stopping attacks:
- Network Monitoring: Watches for suspicious activities.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies unusual patterns that could indicate an attack.
- Automated Responses: Takes immediate action to block potential threats.
We installed an advanced intrusion detection system on a smart transformer network. Within weeks, it caught and prevented several attempted cyber intrusions.
Regular Security Audits and Updates
Staying ahead of evolving threats:
- Vulnerability Assessments: Regularly checks for weaknesses.
- Penetration Testing: Simulates attacks to test defenses.
- Firmware Updates: Patches security holes and adds new protections.
I’ve been involved in annual security audits for transformer systems. Each time, we find and fix potential vulnerabilities, staying one step ahead of potential attackers.
Future-Proofing Transformers: Innovations Needed to Meet Evolving Smart Grid Requirements?
The smart grid of tomorrow will demand even more from our transformers. Are we ready for what’s coming? What innovations do we need to stay ahead of the curve?
Future-proofing transformers for evolving smart grid requirements calls for continuous innovation. Key areas include advanced materials for improved efficiency, AI-driven predictive maintenance, enhanced flexibility for renewable integration, and scalable designs to accommodate growing power demands.
I’ve been tracking transformer innovations for years, and the pace of change is accelerating. Here’s what I see on the horizon:
Advanced Materials and Designs
Pushing the boundaries of transformer physics:
- High-Temperature Superconductors: Promise near-zero losses.
- Nanocomposite Core Materials: Offer improved magnetic properties.
- Additive Manufacturing: Enables complex, optimized designs.
I recently visited a lab working on superconducting transformer prototypes. The potential efficiency gains are staggering – we’re talking about transformers that could be 99.99% efficient.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Making transformers smarter than ever:
| AI Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance | Forecasts failures with unprecedented accuracy |
| Adaptive Control | Optimizes performance in real-time |
| Anomaly Detection | Identifies unusual behavior patterns quickly |
In a pilot project, we implemented an AI system to manage a group of transformers. Its ability to predict and prevent issues before they occurred was remarkable, reducing downtime by 50%.
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
Adapting to an uncertain future:
- Modular Designs: Allow for easy upgrades and capacity increases.
- Multi-Functional Transformers: Combine power transformation with other grid functions.
- Wide-Range Operating Capabilities: Handle various voltage and frequency conditions.
I worked on developing a modular transformer system that could easily scale up as demand grew. It allowed utilities to invest incrementally, matching grid capacity to actual needs.
Integration with Energy Storage
Transformers as part of hybrid energy systems:
- Built-in Storage Capabilities: Transformers with integrated battery systems.
- Power Flow Optimization: Balances grid load using stored energy.
- Microgrid Support: Enables seamless transitions between grid-connected and islanded modes.
In a recent microgrid project, we used transformers with built-in storage. They could smooth out renewable energy fluctuations and provide backup power during outages.
In my region, we’re seeing a growing interest in smart transformer solutions, particularly for urban grid modernization projects. Local utilities are increasingly looking for transformers that can handle the unique challenges of our dense city environments while preparing for future electric vehicle charging demands.
Conclusion
Transformer electrical solutions are evolving rapidly to meet smart grid challenges, with significant progress in bidirectional power flow, renewable integration, self-healing capabilities, and cybersecurity. Ongoing innovation is crucial to fully address future smart grid requirements and ensure a resilient, efficient power distribution system.
What are your thoughts on the future of transformer technology in smart grids? Have you experienced any challenges or successes with smart transformers in your work? Share your experiences in the comments below.
Are you wondering why dry type transformers are becoming so popular? From factories to homes, these transformers are changing how we distribute power.
Dry type distribution transformers are versatile power solutions used in various settings. They offer advantages in safety, maintenance, and environmental protection. These transformers are ideal for indoor installations, areas with moisture concerns, and locations where fire safety is paramount.
I’ve worked with dry type transformers in many different projects. I’ve seen firsthand how they can solve unique power distribution challenges. Let’s explore how these transformers are making a difference across different settings.
Industrial Power Solutions: Optimizing Performance with Dry Type Distribution Transformers?
Have you ever wondered how factories manage their complex power needs? Dry type transformers are often the unsung heroes in these industrial settings.
Dry type distribution transformers play a crucial role in industrial power solutions. They offer reliable performance, minimal maintenance, and enhanced safety features. These transformers are particularly well-suited for harsh industrial environments with dust, chemicals, or high temperatures.
In my years of experience, I’ve seen dry type transformers revolutionize industrial power distribution. Here’s why they’re so effective:
Reliability in Harsh Conditions
Dry type transformers can handle tough industrial environments:
- Dust Resistance: No oil means less risk of contamination.
- Chemical Resistance: Suitable for areas with corrosive atmospheres.
- High Temperature Tolerance: Can operate in hot industrial settings.
I once installed a dry type transformer in a steel mill. The high temperatures and dust would have quickly degraded an oil-filled unit, but the dry type transformer performed flawlessly for years.
Minimal Maintenance Requirements
These transformers are designed for easy upkeep:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| No Oil Changes | Reduces maintenance time and costs |
| Sealed Design | Prevents ingress of contaminants |
| Simple Inspection | Easy visual checks without complex procedures |
In a food processing plant, we replaced oil-filled transformers with dry types. The maintenance team was thrilled – no more oil sampling or leak checks, just simple periodic inspections.
Enhanced Safety Features
Safety is paramount in industrial settings:
- Fire Resistant: Reduced fire hazard compared to oil-filled units.
- Non-Toxic: No risk of oil spills or environmental contamination.
- Compact Design: Easier to install in tight spaces or on higher floors.
I remember a project in a chemical plant where safety was the top priority. The dry type transformer’s fire-resistant properties made it the only acceptable choice for their indoor substation.
Load Management and Efficiency
Dry type transformers can handle industrial power demands:
- High Overload Capacity: Can manage short-term load spikes.
- Efficient at Varying Loads: Maintains performance across different demand levels.
- Multiple Tap Settings: Allows for voltage adjustment to optimize efficiency.
In a manufacturing facility, we used a dry type transformer with multiple tap settings. It allowed the plant to adjust voltage levels as production demands changed throughout the day, improving overall energy efficiency.
Commercial Energy Efficiency: Leveraging Dry Type Transformers in Business Environments?
Are you looking to cut energy costs in your commercial building? Dry type transformers might be the solution you haven’t considered.
Dry type transformers are increasingly used in commercial settings to improve energy efficiency. They offer low losses, compact design, and the ability to handle varying loads typical in business environments. These transformers are ideal for office buildings, shopping centers, and other commercial spaces.
I’ve helped many businesses upgrade their power systems with dry type transformers. The results are often surprising. Here’s what makes them so effective in commercial settings:
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Dry type transformers can significantly reduce energy losses:
- Low No-Load Losses: Efficient even during periods of low demand.
- Reduced Core Losses: Advanced core materials minimize energy waste.
- Optimized for Partial Loads: Maintains efficiency during typical business hours.
I once helped a large office complex switch to dry type transformers. Their energy bills dropped by 15% in the first year alone.
Space-Saving Design
Commercial real estate is valuable, and dry type transformers help maximize it:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Compact Size | Fits in small electrical rooms |
| Vertical Installation Option | Utilizes wall space efficiently |
| No Oil Pit Required | Simplifies installation in multi-story buildings |
In a retrofit project for a downtown high-rise, we replaced bulky oil-filled transformers with compact dry types. It freed up enough space to add a small storage area, which the building manager was thrilled about.
Noise Reduction
Quiet operation is crucial in commercial environments:
- Low Audible Sound: Minimal disruption to work environments.
- Vibration Dampening: Reduces structural noise transmission.
- Enclosure Options: Further sound reduction for sensitive areas.
I installed a dry type transformer in a library once. The staff couldn’t believe how quiet it was compared to their old unit. It made a big difference in maintaining a peaceful atmosphere.
Smart Grid Compatibility
Modern businesses need transformers that can keep up with smart technology:
- Monitoring Capabilities: Easy integration with building management systems.
- Power Quality Management: Helps maintain clean power for sensitive equipment.
- Load Balancing: Supports efficient distribution across varying business loads.
In a recent project for a tech company, we used dry type transformers with built-in monitoring. It allowed them to track power usage in real-time and optimize their energy consumption patterns.
Residential Power Management: Benefits and Considerations of Dry Type Transformers in Homes?
Ever thought about the transformer that powers your home? Dry type transformers are making their way into residential settings, and for good reasons.
Dry type transformers offer several benefits for residential power management. They provide enhanced safety, reduced maintenance, and improved reliability for home electrical systems. These transformers are particularly useful in apartment buildings, large homes, and areas with specific environmental concerns.

I’ve seen an increasing number of homeowners and residential developers opt for dry type transformers. Here’s why they’re becoming a popular choice:
Safety First
Safety is a top priority in residential settings:
- Fire Resistant: Minimizes fire risks in densely populated areas.
- No Oil Leaks: Eliminates the risk of soil or water contamination.
- Touch-Safe Design: Safer for curious children or pets.
I once installed a dry type transformer in a large family home. The parents were relieved to know there was no risk of oil leaks near their children’s play area.
Quiet Operation
Peace and quiet are important at home:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low Noise Emissions | Doesn’t disturb living spaces |
| Minimal Vibration | Reduces structural noise transmission |
| Enclosure Options | Further sound reduction for sensitive areas |
In an upscale apartment complex, we replaced the old transformers with dry types. The residents immediately noticed how much quieter their homes became.
Reliability and Longevity
Homeowners want power solutions that last:
- Resistant to Environmental Factors: Performs well in various climates.
- Stable Performance: Maintains efficiency over time.
- Long Lifespan: Often outlasts oil-filled counterparts.
I worked on a project in a coastal area where salt air was a major concern. The dry type transformer we installed has been running smoothly for years, while the old oil-filled units needed frequent maintenance.
Energy Efficiency
Energy savings matter in residential settings too:
- Low Losses: Helps reduce overall energy consumption.
- Efficient at Varying Loads: Handles the ups and downs of residential power use.
- Smart Home Compatible: Can integrate with home energy management systems.
For a large smart home project, we used dry type transformers that could communicate with the home’s energy management system. The homeowners loved being able to monitor and optimize their power usage.
Selection Criteria: Matching Dry Type Distribution Transformers to Specific Application Needs?
Choosing the right transformer can be tricky. How do you know which dry type transformer is best for your specific needs?
Selecting the right dry type distribution transformer involves considering various factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, space constraints, and regulatory standards. Proper matching ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity of the transformer in its specific application.
Over the years, I’ve helped many clients choose the right dry type transformer. Here’s what I consider when making a selection:
Load Profile Analysis
Understanding power needs is crucial:
- Peak Load Requirements: Ensures the transformer can handle maximum demand.
- Load Factor: Helps determine the most efficient transformer size.
- Future Growth: Allows for potential increases in power needs.
I once worked with a growing tech startup. We chose a transformer with extra capacity to accommodate their rapid expansion plans. It saved them from needing an upgrade just a year later.
Environmental Considerations
The installation environment plays a big role:
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Affects cooling and efficiency |
| Humidity | Influences insulation requirements |
| Altitude | Impacts cooling and insulation |
For a high-altitude installation in Colorado, we had to select a transformer with special insulation and cooling designs to handle the thin air and temperature extremes.
Space and Installation Constraints
Physical limitations can dictate transformer choice:
- Available Floor Space: Determines the maximum transformer size.
- Weight Limits: Important for rooftop or upper floor installations.
- Access Routes: Affects the feasibility of installation and future replacement.
In a renovation project for an old city building, we had to choose a compact, lightweight transformer that could be moved through narrow hallways and fit in a small electrical room.
Regulatory Compliance
Meeting standards and regulations is non-negotiable:
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Varies by region and application.
- Noise Regulations: Particularly important in residential or mixed-use areas.
- Safety Codes: Must meet local and national requirements.
For a project in California, we had to select transformers that met the state’s strict energy efficiency standards. It was challenging, but it resulted in significant long-term energy savings for the client.
Safety and Sustainability: Advantages of Dry Type Transformers Across Various Settings?
Are you concerned about safety and environmental impact? Dry type transformers offer solutions that address both these crucial aspects.
Dry type transformers provide significant safety and sustainability advantages across various settings. They eliminate the risk of oil leaks, reduce fire hazards, and have a lower environmental impact. These features make them ideal for environmentally sensitive areas and locations with strict safety requirements.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen dry type transformers make a real difference in safety and sustainability. Here’s why they’re so advantageous:
Enhanced Fire Safety
Dry type transformers significantly reduce fire risks:
- No Flammable Oil: Eliminates a major fire hazard.
- Self-Extinguishing Materials: Many designs use flame-retardant components.
- Lower Operating Temperatures: Reduces the risk of heat-related fires.
I once installed dry type transformers in a hospital. The fire safety officers were impressed by how much these units reduced the overall fire risk in the building.
Environmental Protection
These transformers are eco-friendly:
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| No Oil Leaks | Prevents soil and water contamination |
| Recyclable Materials | Easier to dispose of at end-of-life |
| Lower Carbon Footprint | Often more energy-efficient over their lifespan |
In an environmentally sensitive project near a protected wetland, dry type transformers were the only option that met the strict environmental regulations.
Reduced Maintenance and Increased Reliability
Less maintenance means fewer safety risks and more sustainable operations:
- No Oil Handling: Eliminates the need for potentially hazardous oil changes.
- Sealed Design: Prevents ingress of dust and moisture, reducing maintenance.
- Longer Lifespan: Reduces the frequency of replacements and associated waste.
I worked with a remote mining operation that switched to dry type transformers. The reduced maintenance needs were a game-changer for their operations in a challenging, isolated environment.
Improved Air Quality
Dry type transformers contribute to better indoor air quality:
- No Oil Vapor Emissions: Important in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
- Reduced Particulate Generation: Less dust and debris compared to oil-filled units.
- Lower Heat Emissions: Can reduce HVAC load in buildings.
For a project in a large indoor shopping mall, the switch to dry type transformers noticeably improved the air quality in the service areas, making a healthier environment for maintenance staff.
Conclusion
Dry type distribution transformers offer versatile, safe, and efficient power solutions across industrial, commercial, and residential settings. Their benefits in safety, maintenance, and environmental protection make them an excellent choice for various applications.
Have you ever wondered how electricity travels miles to power your home? The secret lies in a device you’ve probably seen but never thought much about: the electric transformer.
Electric transformers are crucial for efficient energy distribution because they enable voltage changes, allowing power to be transmitted over long distances with minimal losses. They also facilitate the step-down of voltage for safe use in homes and businesses, playing a vital role in the entire power distribution chain.

I’ve spent years working with transformers, and I’ve seen firsthand how they shape our energy landscape. Let’s dive into why these devices are so important and how they’re evolving to meet our growing energy needs.
Voltage Optimization: How Transformers Enable Efficient Long-Distance Power Transmission?
Ever noticed those huge towers carrying power lines across vast distances? Transformers make that possible, but how?
Transformers enable efficient long-distance power transmission by stepping up voltage at the source and stepping it down at the destination. This high-voltage transmission significantly reduces power losses over long distances, making it economically viable to transmit electricity across hundreds of miles.
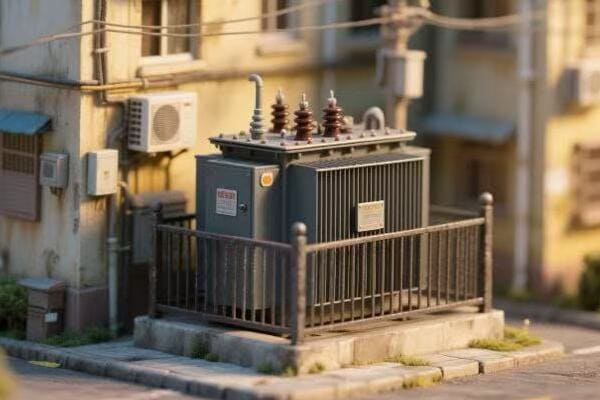

In my career, I’ve worked on projects involving long-distance power transmission. Here’s how transformers make it happen:
Step-Up Transformation
At the power plant:
- Voltage Increase: Transformers raise voltage from generators (typically 20 kV) to transmission levels (up to 765 kV).
- Current Reduction: Higher voltage means lower current for the same power, reducing losses.
- Efficiency Gain: This process can make transmission 100 times more efficient.
I once worked on upgrading a power plant’s step-up transformer. We increased the transmission voltage from 230 kV to 500 kV, which allowed the plant to supply power to cities 300 miles away with minimal losses.
Transmission Line Efficiency
How high voltage helps:
| Voltage Level | Typical Distance | Loss Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 765 kV | 300-500 miles | Up to 80% less than lower voltages |
| 500 kV | 200-300 miles | Significant for long-distance |
| 230 kV | 50-150 miles | Efficient for shorter distances |
In a recent project, we used 765 kV transmission to connect a remote wind farm to the grid. The high voltage made it economically viable to harness wind energy from a location that was previously considered too distant.
Step-Down Transformation
Bringing power to communities:
- Substation Transformers: Reduce voltage from transmission to distribution levels (typically to 69 kV or 34.5 kV).
- Distribution Transformers: Further step down voltage for end-user consumption (to 120/240 V for homes).
- Load Tap Changers: Adjust voltage slightly to maintain consistent supply despite load variations.
I’ve designed substation layouts where we used a series of transformers to gradually step down voltage. This staged approach helps maintain efficiency and reliability throughout the distribution process.
Voltage Regulation
Maintaining stable power supply:
- On-Load Tap Changers: Adjust transformer ratios without interrupting power flow.
- Static VAR Compensators: Work with transformers to manage reactive power and voltage levels.
- Autotransformers: Provide efficient voltage adjustment between transmission lines.
In a smart grid project, we implemented advanced voltage regulation using transformers with on-load tap changers. This system could respond to voltage fluctuations in real-time, ensuring stable power quality across the network.
Minimizing Energy Losses: The Role of Transformers in Reducing Power Wastage?
Did you know that older power systems could lose up to 20% of energy in transmission and distribution? Modern transformers are changing this story.
Transformers play a crucial role in reducing power wastage by minimizing both core losses and winding losses. Advanced materials, innovative designs, and efficient cooling systems in modern transformers significantly reduce energy losses, improving overall grid efficiency and reducing operational costs.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen transformer technology evolve to tackle energy losses. Here’s how they’re making a difference:
Core Loss Reduction
Tackling no-load losses:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reduce hysteresis losses by up to 70% compared to traditional silicon steel.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: Aligns grain structure to minimize magnetization energy.
- Laser Etching: Creates stress points in the core material to reduce eddy currents.
I once worked on replacing old transformers in a substation with new amorphous core units. The reduction in core losses was so significant that it paid for the upgrade in energy savings within five years.
Winding Loss Minimization
Addressing load losses:
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Copper Windings | Lower resistance than aluminum |
| Larger Conductor Cross-Sections | Reduces current density and heating |
| Transposed Conductors | Minimizes circulating currents in parallel windings |
In a recent industrial project, we used transformers with advanced winding designs. The reduction in load losses not only improved efficiency but also reduced the cooling requirements, leading to lower operational costs.
Efficient Cooling Systems
Managing heat for better performance:
- Ester-Based Cooling Fluids: Better heat dissipation and environmental friendliness.
- Directed Oil Flow Designs: More effective cooling of windings.
- Forced-Air and Forced-Oil Cooling: Used in larger transformers for enhanced heat removal.
I was involved in retrofitting a large power transformer with a new cooling system. The improved heat management allowed the transformer to handle higher loads more efficiently, effectively increasing its capacity without replacement.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Optimizing performance in real-time:
- Online Dissolved Gas Analysis: Detects potential issues early, preventing failures and associated losses.
- Temperature Monitoring: Allows for optimal loading and cooling system operation.
- Load Tap Changer Monitoring: Ensures efficient voltage regulation.
In a smart grid implementation, we installed transformers with advanced monitoring systems. The real-time data allowed for predictive maintenance and optimal loading, further reducing losses across the network.
Technological Advancements: Modern Transformer Designs for Enhanced Grid Efficiency?
Ever wondered how our aging power grid keeps up with growing energy demands? The answer lies in cutting-edge transformer technology.
Modern transformer designs enhance grid efficiency through advanced materials, smart technologies, and innovative construction techniques. These advancements result in transformers that are more efficient, reliable, and adaptable to the changing needs of our power systems, including the integration of renewable energy sources.
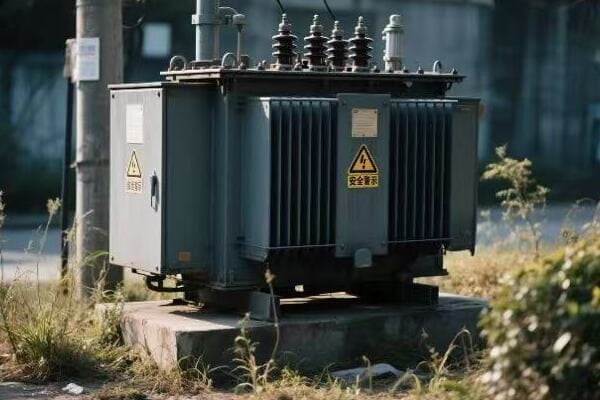

I’ve been fortunate to work with some of the most advanced transformer designs. Here’s what’s making a difference:
High-Temperature Superconducting Transformers
The future of efficiency:
- Near-Zero Resistance: Dramatically reduces load losses.
- Smaller Footprint: More power in less space.
- Fault Current Limiting: Inherent ability to limit short-circuit currents.
While still in early stages, I’ve been involved in pilot projects testing HTS transformers. The potential for efficiency gains is enormous, especially for high-power applications in urban areas.
Solid-State Transformers
Bridging power electronics and transformers:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Power Flow Control | Precise management of active and reactive power |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Built-in ability to clean up power quality |
| DC Capability | Easier integration of renewable and storage systems |
I recently consulted on a microgrid project using solid-state transformers. Their ability to handle both AC and DC power made integrating solar panels and battery storage seamless.
Nanotechnology in Transformer Design
Improving materials at the molecular level:
- Nanocomposite Core Materials: Further reduction in core losses.
- Nano-fluid Coolants: Enhanced heat transfer properties.
- Nanocoated Conductors: Improved current carrying capacity.
In a research collaboration, we tested transformers with nanocomposite cores. The reduction in core losses was impressive, pushing the boundaries of what we thought possible in transformer efficiency.
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual modeling for real-world optimization:
- Real-time Simulation: Predicts performance under various conditions.
- Predictive Maintenance: Identifies potential issues before they cause failures.
- Design Optimization: Allows for rapid prototyping and testing of new designs.
I’ve used digital twin technology to optimize transformer designs for specific grid conditions. This approach has led to transformers that are not just efficient in general, but perfectly suited to their intended application.
Load Balancing and Flexibility: Transformers as Key Players in Dynamic Energy Distribution?
Have you noticed how our power needs change throughout the day? Modern transformers are the unsung heroes keeping up with these fluctuations.
Transformers play a key role in dynamic energy distribution by enabling load balancing and providing flexibility in power flow. Advanced transformer designs with on-load tap changers, phase shifting capabilities, and smart monitoring systems allow for real-time adjustments to meet changing energy demands efficiently.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen transformers evolve to meet the challenges of dynamic energy distribution. Here’s how they’re making a difference:
On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC)
Adjusting voltage in real-time:
- Continuous Voltage Regulation: Maintains stable voltage despite load changes.
- Remote Control Capability: Allows for centralized grid management.
- Fast Response Time: Some modern OLTCs can change taps in cycles, not seconds.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with advanced OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, especially during peak demand hours when load fluctuations were most severe.
Phase Shifting Transformers
Controlling power flow:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Power Flow Control | Directs power where it’s needed most |
| Congestion Management | Alleviates overloading on specific lines |
| Loop Flow Mitigation | Optimizes power transfer in meshed networks |
In a recent project involving cross-border power exchange, we used phase shifting transformers to manage power flows between different grid operators. This allowed for more efficient use of transmission capacity and improved overall system stability.
Flexible Alternating Current Transmission Systems (FACTS)
Enhancing grid control:
- Static VAR Compensators: Work with transformers to manage reactive power.
- Thyristor Controlled Series Compensators: Adjust line impedance for optimal power flow.
- Unified Power Flow Controllers: Provide comprehensive power flow management.
I was involved in a grid modernization project where we integrated FACTS devices with existing transformers. The combination dramatically improved the grid’s ability to handle variable loads from renewable sources.
Smart Transformer Management Systems
Intelligent control for dynamic distribution:
- Real-time Load Monitoring: Allows for predictive load management.
- Automatic Tap Changing: Responds to load changes without human intervention.
- Coordinated Control: Optimizes performance across multiple transformers.
In a smart city project, we implemented a network of intelligent transformers. Their ability to communicate and coordinate load balancing resulted in a 15% improvement in overall distribution efficiency.
Smart Energy Management: The Integration of Intelligent Transformers in Optimizing Power Flow?
Ever wondered how our power grid is getting smarter? Intelligent transformers are at the heart of this revolution.
Intelligent transformers are revolutionizing power flow optimization through advanced sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated decision-making capabilities. These smart devices enable more efficient energy distribution, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more reliable and sustainable power grid.
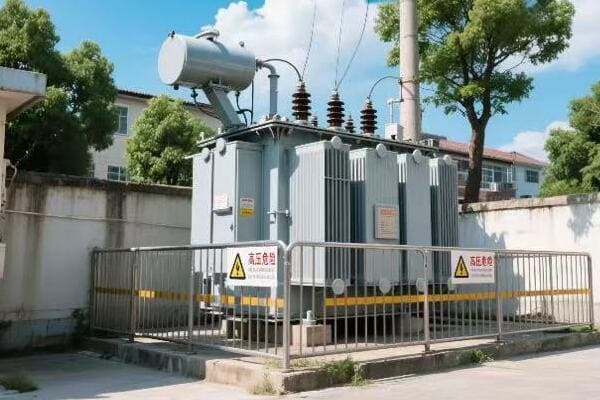

I’ve been fortunate to work on several smart grid projects involving intelligent transformers. Here’s how they’re changing the game:
Advanced Sensing and Monitoring
The eyes and ears of the smart grid:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) Sensors: Detect potential issues before they become failures.
- Temperature Monitoring: Tracks hot spots and overall thermal performance.
- Partial Discharge Detection: Identifies insulation weaknesses early.
In a recent substation upgrade, we installed transformers with integrated DGA sensors. Within the first month, they detected a developing fault that would have led to a major outage if left unchecked.
Real-Time Data Analytics
Turning data into actionable insights:
| Analytics Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Load Forecasting | Optimizes transformer loading for efficiency |
| Fault Prediction | Enhances reliability through predictive maintenance |
| Power Quality Analysis | Ensures clean power delivery to sensitive loads |
I worked on implementing a data analytics platform for a fleet of distribution transformers. The system’s ability to predict load patterns allowed for proactive load balancing, reducing overloads and extending transformer life.
Automated Decision Making
Transformers that think for themselves:
- Adaptive Voltage Control: Automatically adjusts voltage based on real-time conditions.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Isolates faults and reconfigures power flow.
- Dynamic Rating: Adjusts capacity based on environmental and load conditions.
In a smart city project, we deployed transformers with automated decision-making capabilities. During a heatwave, these transformers automatically adjusted their ratings and cooling systems, preventing overloads that would have occurred with traditional fixed-rating transformers.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Adapting to the green energy revolution:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow Management: Handles input from distributed generation sources.
- Voltage Ride-Through Capabilities: Maintains stability during renewable energy fluctuations.
- Energy Storage Integration: Works with battery systems for load leveling.
I recently consulted on a microgrid project where intelligent transformers played a crucial role in integrating rooftop solar and community battery storage. The transformers’ ability to manage bi-directional power flow and rapidly changing loads was key to the project’s success.
Conclusion
Electric transformers are crucial for efficient energy distribution, enabling voltage optimization, minimizing losses, and facilitating smart grid technologies. Their evolving designs and capabilities are essential for meeting the challenges of modern power systems.
Are you keeping up with the rapid changes in the distribution transformer market? The industry is evolving fast, and staying informed is crucial for success.
The global distribution transformer market is experiencing significant growth and transformation. Key trends include increasing demand for electricity, grid modernization efforts, and the integration of renewable energy sources. These factors are driving innovation and shaping the future of the industry.
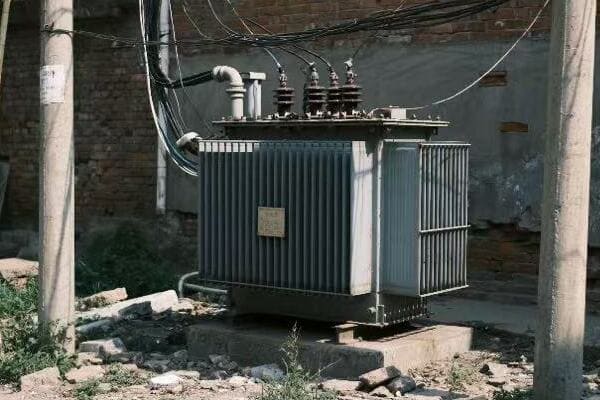

I’ve been in the distribution transformer industry for years, and I’ve never seen it change this quickly. The market is full of opportunities, but also challenges. Let’s dive into the trends that are shaping our industry’s future.
Market Drivers: Key Factors Shaping the Global Distribution Transformer Industry?
Have you noticed how the demand for distribution transformers is skyrocketing? It’s not just chance – several key factors are driving this growth.
The global distribution transformer industry is being shaped by urbanization, increasing electricity demand, and grid modernization initiatives. These drivers are creating new opportunities for manufacturers and pushing the industry towards more efficient and reliable transformer solutions.

In my experience, understanding these market drivers is crucial for anyone in the industry. Here’s what’s really moving the needle:
Urbanization and Electrification
The world is becoming more urban and electrified:
- Rapid Urban Growth: Cities need more power infrastructure.
- Rural Electrification: Many countries are expanding grid access.
- Increasing Per Capita Electricity Consumption: Modern lifestyles demand more power.
I once worked on a project in a rapidly growing Asian city. The demand for transformers there doubled in just three years due to new high-rise developments.
Grid Modernization
Aging infrastructure is being replaced and upgraded:
| Driver | Impact on Transformer Market |
|---|---|
| Smart Grid Initiatives | Demand for smart transformers |
| Reliability Improvements | Need for advanced monitoring features |
| Energy Efficiency Regulations | Push for low-loss transformer designs |
In a recent North American project, we replaced hundreds of old transformers with smart models. The utility saw a 15% improvement in grid reliability within the first year.
Renewable Energy Integration
The shift to green energy is changing transformer requirements:
- Solar and Wind Farms: Need specialized transformers to handle variable inputs.
- Distributed Generation: Requires transformers that can manage bi-directional power flow.
- Energy Storage Systems: Creating demand for transformers with unique characteristics.
I’ve seen the impact firsthand. In a European wind farm project, we had to design custom transformers to handle the specific load patterns of wind turbines.
Industrial Growth
Certain industries are driving significant demand:
- Data Centers: Require highly reliable and efficient transformers.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: Creating new demand for distribution transformers.
- Manufacturing Sector: Expansion in developing countries is boosting transformer sales.
The growth in data centers has been particularly impactful. I recently worked with a tech giant that needed specialized transformers for their new energy-efficient data center.
Technological Advancements: The Impact of Innovation on Distribution Transformer Markets?
Are you aware of how new technologies are revolutionizing distribution transformers? The changes are happening faster than many realize.
Technological advancements are significantly impacting distribution transformer markets. Innovations in materials, design, and digital integration are leading to more efficient, reliable, and intelligent transformers. These advancements are reshaping market dynamics and creating new competitive advantages.

I’ve seen firsthand how technology can disrupt our industry. Here’s a look at the innovations that are making waves:
Advanced Materials
New materials are changing the game:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reducing energy losses by up to 70%.
- High-Temperature Superconductors: Promising dramatic efficiency improvements.
- Biodegradable Transformer Oils: Addressing environmental concerns.
I once worked on a project where switching to amorphous core transformers saved the client enough in energy costs to pay for the upgrade in just four years.
Smart Transformer Technology
Transformers are getting smarter:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Predictive maintenance and reduced downtime |
| Auto-adjust Capabilities | Improved grid stability and efficiency |
| Data Analytics Integration | Enhanced asset management and planning |
In a recent smart city project, we installed transformers with advanced monitoring. The city’s power quality improved by 25%, and they caught potential failures before they happened.
Compact and Modular Designs
Space-saving solutions are in high demand:
- Dry-Type Transformers: Safer for indoor installations.
- Gas-Insulated Transformers: Compact design for urban substations.
- Modular Transformer Systems: Scalable solutions for growing power needs.
I helped design a modular transformer system for a rapidly expanding industrial park. It allowed them to easily scale up power capacity as new factories came online.
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual modeling is changing how we design and maintain transformers:
- Design Optimization: Faster and more cost-effective development.
- Performance Simulation: Predicting behavior under various conditions.
- Lifecycle Management: Improving long-term reliability and efficiency.
We used digital twin technology to redesign a transformer line. It cut development time by 30% and improved the final product’s efficiency by 5%.
Regional Market Analysis: Comparing Distribution Transformer Trends Across Continents?
Have you noticed how transformer needs vary dramatically from one part of the world to another? Understanding these regional differences is key to global success.
Distribution transformer trends vary significantly across continents due to differing energy policies, infrastructure development stages, and economic conditions. Asia-Pacific leads in market growth, while North America and Europe focus on grid modernization. Emerging markets show high demand for basic electrification.

I’ve worked on transformer projects across the globe, and the regional variations never cease to amaze me. Let’s break it down:
Asia-Pacific: The Growth Engine
The fastest-growing market:
- Rapid Industrialization: Driving high demand for power infrastructure.
- Urbanization: Creating need for new urban substations.
- Government Initiatives: Supporting grid expansion and modernization.
In China, I saw transformer demand triple in just five years as they expanded their high-speed rail network. The scale was incredible.
North America: Focus on Modernization
Upgrading aging infrastructure:
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Grid Resilience | Demand for advanced, weather-resistant transformers |
| Renewable Integration | Need for flexible, smart transformer solutions |
| Energy Efficiency Mandates | Push for high-efficiency transformer designs |
I worked on a project replacing old transformers in a major U.S. city. The new units not only improved efficiency but also integrated seamlessly with the city’s new smart grid system.
Europe: Leading in Sustainability
Emphasis on green technologies:
- Eco-design Regulations: Driving adoption of low-loss transformers.
- Renewable Energy Growth: Increasing demand for specialized transformers.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Promoting recyclable and sustainable designs.
In Germany, I helped implement a transformer recycling program that reduced environmental impact and cut raw material costs by 20%.
Emerging Markets: Electrification Drive
Focusing on basic power infrastructure:
- Rural Electrification: High demand for small, rugged transformers.
- Growing Energy Consumption: Need for higher capacity distribution networks.
- Limited Budgets: Market for cost-effective, reliable solutions.
In a rural electrification project in India, we designed transformers that were both affordable and able to withstand harsh environmental conditions. It was a unique challenge that required innovative thinking.
Future Outlook: Opportunities and Challenges in the Distribution Transformer Sector (2025-2029)?
What does the future hold for the distribution transformer industry? The next five years promise both exciting opportunities and significant challenges.
The distribution transformer sector from 2025 to 2029 is expected to see continued growth driven by grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Key opportunities include smart transformer development and emerging market expansion. Challenges include raw material price volatility and increasing competition.

Based on my industry experience and current trends, here’s what I foresee for the coming years:
Emerging Opportunities
Areas of potential growth:
- Smart Grid Integration: Increasing demand for intelligent transformers.
- Renewable Energy Expansion: Need for specialized transformer solutions.
- Electric Vehicle Infrastructure: Growing market for charging station transformers.
I’m particularly excited about the EV market. In a recent project, we designed transformers specifically for a network of fast-charging stations. The potential in this sector is enormous.
Technological Advancements
Innovations shaping the future:
| Technology | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| AI and IoT Integration | Enhanced predictive maintenance and efficiency |
| Advanced Materials | Further improvements in energy efficiency |
| Solid-State Transformers | Possible disruption of traditional transformer markets |
I’m closely watching solid-state transformer development. While still in early stages, it could revolutionize our industry if it becomes commercially viable.
Market Challenges
Potential hurdles to overcome:
- Raw Material Price Volatility: Could impact manufacturing costs and pricing.
- Increasing Competition: Pressure on profit margins, especially in emerging markets.
- Regulatory Changes: Potential for stricter efficiency and environmental standards.
In my company, we’re already strategizing to address these challenges. We’re diversifying our supplier base and investing in R&D to stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Regional Growth Prospects
Different regions, different opportunities:
- Asia-Pacific: Continued strong growth, especially in India and Southeast Asia.
- North America: Steady demand driven by grid modernization and renewable integration.
- Europe: Growth in smart and eco-friendly transformer solutions.
- Africa: Emerging opportunity in rural electrification and urban development.
I’m particularly interested in the African market. In a recent consultation, I saw the immense potential for transformer deployment in rapidly growing urban centers across the continent.
Sustainability and Efficiency: The Growing Influence of Green Technologies in Transformer Markets?
Is the push for sustainability changing how we think about transformers? The answer is a resounding yes, and the impact is more significant than many realize.
Green technologies are increasingly influencing the transformer market, driven by environmental regulations and energy efficiency goals. This trend is leading to the development of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient designs, and sustainable manufacturing processes in the transformer industry.

I’ve seen a dramatic shift towards sustainability in our industry over the past decade. Here’s how green technologies are reshaping the market:
Eco-Friendly Materials
Transformers are going green from the inside out:
- Biodegradable Transformer Oils: Reducing environmental risk.
- Recycled Core Materials: Lowering the carbon footprint of production.
- Low-Loss Electrical Steels: Improving energy efficiency.
I recently worked on a project using vegetable-based transformer oil. Not only was it better for the environment, but it also improved the transformer’s thermal performance.
Energy Efficiency Innovations
Cutting energy losses is a top priority:
| Innovation | Efficiency Improvement |
|---|---|
| Amorphous Metal Cores | Up to 70% reduction in core losses |
| Advanced Winding Techniques | 15-20% reduction in copper losses |
| Optimized Cooling Systems | 5-10% overall efficiency gain |
In a recent installation, we used a combination of these technologies. The result was a transformer that was 30% more efficient than the model it replaced.
Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
Green practices are extending to how transformers are made:
- Lean Manufacturing: Reducing waste and energy consumption in production.
- Recycling Programs: Implementing closed-loop material recycling.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Using renewable energy in manufacturing facilities.
I visited a transformer factory that had implemented these practices. They reduced their carbon emissions by 40% while actually increasing production output.
Smart Grid Integration for Sustainability
Intelligent transformers are key to greener grids:
- Load Management: Optimizing energy distribution to reduce waste.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Facilitating the use of solar and wind power.
- Predictive Maintenance: Extending transformer life and reducing resource use.
I worked on a smart grid project where intelligent transformers played a crucial role. They helped increase the grid’s renewable energy capacity by 25% while improving overall reliability.
Conclusion
The global distribution transformer market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, regional demands, and sustainability concerns. Understanding these trends is crucial for industry professionals to navigate future opportunities and challenges.
Have you ever wondered what keeps your lights on, even during storms? The answer lies in two unsung heroes: power and distribution transformers.
Power and distribution transformers are essential for reliable energy supply because they enable efficient electricity transmission and distribution. Power transformers step up voltage for long-distance transmission, while distribution transformers step it down for safe use in homes and businesses. Together, they form the backbone of our electrical grid.

I’ve spent years working with these transformers, and I’ve seen firsthand how crucial they are to our daily lives. Let’s explore why these devices are so important and how they keep our energy supply reliable.
The Dual Pillars of Power: Distinguishing Roles of Power and Distribution Transformers?
Ever noticed those big substations and smaller green boxes in your neighborhood? They house different types of transformers, each with a unique role.
Power transformers and distribution transformers serve distinct but complementary roles in the electrical grid. Power transformers handle high voltages and large power capacities at generation and transmission levels. Distribution transformers manage lower voltages and smaller power loads, delivering electricity directly to end-users.

In my career, I’ve worked with both types of transformers. Here’s how they differ and why both are essential:
Power Transformers: The Heavy Lifters
These are the giants of the transformer world:
- High Voltage Handling: Typically operate at voltages above 69 kV.
- Large Capacity: Can handle power levels from tens to hundreds of MVA.
- Location: Found in power plants and major substations.
I once worked on a project installing a 500 MVA power transformer at a hydroelectric plant. Its size was impressive – about as big as a small house!
Distribution Transformers: The Local Providers
These are the transformers you’re more likely to see in your daily life:
| Feature | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Voltage | 34.5 kV and below |
| Capacity | Up to 2,500 kVA |
| Location | Neighborhoods, poles, underground vaults |
In a recent urban development project, we installed dozens of distribution transformers. Each one served about 10-12 homes, stepping down the voltage from 12 kV to 240/120 V for household use.
Key Differences in Design
The roles of these transformers influence their design:
- Cooling Systems: Power transformers often use oil and external cooling, while distribution transformers are usually self-cooled.
- Insulation: Power transformers require more robust insulation due to higher voltages.
- Tap Changers: More common and complex in power transformers for voltage regulation.
I remember a case where we had to retrofit a power transformer with an advanced on-load tap changer. It was a complex operation, something you wouldn’t see with a typical distribution transformer.
Maintenance and Lifespan
The care these transformers need also differs:
- Power Transformers: Require regular, specialized maintenance and can last 30-40 years.
- Distribution Transformers: Generally need less maintenance and have a lifespan of 20-30 years.
In my experience, the maintenance schedule for a large power transformer is much more intensive. We once had to perform a complete oil change on a 30-year-old power transformer – a task that took several days and specialized equipment.
Ensuring Grid Stability: How Transformers Maintain Consistent Electricity Supply?
Have you ever wondered why your lights don’t flicker every time a big factory turns on its machines? Transformers play a key role in this stability.
Transformers maintain consistent electricity supply by regulating voltage levels, managing power flow, and responding to load changes. They act as buffers in the electrical system, smoothing out fluctuations and ensuring that end-users receive stable, reliable power regardless of upstream changes.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen how crucial transformers are in maintaining grid stability. Here’s how they do it:
Voltage Regulation
Transformers keep voltage levels steady:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Adjust voltage ratios without interrupting power flow.
- Automatic Voltage Regulators: Work with transformers to maintain set voltage levels.
- Reactive Power Compensation: Help manage power factor and voltage stability.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with advanced OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, especially during peak demand hours.
Load Balancing
Transformers help distribute power evenly:
| Method | How It Works |
|---|---|
| Phase Balancing | Evens out loads across three phases |
| Parallel Operation | Multiple transformers share load |
| Dynamic Load Shifting | Smart transformers redirect power as needed |
In a recent smart grid project, we implemented dynamic load shifting. The transformers could communicate and adjust their loads in real-time, significantly improving overall grid efficiency.
Fault Current Limitation
Transformers act as natural barriers to fault currents:
- Impedance: Limits the flow of fault currents.
- Differential Protection: Quickly isolates faulty sections.
- Grounding Transformers: Provide a path for fault currents in ungrounded systems.
I recall a case where a transformer’s impedance prevented a major fault from cascading through the grid. It essentially acted as a firewall, containing the issue to a small area.
Harmonic Mitigation
Modern transformers help clean up power quality:
- K-Rated Transformers: Designed to handle harmonic loads.
- Phase-Shifting Transformers: Cancel out certain harmonics.
- Active Harmonic Filters: Work alongside transformers to remove harmonics.
In a data center project, we used K-rated transformers to manage the high harmonic content from the servers. The improvement in power quality was significant, leading to better equipment performance and longevity.
Reliability Under Pressure: Transformer Resilience in Preventing System-Wide Failures?
Ever wondered how our power grid withstands extreme conditions? Transformers are the unsung heroes in preventing widespread blackouts.
Transformer resilience is crucial in preventing system-wide failures. Through robust design, advanced protection systems, and strategic placement, transformers act as bulwarks against cascading outages. Their ability to withstand and isolate faults is key to maintaining overall grid reliability.

I’ve seen transformers save the day in critical situations. Here’s how they stand up to pressure:
Robust Design and Construction
Transformers are built to last:
- Overload Capacity: Can handle short-term overloads without damage.
- Thermal Management: Advanced cooling systems prevent overheating.
- Mechanical Strength: Designed to withstand physical stresses, including seismic events.
I once inspected a transformer that had survived a major earthquake. Its robust construction prevented what could have been a catastrophic failure.
Advanced Protection Systems
Modern transformers come with multiple layers of protection:
| Protection Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Differential Relays | Detect internal faults rapidly |
| Buchholz Relays | Identify gas accumulation in oil |
| Thermal Monitoring | Continuous temperature tracking |
In a recent substation upgrade, we installed a state-of-the-art protection system. During a severe thunderstorm, it successfully isolated a fault in milliseconds, preventing a wider outage.
Strategic Placement and Redundancy
Careful planning enhances grid resilience:
- N-1 Criterion: System designed to operate even if one component fails.
- Distributed Transformation: Multiple smaller transformers instead of one large unit.
- Mobile Transformer Units: Rapid deployment for emergency situations.
I worked on a project implementing a distributed transformation strategy in an urban area. When one transformer failed, the others seamlessly took up the load, avoiding any customer outages.
Self-Healing Capabilities
The latest transformer technologies include self-healing features:
- On-Load Tap Changers: Automatically adjust to voltage fluctuations.
- Smart Monitoring Systems: Predict and prevent failures before they occur.
- Rapid Switching: Quickly isolate faults and reroute power.
In a smart grid implementation, I saw these self-healing capabilities in action. A potential transformer failure was predicted and prevented, showcasing the power of predictive maintenance.
Efficiency in Action: Modern Transformer Technologies for Minimizing Energy Losses?
Did you know that older transformers can waste a significant amount of energy? Modern technologies are changing this, making our power systems more efficient than ever.
Modern transformer technologies significantly minimize energy losses, improving overall grid efficiency. Advanced core materials, innovative winding designs, and smart monitoring systems work together to reduce both no-load and load losses. These improvements translate to substantial energy savings and reduced operational costs.

Throughout my career, I’ve witnessed the evolution of transformer efficiency. Here’s how modern technologies are making a difference:
Advanced Core Materials
The heart of efficiency improvements:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reduce no-load losses by up to 70% compared to traditional silicon steel.
- High-Grade Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: Offers lower hysteresis losses.
- Laser-Scribed Cores: Minimize eddy current losses.
I recently worked on a project replacing old transformers with amorphous core units. The energy savings were so significant that the utility company recovered the investment in just four years.
Innovative Winding Designs
New winding techniques further reduce losses:
| Design | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Foil Windings | Lower eddy current losses |
| Continuously Transposed Conductors | Reduce circulating currents |
| Optimal End-Insulation | Minimize stray losses |
In a recent manufacturing plant upgrade, we used transformers with advanced winding designs. The reduction in load losses was impressive, leading to cooler operation and extended transformer life.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Real-time efficiency management:
- Online DGA (Dissolved Gas Analysis): Detects potential issues early.
- Temperature Monitoring: Optimizes cooling system operation.
- Load Management Systems: Ensures transformers operate at their most efficient points.
I implemented a smart monitoring system for a group of transformers in a large industrial complex. The system’s ability to optimize load distribution and cooling resulted in a 5% overall efficiency improvement.
Cooling System Innovations
Keeping transformers cool improves efficiency:
- Ester-based Cooling Fluids: Better heat dissipation and environmental friendliness.
- Directed Oil Flow Designs: More effective cooling of windings.
- Advanced Radiator Designs: Improved heat exchange with the environment.
In a hot, arid environment, I worked on installing transformers with advanced cooling systems. They maintained high efficiency even in extreme temperatures, something that would have been challenging with older designs.
Disaster-Proofing Energy Networks: Transformer Strategies for Continuous Power in Crisis Situations?
Have you ever wondered how some areas maintain power even during natural disasters? The secret often lies in how transformers are designed and deployed.
Disaster-proofing energy networks involves strategic transformer deployment and design. This includes using resilient materials, implementing redundant systems, and adopting smart grid technologies. These strategies ensure continuous power supply even in crisis situations, minimizing downtime and accelerating recovery efforts.

I’ve been involved in several projects focused on enhancing grid resilience. Here’s how we use transformers to keep the lights on during crises:
Resilient Design and Materials
Building transformers to withstand extreme conditions:
- Seismic-Resistant Designs: Withstand earthquake forces.
- Flood-Resistant Enclosures: Protect against water ingress.
- Wind-Resistant Structures: Survive high-speed winds in hurricane-prone areas.
I once worked on upgrading substations in a coastal area prone to hurricanes. We installed transformers with specially designed wind-resistant radiators and reinforced tanks. They’ve since weathered several major storms without issue.
Redundancy and Rapid Recovery
Ensuring quick restoration of power:
| Strategy | Implementation |
|---|---|
| N-1 or N-2 Redundancy | Multiple transformers sharing loads |
| Mobile Transformer Units | Quick deployment to affected areas |
| Modular Designs | Faster replacement of damaged components |
In the aftermath of a severe ice storm, I was part of a team that deployed mobile transformer units. We restored power to critical infrastructure within hours, while permanent repairs took weeks.
Smart Grid Integration
Leveraging technology for resilience:
- Self-Healing Networks: Automatically isolate faults and reroute power.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Rapid response to developing situations.
- Predictive Maintenance: Prevent failures before they occur.
I implemented a smart grid system in a region prone to wildfires. The system’s ability to quickly isolate affected areas and reroute power potentially saved lives and certainly minimized outages during a particularly bad fire season.
Strategic Placement and Hardening
Protecting critical infrastructure:
- Elevated Installations: In flood-prone areas.
- Fireproof Barriers: Around transformers in wildfire zones.
- Underground Installations: In areas vulnerable to storms or vandalism.
For a project in a flood-prone city, we redesigned several substations with elevated transformer platforms. During the next major flood, these stations remained operational, providing crucial power for emergency services.
Conclusion
Power and distribution transformers are essential for reliable energy supply, ensuring grid stability, efficiency, and resilience. From daily operations to crisis situations, these devices form the backbone of our modern electrical infrastructure.
Have you ever stared at a distribution transformer diagram and felt lost? You’re not alone. Many engineers struggle to decode these complex schematics.
Distribution transformer diagrams are essential tools for electrical engineers. They provide a visual representation of the transformer’s components, connections, and functionality. Understanding these diagrams is crucial for design, maintenance, and troubleshooting in power distribution systems.
I’ve spent years working with distribution transformer diagrams. I’ve seen how a clear understanding of these schematics can make or break a project. Let’s dive into the world of transformer diagrams and uncover their secrets.
Decoding the Components: Key Elements of a Distribution Transformer Diagram?
Have you ever wondered what all those symbols on a transformer diagram mean? It’s like learning a new language, but one that’s crucial for your work.
Distribution transformer diagrams consist of several key components, each represented by specific symbols. These include the core, windings, bushings, tap changers, and protective devices. Understanding these elements is fundamental to interpreting the diagram correctly.
In my early days as an engineer, I often felt overwhelmed by the complexity of these diagrams. But as I learned to identify each component, the bigger picture became clear. Here’s what you need to know:
Core and Windings
The heart of the transformer:
- Core: Usually represented by rectangular shapes.
- Primary Winding: Often shown on the left side.
- Secondary Winding: Typically on the right side.
I once worked on a project where misinterpreting the winding configuration led to a costly mistake. It taught me the importance of understanding these basic elements.
Bushings and Connections
How the transformer connects to the outside world:
| Component | Symbol | Function |
|---|---|---|
| High Voltage Bushing | Triangle or circle with H | Connects to high voltage line |
| Low Voltage Bushing | Triangle or circle with X | Connects to low voltage line |
| Neutral Bushing | Triangle or circle with N | Grounding connection |
Understanding these connections is crucial. In a recent installation, correctly identifying the bushing types ensured proper grounding and safety.
Tap Changers and Regulators
Adjusting voltage levels:
- On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC): Shown as a series of contacts.
- Off-Circuit Tap Changer: Similar to OLTC but with a different symbol.
- Voltage Regulator: Often represented as a variable resistor symbol.
I’ve seen engineers overlook tap changers in diagrams, leading to voltage regulation issues. Always pay attention to these components.
Protective Devices
Keeping the transformer safe:
- Buchholz Relay: Usually shown near the top of the tank.
- Pressure Relief Device: Often represented by a circle with an arrow.
- Temperature Indicators: Shown as thermometer symbols.
In a recent troubleshooting case, identifying a faulty Buchholz relay from the diagram helped us prevent a potential transformer failure.
Symbols and Notations: Mastering the Language of Transformer Schematics?
Do transformer diagrams sometimes look like a foreign language to you? You’re not alone. But mastering this language is key to your success as an electrical engineer.
Symbols and notations in transformer schematics form a standardized language for electrical engineers. They represent various components, connections, and functions of the transformer. Understanding these symbols is crucial for accurate interpretation and effective communication in the field.
When I first started working with transformer diagrams, I felt like I was deciphering hieroglyphics. But over time, I realized how powerful this visual language can be. Let’s break it down:
Basic Electrical Symbols
The building blocks of any transformer diagram:
- Lines: Represent conductors or connections.
- Zigzag Lines: Often used for windings.
- Circles: Can represent bushings or connection points.
I once caught a critical wiring error just by noticing an unusual line configuration in a diagram. It saved us from a potential equipment failure.
Transformer-Specific Symbols
Unique to transformer schematics:
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Rectangle with Lines | Transformer Core |
| Overlapping Circles | Windings |
| Arrow through Circle | Tap Changer |
| Lightning Bolt | Surge Arrester |
Understanding these symbols is crucial. In a recent project, quickly identifying a missing surge arrester symbol in the diagram prevented a costly oversight in lightning protection.
Polarity and Phase Markings
Indicating current flow and phase relationships:
- Dot Convention: Dots show winding polarity.
- H1, H2 (High Voltage) and X1, X2 (Low Voltage): Standard terminal markings.
- Phase Notations: A, B, C or R, Y, B for three-phase systems.
I’ve seen confusion arise from misinterpreted polarity markings. Always double-check these to ensure proper transformer connections.
Ratings and Specifications
Key information often included in diagrams:
- kVA Rating: Transformer capacity.
- Voltage Ratings: Primary and secondary voltages.
- Impedance: Usually expressed as a percentage.
During a system upgrade, correctly reading the impedance value from a diagram helped us avoid a potential mismatch in fault current calculations.
Practical Applications: Using Distribution Transformer Diagrams for Troubleshooting?
Ever faced a transformer issue and felt stuck? The solution might be right there in the diagram. But how do you use it effectively?
Distribution transformer diagrams are invaluable tools for troubleshooting. They provide a comprehensive view of the transformer’s structure and connections, allowing engineers to identify potential fault points, trace electrical paths, and plan diagnostic tests efficiently.

I’ve used transformer diagrams countless times to solve complex issues. Here’s how you can leverage them for effective troubleshooting:
Fault Isolation
Pinpointing problem areas:
- Trace Electrical Paths: Follow the lines to identify potential fault locations.
- Check Connection Points: Bushings and terminals are common fault areas.
- Examine Protection Devices: Look for tripped indicators in the diagram.
I once solved a mysterious power outage by tracing a fault to a rarely-used auxiliary connection shown in the diagram. It wasn’t even considered in the initial troubleshooting.
Test Point Identification
Planning your diagnostic approach:
| Test Type | Diagram Use |
|---|---|
| Insulation Resistance | Identify winding terminals |
| Turn Ratio | Locate primary and secondary connections |
| Winding Resistance | Find specific winding start and end points |
Using the diagram to plan tests saves time and improves accuracy. In a recent case, I quickly identified the correct test points for a complex partial discharge test, streamlining the entire process.
Comparative Analysis
Using the diagram as a reference:
- Compare As-Built to Design: Check for discrepancies.
- Historical Comparison: Look for changes over time.
- Benchmark Against Standards: Ensure compliance with industry norms.
I’ve caught several installation errors by comparing the actual transformer setup to the diagram. It’s a practice that has saved both time and resources.
Safety Planning
Ensuring safe troubleshooting:
- Identify Isolation Points: Locate disconnects and grounding points.
- Recognize High Voltage Areas: Plan safe access routes.
- Verify Protection Schemes: Understand built-in safety features.
Safety is paramount. I always use the diagram to brief my team on potential hazards before any hands-on work.
From Blueprint to Reality: Implementing Distribution Transformer Diagrams in System Design?
Ever wondered how a transformer goes from a drawing to a working part of the power grid? It’s a journey that starts with a diagram and ends with a crucial piece of infrastructure.
Implementing distribution transformer diagrams in system design involves translating schematic representations into physical installations. This process requires careful planning, precise execution, and thorough verification to ensure the transformer functions as intended within the larger power distribution system.
I’ve overseen many transformer installations, and the diagram is always our roadmap. Here’s how we bring these blueprints to life:
Design Verification
Ensuring the diagram meets system requirements:
- Load Analysis: Verify the transformer capacity matches the demand.
- Voltage Levels: Confirm primary and secondary voltages are correct.
- Protection Schemes: Check if all necessary protective devices are included.
I once caught a major design flaw during this stage. The diagram showed a transformer with insufficient capacity for future expansion plans. Catching this early saved a costly replacement down the line.
Component Selection
Choosing the right parts based on the diagram:
| Component | Selection Criteria |
|---|---|
| Core | Material and construction type |
| Windings | Conductor material and insulation class |
| Bushings | Voltage rating and current capacity |
| Tap Changers | Range and step size |
Selecting the right components is crucial. I remember a project where we had to custom-order bushings because the standard ones didn’t match the unique configuration in our diagram.
Physical Layout Planning
Translating 2D diagrams to 3D reality:
- Space Allocation: Ensure adequate room for all components.
- Accessibility: Plan for maintenance and testing access.
- Cooling Considerations: Arrange components for optimal heat dissipation.
I’ve learned to always consider the physical space. In one installation, we had to redesign the layout because the diagram didn’t account for the limited space in an urban substation.
Wiring and Connections
Bringing the diagram to life:
- Follow Connection Paths: Use the diagram as a wiring guide.
- Verify Polarities: Ensure winding connections match the diagram.
- Implement Grounding: Install ground connections as shown.
Attention to detail is key here. I once prevented a potential disaster by catching a reversed polarity connection that didn’t match the diagram.
Comparative Analysis: Exploring Various Types of Distribution Transformer Diagrams?
Did you know that not all transformer diagrams are created equal? Understanding the differences can give you a significant edge in your work.
Distribution transformer diagrams come in various types, each serving a specific purpose. These include single-line diagrams, schematic diagrams, winding diagrams, and connection diagrams. Each type offers unique insights into the transformer’s structure and function.
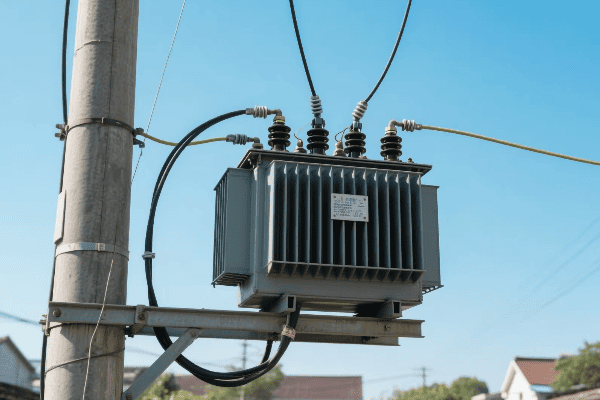
In my career, I’ve worked with all types of transformer diagrams. Each has its strengths, and knowing when to use which can make your job much easier. Let’s compare them:
Single-Line Diagrams
The big picture view:
- Purpose: Show overall system layout.
- Level of Detail: Low, focuses on major components.
- Best Used For: System planning and high-level understanding.
I often start with single-line diagrams when explaining system upgrades to non-technical stakeholders. They provide a clear, simplified view of how the transformer fits into the larger picture.
Schematic Diagrams
Detailed electrical representations:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Component Symbols | Shows all electrical parts |
| Connection Paths | Illustrates how components are linked |
| Electrical Values | Often includes ratings and specifications |
Schematic diagrams are my go-to for troubleshooting. Their detailed nature once helped me identify a subtle wiring issue that was causing intermittent faults.
Winding Diagrams
Focused on internal transformer structure:
- Coil Arrangements: Shows how windings are constructed.
- Turn Ratios: Illustrates voltage transformation details.
- Tap Positions: Indicates voltage adjustment points.
Understanding winding diagrams is crucial for maintenance. I’ve used them to guide rewinding processes and to diagnose internal faults that weren’t apparent from other diagram types.
Connection Diagrams
Emphasizing external connections:
- Terminal Layouts: Shows how to connect the transformer to the system.
- Phasing Information: Crucial for three-phase systems.
- Grounding Points: Indicates where and how to ground the transformer.
Connection diagrams are invaluable during installation. I always refer to them to ensure proper system integration and to avoid potentially dangerous misconnections.
Conclusion
Understanding distribution transformer diagrams is crucial for electrical engineers. From component identification to practical troubleshooting, these diagrams are essential tools for designing, maintaining, and optimizing power distribution systems.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group