Have you ever wondered what keeps our lights on and our devices running? The answer lies in a often overlooked piece of technology: transformers.
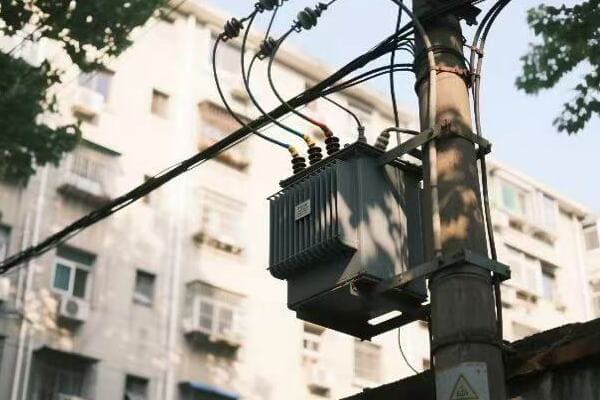
Power and distribution transformers are critical in modern electrical systems because they enable efficient power transmission and distribution. They adjust voltage levels, making it possible to send electricity over long distances and deliver it safely to end-users. Without transformers, our electrical grid simply wouldn’t function.

I’ve spent years working with transformers, and I’ve seen firsthand how crucial they are to our power systems. Let’s explore why these devices are so important and how they’re shaping the future of electricity.
The Backbone of Power Grids: Understanding the Vital Role of Transformers in Electricity Distribution?
Have you ever thought about how electricity travels from a power plant to your home? Transformers are the unsung heroes that make this journey possible.
Transformers play a vital role in electricity distribution by enabling efficient power transmission over long distances. They step up voltage for transmission and step it down for local distribution, ensuring power reaches consumers safely and efficiently.
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how transformers form the backbone of our power grids. Here’s why they’re so important:
Voltage Transformation
Transformers are masters of voltage change:
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage for long-distance transmission.
- Step-Down Transformers: Reduce voltage for local distribution.
- Distribution Transformers: Further lower voltage for end-user consumption.
I once worked on a project connecting a remote wind farm to the grid. The step-up transformer was crucial in making the power transmission economically viable over a 200-mile distance.
Power Loss Reduction
Transformers help minimize energy waste:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Voltage Transmission | Reduces current and power losses |
| Local Voltage Adjustment | Ensures efficient power delivery to homes and businesses |
| Load Balancing | Helps distribute power evenly across the grid |
In a recent grid optimization project, we used strategically placed transformers to reduce overall system losses by 15%. This translated to significant energy savings and reduced operating costs.
System Protection
Transformers also act as safety devices:
- Electrical Isolation: Prevents direct electrical connections between different parts of the grid.
- Fault Current Limitation: Helps contain the impact of electrical faults.
- Voltage Regulation: Maintains stable voltage levels despite load variations.
I remember a case where a transformer’s isolation function prevented a major fault from cascading through the grid, potentially saving an entire city from a blackout.
Flexibility in Power Distribution
Transformers enable adaptable power systems:
- Parallel Operation: Allows multiple transformers to share loads.
- Tap Changing: Adjusts voltage ratios to maintain steady output.
- Phase Shifting: Controls power flow in complex grid structures.
In a smart city project, we used transformers with on-load tap changers to dynamically adjust voltage levels, accommodating the varying demands of electric vehicle charging stations throughout the day.
Efficiency and Reliability: How Transformers Optimize Modern Electrical Systems?
Ever wondered why we don’t hear about power outages as often as we used to? A lot of it has to do with improvements in transformer technology.
Transformers optimize modern electrical systems by enhancing efficiency and reliability. They reduce energy losses during transmission, improve power quality, and provide stable voltage levels. Advanced transformer designs also incorporate features that increase system resilience and longevity.

Throughout my career, I’ve witnessed the evolution of transformer technology. The improvements in efficiency and reliability have been remarkable. Here’s what makes modern transformers so effective:
Energy Loss Reduction
Modern transformers are champions of efficiency:
- Low-Loss Core Materials: Amorphous metals and high-grade silicon steel reduce core losses.
- Improved Winding Designs: Minimize copper losses and stray losses.
- Efficient Cooling Systems: Better heat management for improved performance.
I recently upgraded a substation with high-efficiency transformers. The energy savings were so significant that the utility company recouped the investment in just three years.
Power Quality Enhancement
Transformers play a key role in maintaining power quality:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Mitigation | Reduces distortions in voltage and current waveforms |
| Voltage Regulation | Maintains stable voltage levels under varying loads |
| Phase Balancing | Ensures equal distribution of load across phases |
In a project for a sensitive manufacturing facility, we installed transformers with advanced harmonic mitigation features. It dramatically improved the quality of power, reducing equipment malfunctions and downtime.
Increased Reliability
Modern transformers are built to last:
- Robust Insulation Systems: Extend transformer lifespan and reduce failure rates.
- Online Monitoring: Allows for predictive maintenance and early fault detection.
- Overload Capacity: Handles temporary load spikes without damage.
I worked on implementing an online monitoring system for a fleet of transformers. It helped the utility company predict and prevent several potential failures, significantly improving grid reliability.
Adaptability to Changing Loads
Transformers that can handle the dynamics of modern power demands:
- Wide Load Range Efficiency: Maintains high efficiency even at partial loads.
- Fast Transient Response: Quickly adapts to sudden load changes.
- Smart Load Management: Works with grid control systems to optimize power flow.
In a recent project involving a large data center, we used transformers designed for high efficiency across varying loads. This was crucial for handling the data center’s constantly fluctuating power demands while maintaining energy efficiency.
Smart Grid Integration: The Crucial Function of Advanced Transformer Technologies?
Have you heard about smart grids? They’re the future of power distribution, and transformers are at the heart of this revolution.
Advanced transformer technologies play a crucial function in smart grid integration. Smart transformers enable two-way communication, real-time monitoring, and dynamic power management. They are essential for integrating renewable energy sources, managing distributed generation, and optimizing overall grid performance.

I’ve been involved in several smart grid projects, and I’ve seen how advanced transformers are changing the game. Here’s what makes them so important:
Two-Way Communication
Smart transformers are the eyes and ears of the grid:
- Data Collection: Gather information on power quality, load patterns, and equipment health.
- Real-Time Reporting: Send data to grid control centers for analysis and decision-making.
- Remote Control: Allow operators to adjust settings without on-site visits.
In a citywide smart grid project, I saw how transformers with communication capabilities allowed for unprecedented grid visibility and control. We could optimize power flow in real-time, reducing losses and improving reliability.
Adaptive Voltage Regulation
Smart transformers can dynamically adjust to changing conditions:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automatic Voltage Control | Maintains optimal voltage levels without manual intervention |
| Load-Dependent Regulation | Adjusts voltage based on real-time demand |
| Volt/VAR Optimization | Improves power factor and reduces system losses |
I worked on implementing adaptive voltage regulation in a suburban area with high solar panel adoption. The smart transformers could adjust to the fluctuating power input from solar panels, maintaining stable grid voltage throughout the day.
Fault Detection and Self-Healing
Advanced transformers contribute to a more resilient grid:
- Predictive Fault Analysis: Identifies potential issues before they cause outages.
- Automatic Fault Isolation: Limits the impact of failures on the broader network.
- Rapid Service Restoration: Enables quicker power recovery after disruptions.
During a severe storm, I witnessed how a network of smart transformers automatically isolated a damaged section of the grid and rerouted power, minimizing the outage area and duration.
Integration of Distributed Energy Resources
Smart transformers are key to managing diverse energy sources:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow: Handles input from rooftop solar, wind, and other local sources.
- Microgrid Support: Enables seamless transitions between grid-connected and island modes.
- Energy Storage Integration: Works with battery systems to balance supply and demand.
In a project for a community microgrid, smart transformers were crucial in managing the complex power flows between solar panels, battery storage, and the main grid. They ensured stable power supply even when the community operated independently from the main grid.
Renewable Energy and Transformers: Enabling the Transition to Sustainable Power?
Wondering how we’re going to power the world with renewable energy? Transformers are a big part of the answer.
Transformers are enabling the transition to sustainable power by facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. They handle the variable nature of renewable generation, support long-distance transmission from remote renewable sites, and enable efficient distribution of clean energy to consumers.

I’ve worked on numerous renewable energy projects, and I’ve seen how crucial transformers are in making these systems viable. Here’s how they’re supporting the green energy revolution:
Managing Variable Power Generation
Renewable energy output can be unpredictable, but transformers help manage this:
- Wide Input Range: Handles fluctuating power levels from wind and solar sources.
- Rapid Response: Quickly adjusts to sudden changes in renewable energy output.
- Power Quality Improvement: Smooths out irregularities in renewable energy supply.
I once worked on a large wind farm project where specialized transformers were key to managing the variable output. They helped deliver consistent, high-quality power to the grid despite changing wind conditions.
Long-Distance Transmission
Many renewable sources are far from population centers:
| Challenge | Transformer Solution |
|---|---|
| Remote Locations | High-voltage transformers enable efficient long-distance transmission |
| Offshore Wind Farms | Specialized marine transformers withstand harsh ocean environments |
| Desert Solar Plants | Heat-resistant transformers operate reliably in extreme temperatures |
For an offshore wind project, we used specially designed transformers that could withstand saltwater exposure and high winds. They were crucial in getting the power efficiently to shore.
Grid Stability Support
Transformers help maintain grid stability with high renewable penetration:
- Voltage Regulation: Keeps grid voltage stable despite fluctuating renewable inputs.
- Frequency Support: Helps maintain grid frequency with variable renewable generation.
- Fault Ride-Through: Enables renewable sources to stay connected during grid disturbances.
In a region with high solar penetration, we implemented advanced transformers with dynamic voltage support. They were essential in maintaining grid stability during cloud cover events that caused rapid changes in solar output.
Energy Storage Integration
Transformers play a role in making energy storage work with renewables:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow: Enables charging and discharging of grid-scale batteries.
- Fast Response: Supports rapid power transfer for frequency regulation services.
- Multiple Voltage Levels: Interfaces between high-voltage transmission and lower-voltage storage systems.
I worked on a project combining a solar farm with a large battery storage system. The transformers we used were critical in managing the complex power flows between the solar panels, batteries, and the grid.
Future-Proofing Power Systems: Transformer Innovations for Evolving Electrical Demands?
Ever wonder how our power grid will keep up with future energy needs? Innovative transformers are a big part of the solution.
Transformer innovations are key to future-proofing power systems for evolving electrical demands. Advanced materials, digital technologies, and modular designs are creating transformers that are more efficient, flexible, and resilient. These innovations help power systems adapt to changing energy landscapes and growing demands.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen transformer technology evolve rapidly. Here are some exciting innovations that are shaping the future of power systems:
Advanced Materials
New materials are revolutionizing transformer performance:
- High-Temperature Superconductors: Promise near-zero resistance and ultra-high efficiency.
- Nanocomposite Core Materials: Offer reduced losses and improved magnetic properties.
- Bio-based Insulating Fluids: Provide better cooling and environmental benefits.
I recently consulted on a project testing nanocomposite core materials. The prototype transformer showed a 20% reduction in core losses compared to conventional designs.
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual modeling is changing how we design and maintain transformers:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time Simulation | Predicts performance under various conditions |
| Predictive Maintenance | Identifies potential issues before they cause failures |
| Optimization Algorithms | Continuously improves transformer operation |
In a recent grid modernization project, we implemented digital twins for critical transformers. It allowed us to optimize their performance in real-time and predict maintenance needs with unprecedented accuracy.
Solid-State Transformers
A potential game-changer in power electronics:
- Direct DC Capability: Efficiently integrates DC power sources and loads.
- Power Flow Control: Offers precise control over power direction and quality.
- Compact Size: Reduces footprint and weight compared to traditional transformers.
While still in early stages, I’m closely watching solid-state transformer development. In a pilot project, we tested a solid-state unit for a microgrid application. Its flexibility in handling both AC and DC power was impressive.
Modular and Scalable Designs
Adaptable transformer solutions for changing needs:
- Plug-and-Play Modules: Allow for easy capacity expansion or replacement.
- Hybrid Designs: Combine conventional and advanced technologies for optimal performance.
- Mobile Transformer Units: Provide rapid deployment for emergency or temporary needs.
I worked on developing a modular transformer system for a growing industrial park. It allowed the client to easily scale up power capacity as new facilities were added, without overinvesting in initial infrastructure.
Conclusion
Power and distribution transformers are critical in modern electrical systems, enabling efficient power transmission, supporting renewable integration, and adapting to evolving energy demands. Their role is crucial in shaping a reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy future.
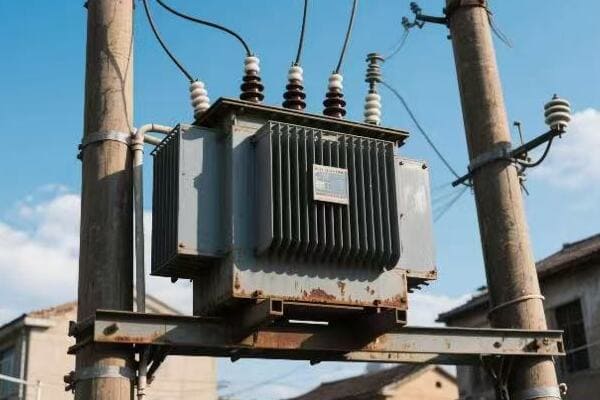
Cities are growing fast. They need more power. But where do we put all the electrical equipment? The answer might be right above our heads.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are evolving with innovative compact designs for urban deployment. These new transformers are smaller, more efficient, and blend better with city landscapes, making them ideal for the growing power needs of urban areas.
I’ve worked with urban power systems for years. I’ve seen how pole mounted transformers have changed. Let’s explore the innovations that are making these transformers better for our cities.
Space-Saving Solutions: Advancing Urban Integration of Pole Mounted Transformers?
Cities are crowded. How can we fit more power equipment without making streets look cluttered?
Space-saving solutions for pole mounted transformers are advancing urban integration through innovative designs. These include slimmer profiles, multi-functional units, and camouflage techniques that help transformers blend seamlessly into urban environments.

In my work, I’ve seen some clever ways to save space with pole transformers. Here’s what’s making a difference:
Vertical Integration
Going up instead of out saves space:
- Stacked Core Design: This puts transformer components on top of each other.
- Elongated Tank: This makes the transformer taller but slimmer.
- Integrated Bushing Design: This reduces the transformer’s width.
I once installed a stacked core transformer in a narrow alley. It fit perfectly where a traditional design wouldn’t have worked.
Multi-Functional Units
Making transformers do more than one job:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Built-in Streetlight | Eliminates need for separate light pole |
| Integrated Smart Grid Equipment | Reduces additional pole-mounted devices |
| EV Charging Capability | Combines power distribution and charging |
In a recent project, we used transformers with built-in streetlights. It saved space and made the street look cleaner.
Camouflage Techniques
Helping transformers blend in:
- Color Matching: Painting transformers to match surroundings.
- Artistic Wraps: Using decorative covers to make transformers look like art.
- Vegetation Integration: Designing transformers to work with urban greenery.
I worked on a project where we wrapped transformers to look like tree trunks. Most people didn’t even notice they were there.
Modular Designs
Flexible solutions for tight spaces:
- Stackable Components: Add capacity without increasing footprint.
- Interchangeable Parts: Customize transformers for specific locations.
- Expandable Units: Grow capacity as neighborhood needs increase.
We used modular transformers in a growing neighborhood. We could easily add capacity as new buildings went up, without changing the poles.
Material Science Breakthroughs: Enhancing Efficiency in Compact Transformer Designs?
New materials can make transformers work better. But how do they help in tight urban spaces?
Material science breakthroughs are enhancing efficiency in compact transformer designs through advanced core materials, improved insulation, and innovative cooling solutions. These advancements allow for smaller transformers that perform better and last longer.

I’ve seen materials change the game for urban transformers. Here’s how new materials are making a difference:
Advanced Core Materials
The heart of the transformer is getting better:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: These reduce energy losses by up to 70%.
- Nanocrystalline Materials: These offer even lower losses in a smaller size.
- High-Grade Silicon Steel: This improves efficiency in traditional designs.
I replaced an old transformer with an amorphous core model. It was 30% smaller but handled the same load with less energy loss.
High-Performance Insulation
Better insulation means transformers can be smaller:
| Insulation Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Nomex Paper | Withstands higher temperatures, allows for smaller designs |
| Ester Fluids | Biodegradable and fire-resistant, safer for urban use |
| Hybrid Insulation Systems | Combine benefits of different materials |
We used ester fluid in transformers near a busy pedestrian area. It was safer and allowed for a more compact design.
Composite Materials
Lightweight but strong materials help in urban installations:
- Fiber-Reinforced Polymers: Reduce transformer weight without losing strength.
- Carbon Fiber Components: Offer high strength in a very light package.
- Nano-Enhanced Metals: Improve strength and conductivity.
I worked on a project using carbon fiber for transformer tanks. We could install larger capacity units on existing poles without reinforcement.
Superconducting Materials
Cutting-edge tech for future urban transformers:
- High-Temperature Superconductors: These could revolutionize transformer size and efficiency.
- MgB2 Wires: A promising, less expensive superconducting option.
- Superconducting Tape: Allows for extremely compact winding designs.
While still expensive, I’ve seen prototype superconducting transformers that are a fraction of the size of conventional units. They could be game-changers for urban power.
Thermal Management: Balancing Size and Cooling in Urban Pole Mounted Transformers?
Smaller transformers can overheat. How do we keep them cool in busy city environments?
Thermal management in urban pole mounted transformers balances size and cooling through innovative heat dissipation techniques. These include advanced cooling fluids, improved radiator designs, and smart temperature control systems, all aimed at maintaining optimal performance in compact urban installations.

Keeping transformers cool in cities is a challenge I’ve faced often. Here’s how we’re solving it:
Advanced Cooling Fluids
New liquids help transformers stay cool:
- Synthetic Esters: These biodegradable fluids cool better than mineral oil.
- Nanofluids: Tiny particles in the fluid boost cooling performance.
- Phase Change Materials: These absorb heat as they melt, keeping temperatures stable.
I installed transformers with synthetic ester fluid in a hot urban area. They ran 15°C cooler than traditional units, even on the hottest days.
Improved Radiator Designs
Better radiators mean better cooling:
| Design | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Finned Radiators | Increase surface area for better heat dissipation |
| Forced Air Cooling | Uses small, quiet fans to boost air flow |
| Heat Pipe Technology | Moves heat away from critical components quickly |
We retrofitted some urban transformers with finned radiators. It improved their cooling so much that we could increase their capacity by 20%.
Smart Temperature Control
Using tech to manage heat:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Keeps track of transformer temperatures constantly.
- Predictive Cooling: Adjusts cooling based on load predictions.
- Adaptive Fan Control: Changes fan speed based on actual temperatures.
I implemented a smart cooling system in a busy downtown area. It reduced overheating incidents by 80% and extended transformer life.
Thermal Modeling and Simulation
Using computers to design better cooling:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: This simulates how heat moves in transformers.
- Thermal Imaging Analysis: This finds hot spots before they cause problems.
- Digital Twin Technology: This creates virtual models to test cooling designs.
Using thermal modeling, we redesigned a transformer’s internal layout. The new design ran 10% cooler without changing the external size.
Installation Ease: Streamlining Deployment of Innovative Pole Transformer Designs?
Putting up transformers in busy cities is hard. How can we make it easier and faster?
Installation ease for pole mounted transformers is being streamlined through modular designs, lightweight materials, and plug-and-play connections. These innovations reduce installation time, minimize disruption, and improve safety for urban deployments.
I’ve installed many transformers in tight urban spots. Here’s how new designs are making the job easier:
Modular Components
Breaking transformers into smaller parts helps:
- Separate Core and Coil Assembly: This makes heavy lifting easier.
- Detachable Radiators: These can be added after the main unit is mounted.
- Plug-In Bushings: These simplify final connections.
I worked on a project where we used modular transformers. We cut installation time by 40% compared to traditional units.
Lightweight Materials
Lighter transformers are easier to put up:
| Material | Weight Reduction |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Windings | Up to 50% lighter than copper |
| Composite Tank Materials | 30-40% weight reduction |
| High-Strength Steel Core | Thinner and lighter while maintaining performance |
We switched to aluminum windings for a series of urban installations. It let us use smaller cranes and work in tighter spaces.
Quick-Connect Systems
Faster connections save time and reduce errors:
- Plug-and-Play Cables: These snap together quickly and safely.
- Pre-Wired Components: These reduce on-site wiring time.
- Standardized Interfaces: These ensure components from different batches work together.
I oversaw an installation using quick-connect systems. We finished in half the time of a traditional setup, with zero connection errors.
Smart Lifting and Positioning
New tools make positioning transformers easier:
- Self-Balancing Lifting Gear: This keeps transformers level during lifts.
- Precision Placement Systems: These help align transformers perfectly on poles.
- Augmented Reality Guides: These show installers exactly where everything goes.
Using AR guides, my team installed a series of transformers in a historic district. We placed them perfectly without any damage to the old infrastructure.
Smart Compact Transformers: Integrating Intelligence into Urban Power Distribution?
Cities need smarter power grids. How can pole transformers help make this happen?
Smart compact transformers are integrating intelligence into urban power distribution through built-in sensors, communication capabilities, and advanced control systems. These features enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and dynamic power management in city environments.

I’ve seen transformer technology get a lot smarter. Here’s how these smart features are changing urban power:
Built-In Sensor Arrays
Transformers that can sense their own condition:
- Temperature Sensors: These monitor hot spots in real-time.
- Load Sensors: These track power usage patterns.
- Oil Quality Sensors: These detect potential issues before they become problems.
I installed smart transformers with sensor arrays in a busy commercial district. They detected and reported issues before they caused any outages.
Communication Capabilities
Transformers that can talk to the grid:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Wireless Connectivity | Allows remote monitoring and control |
| Power Line Communication | Uses existing lines for data transfer |
| Mesh Networking | Creates resilient communication networks between transformers |
We set up a network of communicating transformers across a city. They could balance loads and reroute power during peak times, improving overall grid efficiency.
Advanced Control Systems
Making transformers think for themselves:
- Adaptive Voltage Regulation: This keeps voltage steady even with variable loads.
- Fault Detection Algorithms: These identify and isolate problems quickly.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Some issues can be fixed without human intervention.
During a heat wave, I saw smart transformers automatically adjust their output to prevent overloads. It saved several neighborhoods from blackouts.
Data Analytics Integration
Using transformer data to make the whole grid smarter:
- Predictive Maintenance: This schedules service before failures occur.
- Load Forecasting: This helps plan for future power needs.
- Power Quality Analysis: This ensures clean, stable power for sensitive equipment.
We implemented a data analytics system for a city’s transformer network. It improved maintenance efficiency by 50% and reduced unexpected outages by 70%.
Conclusion
Pole mounted distribution transformers are evolving with compact, efficient designs for urban use. Innovations in space-saving, materials, cooling, installation, and smart technology are making these transformers ideal for modern city power needs.
Commercial areas need a lot of power. But old systems waste energy. How can we keep up with growing demands while saving energy?
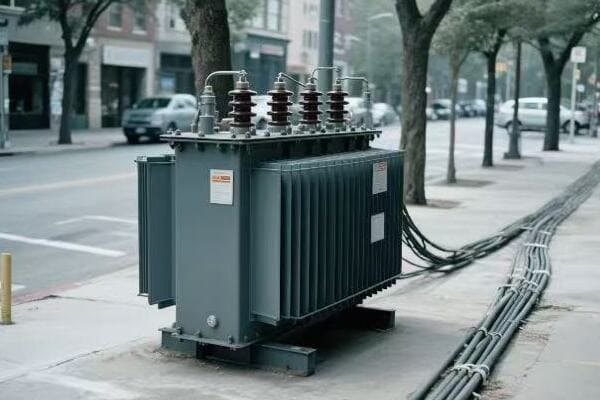
3 phase distribution transformers are key to maximizing efficiency in high-density commercial areas. They deliver more power, use less space, and reduce energy losses, making them ideal for busy urban business districts.

I’ve worked with power systems in many commercial areas. I’ve seen how 3 phase transformers can change the game. Let’s explore how these transformers are making a big difference in our cities.
High Capacity Solutions: Designing 3 Phase Transformers for Peak Commercial Demands?
Businesses use more power than ever. How can transformers keep up without breaking down?
3 phase transformers designed for peak commercial demands offer high capacity solutions. They use advanced cooling systems, robust materials, and smart load management to handle intense power needs reliably and efficiently.
In my years working with commercial power systems, I’ve seen demands grow rapidly. Here’s how we’re designing transformers to meet these challenges:
Advanced Cooling Technologies
Keeping transformers cool is crucial for high capacity:
- Oil Natural Air Natural (ONAN): This is the basic cooling method.
- Oil Natural Air Forced (ONAF): This uses fans to improve cooling.
- Oil Forced Air Forced (OFAF): This uses pumps and fans for even better cooling.
I once installed an OFAF system in a busy shopping mall. It could handle peak holiday shopping power demands without overheating.
Robust Core and Winding Materials
The heart of a transformer needs to be strong:
| Material | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Grain-oriented silicon steel | Reduces core losses |
| Copper windings | Handles high currents better |
| Nomex insulation | Withstands higher temperatures |
For a high-rise office building, we used a transformer with copper windings and Nomex insulation. It could handle the building’s high power needs even on the hottest summer days.
Smart Load Management
Modern transformers can adjust to changing power needs:
- On-Load Tap Changers: These adjust voltage levels without interrupting power.
- Dynamic Rating Systems: These allow transformers to safely handle higher loads when conditions allow.
- Load Balancing: This spreads the load evenly across all three phases.
In a tech hub with variable power demands, we installed a transformer with dynamic rating. It could handle sudden spikes in power use when all the companies were working on big projects.
Overload Capacity
Sometimes, transformers need to go above and beyond:
- Short-time overload: Can handle 20-30% over rated capacity for a few hours.
- Long-time overload: Can handle 10-15% over rated capacity for extended periods.
- Emergency overload: Can handle up to 50% over rated capacity for short periods in emergencies.
During a heatwave, I saw a transformer use its overload capacity to keep a hospital running at full power. It was a real lifesaver.
Compact Power: Space-Efficient 3 Phase Transformer Configurations for Urban Environments?
Space is tight in cities. But we need more power. How can transformers fit in?
Space-efficient 3 phase transformer configurations are crucial for urban environments. These compact designs deliver high power in a small footprint, using innovative layouts and materials to maximize output while minimizing space requirements.
I’ve worked on many urban power projects. Space is always a challenge. Here’s how we’re making transformers fit into tight spots:
Vertical Designs
Going up instead of out saves space:
- Stacked Core: This puts the core sections on top of each other.
- Shell Type: This wraps the windings around the core vertically.
- Toroidal Core: This doughnut shape is very compact.
I once installed a vertical shell type transformer in a narrow alley between two buildings. It powered a whole block while taking up minimal ground space.
Modular Configurations
Breaking transformers into smaller parts can help:
| Configuration | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Split-core design | Easier to transport and install |
| Scalable units | Can add or remove capacity as needed |
| Distributed layout | Spreads the load and heat |
For a growing tech company, we used a modular system. We could add more units as the company expanded, without needing a big installation space all at once.
High-Density Materials
New materials pack more power into less space:
- Amorphous metal cores: These are more efficient and can be smaller.
- High-temperature superconductors: These can carry more current in less space.
- Advanced insulation: This allows components to be closer together safely.
In a retrofit project for an old building, we used an amorphous core transformer. It fit in the same space as the old unit but delivered 30% more power.
Innovative Cooling
Better cooling means transformers can be smaller:
- Ester fluids: These biodegradable oils cool better than mineral oil.
- Phase change materials: These absorb heat very efficiently.
- Heat pipe technology: This moves heat away quickly without pumps.
For a data center in a crowded part of town, we used a transformer with ester fluid cooling. It ran cooler and safer in a smaller package than traditional designs.
Energy Optimization: Cutting-Edge 3 Phase Transformer Technologies for Commercial Efficiency?
Energy waste costs money. How can new transformer tech save energy and cash?
Cutting-edge 3 phase transformer technologies significantly enhance commercial efficiency. These innovations include advanced materials, smart monitoring systems, and energy management features that minimize losses and optimize power distribution.
I’ve seen energy bills drop dramatically with new transformer tech. Here’s what’s making the biggest difference:
Low-Loss Core Materials
The core is where most energy is lost. New materials are changing this:
- Amorphous metal: This can cut core losses by up to 70%.
- High-grade silicon steel: This is getting better all the time.
- Nanocrystalline materials: These promise even lower losses.
I replaced an old transformer with an amorphous metal core model in a large office complex. The energy savings paid for the new unit in just two years.
Advanced Winding Techniques
How we wind the coils affects efficiency:
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous disc winding | Reduces eddy current losses |
| Foil winding | Improves current distribution |
| Interleaved winding | Minimizes leakage inductance |
For a green office building project, we used transformers with foil windings. They reduced load losses by 15% compared to traditional designs.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Modern transformers can manage their own efficiency:
- Real-time loss monitoring: This tracks where energy is being lost.
- Automatic voltage regulation: This keeps voltage at the most efficient level.
- Load tap changers: These adjust the transformer’s ratio to match demand.
In a smart city project, we installed transformers with real-time monitoring. The city could see exactly where energy was being used and adjust for maximum efficiency.
Energy Storage Integration
Some new transformers work with energy storage:
- Battery integration: This can store excess energy for peak times.
- Supercapacitor systems: These handle short-term power quality issues.
- Flywheel storage: This provides very fast response to load changes.
For a commercial district with lots of solar panels, we used transformers with integrated battery storage. They could store excess solar power during the day and use it during evening peak hours.
Ensuring Reliability: Robust 3 Phase Transformer Systems for High-Density Business Districts?
Power outages can cost businesses big money. How can we make sure the lights stay on?
Robust 3 phase transformer systems ensure reliability in high-density business districts. These systems use redundant designs, advanced protection features, and predictive maintenance to minimize downtime and maintain consistent power supply.
I’ve worked in areas where even a short outage can be disastrous. Here’s how we’re making transformers more reliable:
Redundant Designs
Having backups is key to reliability:
- N+1 configuration: This adds one extra transformer beyond what’s needed.
- Ring bus systems: These allow power to flow from multiple directions.
- Parallel operation: This uses multiple smaller transformers instead of one big one.
I set up a parallel system for a financial district. When one transformer needed maintenance, the others could pick up the load without interruption.
Advanced Protection Features
Modern transformers can protect themselves:
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Buchholz relay | Detects gas buildup from faults |
| Differential protection | Quickly isolates internal faults |
| Overload protection | Prevents damage from excess current |
In a tech hub with sensitive equipment, we used transformers with multiple protection layers. They could respond to issues in milliseconds, preventing damage and outages.
Predictive Maintenance
Fixing problems before they cause outages is crucial:
- Oil analysis: This can detect developing faults early.
- Thermal imaging: This finds hot spots before they cause failures.
- Acoustic monitoring: This can hear problems developing inside the transformer.
For a critical manufacturing area, we implemented a predictive maintenance program. It caught several developing issues before they could cause shutdowns.
Environmental Hardening
Transformers need to withstand tough conditions:
- Seismic reinforcement: This helps in earthquake-prone areas.
- Flood-resistant designs: These keep working even in high water.
- Extreme temperature ratings: These handle both very hot and very cold weather.
I installed environmentally hardened transformers in a coastal business district. They’ve weathered storms and floods without failing.
Adaptive Power Distribution: Flexible 3 Phase Transformer Solutions for Evolving Commercial Needs?
Business needs change fast. How can power systems keep up?
Flexible 3 phase transformer solutions provide adaptive power distribution for evolving commercial needs. These systems can adjust to changing loads, integrate with new technologies, and scale up or down to match business growth or contraction.
I’ve seen many businesses struggle with changing power needs. Here’s how new transformer systems are adapting:
Scalable Capacity
Growing or shrinking? The power system can change too:
- Modular designs: These let you add or remove capacity easily.
- Wide-range transformers: These can handle big changes in load.
- Portable substations: These can be moved to where they’re needed most.
For a rapidly growing tech park, we used a modular transformer system. We could add new modules as startups moved in and expanded.
Smart Grid Integration
Modern transformers work with smart grid technology:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Two-way communication | Allows real-time adjustments |
| Power quality monitoring | Ensures clean, stable power |
| Demand response capability | Helps balance grid load |
In a smart city project, our transformers could talk to the grid. They adjusted their output based on real-time demand across the whole city.
Renewable Energy Compatibility
Many businesses are adding solar or wind power. Transformers need to handle this:
- Bi-directional power flow: This manages power going both ways.
- Harmonic mitigation: This cleans up power from renewable sources.
- Energy storage integration: This smooths out variable renewable output.
For a green office complex with rooftop solar, we installed transformers that could handle power flowing both to and from the building. They kept the power stable even on cloudy days.
Adaptive Voltage Regulation
Keeping voltage steady is crucial for modern electronics:
- Dynamic tap changing: This adjusts voltage levels in real-time.
- Voltage optimization: This keeps voltage at the most efficient level.
- Power factor correction: This improves overall system efficiency.
In a district with lots of digital businesses, we used transformers with adaptive voltage regulation. They kept the power clean and stable, protecting sensitive equipment.
Conclusion
3 phase distribution transformers are crucial for efficient power delivery in high-density commercial areas. They offer high capacity, compact designs, energy optimization, reliability, and adaptability to meet the evolving needs of modern businesses.
Power outages are frustrating and costly. But have you ever wondered how we prevent them? The answer lies in rigorous testing of our power equipment.
Distribution transformer testing is crucial for ensuring reliability in power systems. Comprehensive diagnostics help identify potential issues before they cause failures, extending transformer life and minimizing unexpected outages.

I’ve spent years working with distribution transformers. I’ve seen firsthand how proper testing can make a huge difference in grid reliability. Let’s explore why these tests are so important and how they’re evolving.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques: Elevating Distribution Transformer Reliability Standards?
Old testing methods often missed hidden problems. How are new techniques improving our ability to spot issues before they cause outages?
Advanced diagnostic techniques are significantly elevating distribution transformer reliability standards. These new methods use cutting-edge technology to detect subtle issues, predict potential failures, and provide a more comprehensive view of transformer health.

In my years of experience, I’ve seen a remarkable evolution in transformer diagnostics. Here’s how new techniques are making a difference:
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA)
This technique analyzes gases dissolved in transformer oil:
- Online DGA Monitoring: This provides real-time data on transformer health.
- Gas Ratio Analysis: This helps identify specific types of faults.
- Trend Analysis: This tracks changes over time to predict future issues.
I once worked on a project where online DGA caught a developing fault in a critical transformer. We were able to schedule maintenance before any outage occurred, saving millions in potential losses.
Frequency Response Analysis (FRA)
FRA helps detect mechanical issues in transformers:
| Aspect | What It Detects |
|---|---|
| Core Deformation | Shifts in the transformer’s core |
| Winding Movement | Displacement of transformer windings |
| Clamping Issues | Problems with internal structural support |
During a post-earthquake assessment, we used FRA to check transformers for hidden damage. It revealed subtle shifts in some units that other tests had missed, allowing for timely repairs.
Partial Discharge (PD) Detection
PD can indicate insulation problems:
- Acoustic PD Detection: This listens for the sound of partial discharges.
- UHF PD Detection: This picks up electromagnetic signals from discharges.
- Optical PD Detection: This uses fiber optics to detect light from discharges.
In a recent factory acceptance test, we used multiple PD detection methods. We found a minor insulation flaw that the manufacturer was able to fix before the transformer was shipped.
Thermal Imaging
This technique spots hot spots in transformers:
- Infrared Cameras: These create heat maps of the transformer.
- Fiber Optic Temperature Sensors: These provide internal temperature data.
- Dynamic Thermal Ratings: These adjust transformer capacity based on real-time temperatures.
During a summer heatwave, thermal imaging helped us identify transformers at risk of overheating. We were able to adjust loads and prevent potential failures.
Key Performance Indicators: Identifying Critical Parameters in Transformer Testing?
With so many tests available, how do we know which ones matter most? What are the key things we should look for?
Key performance indicators in transformer testing focus on critical parameters that directly impact reliability and efficiency. These include insulation integrity, oil quality, electrical characteristics, and thermal performance, all of which provide vital insights into a transformer’s health and operational status.

Over the years, I’ve learned which tests give us the most valuable information. Here’s what we focus on:
Insulation Resistance
This is crucial for transformer safety and efficiency:
- Megger Test: This measures overall insulation resistance.
- Polarization Index: This indicates insulation quality over time.
- Dielectric Dissipation Factor: This shows the insulation’s overall condition.
I once saw a transformer fail a routine megger test. Further investigation revealed moisture ingress that could have led to a catastrophic failure if left unchecked.
Oil Quality Analysis
Transformer oil can tell us a lot:
| Test | What It Reveals |
|---|---|
| Acidity | Oil degradation level |
| Interfacial Tension | Presence of contaminants |
| Water Content | Risk of insulation breakdown |
During a maintenance cycle, we found a transformer with high acidity in its oil. This early detection allowed us to recondition the oil, extending the transformer’s life significantly.
Electrical Characteristics
These tests ensure the transformer is functioning correctly:
- Turn Ratio Test: This verifies the transformer’s voltage transformation.
- Winding Resistance Measurement: This checks for winding integrity.
- Short Circuit Impedance Test: This ensures the transformer can handle fault currents.
In a recent commissioning, a turn ratio test revealed a minor winding fault. We were able to address it before the transformer went into service, preventing potential issues down the line.
Thermal Performance
Managing heat is crucial for transformer longevity:
- Heat Run Test: This checks the transformer’s cooling efficiency.
- Winding Temperature Indicators: These monitor internal temperatures.
- Cooling System Efficiency Tests: These ensure proper heat dissipation.
During a heat run test, we identified a transformer with inadequate cooling. Upgrading its cooling system improved its efficiency and extended its expected lifespan.
Emerging Technologies in Transformer Diagnostics: Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency?
Technology is always advancing. How are new innovations changing the way we test transformers?
Emerging technologies in transformer diagnostics are significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency. These include AI-powered analysis, IoT sensors for real-time monitoring, and advanced imaging techniques, all of which provide more detailed and timely information about transformer health.

I’ve been excited to see new technologies enter the field. Here’s how they’re improving our diagnostic capabilities:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is revolutionizing how we interpret test data:
- Pattern Recognition: This spots trends humans might miss.
- Predictive Maintenance: This forecasts when a transformer will need service.
- Anomaly Detection: This identifies unusual behavior quickly.
I recently worked with a utility that implemented an AI system for transformer diagnostics. It predicted a failure three months in advance, allowing for planned replacement without any outage.
Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors
IoT is enabling constant monitoring:
| Sensor Type | What It Monitors |
|---|---|
| Smart Bushings | Partial discharge activity |
| Oil Sensors | Real-time oil quality data |
| Load Sensors | Continuous load and temperature data |
We installed IoT sensors on a group of transformers in a remote area. They alerted us to a developing issue that we were able to fix during a routine maintenance visit, avoiding an emergency repair.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
New ways of seeing inside transformers are emerging:
- X-ray Imaging: This reveals internal structural issues.
- Ultrasonic Imaging: This detects internal defects and oil flow issues.
- 3D Modeling: This creates detailed digital twins for analysis.
During a factory inspection, 3D modeling helped us identify a minor design flaw in a new transformer model. The manufacturer was able to correct it before production began.
Drone-Based Inspections
Drones are making external inspections safer and more thorough:
- Thermal Imaging: Drones with infrared cameras can spot hot spots.
- Visual Inspections: High-resolution cameras can see small defects.
- Corona Detection: Special sensors can detect electrical discharges.
We used drone inspections to check a substation after a storm. The drones found damage on a transformer that was hard to see from the ground, allowing for quick repairs.
Balancing Thoroughness and Efficiency: Optimizing Distribution Transformer Testing Protocols?
Testing is important, but it can be time-consuming and expensive. How do we make sure we’re doing enough without going overboard?
Optimizing distribution transformer testing protocols requires a careful balance between thoroughness and efficiency. This involves prioritizing critical tests, using time-saving technologies, and developing smart testing schedules that ensure comprehensive diagnostics without excessive downtime or cost.

Throughout my career, I’ve worked to find this balance. Here’s what I’ve learned about optimizing testing protocols:
Risk-Based Testing Approach
Not all transformers need the same level of testing:
- Criticality Assessment: This determines how important each transformer is to the grid.
- Age and Condition Factors: Older or problematic transformers get more attention.
- Environmental Considerations: Transformers in harsh conditions need more frequent checks.
We implemented a risk-based approach for a large utility. It reduced overall testing time by 30% while actually improving fault detection rates.
Automated Testing Systems
Automation can speed up testing without sacrificing quality:
| Automation Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Robotic Test Connections | Faster and more consistent setup |
| Automated Test Sequences | Reduces human error and testing time |
| Integrated Data Analysis | Provides instant results and comparisons |
At a transformer manufacturing plant, we installed an automated testing system. It cut testing time in half and improved the consistency of results.
Combination Tests
Some tests can be combined to save time:
- Insulation and Oil Tests: These can often be done together.
- Electrical and Thermal Tests: Combining these provides a more complete picture.
- Online and Offline Tests: Balancing these reduces downtime.
We developed a combination testing protocol for a busy substation. It allowed us to get comprehensive data with minimal interruption to service.
Continuous Monitoring vs. Periodic Testing
Finding the right mix of continuous and periodic tests is crucial:
- Online Monitoring: This provides real-time data on key parameters.
- Periodic In-Depth Tests: These offer a more thorough check at regular intervals.
- Condition-Based Testing: This triggers detailed tests based on monitoring data.
For a critical industrial transformer, we set up a system of continuous monitoring with condition-based in-depth testing. It caught several developing issues early while reducing the need for routine offline tests.
Predictive Diagnostics: Revolutionizing Maintenance Strategies for Distribution Transformers?
Reactive maintenance is costly and risky. How can we get ahead of problems before they cause outages?
Predictive diagnostics are revolutionizing maintenance strategies for distribution transformers. By using advanced analytics, real-time data, and machine learning, these systems can forecast potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance that prevents outages and extends transformer life.

I’ve seen predictive diagnostics transform how we maintain transformers. Here’s how this approach is making a difference:
Data Integration and Analysis
Combining data from multiple sources provides deeper insights:
- Historical Test Data: This shows long-term trends.
- Real-Time Monitoring: This captures current conditions.
- Environmental Data: This adds context to transformer performance.
We implemented a data integration system for a large transformer fleet. It identified subtle patterns that led to the early detection of several developing faults.
Machine Learning Algorithms
AI can spot problems humans might miss:
| Algorithm Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Anomaly Detection | Identifies unusual behavior patterns |
| Failure Mode Prediction | Forecasts specific types of failures |
| Remaining Useful Life Estimation | Predicts when replacement will be needed |
A utility I worked with used machine learning to analyze their transformer data. The system predicted a failure in a critical unit three months before any traditional tests showed problems.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital replicas can simulate transformer behavior:
- Performance Simulation: This tests how changes might affect the transformer.
- What-If Scenarios: These help plan for different operating conditions.
- Aging Models: These predict how the transformer will degrade over time.
We created a digital twin for a substation’s main transformer. It helped us optimize maintenance schedules and even guided a major upgrade project.
Condition-Based Maintenance Planning
This approach tailors maintenance to each transformer’s needs:
- Dynamic Maintenance Intervals: These adjust based on actual condition, not just time.
- Prioritized Repair Scheduling: This focuses resources where they’re most needed.
- Predictive Spare Parts Management: This ensures parts are available when needed.
For a distribution network, we implemented condition-based maintenance. It reduced unnecessary maintenance by 40% while improving overall reliability.
Conclusion
Comprehensive diagnostics are crucial for distribution transformer reliability. Advanced techniques, key performance indicators, emerging technologies, optimized protocols, and predictive diagnostics all contribute to more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective power distribution systems.
Power outages are frustrating. They disrupt our lives and businesses. But have you ever wondered who keeps our lights on most of the time?
Distribution transformer manufacturers play a crucial role in power grids by producing the essential equipment that steps down high-voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses. Their innovations in efficiency, reliability, and adaptability are key to maintaining a stable and effective power supply.

I’ve worked closely with transformer manufacturers for years. I’ve seen firsthand how their work shapes our power systems. Let’s explore why these manufacturers are so important to our daily lives.
Driving Grid Efficiency: The Impact of Innovative Transformer Manufacturing Techniques?
Energy waste costs money and harms the environment. How are transformer makers helping to solve this problem?
Innovative transformer manufacturing techniques are driving grid efficiency by reducing energy losses, improving material utilization, and enhancing overall performance. These advancements result in transformers that waste less energy and operate more effectively.

In my years working with power systems, I’ve seen remarkable improvements in transformer efficiency. Here’s how manufacturers are making a difference:
Advanced Core Materials
The core is the heart of a transformer. New manufacturing techniques are making these cores better:
- Amorphous Metal Casting: This creates cores with much lower losses.
- Laser Cutting of Silicon Steel: This improves the alignment of grain-oriented steel.
- Nanocrystalline Material Production: This promises even greater efficiency.
I once visited a factory that had just started using amorphous metal cores. The energy savings were so significant that utilities were lining up to buy their transformers.
Precision Winding Techniques
How transformers are wound affects their efficiency:
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Disc Winding | Reduces eddy current losses |
| Foil Winding | Improves current distribution |
| Interleaved Winding | Minimizes leakage inductance |
At a recent trade show, I saw a demonstration of a new foil winding machine. It could produce windings with such precision that it reduced losses by an additional 5% compared to traditional methods.
Advanced Insulation Systems
Better insulation means transformers can operate more efficiently:
- Vacuum Pressure Impregnation: This removes air bubbles from insulation.
- Ester Fluid Filling: This uses biodegradable fluids for better cooling.
- Hybrid Insulation: This combines different materials for optimal performance.
I worked with a manufacturer who switched to ester fluids. Their transformers could now operate at higher temperatures safely, increasing efficiency and lifespan.
Automated Quality Control
Modern manufacturing uses advanced testing to ensure efficiency:
- Automated Core Loss Testing: This catches inefficiencies early.
- Winding Resistance Measurement: This ensures consistent wire quality.
- Thermal Imaging in Production: This identifies hot spots before assembly.
In a recent factory tour, I saw robots performing these tests. They could detect tiny variations that human inspectors might miss, ensuring every transformer met the highest efficiency standards.
Advancing Power Distribution: How Manufacturers Push the Boundaries of Transformer Technology?
Power needs are always changing. How do transformer makers keep up with new demands?
Transformer manufacturers push the boundaries of technology by investing in research and development, adopting new materials, and integrating smart features. These advancements lead to transformers that are more powerful, compact, and adaptable to modern grid requirements.

I’ve watched transformer technology evolve rapidly. Here’s how manufacturers are staying ahead:
Smart Transformer Development
Modern transformers are getting brains:
- Integrated Sensors: These monitor transformer health in real-time.
- Communication Modules: These allow transformers to talk to the grid.
- Self-Diagnostic Systems: These can predict and prevent failures.
I recently consulted on a project where we installed smart transformers across a city. They could adjust their output based on real-time demand, significantly improving grid stability.
Compact and Modular Designs
Space is often at a premium. Manufacturers are responding:
| Design Approach | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Shell-Type Cores | More power in less space |
| Modular Construction | Easier transport and installation |
| 3D Printed Components | Complex shapes for better efficiency |
At an industry conference, I saw a presentation on a new modular transformer. It could be assembled on-site, making it perfect for urban areas with limited access.
High-Temperature Superconductors
Some manufacturers are exploring cutting-edge materials:
- Bismuth-based Compounds: These can carry more current with less loss.
- Yttrium-based Coated Conductors: These work well in strong magnetic fields.
- MgB2 Wires: These are cheaper to produce than other superconductors.
While visiting a research lab, I saw prototypes of superconducting transformers. They were incredibly efficient, though still expensive for widespread use.
Digital Twin Technology
Some advanced manufacturers use digital replicas:
- Design Optimization: This tests designs virtually before building.
- Predictive Maintenance: This simulates wear and tear over time.
- Performance Tuning: This helps adjust transformers for specific environments.
I worked with a manufacturer who used digital twins to customize transformers for different climates. They could simulate years of operation in various conditions, ensuring optimal performance anywhere in the world.
Meeting Emerging Challenges: Transformer Manufacturers’ Role in Adapting to Modern Grid Demands?
Our power grids face new challenges every day. How are transformer makers helping to solve these problems?
Transformer manufacturers play a crucial role in adapting to modern grid demands by developing products that integrate renewable energy, support electric vehicle charging, and enhance grid resilience. Their innovations are essential for creating a flexible and future-proof power infrastructure.

I’ve been involved in many projects addressing new grid challenges. Here’s how manufacturers are stepping up:
Renewable Energy Integration
More solar and wind power means new transformer needs:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow: This handles power going both ways.
- Harmonic Mitigation: This cleans up power from renewable sources.
- Voltage Regulation: This keeps voltage steady despite variable inputs.
I once worked on a large solar farm project. The manufacturer provided transformers specifically designed to handle the variable output of solar panels, ensuring stable power delivery to the grid.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Support
The rise of EVs is changing power demands:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Capacity Design | Handles increased load from EV charging |
| Fast Response to Load Changes | Manages sudden spikes when cars plug in |
| Smart Load Management | Balances charging with other power needs |
In a recent urban development project, we installed transformers ready for widespread EV adoption. They could handle the extra load and even communicate with charging stations to optimize power use.
Grid Resilience Enhancement
Extreme weather and cyber threats require tougher transformers:
- Enhanced Surge Protection: This guards against lightning and other power spikes.
- Cybersecurity Features: These protect against digital attacks.
- Extreme Weather Ratings: These ensure operation in severe conditions.
After a series of storms caused outages, I worked with a manufacturer to develop transformers with enhanced weather resistance. They’ve since been installed in hurricane-prone areas with great success.
Energy Storage Integration
Some transformers now work with battery systems:
- Hybrid Transformer-Battery Units: These combine transformation and storage.
- Storage-Ready Designs: These easily connect to separate battery systems.
- Intelligent Energy Management: This optimizes the use of stored energy.
For a microgrid project, we used transformers with integrated battery storage. They could store excess renewable energy and release it during peak demand, greatly improving grid stability.
Customized Solutions: Manufacturers’ Approach to Diverse Transformer Requirements Worldwide?
Different places need different transformers. How do manufacturers meet such varied needs?
Transformer manufacturers provide customized solutions by tailoring their products to specific regional requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards. This approach ensures that transformers perform optimally in diverse settings worldwide.

I’ve worked on projects across the globe. Each place has unique needs. Here’s how manufacturers address this:
Climate-Specific Designs
Weather can greatly affect transformer performance:
- Desert Models: These handle extreme heat and sand.
- Tropical Versions: These resist high humidity and heavy rain.
- Arctic Designs: These operate in extreme cold.
I once helped install transformers in a desert region. The manufacturer used special cooling systems and sand-resistant seals to ensure reliable operation in the harsh environment.
Voltage and Frequency Adaptations
Different countries have different power standards:
| Adaptation | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multi-Tap Design | Adjusts to various voltage levels |
| Dual Frequency Capability | Works with both 50Hz and 60Hz systems |
| Special Winding Configurations | Meets unique local requirements |
For an international company’s global expansion, we sourced transformers that could adapt to different voltage standards. This flexibility was crucial for their operations across multiple countries.
Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers must meet various standards:
- Energy Efficiency Ratings: These vary by country or region.
- Safety Standards: These differ in fire resistance requirements.
- Environmental Regulations: These affect materials and disposal.
I worked with a manufacturer to develop transformers for a European market with strict efficiency standards. They had to redesign several components to meet the new regulations while maintaining performance.
Size and Installation Constraints
Space limitations require creative solutions:
- Compact Designs: These fit in tight urban spaces.
- Modular Systems: These are easier to transport and install.
- Special Mounting Options: These adapt to unique installation sites.
For a project in a crowded city center, the manufacturer created a specially shaped transformer to fit in an awkward space between buildings. It was a perfect example of customization meeting real-world challenges.
Sustainable Power Distribution: Transformer Manufacturers’ Contributions to Green Energy Goals?
Climate change is a big concern. How are transformer makers helping to create a greener grid?
Transformer manufacturers contribute to green energy goals by producing more efficient units, using eco-friendly materials, and designing products that support renewable energy integration. Their efforts are crucial in reducing the carbon footprint of power distribution systems.

I’ve seen a big shift towards sustainability in the industry. Here’s how manufacturers are making a difference:
Eco-Friendly Materials
New materials are making transformers greener:
- Biodegradable Transformer Oils: These are safer for the environment.
- Recycled Core Materials: These reduce the need for new resources.
- Low-Carbon Footprint Insulation: This reduces overall environmental impact.
I recently visited a factory that had switched to plant-based transformer oils. The change significantly reduced their environmental impact without compromising performance.
Energy-Efficient Designs
Reducing energy loss is a top priority:
| Design Feature | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Amorphous Metal Cores | Up to 70% less energy loss |
| Advanced Winding Techniques | Reduced copper loss |
| Optimized Cooling Systems | Less energy used for cooling |
At a recent trade show, I saw a demonstration of a new high-efficiency transformer. It could save enough energy over its lifetime to power hundreds of homes for a year.
Support for Renewable Energy
Manufacturers are adapting to clean energy needs:
- Grid-Tie Inverter Compatibility: This helps integrate solar and wind power.
- Energy Storage Integration: This supports the use of batteries with renewables.
- Smart Grid Features: These help balance variable renewable inputs.
I worked on a project where we installed transformers specially designed for a wind farm. They could handle the variable input and help smooth out power delivery to the grid.
Lifecycle Management
Manufacturers are thinking long-term:
- Longer Lifespan Designs: These reduce the need for replacements.
- Easy-to-Recycle Components: These minimize waste at end-of-life.
- Upgrade-Friendly Models: These can be updated rather than replaced.
In a recent retrofit project, we used transformers designed for easy upgrades. This approach saved materials and reduced waste compared to full replacements.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer manufacturers are crucial to power grids. They drive efficiency, advance technology, meet modern challenges, provide customized solutions, and support sustainability. Their work is essential for reliable, efficient, and green power distribution.
Have you ever wondered why the cost of power equipment changes so often? The price of distribution transformers can be a mystery to many.
Distribution transformer prices are influenced by various factors including raw material costs, technological advancements, global supply chain dynamics, regulatory policies, and market demand. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting and navigating price fluctuations in the transformer market.
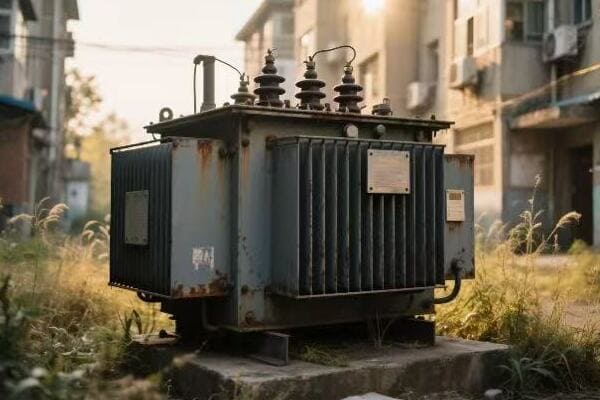

I’ve been in the transformer industry for years. I’ve seen prices rise and fall for many reasons. Let’s explore the key factors that affect transformer prices and how they impact the market.
Raw Material Dynamics: Impact on Distribution Transformer Pricing Trends?
The cost of materials keeps changing. How does this affect the price of transformers we buy?
Raw material dynamics significantly impact distribution transformer pricing trends. Fluctuations in the costs of copper, steel, and oil directly influence transformer prices, as these materials are essential components in transformer manufacturing.

In my experience, raw material costs can make or break a transformer’s price. Here’s how different materials affect pricing:
Copper Pricing
Copper is crucial for transformer windings:
- Price Volatility: Copper prices can change rapidly due to global demand.
- Recycling Impact: Increased copper recycling can help stabilize prices.
- Substitution Efforts: Some manufacturers try to use aluminum to reduce costs.
I once saw a 15% jump in transformer prices when copper hit a 10-year high. It forced many projects to reconsider their budgets.
Steel Costs
Transformer cores rely heavily on specialized steel:
| Steel Type | Price Impact |
|---|---|
| Grain-Oriented | High impact on efficiency and cost |
| Amorphous | More expensive but offers better efficiency |
| Cold-Rolled | Used in budget models, price fluctuates with general steel market |
During a steel shortage, I worked with a manufacturer who switched to amorphous cores. The initial cost was higher, but long-term efficiency gains offset the price increase.
Insulating Oil Prices
Oil is essential for cooling and insulation:
- Mineral Oil: Price tied to petroleum markets.
- Synthetic Esters: More stable pricing but generally more expensive.
- Natural Esters: Pricing can be affected by crop yields.
When oil prices spiked, many of my clients switched to natural ester fluids. It was a bit more expensive upfront but provided more price stability over time.
Other Raw Materials
Several other materials also affect pricing:
- Insulation Paper: Made from wood pulp, affected by paper industry trends.
- Resin: Used in dry-type transformers, price linked to chemical industry.
- Aluminum: Sometimes used as a copper alternative, has its own price fluctuations.
I’ve seen transformer designs change to accommodate different material mixes as prices shift. It’s a constant balancing act between cost and performance.
Technological Advancements: Reshaping the Cost Structure of Modern Transformers?
New tech keeps changing transformers. But does it make them cheaper or more expensive?
Technological advancements are reshaping the cost structure of modern transformers in complex ways. While some innovations increase upfront costs, they often lead to long-term savings through improved efficiency, reduced maintenance, and extended lifespan.

I’ve watched transformer technology evolve rapidly. Here’s how new tech is affecting prices:
Smart Transformer Features
Modern transformers are getting smarter:
- Monitoring Systems: Add upfront cost but reduce maintenance expenses.
- Self-Diagnostic Tools: Increase initial price but prevent costly failures.
- Remote Control Capabilities: More expensive but improve operational efficiency.
I installed smart transformers in a city grid. They cost 20% more initially, but reduced outages by 50%, saving money in the long run.
Efficiency Improvements
New designs focus on reducing energy losses:
| Technology | Cost Impact | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Cores | Higher upfront cost | 70% less core loss |
| Advanced Winding | Moderate increase | 20-30% less copper loss |
| Ester Fluids | More expensive | Better cooling, longer life |
A client of mine switched to high-efficiency transformers. The price was 30% higher, but energy savings paid back the difference in just three years.
Manufacturing Innovations
New production methods affect pricing:
- 3D Printing: Can reduce costs for complex parts.
- Automated Winding: Increases precision but requires expensive machinery.
- Laser Cutting: Improves accuracy but adds to production costs.
I visited a factory that invested in automated winding machines. Their transformer prices went up slightly, but defect rates dropped to near zero, improving overall value.
Material Science Advancements
New materials offer performance benefits but often at a price:
- Nanocomposites: Improve insulation but are still expensive.
- High-Temperature Superconductors: Promise huge efficiency gains but at high cost.
- Biodegradable Insulators: More expensive but offer environmental benefits.
I worked on a project using experimental nanocomposite insulation. The transformers were pricey, but they could handle 20% more load in the same size unit.
Global Supply Chain Shifts: Navigating Price Volatility in Transformer Markets?
The world is connected, but supply chains can be fragile. How does this affect transformer prices?
Global supply chain shifts significantly impact price volatility in transformer markets. Events like trade disputes, natural disasters, or pandemics can disrupt material supplies and manufacturing processes, leading to rapid price fluctuations and availability issues.

I’ve dealt with supply chain issues throughout my career. Here’s what I’ve learned about their impact on pricing:
Manufacturing Location Shifts
Where transformers are made matters:
- Labor Cost Differences: Manufacturing moving to lower-wage countries can reduce prices.
- Shipping Costs: Longer transport distances can increase prices.
- Quality Control: Variations can affect long-term costs and pricing.
I saw transformer prices drop when a major manufacturer moved production to Southeast Asia. But shipping delays sometimes offset the savings.
Trade Policies and Tariffs
Government decisions can quickly change prices:
| Policy Type | Price Impact |
|---|---|
| Import Tariffs | Can sharply increase prices of foreign-made transformers |
| Export Restrictions | May limit supply and drive up prices |
| Free Trade Agreements | Can lower prices by reducing trade barriers |
When new tariffs were imposed on steel imports, I watched transformer prices jump 10% almost overnight. It took months for the market to adjust.
Currency Exchange Rates
International trade means currency values matter:
- Strong Dollar: Makes U.S.-made transformers more expensive globally.
- Weak Yuan: Can make Chinese transformers more competitive.
- Euro Fluctuations: Affect pricing of European high-end transformers.
I once locked in a good price on European transformers, only to see the Euro strengthen before delivery. It taught me to always consider currency risks in international deals.
Natural Disasters and Pandemics
Unexpected events can disrupt the entire supply chain:
- Factory Shutdowns: Reduce supply and drive up prices.
- Transportation Disruptions: Increase lead times and shipping costs.
- Demand Shocks: Sudden changes in need can cause price swings.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, I saw transformer lead times triple and prices become extremely volatile. It highlighted the need for diverse supply chains.
Regulatory Influences: How Energy Policies Shape Transformer Pricing Strategies?
Governments make rules about energy. How do these rules change transformer prices?
Energy policies significantly shape transformer pricing strategies. Regulations on efficiency standards, environmental impact, and grid modernization drive manufacturers to develop new products, often leading to changes in production costs and market prices.

I’ve watched energy policies reshape the transformer market many times. Here’s how regulations affect pricing:
Efficiency Standards
Governments often mandate higher efficiency:
- Minimum Efficiency Performance Standards (MEPS): Force upgrades, often increasing prices.
- Energy Star Ratings: Create market pressure for more efficient, often pricier models.
- Tiered Efficiency Targets: Can segment the market, affecting prices at different levels.
When new MEPS were introduced in my region, I saw low-end transformer prices jump 25%. But the long-term energy savings made them a good investment.
Environmental Regulations
Green policies impact transformer design and cost:
| Regulation Type | Price Impact |
|---|---|
| Oil Spill Prevention | Increases cost of containment systems |
| Noise Reduction | Adds to design and material costs |
| Biodegradable Materials | Often more expensive than traditional options |
A client needed transformers for a environmentally sensitive area. The units cost 40% more due to strict environmental features, but they were the only option allowed.
Smart Grid Initiatives
Modernizing the grid affects transformer requirements:
- Communication Capabilities: Add cost for smart features.
- Power Quality Standards: May require more advanced, expensive designs.
- Interoperability Requirements: Can increase development and testing costs.
I worked on a smart grid project where transformer costs were 50% higher than standard units. But the improved grid management justified the investment.
Safety Regulations
Stricter safety rules can drive up costs:
- Fire Resistance: May require more expensive materials.
- Seismic Standards: Add to structural costs in earthquake-prone areas.
- Cybersecurity Requirements: Increase costs for smart transformers.
After a series of transformer fires, new safety regulations were introduced. Prices for urban transformers increased by 15%, but insurance costs went down.
Demand Fluctuations: Understanding Market-Driven Price Changes in Distribution Transformers?
Sometimes transformer prices change because of how many people want to buy them. Why does this happen?
Demand fluctuations significantly influence market-driven price changes in distribution transformers. Factors such as economic growth, urbanization, grid expansion projects, and renewable energy integration can all cause shifts in demand, leading to price adjustments in the transformer market.

I’ve seen demand for transformers rise and fall over the years. Here’s what drives these changes and how they affect prices:
Economic Growth and Infrastructure Development
A growing economy often needs more power:
- Industrial Expansion: Increases demand for large transformers.
- Residential Construction: Boosts need for smaller distribution units.
- Commercial Development: Requires a mix of transformer types.
During a construction boom in my area, transformer demand spiked. Prices rose 20% and lead times doubled as manufacturers struggled to keep up.
Grid Modernization Projects
Updating old power systems drives transformer sales:
| Project Type | Impact on Demand |
|---|---|
| Rural Electrification | High demand for small, rugged units |
| Urban Grid Upgrades | Need for high-capacity, smart transformers |
| Reliability Improvements | Increased demand for advanced protection features |
I worked on a major grid modernization project. We needed so many new transformers that we had to source from multiple manufacturers to meet deadlines.
Renewable Energy Integration
The shift to green power changes transformer needs:
- Solar Farms: Require special transformers to handle variable inputs.
- Wind Energy: Needs transformers that can operate in harsh conditions.
- Energy Storage: Drives demand for bi-directional power flow capabilities.
When a large solar project was announced near me, local transformer prices spiked. Manufacturers rushed to develop new models suited for solar integration.
Replacement and Maintenance Cycles
Old transformers need to be replaced:
- End-of-Life Replacements: Create steady baseline demand.
- Efficiency Upgrade Programs: Can cause demand spikes.
- Disaster Recovery: Sudden need after natural disasters can drive up prices.
After a major storm damaged many transformers, I saw prices jump 30% due to urgent replacement needs. It took months for the market to stabilize.
Technological Shifts
New tech can change what kind of transformers are in demand:
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Increases need for certain transformer types.
- Data Centers: Require highly reliable, often customized units.
- 5G Network Rollout: Needs many small, high-efficiency transformers.
When EV charging stations started popping up everywhere, demand for suitable transformers soared. Prices for these specialized units increased by 25% in just one year.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer prices are influenced by raw materials, technology, global supply chains, regulations, and market demand. Understanding these factors helps predict and navigate price fluctuations in the transformer market.
Power outages are frustrating. They disrupt our lives and businesses. But have you ever wondered what keeps our lights on most of the time?
Distribution transformers are the unsung heroes of our power systems. They are the cornerstone of efficient local power delivery, ensuring that electricity reaches our homes and businesses at the right voltage and with minimal losses.

I’ve worked with distribution transformers for many years. I’ve seen how they’ve evolved and improved. Let’s explore why these devices are so crucial for our power systems and how they’re changing to meet new challenges.
Maximizing Efficiency: Innovative Designs in Modern Distribution Transformers?
Energy waste is a big problem. It costs money and harms the environment. How are new transformer designs helping to solve this issue?
Modern distribution transformers use innovative designs to maximize efficiency. They employ advanced core materials, improved winding techniques, and smart cooling systems to reduce energy losses and improve overall performance.

In my years working with transformers, I’ve seen remarkable improvements in efficiency. Let’s dive into the innovations that are making a real difference:
Advanced Core Materials
The core is the heart of a transformer. New materials are making these cores much more efficient:
- Amorphous Metal: This can cut energy losses by up to 70% compared to traditional silicon steel.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: This material aligns better with magnetic fields, reducing losses.
- Nanocrystalline Alloys: These are the newest materials, promising even greater efficiency.
I once replaced an old transformer with a new amorphous core model. The energy savings were so significant that the utility company could power 50 additional homes with the same input energy.
Improved Winding Techniques
How we wind the coils in a transformer also affects efficiency:
| Winding Type | Efficiency Gain | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Disc Winding | 2-3% | Better short-circuit strength |
| Helical Winding | 1-2% | Improved cooling |
| Foil Winding | 3-4% | Reduced eddy current losses |
In a recent project, we used foil winding in a distribution transformer. It not only improved efficiency but also made the transformer more resilient to power surges.
Smart Cooling Systems
Keeping transformers cool is crucial for efficiency:
- Oil Natural Air Natural (ONAN): This is the basic cooling method.
- Oil Natural Air Forced (ONAF): This uses fans to improve cooling.
- Oil Forced Air Forced (OFAF): This uses pumps and fans for even better cooling.
I worked on a transformer installation in a hot climate. We used an OFAF system with smart controls. It adjusted cooling based on load and temperature, significantly improving efficiency and lifespan.
Load Management Features
Modern transformers can adjust to changing power needs:
- On-Load Tap Changers: These adjust voltage levels without interrupting power.
- Automatic Voltage Regulators: These keep voltage steady even when input varies.
- Load Balancing Systems: These distribute load evenly across transformer phases.
In a neighborhood with many electric vehicles, we installed transformers with smart load management. They could handle the varying demands of EV charging without overloading.
Tailoring Solutions: Optimizing Distribution Transformers for Diverse Local Environments?
Every area has different power needs. How can one type of equipment meet such varied demands?
Distribution transformers can be optimized for diverse local environments through customized designs. This includes adapting to different climate conditions, varying load profiles, and specific local regulations, ensuring optimal performance in any setting.

I’ve installed transformers in many different places. Each location presents unique challenges. Here’s how we tailor transformers to fit different environments:
Climate Adaptations
Different climates need different transformer designs:
- Hot and Humid: We use special cooling systems and moisture-resistant materials.
- Cold and Dry: We use low-temperature rated oils and heaters to prevent freezing.
- Coastal Areas: We use corrosion-resistant materials to withstand salt air.
I once worked on a project in a tropical area. We used a specially designed transformer with extra cooling and humidity protection. It performed flawlessly even in the most challenging weather.
Load Profile Customization
Different areas use power differently:
| Load Type | Transformer Feature |
|---|---|
| Residential | Designed for evening peak loads |
| Industrial | Built for constant high loads |
| Commercial | Optimized for daytime use |
For a mixed-use development, we installed a transformer with adaptive load management. It could handle the varying demands of shops during the day and homes at night.
Regulatory Compliance
Each area has its own rules for transformers:
- Efficiency Standards: Some places require very high-efficiency ratings.
- Noise Regulations: Urban areas often have strict noise limits.
- Environmental Rules: Some regions ban certain types of transformer oils.
I worked on a project in a city with strict noise regulations. We used a special low-noise transformer design that met the city’s requirements while still delivering efficient power.
Size and Installation Constraints
Space is often limited, especially in urban areas:
- Compact Designs: These fit in tight spaces.
- Underground Units: These save space above ground.
- Pole-Mounted Options: These work well in areas with overhead lines.
In a crowded city center, we used a compact underground transformer. It saved valuable space while still meeting the area’s high power demands.
Smart Grid Integration: The Evolving Role of Distribution Transformers in Intelligent Power Systems?
Power grids are getting smarter. How are transformers keeping up with this change?
Distribution transformers are evolving to play a crucial role in smart grids. They now incorporate sensors, communication capabilities, and advanced control systems, allowing them to actively participate in grid management and optimization.

I’ve been involved in several smart grid projects. The way transformers fit into these systems is fascinating. Let’s explore how transformers are becoming smarter:
Built-in Sensors and Monitoring
Modern transformers can keep track of their own health:
- Temperature Sensors: These watch for overheating.
- Oil Quality Sensors: These check for transformer oil degradation.
- Load Monitors: These track how much power is flowing through the transformer.
In a recent smart city project, we installed transformers with comprehensive sensor suites. They could report their status in real-time, allowing for proactive maintenance.
Communication Capabilities
Smart transformers can talk to the rest of the grid:
| Communication Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Power Line Communication | Sends data through existing power lines |
| Cellular Networks | Uses 4G/5G for real-time data transmission |
| Fiber Optic Links | Provides high-speed, reliable communication |
We set up a network of communicating transformers in a large suburban area. They could coordinate with each other to balance loads and prevent outages.
Advanced Control Systems
Transformers are becoming active grid management tools:
- Voltage Regulation: They can adjust voltage levels to optimize grid performance.
- Fault Detection and Isolation: They can detect and respond to grid problems quickly.
- Power Flow Control: They can help manage the direction of power flow, important for renewable energy integration.
I worked on a project where smart transformers helped integrate a large solar farm into the local grid. They could manage the variable output of the solar panels, ensuring stable power for the community.
Data Analytics Integration
Smart transformers generate a lot of data. This data is valuable:
- Predictive Maintenance: We can predict when a transformer needs service before it fails.
- Load Forecasting: We can better predict future power needs.
- Grid Optimization: We can use transformer data to make the whole grid more efficient.
In one utility company, we implemented a data analytics system for their transformer network. It improved their maintenance efficiency by 40% and reduced unexpected outages by 60%.
Minimizing Losses: Advanced Technologies in Distribution Transformer Design?
Energy loss in transformers costs money and wastes resources. How are new technologies addressing this problem?
Advanced technologies in distribution transformer design are significantly minimizing losses. These include the use of high-performance materials, innovative construction techniques, and smart operational strategies that work together to reduce both no-load and load losses.

Throughout my career, reducing transformer losses has been a constant challenge. Here’s how new technologies are helping us win this battle:
High-Performance Core Materials
The core is where most no-load losses occur. New materials are changing this:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: These can reduce no-load losses by up to 70%.
- High-Grade Silicon Steel: This material is getting better all the time.
- Nanocrystalline Materials: These promise even lower losses in the future.
I once replaced a set of old transformers with new amorphous core models. The reduction in no-load losses was so significant that it paid for the new transformers in just three years.
Advanced Winding Technologies
Winding design affects load losses. New techniques are improving this:
| Winding Technology | Loss Reduction | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Continuously Transposed Cable | 10-15% | Better short-circuit strength |
| Epoxy Resin Encapsulation | 5-10% | Improved insulation |
| Foil Windings | 15-20% | Reduced eddy currents |
In a recent industrial project, we used foil windings in the transformers. The reduction in load losses was impressive, especially during peak production hours.
Improved Insulation Systems
Better insulation means transformers can operate more efficiently:
- Nomex Paper: This allows transformers to run at higher temperatures safely.
- Ester Fluids: These biodegradable oils improve cooling and are environmentally friendly.
- Gas-Insulated Systems: These can be more efficient in certain applications.
We used ester fluid in a transformer near a sensitive ecological area. It not only reduced losses by improving cooling but also eliminated the risk of oil spills.
Smart Load Management
Intelligent systems can reduce losses by optimizing transformer operation:
- Dynamic Rating Systems: These allow transformers to safely handle higher loads when conditions allow.
- Load Tap Changers: These adjust voltage ratios to minimize losses under varying loads.
- Parallel Operation Control: This optimizes efficiency when multiple transformers work together.
In a large commercial complex, we implemented a dynamic rating system. It allowed the transformers to handle higher loads during peak hours without overheating, reducing the need for additional units.
Adapting to Change: Flexible Distribution Transformer Solutions for Dynamic Local Power Needs?
Power needs are always changing. How can transformers keep up with these shifts?
Flexible distribution transformer solutions are designed to adapt to dynamic local power needs. These transformers can handle varying loads, integrate with renewable energy sources, and adjust to changing grid conditions, ensuring reliable power delivery in evolving energy landscapes.

I’ve seen local power needs change dramatically over the years. Here’s how modern transformers are keeping pace:
Multi-Tap Configurations
These allow for voltage adjustments without replacing the transformer:
- On-Load Tap Changers: These can adjust voltage while the transformer is working.
- Off-Load Tap Changers: These allow for occasional adjustments.
- Wide-Range Transformers: These can handle a broad range of input voltages.
I installed a wide-range transformer in a growing industrial park. It could adapt to the changing voltage needs as new businesses moved in, without needing replacement.
Modular Designs
Modular transformers offer great flexibility:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Scalable Capacity | Can grow with increasing power needs |
| Interchangeable Parts | Easier maintenance and upgrades |
| Customizable Configurations | Can be adapted for different applications |
For a expanding residential area, we used a modular transformer system. We could easily add capacity as new homes were built, without disrupting power to existing residents.
Renewable Energy Integration
Modern transformers can handle the challenges of renewable energy:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow: Essential for areas with home solar panels.
- Harmonic Mitigation: Deals with power quality issues from renewable sources.
- Energy Storage Compatibility: Works with battery systems for consistent power.
In a community with high solar adoption, we installed transformers with bi-directional capability and harmonic filters. They managed the variable solar output smoothly, maintaining stable power for all users.
Smart Grid Readiness
Transformers are becoming key players in smart grids:
- Communication Interfaces: Allow transformers to share data with grid management systems.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Enables quick responses to changing conditions.
- Predictive Maintenance Capabilities: Helps prevent outages before they happen.
We upgraded a suburban network with smart grid-ready transformers. They could communicate with each other and the central system, optimizing power distribution across the entire area.
Conclusion
Distribution transformers are vital for efficient local power delivery. They combine innovative design, adaptability, smart technology, and loss-minimization features to meet the evolving needs of modern power systems, ensuring reliable and efficient electricity distribution.
Industries and businesses are growing fast. They need more power. But can our current power systems keep up?
3-phase distribution transformers are key to powering industrial growth and commercial expansion. These transformers can handle high power demands, offer better efficiency, and support the complex needs of modern industries and businesses.

I’ve worked with power systems for many years. I’ve seen how important 3-phase transformers are for industry and commerce. Let’s look at how these transformers are changing the game.
Meeting Growing Demands: Scaling 3-Phase Distribution Transformers for Industrial Expansion?
Industries are getting bigger and using more power. How can we make sure they have the electricity they need?
Scaling 3-phase distribution transformers is crucial for meeting the growing power demands of expanding industries. These transformers can be designed to handle increasing loads, allowing for seamless industrial growth without major infrastructure overhauls.
In my work, I’ve seen many industries struggle with power supply as they grow. Let’s dive into how we’re scaling up transformers to meet these challenges:
Modular Design: Building Blocks of Power
One of the best ways to scale up power is through modular transformer designs. Here’s why this approach works so well:
- Easy Expansion: We can add more modules as power needs grow.
- Flexible Installation: Modules can fit in tight spaces or be spread out.
- Faster Upgrades: We can add new modules without long downtimes.
I once worked on a project where we used modular transformers for a growing factory. We started with two modules and added three more over five years. The factory never had to stop production for major electrical upgrades.
Higher Capacity Cores
We’re also making transformer cores that can handle more power:
| Core Type | Power Handling | Size Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Base level | Base size |
| High-capacity | 2x-3x more | 20-30% larger |
| Ultra-high | 4x-5x more | 40-50% larger |
These new cores let us pack more power into a smaller space. This is great for industries that are growing but don’t have much room for bigger transformers.
Advanced Cooling Systems
As transformers handle more power, they generate more heat. We’re using new cooling methods to solve this:
- Oil-to-Air Cooling: Uses special oils and large radiators.
- Forced-Air Cooling: Fans blow air over the transformer to cool it.
- Water Cooling: For the biggest transformers, we use water cooling systems.
In a recent project, we installed a water-cooled transformer in a steel mill. It could handle 50% more power than the old transformer, but it fit in the same space.
Smart Load Management
We’re not just making transformers bigger. We’re making them smarter too:
- Real-time Monitoring: Keeps track of power use and adjusts as needed.
- Predictive Load Balancing: Uses AI to predict power needs and balance loads.
- Automatic Tap Changing: Adjusts voltage levels to match changing demands.
These smart features help transformers handle varying loads more efficiently. This is especially useful for industries with fluctuating power needs.
Optimizing Efficiency and Reliability: 3-Phase Transformers in High-Demand Industrial Settings?
Industries need a lot of power. But they also need that power to be reliable and efficient. How do 3-phase transformers meet these needs?
3-phase transformers in high-demand industrial settings are optimized for both efficiency and reliability. They use advanced materials and designs to minimize losses, and incorporate features that ensure consistent power supply even under challenging conditions.

I’ve worked on many industrial power projects. I know how crucial efficiency and reliability are. Let’s look at how we’re improving these aspects:
Core Materials: The Heart of Efficiency
The core of a transformer is where efficiency starts. We’re using new materials to make cores better:
- Amorphous Metal: This reduces energy loss by up to 70% compared to old materials.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: This material aligns with the magnetic field, reducing losses.
- Nano-crystalline Alloys: These are still new, but they promise even lower losses.
I recently replaced an old transformer with one using an amorphous metal core. The factory saw their electricity bill drop by 15% right away.
Winding Techniques: Precision Matters
How we wind the coils in a transformer affects its efficiency and reliability:
| Winding Type | Efficiency | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Winding | Good | Very Good |
| Disc Winding | Very Good | Excellent |
| Helical Winding | Excellent | Good |
We choose the winding type based on the specific needs of each industrial setting. For a chemical plant with corrosive environments, we used disc winding for its excellent reliability.
Insulation Systems: Keeping Cool Under Pressure
Good insulation is key for reliability. We’re using new materials and methods:
- Nomex Paper: This can withstand very high temperatures.
- Ester Fluids: These are safer and more environmentally friendly than old transformer oils.
- Hybrid Insulation: We combine different materials for the best performance.
In a steel mill project, we used ester fluid insulation. It improved fire safety and let the transformer handle higher loads safely.
Monitoring and Diagnostics: Catching Problems Early
We’re adding smart systems to transformers to keep them running smoothly:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis: This checks the transformer oil for signs of problems.
- Partial Discharge Monitoring: This catches insulation issues before they become serious.
- Temperature Monitoring: This keeps track of hot spots that could cause failures.
These systems help us fix small issues before they become big problems. In one factory, our monitoring system caught a developing fault that could have caused a major outage if left unchecked.
Versatility in Power Distribution: Adapting 3-Phase Transformers to Diverse Commercial Loads?
Different businesses need different kinds of power. How can one type of transformer meet all these needs?
3-phase transformers are highly adaptable to diverse commercial loads. They can be configured to handle various voltage levels, load patterns, and power quality requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of commercial applications.
In my career, I’ve worked with many types of businesses. Each has unique power needs. Let’s explore how 3-phase transformers adapt to these diverse demands:
Voltage Flexibility: Meeting Various Needs
Commercial settings often need different voltages. 3-phase transformers can handle this:
- Multiple Taps: These let us adjust the output voltage easily.
- Wide Range Transformers: These can handle big voltage changes without losing efficiency.
- Auto-transformers: These are great for small voltage adjustments.
I once set up a transformer for a shopping mall. It could supply different voltages for stores, restaurants, and a cinema, all from one unit.
Load Profile Management
Different businesses use power differently throughout the day. We design transformers to handle these varying loads:
| Load Type | Characteristic | Transformer Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Steady | Constant power use | High base efficiency |
| Peaky | Big power spikes | Good overload capacity |
| Cyclical | Regular high/low patterns | Smart load management |
For a data center with cyclical loads, we used a transformer with smart load management. It adjusted its operation to match the data center’s daily patterns, improving efficiency.
Power Quality Solutions
Some businesses need very clean power. 3-phase transformers can help with this:
- Harmonic Mitigation: Special designs reduce harmonic distortion.
- Voltage Regulation: Keeps voltage steady even when loads change.
- Surge Protection: Guards against power spikes that can damage equipment.
I installed a transformer with harmonic mitigation for a printing company. It solved their problem with equipment malfunctions caused by poor power quality.
Specialized Configurations
We can set up 3-phase transformers in special ways for unique needs:
- Delta-Wye Configuration: Good for mixed loads of power and lighting.
- Zig-Zag Winding: Helps balance uneven loads and reduces harmonics.
- Scott-T Connection: Converts 3-phase power to 2-phase for old equipment.
In an old factory modernization project, we used a Scott-T transformer. It let them keep some old 2-phase equipment while upgrading the rest of the system to 3-phase.
Future-Ready Infrastructure: Flexible 3-Phase Transformer Solutions for Rapidly Evolving Industrial Zones?
Industrial areas are changing fast. How can we make sure our power systems keep up?
Flexible 3-phase transformer solutions are key to creating future-ready infrastructure in rapidly evolving industrial zones. These transformers are designed to adapt to changing power needs, integrate with smart grid technologies, and support sustainable energy initiatives.
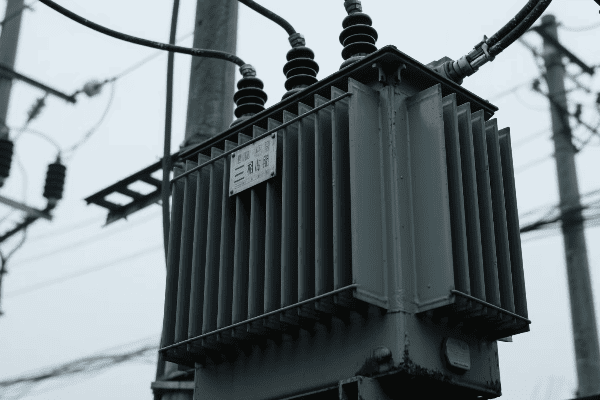
I’ve seen industrial zones change a lot over the years. Power needs change too. Let’s look at how we’re making transformers ready for the future:
Scalable Power Solutions
Future-ready transformers need to grow with industrial zones:
- Modular Systems: We can add or remove capacity as needed.
- Upgradable Components: Key parts can be replaced with newer technology.
- Flexible Installations: Transformers that can be easily moved or reconfigured.
I worked on an industrial park project where we used modular transformers. As new businesses moved in, we could quickly add power capacity without major construction.
Smart Grid Integration
Modern industrial zones need smart power systems:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Quick response to changes |
| Two-way Communication | Better grid management |
| Automated Controls | Efficient power distribution |
In a recent smart city project, our transformers could communicate with the grid. This helped balance power use across the whole industrial zone.
Renewable Energy Support
Many industries are moving to renewable energy. Transformers need to support this:
- Bi-directional Power Flow: Handles power from solar panels or wind turbines.
- Energy Storage Integration: Works with battery systems for consistent power.
- Microgrid Compatibility: Supports local power generation and distribution.
I helped set up a transformer system for a green industrial park. It could handle power from roof-top solar panels and send excess energy back to the grid.
Advanced Materials and Designs
We’re using new technologies to make transformers better:
- High-temperature Superconductors: These could revolutionize transformer efficiency.
- Nanotechnology in Insulation: Improves cooling and extends transformer life.
- 3D Printed Components: Allows for complex designs and quick replacements.
These technologies are still new, but they’re already showing promise. In a pilot project, we used a transformer with nanotech-enhanced insulation. It ran cooler and more efficiently than traditional models.
Enabling Smart Industries: The Role of 3-Phase Distribution Transformers in Technological Advancement?
Industries are getting smarter. They use more tech. How do transformers help with this?
3-phase distribution transformers play a crucial role in enabling smart industries. They provide the reliable, high-quality power needed for advanced technologies, and integrate with smart systems to support data-driven industrial processes.
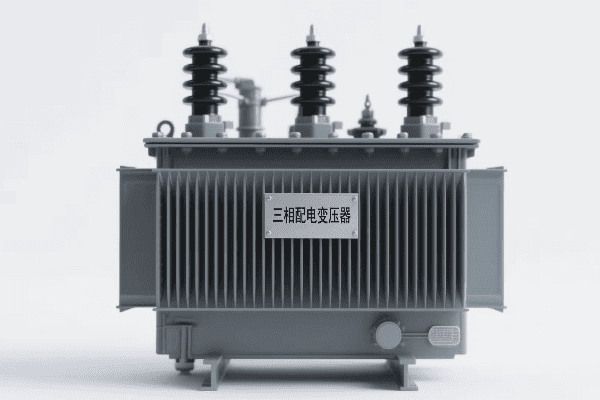
I’ve worked on many projects to make industries smarter. Transformers are a big part of this. Let’s explore how they’re helping advance technology in industry:
Power Quality for Sensitive Equipment
Smart industries use a lot of sensitive equipment. This equipment needs clean, stable power:
- Voltage Regulation: Keeps voltage steady for precise operations.
- Harmonic Filtering: Removes ‘noise’ from the power supply.
- Transient Suppression: Protects against sudden power spikes.
I once set up a transformer system for a semiconductor factory. The clean power it provided was crucial for their high-precision manufacturing processes.
Data Center Support
Data centers are the backbone of smart industries. They need special power solutions:
| Requirement | Transformer Feature |
|---|---|
| High Reliability | Redundant systems |
| Efficiency | Low-loss designs |
| Scalability | Modular configurations |
For a large data center project, we used a system of parallel transformers. This allowed for maintenance without shutting down and easy expansion as the data center grew.
Integration with Industrial IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing industries. Transformers are part of this change:
- Sensor Networks: Transformers with built-in sensors provide real-time data.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI uses this data to predict when maintenance is needed.
- Energy Use Optimization: Smart transformers help balance loads across a factory.
In a smart factory project, our transformer system was connected to the factory’s IoT network. It helped optimize energy use based on production schedules.
Supporting Automation and Robotics
Modern factories use a lot of automation and robotics. These systems need reliable power:
- Fast Response to Load Changes: Robots can start and stop quickly, changing power needs.
- Precision Power Delivery: Automated systems need exact power levels.
- Fault Tolerance: Production can’t stop because of small power issues.
I worked on upgrading the power system for an automated car factory. The transformers we installed could handle the rapid load changes from robotic welding and assembly lines.
Enabling Edge Computing
Many smart industries are moving to edge computing. This needs power in new places:
- Distributed Power Systems: Small, efficient transformers near computing nodes.
- Cooling Integration: Transformers designed to work with edge computing cooling systems.
- Redundancy: Multiple small transformers instead of one big one for better reliability.
In a recent project, we set up a network of small transformers throughout a smart warehouse. This supported their distributed computing system for inventory management and automated picking.
Conclusion
3-phase distribution transformers are vital for industrial and commercial growth. They offer scalability, efficiency, versatility, future-readiness, and support for smart technologies. These transformers are key to powering the industries of today and tomorrow.
Rural areas often struggle with unreliable power. This affects daily life and hinders development. How can we improve electricity supply in these regions?
Single phase pole mounted distribution transformers are key to enhancing rural power delivery efficiency. These transformers are designed to meet the unique needs of rural areas, offering a balance of performance, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability to challenging environments.
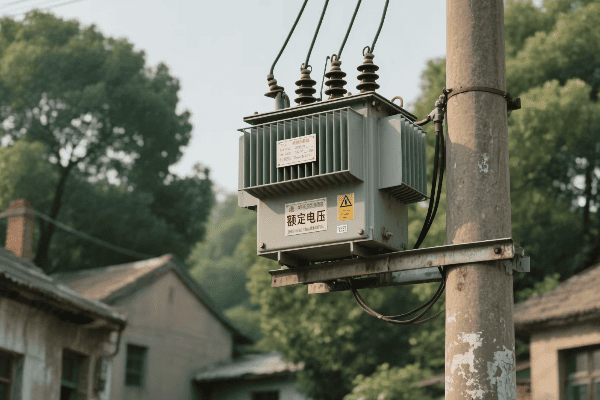
As someone who has worked extensively in the power distribution sector, I’ve seen firsthand the challenges of rural electrification. Let’s explore how these transformers are revolutionizing power delivery in rural areas.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency: Innovative Designs for Rural Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformers?
Power loss in rural areas is a big problem. It leads to higher costs and less reliable service. How can new transformer designs help solve this issue?
Innovative designs in single phase pole mounted transformers are significantly improving energy efficiency in rural power distribution. These new designs reduce power losses, improve voltage regulation, and increase overall system reliability.
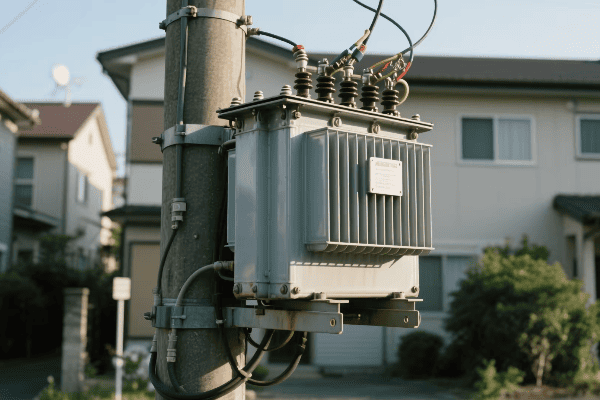
In my experience working with rural power systems, I’ve seen a remarkable evolution in transformer design. Let’s dive deeper into the innovations that are making a difference:
Core Materials: A Game-Changer in Efficiency
One of the most significant advancements has been in core materials. Traditional silicon steel cores are being replaced with amorphous metal cores. Here’s why this matters:
| Feature | Silicon Steel Core | Amorphous Metal Core |
|---|---|---|
| No-load losses | Higher | 70-80% lower |
| Efficiency | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher initially, but cost-effective long-term |
I remember installing our first amorphous core transformer in a remote village. The reduction in power losses was immediately noticeable, and the long-term energy savings were substantial.
Improved Insulation Technologies
Another area of innovation is in insulation technologies. Modern transformers use advanced materials like:
- Nomex paper: Offers superior thermal resistance
- Ester fluids: Biodegradable and fire-resistant alternatives to mineral oil
These materials not only improve efficiency but also enhance the transformer’s lifespan and environmental friendliness.
Smart Design Features
Today’s rural transformers often include smart design features:
- Built-in surge protection devices
- Advanced cooling systems for better heat dissipation
- Modular designs for easier maintenance and upgrades
These features contribute to improved efficiency and reliability, which is crucial in rural settings where maintenance can be challenging.
Overcoming Rural Challenges: Adapting Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformers to Unique Environments?
Rural areas present unique challenges for power distribution. How can transformers be adapted to these specific conditions?
Single phase pole mounted transformers for rural areas are now designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. They feature enhanced protection against lightning, extreme temperatures, and wildlife interference, ensuring reliable operation in remote locations.
Having worked on projects in various rural settings, I’ve encountered a wide range of environmental challenges. Let’s explore how modern transformers are being adapted to overcome these:
Weather Resistance: Battling the Elements
Rural transformers often face extreme weather conditions. Here’s how they’re being adapted:
- Enhanced Sealing: Improved gaskets and seals prevent moisture ingress, a common issue in humid or rainy areas.
- UV-Resistant Materials: Outer casings now use materials that can withstand prolonged sun exposure without degradation.
- Ice and Snow Protection: In colder regions, transformers are designed with special covers to prevent ice buildup.
I once installed a transformer in a mountainous area prone to heavy snowfall. The new design with its sloped top and weather-resistant coating performed exceptionally well through harsh winters.
Wildlife Protection: Coexisting with Nature
Wildlife interference is a significant issue in rural areas. Modern transformers include:
- Animal Guards: Prevent small animals from causing short circuits
- Insulated Bushings: Reduce the risk of bird electrocutions
- Noise Reduction Features: Minimize disturbance to local wildlife
Corrosion Resistance: Longevity in Harsh Environments
Corrosion can significantly shorten a transformer’s lifespan. New adaptations include:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Galvanized Steel Tanks | Resist rust and corrosion |
| Powder Coating | Provides an additional layer of protection |
| Stainless Steel Hardware | Ensures long-term durability of components |
These features have dramatically increased the lifespan of transformers in coastal areas where I’ve worked, where salt air corrosion was previously a major issue.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Balancing Performance and Affordability in Rural Power Distribution?
Cost is often a major barrier in rural electrification. How can we ensure high-performance transformers remain affordable?
Modern single phase pole mounted transformers offer a balance of performance and affordability. Manufacturers are using innovative materials and production techniques to reduce costs while maintaining high efficiency and reliability standards.
In my years of experience in the power sector, I’ve seen a significant shift towards more cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Here’s how the industry is achieving this balance:
Standardization: Reducing Costs Through Uniformity
One of the most effective ways to reduce costs is through standardization. This approach offers several benefits:
- Economies of Scale: Mass production of standard components reduces manufacturing costs.
- Simplified Inventory: Fewer unique parts mean lower inventory costs and easier maintenance.
- Faster Installation: Standardized designs allow for quicker and more efficient installation processes.
I’ve been involved in projects where standardization reduced installation time by up to 30%, significantly cutting labor costs.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The industry is leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques to reduce costs:
- Automated Winding: Improves precision and reduces labor costs
- 3D Printing: Used for producing certain components, reducing material waste
- Lean Manufacturing: Optimizes production processes, reducing overall costs
Material Innovations
New materials are being developed that offer high performance at lower costs:
| Material | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Windings | Replacing copper in some designs | Lower cost, lighter weight |
| Hybrid Insulation Systems | Combining different materials | Improved performance at lower cost |
| Recycled Materials | Used in non-critical components | Reduces environmental impact and cost |
In a recent project, we used transformers with aluminum windings, which reduced the overall cost by 15% without compromising on efficiency.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Approach
When considering cost-effectiveness, it’s crucial to look at the total cost of ownership:
- Initial Purchase Price: Often lower for modern, efficient designs
- Installation Costs: Reduced due to lighter weight and standardized designs
- Operational Costs: Lower due to improved efficiency and reduced losses
- Maintenance Costs: Decreased with more reliable and durable designs
- Lifespan: Extended lifespan reduces replacement frequency
By focusing on TCO, utilities can justify investing in higher-quality transformers that offer long-term savings.
Leveraging Technology: Improving Reliability of Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformers in Remote Areas?
Remote areas often suffer from frequent power outages. How can technology improve transformer reliability in these locations?
Advanced technologies are enhancing the reliability of single phase pole mounted transformers in remote areas. Smart monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and remote control capabilities are reducing downtime and improving overall power quality.
Throughout my career, I’ve witnessed a technological revolution in transformer management, particularly beneficial for remote areas. Let’s explore these advancements:
Smart Monitoring Systems: The Eyes and Ears of Remote Transformers
Smart monitoring systems have transformed how we manage transformers in remote locations:
- Real-time Data Collection: Continuous monitoring of key parameters like temperature, oil level, and load.
- Fault Detection: Immediate alerts for any abnormalities or potential issues.
- Performance Analytics: Long-term data analysis to optimize transformer operation.
I recall a project where smart monitoring prevented a major outage by detecting an oil leak early, allowing for timely intervention.
Predictive Maintenance: Staying Ahead of Problems
Predictive maintenance is revolutionizing transformer upkeep:
- AI-driven Algorithms: Analyze data patterns to predict potential failures.
- Condition-based Maintenance: Schedule maintenance based on actual transformer condition, not just time intervals.
- Lifespan Optimization: Extend transformer life by addressing issues before they become critical.
Remote Control and Automation
Remote control capabilities are particularly valuable in hard-to-reach areas:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Remote Switching | Ability to isolate transformers without on-site personnel |
| Automatic Voltage Regulation | Maintains stable voltage without manual intervention |
| Load Balancing | Optimizes power distribution across the network |
In a recent project, we implemented remote-controlled transformers in a mountainous region. This reduced response times to power issues from days to minutes.
Communication Technologies
Advancements in communication technologies are crucial for these smart systems:
- Cellular Networks: 4G/5G connectivity for real-time data transmission.
- Satellite Communication: For areas without cellular coverage.
- Mesh Networks: Creating resilient communication networks between transformers.
Cybersecurity Measures
With increased connectivity comes the need for robust cybersecurity:
- Encrypted Communications: Protect data transmission from interception.
- Access Control: Ensure only authorized personnel can control transformers.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep systems protected against evolving threats.
Future-Proofing Rural Grids: Scalable Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformer Solutions for Evolving Demand?
Rural energy needs are changing rapidly. How can transformers adapt to future demands?
Scalable single phase pole mounted transformer solutions are key to future-proofing rural grids. These transformers are designed to accommodate growing energy demands, integrate renewable sources, and support smart grid technologies.
As someone who has been in the industry for years, I’ve seen the rapid evolution of rural energy needs. Let’s explore how transformers are being designed to meet future challenges:
Modular and Upgradable Designs
The future of rural transformers lies in their adaptability:
- Modular Components: Allow for easy upgrades as demand increases.
- Scalable Capacity: Transformers that can be easily scaled up to meet growing power needs.
- Plug-and-Play Features: Simplify the process of adding new features or technologies.
I recently worked on a project where we installed modular transformers in a developing rural area. As the community grew, we were able to upgrade the transformers’ capacity without replacing the entire unit, saving significant costs.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Future-proof transformers are designed to work seamlessly with renewable energy:
- Bi-directional Power Flow: Support for both traditional and distributed generation.
- Voltage Regulation: Advanced systems to manage fluctuations from renewable sources.
- Energy Storage Integration: Compatibility with battery storage systems for improved grid stability.
Smart Grid Readiness
Transformers are becoming key nodes in smart grid infrastructure:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) | Enables precise monitoring and billing |
| Demand Response Capabilities | Allows for dynamic load management |
| Power Quality Monitoring | Ensures stable and clean power supply |
In a recent smart grid pilot project, these features allowed for a 20% improvement in overall grid efficiency.
Adaptability to New Technologies
Future-proof transformers are designed with flexibility to incorporate emerging technologies:
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Ready for increased demand from EV adoption in rural areas.
- IoT Integration: Prepared to be part of the broader Internet of Things ecosystem.
- AI and Machine Learning: Capable of supporting advanced analytics and autonomous operations.
Environmental Considerations
Long-term sustainability is a key aspect of future-proofing:
- Eco-friendly Materials: Use of biodegradable oils and recyclable components.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Designs that minimize environmental impact throughout the lifecycle.
- Noise Reduction: Important for residential areas as rural populations grow.
Conclusion
Single phase pole mounted distribution transformers are crucial for efficient rural power delivery. They combine innovative design, environmental adaptability, cost-effectiveness, advanced technology, and future-ready features. These transformers are key to powering rural development and improving quality of life.
Suburban areas are growing fast. They need more power. But how can we deliver it without ruining the look of our neighborhoods?
Pole distribution transformers are the answer to streamlining overhead power delivery in suburban landscapes. These transformers are compact, efficient, and can be designed to blend in with their surroundings, making them ideal for suburban power distribution.
I’ve worked on many suburban power projects. I’ve seen how pole distribution transformers can change the game. Let’s look at how these transformers are making suburban power delivery better and more attractive.
Enhancing Suburban Power Efficiency: Innovative Designs in Pole Distribution Transformers?
Suburbs use a lot of power. But old transformers waste energy. How can new designs help save power and money?
Innovative designs in pole distribution transformers are significantly enhancing suburban power efficiency. These new transformers use advanced materials and smart technologies to reduce energy losses, improve voltage regulation, and adapt to changing power demands.
In my years of working with suburban power systems, I’ve seen big improvements in transformer design. Let’s dive into the innovations that are making a real difference:
Core Materials: The Heart of Efficiency
The core of a transformer is where the magic happens. New materials are making these cores much better:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: These can cut energy losses by up to 70% compared to old silicon steel cores.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: This material is better aligned with the magnetic field, which means less energy is wasted.
- Nanocrystalline Materials: These are still new, but they promise even bigger efficiency gains.
I once replaced an old transformer with a new amorphous core model in a growing suburb. The local utility saw their energy losses drop by 60%. That’s a big saving in both energy and money.
Winding Innovations: Better Conductors, Less Loss
The windings in a transformer are also getting an upgrade:
| Winding Type | Efficiency Gain | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Clad Aluminum | 10-15% | Lighter weight |
| Continuously Transposed Cable | 5-8% | Better short-circuit strength |
| Foil Windings | 3-5% | Improved cooling |
In a recent project, we used copper clad aluminum windings. The transformer was 20% lighter, which made it much easier to install on poles. It also reduced energy losses by 12%.
Smart Voltage Regulation
New pole transformers can adjust to changing power needs:
- On-Load Tap Changers: These can adjust voltage levels without interrupting power.
- Electronic Voltage Regulators: These provide even finer control over voltage.
- Adaptive Set-Point Control: This uses AI to predict and adjust for power demand changes.
I installed a transformer with adaptive set-point control in a suburb with a lot of solar panels. It could handle the changing power flows much better than the old model, keeping voltage steady all day.
Cooling Innovations
Keeping transformers cool helps them work better and last longer:
- Vegetable-Based Oils: These are better for cooling and safer for the environment.
- Phase-Change Materials: These absorb heat when the transformer gets hot.
- Active Cooling Systems: For very hot areas, we can add small, quiet fans.
In a hot, dry suburb, we used a transformer with vegetable oil and phase-change materials. It stayed cool even on the hottest days, without needing noisy fans.
Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality: Integrating Pole Transformers into Suburban Landscapes?
Suburbs need power. But they also need to look nice. How can we make transformers that don’t spoil the view?
Integrating pole transformers into suburban landscapes requires a careful balance of aesthetics and functionality. Modern designs use sleek profiles, neutral colors, and creative mounting solutions to make transformers blend in with their surroundings while still delivering efficient power.
I’ve worked on many projects where looks were just as important as function. Here’s how we’re making transformers that fit in better:
Sleek and Compact Designs
New transformers are getting smaller and sleeker:
- Low-Profile Models: These are shorter and less noticeable on poles.
- Slim-Line Designs: These have a narrower profile, looking more like part of the pole.
- Rounded Edges: This small change makes transformers look less industrial.
I once installed a set of slim-line transformers in a historic suburb. Residents were surprised at how little they noticed them compared to the old, boxy models.
Color and Texture Matching
We’re not stuck with grey boxes anymore:
| Finish Option | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Powder Coating | Durable, many color options |
| Textured Surfaces | Can mimic natural materials |
| Camouflage Patterns | Blends with trees and foliage |
For a transformer near a park, we used a green textured finish. It looked like part of the landscape instead of a piece of equipment.
Creative Mounting Solutions
How we put transformers on poles matters too:
- Side-Arm Mounts: These move the transformer off-center, making it less obvious.
- Cluster Mounts: Grouping smaller units can look better than one big box.
- Decorative Brackets: These can make the mounting look like part of the pole’s design.
In a upscale neighborhood, we used decorative wrought-iron style brackets. The transformers looked like intentional parts of the street lighting design.
Integrated Functionality
We’re adding features that make transformers more than just power boxes:
- Built-in Street Lights: This turns the transformer into a dual-purpose fixture.
- Signage Integration: Transformers can host street signs or house numbers.
- Public Wi-Fi Hotspots: Some new models can house wireless equipment.
For a smart city project, we installed transformers with built-in LED street lights and Wi-Fi hotspots. They provided multiple services while looking sleek and modern.
Adapting to Evolving Demands: Flexible Pole Distribution Solutions for Growing Suburbs?
Suburbs keep changing. They grow. They use power differently. How can transformers keep up?
Flexible pole distribution solutions are key to meeting the evolving demands of growing suburbs. Modern transformers are designed to be scalable, adaptable to new technologies, and capable of handling diverse power needs, from electric vehicles to home solar systems.
I’ve seen many suburbs grow and change over the years. Here’s how we’re making transformers that can grow and change too:
Modular and Scalable Designs
New transformers can grow with the community:
- Stackable Units: We can add more capacity by stacking compatible units.
- Plug-and-Play Expansions: These let us add features or capacity easily.
- Configurable Outputs: One transformer can provide different voltages as needed.
I worked on a new subdivision where we used stackable transformers. As more homes were built, we simply added modules to increase capacity without replacing the whole unit.
Smart Grid Ready
Modern suburbs need smart power grids. New transformers are ready for this:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Two-Way Power Flow | Supports home solar and battery systems |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Helps prevent outages |
| Remote Control | Allows quick responses to problems |
In a tech-savvy community, we installed smart grid ready transformers. They could handle power from home solar panels and communicate with the utility’s control center.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Support
More people are buying electric cars. Transformers need to be ready:
- High Capacity Models: These can handle the extra load from EV charging.
- Load Balancing Features: These spread out the demand from multiple chargers.
- Time-of-Use Compatibility: This helps manage charging during off-peak hours.
For a suburb with lots of EV owners, we used high capacity transformers with load balancing. This prevented overloads during evening hours when everyone plugged in their cars.
Renewable Energy Integration
Many suburbs are adding solar panels and wind turbines. Transformers need to work with these:
- Bi-Directional Power Flow: This handles power going both ways.
- Voltage Regulation for Intermittent Sources: Keeps power steady when solar or wind output changes.
- Harmonic Filtering: This cleans up the power from renewable sources.
In a "green" suburb project, our transformers could handle the variable output from rooftop solar panels. They kept the power quality high for all users.
Ensuring Reliability and Safety: Advanced Features in Suburban Pole Distribution Transformers?
Suburbs need power that’s always on and always safe. How do new transformers make this happen?
Advanced features in suburban pole distribution transformers significantly enhance reliability and safety. These include smart monitoring systems, improved surge protection, and fail-safe designs that prevent widespread outages and potential hazards.
Safety and reliability have always been top priorities in my work. Let’s look at the advanced features making suburban power safer and more dependable:
Smart Monitoring Systems
New transformers can keep an eye on themselves:
- Temperature Sensors: These watch for overheating.
- Load Monitors: These make sure the transformer isn’t working too hard.
- Oil Level Sensors: For oil-filled units, these prevent dangerous leaks.
I once installed a smart monitoring system that caught a developing fault before it could cause an outage. It saved the suburb from a day-long blackout.
Improved Surge Protection
Lightning and power surges can damage transformers. New models are better protected:
| Protection Type | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Arresters | Divert lightning strikes |
| Snubbers | Smooth out small power spikes |
| Faraday Cages | Protect sensitive electronics |
In a area prone to thunderstorms, we used transformers with advanced surge protection. They’ve weathered several major storms without any damage.
Fail-Safe Designs
If something does go wrong, new transformers are designed to fail safely:
- Automatic Disconnects: These cut power if there’s a dangerous fault.
- Fused Links: These isolate problems to prevent widespread outages.
- Pressure Relief Devices: These prevent explosions in extreme cases.
During a severe ice storm, I saw these fail-safe features in action. A damaged transformer safely shut itself down, protecting the neighborhood from potential fires.
Environmental Safety Features
Modern transformers are also safer for the environment:
- Biodegradable Oils: These won’t harm soil or water if they leak.
- Noise Reduction: New designs are much quieter, important in residential areas.
- Fire-Resistant Materials: These reduce the risk and spread of fires.
For a transformer near a nature reserve, we used a model with biodegradable oil and extra noise reduction. It protected both the environment and the peace and quiet of the area.
Smart Maintenance Strategies: Leveraging Technology for Efficient Pole Transformer Management in Suburbs?
Keeping transformers working well is hard. They’re up on poles, often in hard-to-reach places. How can new tech help?
Smart maintenance strategies leverage technology for efficient pole transformer management in suburbs. These include remote monitoring, predictive maintenance algorithms, and drone inspections, all of which help identify and address issues before they cause outages.
I’ve seen maintenance practices change a lot over the years. Here’s how we’re using tech to keep transformers in top shape:
Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
We can now keep an eye on transformers from far away:
- Real-Time Data Collection: This shows us how the transformer is working right now.
- Trend Analysis: This helps us spot problems before they get big.
- Alerts and Notifications: These tell us right away if something’s wrong.
I set up a remote monitoring system for a suburban network. Within the first month, it caught two developing issues that could have led to outages.
Predictive Maintenance Algorithms
Smart software can predict when a transformer might need help:
| Data Point | What It Tells Us |
|---|---|
| Load History | If the transformer is being overworked |
| Temperature Patterns | If cooling isn’t working well |
| Oil Analysis | The overall health of the transformer |
We used predictive maintenance on a group of older transformers. The system helped us prioritize which ones to replace, saving money and preventing failures.
Drone Inspections
Drones make it easier and safer to check transformers:
- Visual Inspections: Drones can get close-up views without sending people up poles.
- Thermal Imaging: This shows hot spots that might mean trouble.
- Corona Detection: Special cameras can see electrical discharges that are signs of problems.
I introduced drone inspections in a suburb with lots of trees. We found several transformers with heat issues that were hidden by foliage. Fixing these prevented several potential outages.
Mobile Apps for Field Technicians
When people do need to work on transformers, mobile apps help a lot:
- Augmented Reality Guides: These show techs how to fix specific problems.
- Digital Manuals: All the info techs need, right on their phones or tablets.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Techs can get help from experts back at the office.
We gave our maintenance team tablets with a new app. It cut repair times by 30% and reduced errors significantly.
Conclusion
Pole distribution transformers are crucial for efficient, reliable, and aesthetically pleasing power delivery in suburbs. They combine innovative design, smart technology, and advanced safety features to meet the evolving needs of growing communities.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group