Step Down Transformers: Essential Guardians of Safe Power Distribution
Are you curious about how electricity safely reaches your home from distant power plants? Step down transformers are the unsung heroes of this process.
Step down transformers are crucial components in power distribution systems, reducing high transmission voltages to safer levels for homes and businesses. These devices ensure electricity is both usable and safe for consumers, acting as essential guardians of our electrical systems. Understanding their function is key to appreciating modern power infrastructure.
As an electrical engineer with over two decades of experience, I’ve witnessed the critical role step down transformers play in our power grid. This comprehensive guide will explore their working principles, design, applications, and evolving role in smart grids. Whether you’re a homeowner, student, or industry professional, you’ll gain valuable insights into these vital devices that keep our modern world powered safely.
Working Principle: The Magic Behind Voltage Reduction
Have you ever wondered how the same electricity that powers industrial machinery can safely run your household appliances? The answer lies in the fascinating working principle of step down transformers.
Step down transformers utilize electromagnetic induction to reduce voltage. They feature a primary coil with more turns and a secondary coil with fewer turns. This turn ratio enables the transformer to decrease voltage while increasing current, maintaining overall power consistency. This principle is fundamental to safe power distribution.
During my university days, I built a simple step down transformer model. Observing the voltage drop firsthand was a pivotal moment that ignited my passion for power systems engineering.
Key Components of the Working Principle
- Electromagnetic Induction: The core mechanism driving transformer operation.
- Turn Ratio: Determines the voltage reduction between primary and secondary coils.
- Power Conservation: Ensures energy is maintained despite voltage changes.
Comparison: Step Up vs. Step Down Transformers
| Aspect | Step Down Transformer | Step Up Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Coil | More turns | Fewer turns |
| Secondary Coil | Fewer turns | More turns |
| Voltage | Decreases | Increases |
| Current | Increases | Decreases |
| Power | Remains constant (minus losses) | Remains constant (minus losses) |
Understanding these principles is crucial for anyone involved in electrical systems. Throughout my career, I’ve found that a solid grasp of these fundamentals is essential for effective troubleshooting and optimization of power distribution networks.
Structural Design: Engineering Marvel of Step Down Transformers
The internal structure of a step down transformer is a testament to ingenious engineering. Let’s explore the key components that make these devices so effective.
Step down transformers are composed of several critical elements: a laminated steel core, primary and secondary windings, insulation materials, and a cooling system. This intricate design enables efficient voltage reduction while managing heat and ensuring operational safety.
Early in my career, I had the opportunity to disassemble an old step down transformer. The complex arrangement of its components gave me a profound appreciation for the engineering expertise involved in their design.
Core Components and Their Functions
- Core: Typically made of silicon steel laminations, providing a path for magnetic flux.
- Windings: Primary (high voltage) and secondary (low voltage) coils, usually copper or aluminum.
- Insulation: Crucial for safety, using materials like oil, paper, or epoxy resin.
- Cooling System: Essential for longevity, varying from oil-filled to dry-type designs.
Structural Components Comparison
| Component | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | Silicon steel laminations |
| Primary Winding | Receives high voltage | Copper or aluminum wire |
| Secondary Winding | Delivers low voltage | Copper or aluminum wire |
| Insulation | Electrical isolation | Oil, paper, or solid materials |
| Cooling System | Heat management | Oil, air, or combination |
My experience has shown that many transformer issues can be traced back to problems with these key structural elements. Understanding their roles is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Application Areas: The Ubiquity of Step Down Transformers
Step down transformers are more prevalent in our daily lives than most people realize. Their applications span from massive power distribution networks to the smallest electronic devices.
Step down transformers are extensively used in power distribution networks, industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and residential areas. They play a pivotal role in reducing high transmission voltages to levels appropriate for end-user consumption, ensuring both safety and efficiency in power delivery.
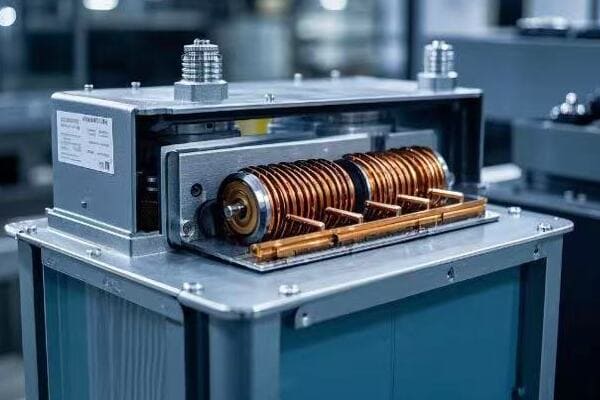

I once led a project to modernize a city’s power distribution system. The strategic placement of step down transformers throughout the network was crucial in ensuring reliable and safe power delivery to every home and business.
Diverse Applications Across Sectors
- Power Distribution Networks: From substations to pole-mounted transformers.
- Industrial Facilities: Powering machinery in factories and data centers.
- Commercial Buildings: Ensuring appropriate voltage for offices and shopping centers.
- Residential Areas: Enabling safe use of electricity in homes.
Application Comparison Table
| Application | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Typical Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substation | 500 kV | 69 kV | 100 MVA |
| Distribution | 69 kV | 12 kV | 10 MVA |
| Pole-Mounted | 12 kV | 240/120 V | 50 kVA |
| Industrial | 12 kV | 480 V | 1 MVA |
| Commercial | 480 V | 208/120 V | 500 kVA |
| Residential | 240 V | 120 V | 5 kVA |
Understanding these diverse applications is crucial for electrical engineers and power system designers. In my professional experience, recognizing the specific needs of each application has been key to selecting and implementing the right step down transformer for optimal performance and safety.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Step Down Transformers
Step down transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical infrastructure, playing a critical role in safe and efficient power distribution. They bridge the gap between high-voltage transmission systems and the lower voltages required in our homes and businesses. As we’ve explored their working principles, intricate designs, and wide-ranging applications, it’s clear that these devices are fundamental to our modern way of life.
Looking ahead, step down transformers will continue to evolve, incorporating smart technologies and more efficient designs. Their role in integrating renewable energy sources and supporting smart grids will become increasingly important. For professionals in the field, staying updated on these advancements is crucial. For the general public, understanding the basics of step down transformers fosters a greater appreciation of the complex systems that power our world.
Whether you’re a student considering a career in electrical engineering, a professional in the power industry, or simply a curious individual, the world of step down transformers offers fascinating insights into the backbone of our electrical systems. As we move towards a more electrified future, these devices will remain at the forefront of safe, efficient, and reliable power distribution.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


