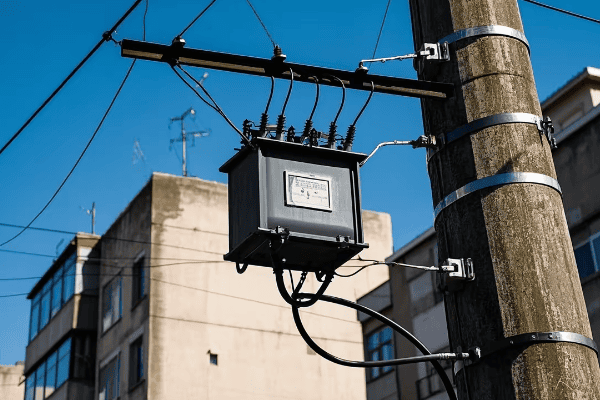
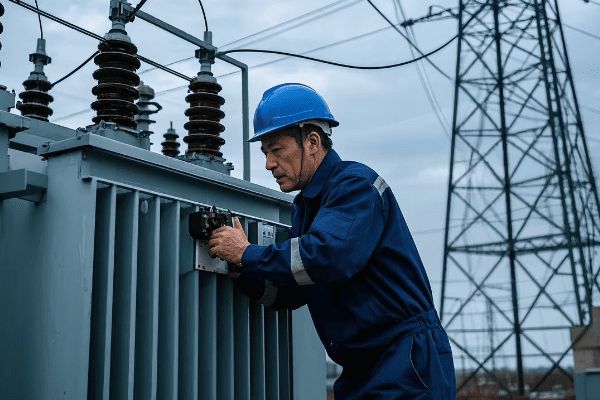
Have you ever wondered how electricity travels from power plants to your home? It’s a journey that involves two unsung heroes: power transformers and distribution transformers.
Power transformers and distribution transformers are the backbone of our electrical grid. They work together to ensure efficient power transmission and distribution, making it possible for us to enjoy reliable electricity in our daily lives.
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in the power industry, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial these transformers are. Let’s dive deeper into their roles and why they’re so important for our modern electrical systems.
What Sets Power Transformers Apart from Distribution Transformers in Grid Operations?
Picture this: a massive power plant generating electricity, but how does that power reach your neighborhood? That’s where power transformers and distribution transformers come into play.
Power transformers handle high voltages at power plants and substations, while distribution transformers lower the voltage for safe use in homes and businesses. They differ in size, capacity, and placement within the electrical grid.
Let’s break down the key differences between these two types of transformers:
Size and Capacity
Power transformers are the giants of the transformer world. I remember the first time I saw one up close – it was as big as a small house! They’re designed to handle enormous amounts of power, often in the range of hundreds of megavolt-amperes (MVA).
Distribution transformers, on the other hand, are much smaller. You’ve probably seen them mounted on utility poles or in green boxes in your neighborhood. They typically handle power in the range of 5 to 500 kVA.
Voltage Levels
Here’s where the real magic happens:
| Transformer Type | Input Voltage | Output Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transformer | 100kV – 1000kV | 20kV – 100kV |
| Distribution Transformer | 4kV – 35kV | 120V – 600V |
Power transformers work with extremely high voltages, stepping them down for long-distance transmission. Distribution transformers take that stepped-down voltage and reduce it further to levels safe for household use.
Location in the Grid
Power transformers are found at power plants and major substations. They’re the first step in the journey of electricity from generation to consumption.
Distribution transformers are the last step before power reaches the end-user. You’ll find them closer to residential and commercial areas.
Efficiency and Losses
Both types of transformers strive for high efficiency, but power transformers generally have higher efficiency ratings due to their larger size and the critical nature of their role. Even a small improvement in efficiency can result in significant energy savings given the large amounts of power they handle.
Distribution transformers, while also efficient, may have slightly lower efficiency ratings. However, their efficiency is crucial too, as losses at this stage directly affect the end-user’s power quality and electricity costs.
How Do Power and Distribution Transformers Synergize to Enhance Grid Performance?
Imagine an orchestra where each instrument plays its part perfectly, but they’re not in sync. The result would be chaos, not music. The same principle applies to our electrical grid.
Power and distribution transformers work in harmony to ensure efficient power transmission. Power transformers step up voltage for long-distance transmission, while distribution transformers step it down for local use, minimizing energy losses and ensuring stable power supply.
Let’s explore how these two types of transformers work together:
The Power Journey
- Generation: At the power plant, electricity is generated at relatively low voltages.
- Step-Up: Power transformers increase this voltage to very high levels (often 400kV or more) for efficient long-distance transmission.
- Transmission: High-voltage power travels through transmission lines, minimizing losses over long distances.
- Step-Down: At substations, power transformers reduce the voltage to medium levels (typically 33kV or 11kV).
- Distribution: Distribution transformers further reduce the voltage to levels suitable for homes and businesses (120V/240V in the US).
Balancing Act
The synergy between power and distribution transformers is all about balance. Power transformers handle the bulk power transfer, while distribution transformers manage the final delivery. This division of labor ensures that each type of transformer can be optimized for its specific role.
Load Management
Distribution transformers play a crucial role in load management. They’re designed to handle the varying power demands of local areas throughout the day. Power transformers, meanwhile, ensure that there’s always enough power available to meet these changing demands.
Fault Protection
Both types of transformers incorporate protective measures, but they work together to isolate faults and prevent widespread outages. A fault at the distribution level can be isolated without affecting the entire grid, thanks to this hierarchical system.
Efficiency Optimization
By working in tandem, power and distribution transformers optimize the overall efficiency of the grid. The high voltages used in transmission (thanks to power transformers) minimize line losses, while the lower voltages at the distribution level (courtesy of distribution transformers) ensure safe and efficient power use by consumers.
The Impact of Power and Distribution Transformers on Energy Efficiency: A Detailed Analysis
As an engineer, I’m always excited about efficiency. It’s not just about saving money – it’s about making the most of our resources and reducing our environmental impact.
Power and distribution transformers significantly impact energy efficiency by minimizing transmission losses and optimizing voltage levels. Their combined efficiency determines how much of the generated power actually reaches end-users, directly affecting energy costs and environmental impact.

Let’s dive into the numbers and see how these transformers affect energy efficiency:
Efficiency Ratings
Transformer efficiency is typically very high, but even small improvements can have a big impact:
| Transformer Type | Typical Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Power Transformer | 99.5% – 99.9% |
| Distribution Transformer | 98% – 99% |
These might seem like small differences, but when you’re dealing with massive amounts of power, every fraction of a percent counts.
Losses in Transformers
Transformers experience two main types of losses:
- No-load losses: These occur even when the transformer is energized but not supplying load. They’re mainly due to the magnetization of the core.
- Load losses: These increase with the load and are primarily due to resistance in the windings.
Power transformers, due to their size and continuous operation, focus more on minimizing no-load losses. Distribution transformers, with their varying loads, need to balance both types of losses.
Impact on Grid Efficiency
Let’s consider a simplified example:
- A power plant generates 100 MW of power.
- It passes through a power transformer (99.7% efficient) for transmission.
- At the substation, it goes through another power transformer (99.7% efficient).
- Finally, it passes through a distribution transformer (98.5% efficient) to reach homes.
The total efficiency would be: 0.997 0.997 0.985 = 0.979 or 97.9%
This means that out of the 100 MW generated, only about 97.9 MW reaches the end-users. The 2.1 MW lost is enough to power thousands of homes!
Economic and Environmental Impact
The efficiency of transformers has a direct impact on:
- Energy Costs: Higher efficiency means less power needs to be generated to meet demand, reducing fuel costs and potentially lowering electricity prices for consumers.
- Carbon Emissions: Improved efficiency reduces the amount of fuel burned for power generation, directly lowering carbon emissions.
- Grid Stability: Efficient transformers help maintain voltage stability, reducing the risk of power quality issues and outages.
Regulatory Push for Efficiency
Recognizing the importance of transformer efficiency, many countries have implemented minimum efficiency standards. For example, the U.S. Department of Energy’s standards for distribution transformers are expected to save 3.63 quads of energy over 30 years – that’s equivalent to the annual energy use of 27 million homes!
Smart Grid Integration: The Evolution of Power and Distribution Transformer Technologies
The term "smart grid" used to sound like science fiction to me. Now, it’s becoming a reality, and transformers are at the heart of this revolution.
Smart grid integration is transforming power and distribution transformers into intelligent, communicative devices. These advanced transformers can monitor their own health, adjust to changing loads, and communicate with other grid components, enhancing overall grid efficiency and reliability.

Let’s explore how transformer technology is evolving to support smart grids:
Smart Features in Modern Transformers
-
Real-time Monitoring: Advanced sensors in transformers can now monitor:
- Oil temperature
- Winding temperature
- Load current
- Voltage levels
- Dissolved gas content
-
Data Analytics: This data is processed to:
- Predict potential failures
- Optimize load distribution
- Schedule maintenance
-
Communication Capabilities: Transformers can now communicate with control centers, allowing for:
- Remote monitoring
- Automatic alerts
- Integration with other smart grid components
-
Adaptive Features: Some advanced transformers can:
- Automatically adjust voltage levels
- Respond to changes in power quality
- Self-diagnose issues
Benefits of Smart Transformer Technology
-
Improved Reliability: By predicting and preventing failures, smart transformers can significantly reduce outages.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Real-time load management and voltage optimization lead to reduced losses.
-
Extended Lifespan: Predictive maintenance helps extend the life of transformers, reducing replacement costs.
-
Better Integration of Renewable Energy: Smart transformers can help manage the variable nature of renewable energy sources.
-
Faster Outage Response: When issues do occur, smart transformers can pinpoint the problem, allowing for faster repairs.
Challenges in Smart Grid Integration
While the benefits are clear, there are challenges to overcome:
-
Cost: Smart transformers are more expensive than traditional ones. The challenge is justifying this cost against long-term benefits.
-
Cybersecurity: With increased connectivity comes increased vulnerability to cyber attacks. Robust security measures are crucial.
-
Data Management: The sheer volume of data generated by smart transformers requires advanced data management and analysis systems.
-
Standardization: For a truly integrated smart grid, we need standardized communication protocols across different manufacturers and systems.
Future Prospects
The future of transformer technology in smart grids is exciting. Some areas of development include:
-
AI Integration: Using artificial intelligence for more advanced predictive maintenance and grid optimization.
-
Solid-State Transformers: These could offer even more flexibility and control in power distribution.
-
Energy Storage Integration: Combining transformers with energy storage systems for better load balancing and renewable energy integration.
-
Self-Healing Grids: Advanced transformers could play a key role in creating grids that can automatically detect, isolate, and repair faults.
Maintenance Strategies for Power and Distribution Transformers: Ensuring Long-term Grid Reliability
In my years working with transformers, I’ve learned one crucial lesson: proper maintenance is not just about preventing failures – it’s about ensuring the long-term health of our entire power grid.
Effective maintenance of power and distribution transformers is crucial for grid reliability. Strategies include regular inspections, oil analysis, thermal imaging, and predictive maintenance techniques. These practices extend transformer life, prevent unexpected failures, and ensure consistent power quality.
Let’s explore the key maintenance strategies for both power and distribution transformers:
Regular Inspections
-
Visual Inspections:
- Frequency: Monthly for power transformers, quarterly for distribution transformers
- Check for: Oil leaks, rust, damaged bushings, unusual sounds
-
Thermal Imaging:
- Frequency: Annually
- Purpose: Detect hot spots that could indicate problems
-
Acoustic Emissions Testing:
- Frequency: Annually for critical transformers
- Purpose: Detect partial discharges and other internal issues
Oil Analysis
Oil is the lifeblood of a transformer. Regular analysis can reveal a lot about a transformer’s health:
-
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA):
- Frequency: Annually for power transformers, every 3-5 years for distribution transformers
- Purpose: Detect internal faults, overheating, and insulation breakdown
-
Oil Quality Tests:
- Frequency: Annually
- Check for: Acidity, moisture content, dielectric strength
-
Furan Analysis:
- Frequency: Every 3-5 years
- Purpose: Assess the condition of paper insulation
Electrical Testing
-
Insulation Resistance Test:
- Frequency: Annually
- Purpose: Check the condition of insulation
-
Power Factor Testing:
- Frequency: Every 3-5 years
- Purpose: Detect deterioration in insulation
-
Turns Ratio Test:
- Frequency: During commissioning and after any suspected impact
- Purpose: Verify the transformer’s turns ratio
Predictive Maintenance Techniques
-
Online Monitoring Systems:
- Continuous monitoring of key parameters
- Real-time alerts for abnormal conditions
-
Data Analytics:
- Use historical data to predict potential failures
- Optimize maintenance schedules
-
Condition-Based Maintenance:
- Schedule maintenance based on actual condition rather than fixed intervals
Maintenance Challenges and Solutions
-
Aging Infrastructure:
- Challenge: Many transformers are nearing the end of their designed lifespan
- Solution: Life extension programs, strategic replacement planning
-
Skill Gap:
- Challenge: Shortage of experienced maintenance personnel
- Solution: Training programs, knowledge transfer from retiring experts
-
Balancing Cost and Reliability:
- Challenge: Justifying maintenance costs
- Solution: Risk-based maintenance strategies, demonstrating long-term cost savings
-
Environmental Concerns:
- Challenge: Handling of transformer oil, PCB contamination in older units
- Solution: Use of environmentally friendly oils, proper disposal procedures
Best Practices for Transformer Maintenance
-
Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan: Tailor plans to each transformer’s criticality and condition.
-
Implement a Robust Record-Keeping System: Track all maintenance activities and test results.
-
Invest in Training: Ensure maintenance personnel are up-to-date with the latest techniques and safety procedures.
-
Utilize Technology: Implement online monitoring and data analytics for more efficient maintenance.
-
Regular Review and Update: Continuously assess and improve maintenance strategies based on outcomes and new technologies.
Conclusion
Power and distribution transformers are indeed the unsung heroes of our electrical grid. Their efficient operation and proper maintenance are crucial for the reliable power supply we often take for granted. As we move towards smarter, more efficient grids, the role of these transformers will only become more important.
Are you struggling with energy inefficiencies in your power system? You’re not alone. Many utilities and industries face challenges in optimizing their power distribution networks.
Power and distribution transformers are revolutionizing modern power systems by enhancing energy efficiency and enabling smart grid integration. These advanced transformers incorporate cutting-edge technologies to reduce energy losses, improve power quality, and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. They play a crucial role in creating more resilient, flexible, and sustainable power networks.
As someone who has spent years working with power and distribution transformers, I’ve witnessed firsthand the remarkable advancements in this field. In this article, I’ll guide you through the latest innovations and explain how these transformers are shaping the future of our power systems.
How Are Advanced Power and Distribution Transformers Boosting Energy Efficiency in Modern Grids?
Are you concerned about energy losses in your power distribution network? You should be. Energy efficiency is crucial for both cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Advanced power and distribution transformers boost energy efficiency through improved core materials, optimized winding designs, and smart load management systems. They significantly reduce no-load and load losses, enhance voltage regulation, and maintain high efficiency across varying load conditions. These improvements lead to substantial energy savings and reduced operational costs in modern grids.

Let’s dive deeper into how these transformers are enhancing energy efficiency:
Advanced Core Materials
Modern transformers use cutting-edge materials to minimize core losses.
Core Innovations:
- Amorphous metal cores for ultra-low no-load losses
- High-grade silicon steel with thinner laminations
- Nanocrystalline materials for improved magnetic properties
Optimized Winding Designs
Innovative winding techniques reduce copper losses and improve efficiency.
Winding Advancements:
- Foil windings for better current distribution
- Continuously transposed conductors to minimize eddy currents
- Advanced insulation materials for improved heat dissipation
Smart Load Management
Intelligent systems optimize transformer performance under varying loads.
Smart Features:
- Real-time load monitoring and adjustment
- Automatic voltage regulation
- Dynamic tap changing for optimal efficiency
Enhanced Cooling Systems
Improved cooling designs contribute to overall efficiency.
Cooling Innovations:
- Advanced oil circulation techniques
- Use of biodegradable and more efficient cooling fluids
- Integration of heat recovery systems for energy reuse
| Efficiency Feature | Energy Saving Potential | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Core Materials | High | Moderate |
| Optimized Windings | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Smart Load Management | High | High |
| Enhanced Cooling | Moderate | Moderate |
In my experience working with utilities and industrial clients, the impact of these efficiency improvements can be substantial. I recall a project where we replaced an aging transformer fleet for a large manufacturing plant. By implementing transformers with amorphous metal cores and advanced winding designs, we achieved a 30% reduction in energy losses. This translated to significant cost savings for the client and a notable decrease in their carbon footprint.
It’s important to note that efficiency gains aren’t just about the hardware. In one case, I worked on integrating smart load management systems into a utility’s transformer network. The ability to dynamically adjust transformer settings based on real-time load conditions led to an additional 10% improvement in overall grid efficiency. This not only reduced energy waste but also extended the lifespan of the transformers by optimizing their operation.
Don’t overlook the importance of proper sizing and selection in maximizing efficiency. I’ve developed a comprehensive assessment process that considers load profiles, environmental conditions, and future growth projections. This approach ensures that each transformer operates at its optimal efficiency point, maximizing energy savings over its lifetime.
Another crucial aspect is the role of enhanced cooling systems in maintaining high efficiency. I recently worked on a project implementing a novel heat recovery system in a substation. The waste heat from the transformers was used to heat nearby buildings, turning an efficiency challenge into an energy-saving opportunity.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials science are pushing the boundaries of transformer efficiency. I’m currently involved in a research project exploring the use of graphene-based materials in transformer cores. While still in the experimental stage, these materials show promise for even lower losses and higher efficiency than current technologies.
The energy efficiency enhancements offered by advanced power and distribution transformers are not just incremental improvements – they represent a significant leap forward in grid optimization. From innovative materials to smart management systems, these transformers are key to creating more sustainable and cost-effective power networks. As we continue to face global energy challenges, the role of high-efficiency transformers in building a more energy-efficient future cannot be overstated.
What Key Features Enable Power and Distribution Transformers to Support Smart Grid Integration?
Are you struggling to adapt your power infrastructure to the demands of smart grids? You’re not alone. The transition to intelligent power systems presents unique challenges for traditional equipment.
Power and distribution transformers support smart grid integration through advanced monitoring systems, communication capabilities, and adaptive control features. They incorporate sensors for real-time data collection, bidirectional power flow management, and voltage regulation technologies. These features enable seamless integration with grid management systems, facilitating efficient energy distribution and responsive grid operations.

Let’s explore the key features that make modern transformers smart grid-ready:
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Smart transformers provide real-time insights into their operation and grid conditions.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Temperature and oil condition sensors
- Load and power quality analyzers
- Partial discharge detection systems
Communication Interfaces
These transformers can exchange data with grid management systems.
Communication Features:
- Integration with SCADA systems
- Support for various protocols (e.g., IEC 61850, DNP3)
- Secure data transmission capabilities
Adaptive Control Mechanisms
Smart transformers can adjust their operation based on grid conditions.
Adaptive Features:
- On-load tap changers for voltage regulation
- Reactive power compensation
- Fault current limiting capabilities
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
These transformers can handle power flow in both directions, crucial for renewable integration.
Bidirectional Capabilities:
- Management of distributed energy resources
- Support for microgrid operations
- Enhanced harmonics management
| Smart Grid Feature | Transformer Capability | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Advanced Sensors | Improved Reliability |
| Data Communication | Multiple Interfaces | Enhanced Grid Management |
| Adaptive Control | Dynamic Adjustments | Increased Stability |
| Bidirectional Power | Flexible Power Handling | Renewable Integration |
In my years of working on smart grid projects, I’ve seen how these features transform the role of transformers from passive components to active grid management tools. I remember a project where we upgraded a suburban substation with smart transformers. The real-time monitoring and communication capabilities allowed the utility to detect and respond to voltage fluctuations caused by rooftop solar installations, significantly improving power quality in the area.
It’s important to note that implementing these smart features often requires a holistic approach to grid modernization. In one case, I worked with a utility to develop a phased smart grid rollout plan. We started by upgrading key transformers with advanced monitoring systems, then gradually implemented communication and control features. This step-by-step approach allowed for a smoother transition and helped the utility staff adapt to the new technologies.
Don’t overlook the importance of cybersecurity in smart grid-enabled transformers. I recently led a team in developing security protocols for a network of smart transformers. We implemented multi-layer encryption, secure boot processes, and intrusion detection systems to protect against potential cyber threats. This aspect of smart grid integration is becoming increasingly critical as our power systems become more interconnected and data-driven.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these transformers in enabling microgrid capabilities. I’m currently advising on a project where smart transformers are key components in a community microgrid. These transformers can seamlessly switch between grid-connected and island modes, providing resilience during main grid outages while also optimizing local energy use and generation.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the integration of artificial intelligence is taking transformer capabilities to new levels. I’m part of a research team exploring the use of machine learning algorithms to predict grid disturbances based on data from smart transformers. This predictive capability could revolutionize grid management, allowing for proactive measures to maintain stability and efficiency.
The key features that enable power and distribution transformers to support smart grid integration are transforming these devices from simple power conversion units to intelligent nodes in our energy networks. As we continue to develop and implement smart grid technologies, the role of these advanced transformers will be crucial in creating more resilient, efficient, and flexible power systems capable of meeting the complex energy needs of the future.
How Are Power and Distribution Transformers Evolving to Meet the Demands of Modern Power Systems?
Are you finding it challenging to keep up with the rapidly changing needs of modern power systems? You’re not alone. The evolution of our energy landscape is pushing transformer technology to new limits.
Power and distribution transformers are evolving through the integration of digital technologies, advanced materials, and flexible designs. They now feature enhanced power electronics, improved insulation systems, and modular architectures. These evolutions enable transformers to handle variable loads, integrate renewable sources, and provide ancillary services to the grid, meeting the complex demands of modern power systems.

Let’s explore how transformers are adapting to meet modern power system demands:
Integration of Power Electronics
Modern transformers incorporate advanced power electronic components.
Power Electronic Features:
- Solid-state tap changers for faster voltage regulation
- Active harmonic filtering capabilities
- Fault current limiting functionalities
Advanced Insulation Systems
New insulation technologies enhance performance and reliability.
Insulation Advancements:
- Nano-composite materials for improved thermal management
- Biodegradable insulating fluids
- Self-healing insulation technologies
Modular and Scalable Designs
Transformers are becoming more adaptable to changing system needs.
Modular Advantages:
- Easily upgradable components
- Customizable configurations for specific applications
- Reduced downtime for maintenance and repairs
Enhanced Grid Support Capabilities
Modern transformers provide various ancillary services to the grid.
Grid Support Features:
- Reactive power compensation
- Voltage and frequency regulation support
- Black start capabilities for grid restoration
| Evolution Area | Key Innovation | System Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Power Electronics | Solid-State Components | Improved Power Quality |
| Insulation | Nano-materials | Enhanced Reliability |
| Design Approach | Modularity | Increased Flexibility |
| Grid Support | Ancillary Services | Better System Stability |
In my experience working with utilities and manufacturers, these evolutions are reshaping how we approach power system design and operation. I recall a project where we implemented a new generation of transformers with integrated power electronics in a rapidly growing urban area. The ability of these units to quickly adjust to load changes and provide power quality improvements significantly reduced the need for additional infrastructure upgrades, saving the utility millions in capital expenditure.
It’s important to note that the evolution of transformers is not just about adding new features – it’s about rethinking their fundamental role in the power system. In one case, I worked on developing a hybrid transformer-converter unit for a renewable energy integration project. This innovative design combined the traditional step-up/step-down functionality with DC-AC conversion capabilities, streamlining the integration of large-scale solar farms into the grid.
Don’t overlook the impact of advanced insulation systems on transformer evolution. I recently consulted on a project using new nano-composite insulation materials. These materials not only improved the thermal performance of the transformers but also allowed for a more compact design, crucial for installations in space-constrained urban substations.
Another crucial aspect is the shift towards modular designs. I’m currently advising on a transformer fleet modernization program where modularity is a key requirement. This approach not only simplifies maintenance and upgrades but also allows the utility to quickly adapt their transformer capabilities as grid needs evolve, providing a future-proof solution.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how transformers are taking on new roles in grid support and stability. I’m part of a research team exploring the use of transformers as active participants in grid frequency regulation. By leveraging their power electronic components and energy storage integration, these advanced transformers can respond to frequency deviations in milliseconds, enhancing overall grid stability.
The evolution of power and distribution transformers to meet the demands of modern power systems is not just about incremental improvements – it’s a fundamental reimagining of their role in our energy infrastructure. From integrating advanced technologies to providing critical grid support services, these evolving transformers are becoming the cornerstone of more flexible, reliable, and efficient power systems. As we continue to face new challenges in our energy landscape, the ongoing evolution of transformer technology will be crucial in shaping the power systems of the future.
What Cutting-Edge Technologies Are Being Incorporated into Transformers for Enhanced Grid Management?
Are you wondering how to improve your grid management capabilities? You’re not alone. Many utilities are seeking advanced solutions to handle the complexities of modern power systems.
Cutting-edge technologies being incorporated into transformers for enhanced grid management include IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, blockchain for secure data management, and advanced power electronics. These innovations enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, improved cybersecurity, and dynamic power flow control, significantly enhancing overall grid efficiency and reliability.
Let’s explore these cutting-edge technologies in detail:
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT sensors and connectivity are revolutionizing transformer monitoring.
IoT Capabilities:
- Real-time data collection on various parameters
- Remote monitoring and control
- Integration with broader smart grid systems
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is enhancing transformer diagnostics and decision-making.
AI Applications:
- Predictive maintenance algorithms
- Load forecasting and optimization
- Anomaly detection and fault prediction
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is improving data security and transaction management.
Blockchain Benefits:
- Secure and transparent data logging
- Improved traceability for regulatory compliance
- Potential for peer-to-peer energy trading support
Advanced Power Electronics
New power electronic solutions are enhancing transformer functionality.
Power Electronic Innovations:
- Solid-state transformers for improved power quality
- Dynamic reactive power compensation
- High-frequency power conversion for size reduction
| Technology | Primary Function | Grid Management Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| IoT | Data Collection | Enhanced Visibility |
| AI/ML | Analytics and Prediction | Improved Decision Making |
| Blockchain | Data Security | Increased Trust and Efficiency |
| Power Electronics | Power Flow Control | Better System Stability |
In my years of working with grid management technologies, I’ve seen how these innovations can transform network operations. I remember a project where we implemented an IoT-based monitoring system across a utility’s transformer fleet. Within months, we were able to reduce unplanned outages by 40% through early detection of developing faults. The real-time data also allowed for more efficient load balancing, improving overall grid stability.
It’s important to note that while these technologies offer powerful capabilities, their implementation often requires a holistic approach. In one case, I worked with a utility to develop an AI-driven asset management system. We had to carefully integrate data from various sources, including transformer IoT sensors, weather patterns, and historical performance records. The resulting system not only optimized maintenance schedules but also provided valuable insights for long-term infrastructure planning.
Don’t overlook the potential of blockchain in enhancing grid management. I recently consulted on a pilot project using blockchain for managing distributed energy resources. The technology provided a secure and transparent way to track energy contributions from various sources, including transformer-level data. This not only improved grid management but also opened up possibilities for new energy trading models.
Another crucial aspect is the role of advanced power electronics in transformer design. I’m currently advising on a project implementing solid-state transformers in a urban microgrid. These devices offer unprecedented control over power flow and quality, allowing for seamless integration of renewable sources and electric vehicle charging stations.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how these technologies are coming together to create truly intelligent grid management systems. I’m part of a research team developing a next-generation grid control system that combines IoT data, AI analytics, and blockchain security. This system promises to provide a level of grid awareness and responsiveness that was previously unimaginable, potentially revolutionizing how we manage and optimize our power networks.
The incorporation of cutting-edge technologies into transformers is not just enhancing grid management – it’s redefining what’s possible in power system operation. From IoT-enabled real-time monitoring to AI-driven predictive maintenance and blockchain-secured data management, these innovations are creating smarter, more efficient, and more reliable grids. As we continue to face new challenges in our evolving energy landscape, these advanced transformer technologies will play a crucial role in building the resilient and responsive power systems of the future.
How Do Power and Distribution Transformers Facilitate the Integration of Renewable Energy Sources?
Are you struggling to integrate renewable energy sources into your power grid? You’re not alone. Many utilities face challenges in managing the variable nature of renewables.
Power and distribution transformers facilitate renewable energy integration through advanced voltage regulation, bidirectional power flow capabilities, and smart grid functionalities. They handle the intermittent nature of renewable sources, manage power quality issues, and enable efficient energy distribution. These transformers also support microgrid operations and energy storage integration, crucial for maximizing renewable energy utilization.
Let’s dive deeper into how transformers are enabling renewable energy integration:
Advanced Voltage Regulation
Modern transformers provide dynamic voltage support for variable renewable inputs.
Voltage Regulation Features:
- On-load tap changers with rapid response times
- Automatic voltage regulators for real-time adjustments
- Reactive power compensation capabilities
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Transformers now handle power flow in both directions, essential for distributed generation.
Bidirectional Capabilities:
- Redesigned windings to support reverse power flow
- Enhanced protection systems for backfeed scenarios
- Smart inverter integration for seamless power management
Power Quality Management
Transformers address power quality issues associated with renewable sources.
Power Quality Solutions:
- Harmonic mitigation technologies
- Flicker reduction capabilities
- Fault ride-through features for grid stability
Microgrid and Energy Storage Support
Modern transformers enable microgrid operations and integrate with storage systems.
Microgrid and Storage Features:
- Islanding detection and support
- Seamless transition between grid-connected and island modes
- Interfaces for battery energy storage systems
| Integration Aspect | Transformer Function | Renewable Energy Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulation | Dynamic Adjustment | Stable Grid Operation |
| Bidirectional Flow | Flexible Power Handling | Enables Distributed Generation |
| Power Quality | Disturbance Mitigation | Improved System Reliability |
| Microgrid Support | Operational Flexibility | Enhanced Energy Resilience |
In my experience working with renewable energy projects, the role of advanced transformers has been crucial. I recall a large-scale solar farm integration project where we faced significant challenges with voltage fluctuations. By implementing transformers with fast-acting on-load tap changers and reactive power compensation, we were able to maintain grid stability even during rapid changes in solar output. This solution not only enabled the successful integration of the solar farm but also improved overall power quality in the region.
It’s important to note that the benefits of these advanced transformers extend beyond just technical performance. In one case, I worked with a utility to develop a comprehensive renewable integration strategy. The flexibility offered by modern transformers allowed for a phased approach to renewable adoption, significantly reducing the upfront costs and risks associated with the transition to cleaner energy sources.
Don’t overlook the importance of transformer design in addressing specific renewable energy challenges. I recently consulted on a wind farm project where we custom-designed transformers to handle the unique load profiles and environmental conditions of offshore wind turbines. These specialized units incorporated enhanced cooling systems and corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring reliable operation in harsh marine environments.
Another crucial aspect is the role of transformers in enabling community-scale renewable projects. I’m currently advising on a microgrid initiative that uses advanced transformers as key nodes in a neighborhood-level renewable energy network. These transformers not only manage the integration of rooftop solar and small wind turbines but also facilitate energy sharing among community members, creating a more resilient and sustainable local energy ecosystem.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how transformers are evolving to support emerging renewable technologies. I’m part of a research team exploring the integration of next-generation solar and storage systems. We’re developing transformer designs that can efficiently handle DC inputs from solar panels and batteries, potentially eliminating the need for multiple conversion stages and improving overall system efficiency.
The facilitation of renewable energy integration by power and distribution transformers is not just a technical achievement – it’s a key enabler of our transition to a more sustainable energy future. These advanced transformers are bridging the gap between traditional grid infrastructure and the dynamic, distributed nature of renewable energy sources. As we continue to increase our reliance on clean energy, the ongoing evolution of transformer technology will be crucial in creating more flexible, efficient, and resilient power systems capable of maximizing the potential of renewable resources.
What Challenges Do Manufacturers Face in Balancing Efficiency and Cost in Modern Transformer Design?
Are you struggling to find transformers that offer high efficiency without breaking the bank? You’re not alone. Manufacturers face significant challenges in balancing performance and affordability.
Manufacturers face challenges in balancing efficiency and cost in modern transformer design, including material selection trade-offs, increased complexity of smart features, and evolving regulatory standards. They must optimize between using advanced, costly materials for higher efficiency and maintaining competitive pricing. Balancing long-term energy savings with upfront costs while meeting diverse market demands adds to the complexity.
Let’s explore the key challenges manufacturers face:
Material Selection Trade-offs
Choosing between standard and advanced materials impacts both efficiency and cost.
Material Considerations:
- High-grade silicon steel vs. amorphous metals for cores
- Copper vs. aluminum for windings
- Advanced insulation materials vs. traditional options
Smart Feature Integration Costs
Adding smart capabilities increases functionality but also raises production costs.
Smart Feature Challenges:
- Incorporating sensors and monitoring systems
- Implementing communication interfaces
- Developing and integrating control software
Regulatory Compliance and Efficiency Standards
Meeting evolving efficiency standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Regulatory Impacts:
- Stricter efficiency requirements driving up production costs
- Varied standards across different markets complicating design processes
- Balancing efficiency improvements with cost constraints
Market Demand Variability
Addressing diverse customer needs while maintaining economies of scale.
Market Challenges:
- Customization requests vs. standardized production
- Balancing high-end and budget-friendly options
- Adapting to rapidly changing technology trends
| Challenge Area | Efficiency Impact | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | High | High |
| Smart Features | Moderate to High | High |
| Regulatory Compliance | High | Moderate to High |
| Market Variability | Moderate | High |
In my years of working with transformer manufacturers, I’ve seen firsthand the complexities of balancing efficiency and cost. I remember collaborating with a manufacturer on developing a new line of distribution transformers. We faced a significant dilemma when choosing core materials. Amorphous metal cores offered superior efficiency but at a much higher cost. After extensive analysis and testing, we developed a hybrid design that used amorphous metals in critical areas and high-grade silicon steel in others. This approach allowed us to achieve a 20% efficiency improvement while keeping the cost increase to just 10%.
It’s important to note that the challenge of integrating smart features goes beyond just the additional component costs. In one project, I advised a manufacturer on implementing IoT capabilities in their transformer line. The real challenge was not just in adding sensors and communication modules, but in redesigning the entire production process to accommodate these new elements. This required significant upfront investment in retooling and staff training, which had to be carefully balanced against the long-term market benefits of offering smart transformers.
Don’t overlook the impact of regulatory changes on the efficiency-cost balance. I recently worked with a global manufacturer to develop a strategy for meeting diverse efficiency standards across different markets. We created a modular design approach that allowed for easy customization to meet various regulatory requirements without completely overhauling the production line for each market. This strategy helped in maintaining cost-effectiveness while ensuring compliance with a range of efficiency standards.
Another crucial aspect is addressing the variability in market demands. I’m currently advising a manufacturer on developing a flexible production system that can efficiently handle both high-volume standard orders and smaller batches of customized, high-efficiency units. This approach involves implementing advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing for certain components and adopting lean production principles to reduce waste and improve adaptability.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some manufacturers are turning these challenges into opportunities for innovation. I’m part of an industry group exploring new business models, such as efficiency-as-a-service, where manufacturers offer high-efficiency transformers at competitive upfront costs and share in the long-term energy savings. This approach could potentially resolve the tension between efficiency and cost by aligning the interests of manufacturers, utilities, and end-users.
The challenges manufacturers face in balancing efficiency and cost in modern transformer design are complex and multifaceted. From material selection to smart feature integration, regulatory compliance, and market variability, each aspect requires careful consideration and innovative solutions. As the demand for more efficient and intelligent transformers continues to grow, manufacturers who can successfully navigate these challenges will be well-positioned to lead in the evolving energy landscape. The key lies in embracing innovation, leveraging new technologies, and developing flexible strategies that can adapt to changing market needs and regulatory requirements.
How Are IoT and AI Technologies Revolutionizing Power and Distribution Transformer Operations?
Are you wondering how to make your transformer operations smarter and more efficient? You’re not alone. Many in the industry are turning to IoT and AI for solutions.
IoT and AI technologies are revolutionizing power and distribution transformer operations through real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent load management. These technologies enable continuous health assessment, automate decision-making processes, and optimize transformer performance. They also facilitate better integration with smart grids, enhancing overall system reliability and efficiency.
Let’s explore how IoT and AI are transforming transformer operations:
Real-Time Monitoring and Diagnostics
IoT sensors provide continuous data on transformer health and performance.
IoT Monitoring Capabilities:
- Temperature and oil level sensing
- Load and power quality monitoring
- Partial discharge detection
Predictive Maintenance
AI algorithms analyze data to predict and prevent failures.
AI-Driven Maintenance:
- Fault prediction based on historical and real-time data
- Optimized maintenance scheduling
- Automated alert systems for potential issues
Intelligent Load Management
AI optimizes transformer operation based on load patterns and grid conditions.
Smart Load Features:
- Dynamic load balancing
- Adaptive voltage regulation
- Energy efficiency optimization
Enhanced Grid Integration
IoT and AI enable better coordination with smart grid systems.
Grid Integration Benefits:
- Improved power flow management
- Support for demand response programs
- Enhanced renewable energy integration
| Technology | Application | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| IoT Sensors | Data Collection | Improved Visibility |
| AI Analytics | Predictive Maintenance | Reduced Downtime |
| Machine Learning | Load Management | Increased Efficiency |
| Cloud Computing | Data Processing | Enhanced Decision Making |
In my experience implementing IoT and AI solutions for transformer operations, the impact has been transformative. I recall a project with a large utility where we installed IoT sensors across their transformer fleet. Within months, we detected a developing fault in a critical substation transformer that would have otherwise gone unnoticed. This early detection prevented a potential citywide blackout and saved the utility millions in repair costs and potential regulatory fines.
It’s important to note that the benefits of IoT and AI extend beyond just preventing failures. In one case, I worked on implementing an AI-driven load management system for a network of distribution transformers. The system’s ability to predict and balance loads across multiple units led to a 15% improvement in overall energy efficiency and significantly extended the lifespan of the transformers.
Don’t overlook the potential of these technologies in improving maintenance practices. I recently advised a utility on transitioning from time-based to condition-based maintenance using IoT and AI. By analyzing real-time data and historical patterns, we were able to reduce unnecessary maintenance visits by 40% while improving the overall reliability of the transformer fleet.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these technologies in enabling more flexible and resilient grid operations. I’m currently working on a project that uses AI to optimize transformer settings in real-time based on renewable energy inputs and demand patterns. This level of dynamic control is crucial for managing the increasingly complex power flows in modern grids with high renewable penetration.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how IoT and AI are opening up new possibilities for transformer design and operation. I’m part of a research team exploring the concept of "self-aware" transformers that can not only monitor their own health but also adapt their operation to changing conditions without human intervention. While still in the early stages, this technology could revolutionize how we approach power distribution and grid management.
The revolution brought about by IoT and AI technologies in power and distribution transformer operations is not just about adding new features – it’s about fundamentally changing how we monitor, maintain, and operate these critical components of our power infrastructure. From predictive maintenance to intelligent load management and enhanced grid integration, these technologies are making transformers smarter, more efficient, and more reliable. As we continue to face new challenges in our evolving energy landscape, the ongoing development and implementation of IoT and AI solutions will be crucial in creating more responsive, efficient, and resilient power systems.
What Role Do Power and Distribution Transformers Play in Enhancing Grid Resilience and Reliability?
Are you concerned about the vulnerability of your power grid to disruptions? You’re not alone. Grid resilience and reliability are top priorities for utilities and energy managers worldwide.
Power and distribution transformers play a crucial role in enhancing grid resilience and reliability through advanced protection systems, smart monitoring capabilities, and flexible operating modes. They provide voltage stability, fault isolation, and rapid recovery features. Modern transformers also support microgrid operations and seamless integration of backup power sources, significantly improving overall grid robustness.

Let’s explore the key ways transformers contribute to grid resilience and reliability:
Advanced Protection Systems
Modern transformers incorporate sophisticated protection mechanisms.
Protection Features:
- Rapid fault detection and isolation
- Self-healing capabilities for minor issues
- Enhanced surge protection
Smart Monitoring and Diagnostics
Real-time monitoring enables proactive maintenance and quick response to issues.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Continuous health assessment
- Early warning systems for developing problems
- Integration with grid-wide monitoring networks
Flexible Operating Modes
Transformers can adapt to various grid conditions to maintain stability.
Operational Flexibility:
- Ability to operate in islanded mode
- Support for bidirectional power flow
- Dynamic load tap changing
Microgrid and Backup Power Support
Transformers enable seamless transitions between different power sources.
Microgrid Features:
- Smooth switching between grid and local power sources
- Support for renewable energy integration in microgrids
- Enhanced local grid stability during main grid outages
| Resilience Aspect | Transformer Function | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Protection | Fault Isolation | Reduced Outage Spread |
| Monitoring | Proactive Maintenance | Improved Reliability |
| Flexibility | Adaptive Operation | Enhanced Stability |
| Microgrid Support | Power Source Integration | Increased Resilience |
In my years of working on grid resilience projects, I’ve seen firsthand how advanced transformers can make a significant difference. I remember a project in a region prone to severe weather events. We implemented a network of smart transformers with advanced protection and self-healing capabilities. During a particularly harsh storm season, these transformers were able to isolate faults quickly and reroute power, reducing outage times by over 60% compared to previous years.
It’s important to note that the role of transformers in grid resilience goes beyond just handling disruptions. In one case, I worked with a utility to develop a comprehensive grid hardening strategy. By strategically placing advanced transformers with enhanced monitoring capabilities, we created a network of "sentinel" nodes that could provide early warning of developing issues across the grid. This proactive approach significantly improved the utility’s ability to prevent outages before they occurred.
Don’t overlook the importance of transformer flexibility in enhancing grid resilience. I recently consulted on a project where we integrated flexible transformers into a city’s power network. These units could dynamically adjust their output based on grid conditions, effectively balancing loads and maintaining voltage stability even during significant demand fluctuations. This flexibility proved crucial during several high-stress events, preventing cascading failures that could have led to widespread blackouts.
Another crucial aspect is the role of transformers in enabling microgrid capabilities. I’m currently advising on a community resilience project where advanced transformers serve as key interfaces between the main grid and local microgrids. These transformers can seamlessly transition between grid-connected and islanded modes, ensuring continuous power supply to critical facilities like hospitals and emergency services during main grid outages.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer technology are pushing the boundaries of grid resilience. I’m part of a research team exploring the use of solid-state transformers in critical infrastructure protection. These devices offer unprecedented speed in fault response and power quality management, potentially revolutionizing our approach to grid stability and reliability.
The role of power and distribution transformers in enhancing grid resilience and reliability is multifaceted and increasingly critical. From advanced protection systems to smart monitoring and flexible operations, modern transformers are at the forefront of creating more robust and responsive power networks. As we continue to face challenges from extreme weather events, cyber threats, and changing energy landscapes, the ongoing evolution of transformer technology will be crucial in building and maintaining resilient, reliable power grids capable of meeting the demands of our increasingly electrified world.
Conclusion
Power and distribution transformers are pivotal in enhancing energy efficiency and enabling smart grid integration. Through advanced technologies, they improve grid resilience, facilitate renewable energy integration, and optimize power distribution. As the energy landscape evolves, these transformers will continue to play a crucial role in shaping efficient, reliable, and sustainable power systems.
Are you concerned about the safety and efficiency of your power distribution network? You’re not alone. Many industries are seeking better solutions for their electrical infrastructure.
Dry type distribution transformers are revolutionizing power networks by offering enhanced safety features, improved efficiency, and environmental benefits. These transformers eliminate the risk of oil leaks, reduce fire hazards, and provide reliable performance in various environments. They are ideal for indoor installations, urban areas, and applications where safety and low maintenance are crucial.
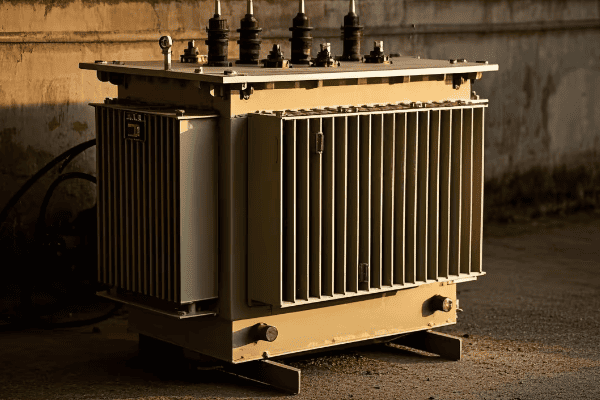
As someone who has worked extensively with various transformer types, I’ve seen firsthand the impact of dry type transformers on modern power distribution networks. In this article, I’ll guide you through the key features and benefits that make these transformers a game-changer in the industry.
What Key Safety Features Make Dry Type Distribution Transformers Ideal for Modern Power Networks?
Have you ever worried about the safety risks associated with traditional oil-filled transformers? Dry type transformers offer a solution that can put your mind at ease.
Dry type distribution transformers excel in safety due to their fire-resistant design, absence of combustible liquids, and reduced risk of environmental contamination. They feature high-temperature insulation materials, enclosed designs, and inherent arc-resistant properties, making them ideal for indoor installations and areas with strict safety requirements.
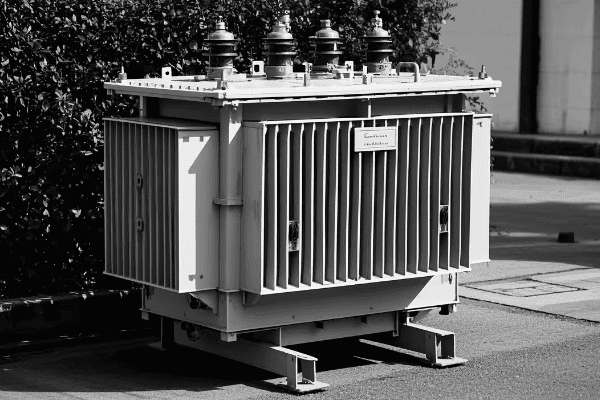
Let’s dive deeper into the safety features that set dry type transformers apart:
Fire-Resistant Design
Dry type transformers significantly reduce fire hazards.
Fire Safety Aspects:
- Use of non-flammable insulation materials
- Self-extinguishing properties
- Lower fire insurance premiums for installations
Environmentally Secure
These transformers eliminate the risk of oil leaks and spills.
Environmental Safety:
- No need for oil containment systems
- Reduced risk of soil and water contamination
- Compliance with strict environmental regulations
Enhanced Electrical Safety
Dry type transformers offer improved protection against electrical faults.
Electrical Safety Features:
- Better short-circuit strength
- Reduced partial discharge
- Improved impulse voltage withstand capability
Safe for Indoor Installations
Their design makes them suitable for a wide range of indoor applications.
Indoor Safety Benefits:
- No oil vapor emissions
- Reduced noise levels
- Compact design for space-constrained areas
| Safety Feature | Benefit | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Reduced Fire Risk | Hospitals, Schools, High-Rise Buildings |
| Environmental Security | No Oil Leaks | Environmentally Sensitive Areas |
| Electrical Safety | Improved Fault Protection | Industrial Facilities |
| Indoor Suitability | Versatile Installation | Shopping Malls, Data Centers |
In my years of experience with transformer installations, I’ve seen the dramatic impact of dry type transformers on safety standards. I recall a project where we replaced oil-filled transformers in a hospital with dry type units. The hospital administration was initially skeptical about the change, but after seeing the enhanced safety features and the elimination of oil leak risks, they were fully convinced. The peace of mind it brought to both staff and patients was palpable.
It’s important to note that while dry type transformers offer significant safety advantages, proper installation and maintenance are still crucial. In one case, I worked on troubleshooting a dry type transformer that was experiencing overheating issues. We discovered that the ventilation system in the installation room was inadequate, highlighting the importance of considering the entire installation environment, not just the transformer itself.
Don’t overlook the importance of regular inspections, even with the enhanced safety features of dry type transformers. I’ve developed maintenance protocols for several facilities that include thermal imaging and partial discharge testing. These proactive measures have helped catch potential issues before they escalate, further enhancing the overall safety of the power distribution system.
Another crucial aspect is the role of dry type transformers in meeting evolving safety regulations. I recently consulted on a project to upgrade a high-rise building’s electrical system to comply with new fire safety codes. The use of dry type transformers was instrumental in achieving compliance without major structural changes to the building.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in insulation materials are further enhancing the safety features of dry type transformers. I’m currently involved in testing a new type of nano-composite insulation that promises even better fire resistance and thermal management properties. These ongoing innovations continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in transformer safety.
The key safety features of dry type distribution transformers make them an ideal choice for modern power networks, especially in environments where safety is paramount. From fire resistance to environmental security, these transformers offer a comprehensive safety package that addresses many of the concerns associated with traditional oil-filled units. As safety regulations become more stringent and as businesses become more safety-conscious, the role of dry type transformers in power distribution networks is likely to grow even further.
How Do Dry Type Transformers Enhance Energy Efficiency in Power Distribution Systems?
Are you struggling with energy losses in your power distribution system? You’re not alone. Many facilities are looking for ways to improve their energy efficiency.
Dry type transformers enhance energy efficiency through reduced core losses, improved thermal management, and optimized winding designs. They maintain high efficiency across varying load conditions, offer better performance in high temperatures, and have longer operational lifespans. These factors contribute to significant energy savings and reduced operational costs over time.
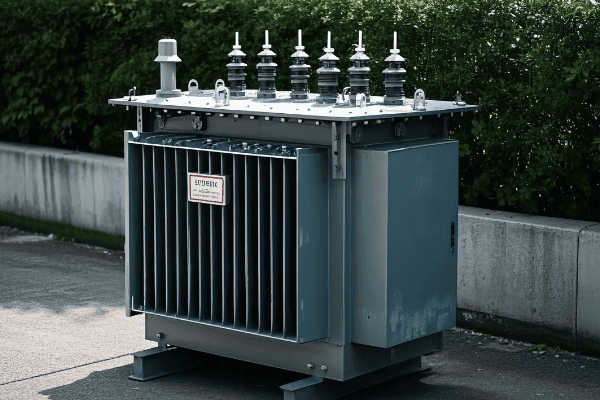
Let’s explore how dry type transformers boost energy efficiency:
Reduced Core Losses
Advanced core materials and designs minimize energy waste.
Core Efficiency Features:
- Use of high-grade silicon steel
- Amorphous metal cores for ultra-low losses
- Optimized core geometry for magnetic flux distribution
Improved Thermal Management
Better heat dissipation leads to more efficient operation.
Thermal Efficiency Aspects:
- Advanced cooling systems (e.g., forced air cooling)
- High-temperature insulation materials
- Optimized ventilation designs
Optimized Winding Designs
Innovative winding techniques reduce copper losses.
Winding Efficiency Improvements:
- Use of copper windings for lower resistance
- Foil winding technology for better current distribution
- Reduced eddy current losses through optimal conductor arrangement
Load Adaptability
Dry type transformers maintain high efficiency across various load conditions.
Load Efficiency Features:
- Stable performance under fluctuating loads
- Reduced no-load losses
- Better efficiency at partial load conditions
| Efficiency Feature | Energy Saving Potential | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Core | High | Reduced Operating Costs |
| Thermal Management | Moderate to High | Extended Lifespan |
| Optimized Windings | Moderate | Improved Performance |
| Load Adaptability | High | Versatility in Applications |
In my experience working with various power distribution systems, the efficiency gains from dry type transformers can be substantial. I remember a project where we replaced conventional transformers with high-efficiency dry type units in a large data center. The energy savings were impressive – we saw a reduction in transformer losses of about 20%, which translated to significant cost savings for the facility. The improved efficiency also meant less heat generation, reducing the load on the data center’s cooling systems.
It’s important to note that the efficiency benefits of dry type transformers extend beyond just energy savings. In one case, I worked with a manufacturing plant that was experiencing production issues due to voltage fluctuations. By installing dry type transformers with advanced voltage regulation capabilities, we not only improved energy efficiency but also enhanced the overall power quality, leading to more reliable operation of sensitive equipment.
Don’t overlook the importance of proper sizing and selection when it comes to maximizing efficiency. I’ve developed a comprehensive assessment process that considers load profiles, environmental conditions, and future growth projections. This approach ensures that the selected transformer operates at its optimal efficiency point, maximizing energy savings over its lifetime.
Another crucial aspect is the role of monitoring and maintenance in maintaining high efficiency. I recently implemented a real-time monitoring system for a network of dry type transformers in an urban substation. This system allows for continuous tracking of efficiency metrics and early detection of any performance degradation, ensuring that the transformers operate at peak efficiency throughout their lifespan.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials science are pushing the boundaries of transformer efficiency. I’m currently involved in a research project exploring the use of high-temperature superconducting materials in transformer windings. While still in the experimental stage, this technology promises to dramatically reduce losses and could revolutionize transformer efficiency in the future.
The energy efficiency enhancements offered by dry type transformers are not just incremental improvements – they represent a significant leap forward in power distribution technology. From advanced core materials to optimized designs, these transformers offer a comprehensive solution for facilities looking to reduce energy losses and operational costs. As energy efficiency becomes an increasingly critical concern in our power-hungry world, the role of dry type transformers in creating more sustainable and cost-effective power distribution systems will only grow in importance.
What Environmental Advantages Do Dry Type Distribution Transformers Offer Over Traditional Models?
Are you concerned about the environmental impact of your power distribution equipment? You’re not alone. Many organizations are seeking greener alternatives in their electrical infrastructure.
Dry type distribution transformers offer significant environmental advantages over traditional oil-filled models. They eliminate the risk of oil leaks and spills, reduce the need for hazardous waste disposal, and have a lower carbon footprint throughout their lifecycle. These transformers also support green building initiatives and can be more easily recycled at the end of their operational life.
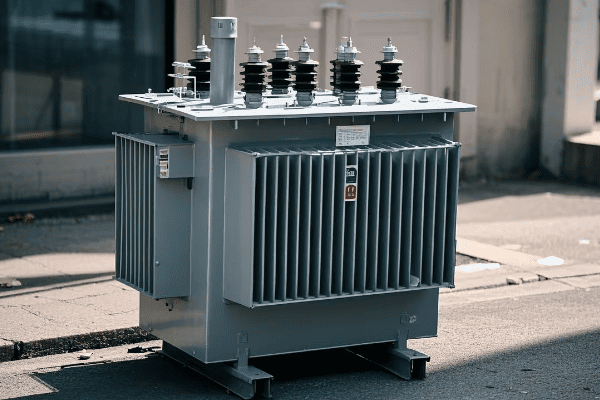
Let’s delve into the environmental benefits of dry type transformers:
Elimination of Oil-Related Risks
Dry type transformers completely remove the environmental hazards associated with oil.
Oil-Free Advantages:
- No risk of soil or water contamination from leaks
- Elimination of oil disposal and recycling issues
- Reduced fire risk and associated environmental damage
Reduced Carbon Footprint
These transformers have a lower environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
Carbon Reduction Aspects:
- Lower transportation emissions due to lighter weight
- Reduced energy losses leading to lower operational emissions
- Longer lifespan reducing the frequency of replacement and associated manufacturing emissions
Support for Green Building Initiatives
Dry type transformers align well with sustainable construction practices.
Green Building Benefits:
- Contribution to LEED certification points
- Improved indoor air quality due to absence of oil vapors
- Reduced need for extensive fire suppression systems
Enhanced Recyclability
The materials used in dry type transformers are often more recyclable.
Recycling Advantages:
- Easier separation of components at end-of-life
- Higher recoverability of copper and steel
- Absence of hazardous oil simplifies the recycling process
| Environmental Aspect | Advantage Over Traditional Models | Impact on Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-Free Design | Eliminates Risk of Contamination | High |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower Lifecycle Emissions | Moderate to High |
| Green Building Support | Aligns with Sustainable Practices | Moderate |
| Recyclability | Easier End-of-Life Management | High |
In my years of working with various transformer types, I’ve seen a significant shift towards dry type transformers in environmentally sensitive applications. I recall a project for a water treatment facility located near a protected wetland. The facility managers were extremely concerned about the potential environmental impact of their electrical equipment. By installing dry type transformers, we eliminated the risk of oil contamination, providing peace of mind to the facility operators and local environmental authorities alike.
It’s important to note that the environmental benefits of dry type transformers extend beyond just eliminating oil-related risks. In one case, I worked on a lifecycle assessment comparing dry type and oil-filled transformers for a large commercial development. The results were eye-opening – the dry type transformers showed a significantly lower carbon footprint over their operational life, primarily due to reduced energy losses and longer lifespan.
Don’t overlook the impact of transformer choice on green building certifications. I recently consulted on a project for a new corporate headquarters aiming for LEED Platinum certification. The use of dry type transformers contributed valuable points towards their energy and environmental quality credits, helping them achieve their sustainability goals.
Another crucial aspect is the end-of-life considerations for transformers. I’ve been involved in developing recycling protocols for electrical equipment, and dry type transformers consistently prove easier to handle and recycle. In a recent decommissioning project, we were able to recover over 95% of the materials from the dry type transformers for recycling or reuse, a figure that would have been much lower with oil-filled units.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the environmental advantages of dry type transformers are driving innovation in other areas of electrical engineering. I’m currently part of a research team exploring the use of biodegradable insulation materials in transformer construction. This could further enhance the environmental credentials of dry type transformers, potentially making them one of the most sustainable options in power distribution equipment.
The environmental advantages of dry type distribution transformers over traditional models are clear and significant. From eliminating oil-related risks to supporting green building initiatives and enhancing recyclability, these transformers offer a comprehensive solution for organizations looking to reduce their environmental footprint. As sustainability becomes an increasingly critical factor in infrastructure decisions, the role of dry type transformers in creating more environmentally friendly power distribution systems is set to grow even further.
Dry vs. Oil-Filled Transformers: How Do They Compare in Modern Power Distribution Networks?
Are you torn between choosing dry type or oil-filled transformers for your power distribution needs? You’re not alone. This decision is crucial for many network operators and facility managers.
In modern power distribution networks, dry type transformers offer advantages in safety, environmental protection, and maintenance, while oil-filled transformers excel in cost-effectiveness for higher power ratings and outdoor applications. Dry types are preferred for indoor, urban, and environmentally sensitive locations, while oil-filled remain popular for high-capacity outdoor substations and areas with less stringent fire safety requirements.
Let’s compare these two transformer types across key aspects:
Safety Considerations
Safety is a primary concern in transformer selection.
Safety Comparison:
- Dry Type: Lower fire risk, no oil leakage hazard
- Oil-Filled: Higher fire risk, potential for oil spills
Environmental Impact
Environmental factors are increasingly important in equipment choices.
Environmental Aspects:
- Dry Type: No oil-related environmental risks, easier to recycle
- Oil-Filled: Potential for soil and water contamination, more complex disposal
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance needs affect long-term operational costs.
Maintenance Comparison:
- Dry Type: Lower maintenance, no oil monitoring or replacement
- Oil-Filled: Regular oil testing and potential replacement, more intensive maintenance
Performance Characteristics
Performance varies depending on the application and environment.
Performance Aspects:
- Dry Type: Better in high temperatures, more suitable for indoor use
- Oil-Filled: Superior cooling properties, better for high-capacity outdoor applications
| Aspect | Dry Type Transformers | Oil-Filled Transformers |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Higher | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Indoor Suitability | Excellent | Limited |
| High Power Capacity | Limited | Excellent |
In my experience working with both dry type and oil-filled transformers, I’ve seen how crucial it is to match the right type to the specific application. I remember a project for a new hospital where we initially considered oil-filled transformers due to their lower cost. However, after a comprehensive risk assessment, we opted for dry type units. The enhanced safety features and reduced maintenance needs aligned perfectly with the hospital’s priorities, justifying the higher initial investment.
It’s important to note that while dry type transformers often have advantages in urban and indoor settings, oil-filled transformers still play a vital role in many applications. In a recent substation upgrade project for a rural electric cooperative, we chose oil-filled transformers for their high-capacity capabilities and cost-effectiveness in outdoor installations. The lower population density and reduced fire risk in the area made this a suitable choice.
Don’t overlook the impact of climate on transformer selection. I once worked on a project in a tropical region where the high ambient temperatures and humidity were causing issues with oil-filled transformers. Switching to dry type units resolved these problems, highlighting the importance of considering environmental factors in the selection process.
Another crucial aspect is the total cost of ownership. While dry type transformers often have a higher upfront cost, their reduced maintenance needs and longer lifespan can result in lower long-term expenses. I developed a comprehensive cost analysis tool that factors in initial costs, maintenance, energy efficiency, and expected lifespan. This tool has helped many clients make more informed decisions based on their specific circumstances and priorities.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how technological advancements are narrowing the gap between these two transformer types. I’m currently involved in testing new hybrid designs that aim to combine the best features of both dry type and oil-filled transformers. These innovations could potentially offer new solutions that blend the safety and environmental benefits of dry type units with the high-capacity capabilities of oil-filled transformers.
The comparison between dry and oil-filled transformers in modern power distribution networks isn’t about declaring an overall winner, but about understanding which type is best suited for specific applications and environments. Both types have their strengths and ideal use cases. As power distribution needs continue to evolve, the choice between dry and oil-filled transformers will remain a critical decision that requires careful consideration of safety, environmental, performance, and economic factors.
What Technological Innovations Are Driving the Evolution of Dry Type Distribution Transformers?
Are you wondering how dry type transformers are keeping pace with the rapidly changing energy landscape? You’re not alone. The technology behind these transformers is evolving at an unprecedented rate.
Technological innovations driving dry type transformer evolution include advanced insulation materials, smart monitoring systems, modular designs, and improved cooling technologies. These innovations enhance efficiency, extend lifespan, enable predictive maintenance, and improve overall performance. The integration of IoT and AI technologies is also making these transformers smarter and more responsive to grid demands.

Let’s explore the key innovations shaping the future of dry type transformers:
Advanced Insulation Materials
New materials are revolutionizing transformer insulation.
Insulation Innovations:
- Nano-composite materials for improved thermal management
- Biodegradable insulation options
- Self-healing insulation technologies
Smart Monitoring Systems
Intelligent monitoring is enhancing transformer management.
Smart Features:
- Real-time temperature and load monitoring
- Predictive maintenance algorithms
- Integration with smart grid systems
Modular and Scalable Designs
Flexibility in design is meeting diverse application needs.
Modular Advantages:
- Customizable configurations
- Easier transportation and installation
- Simplified upgrades and maintenance
Improved Cooling Technologies
Enhanced cooling systems are boosting performance and efficiency.
Cooling Innovations:
- Advanced forced air cooling designs
- Phase change materials for thermal management
- Hybrid cooling systems for extreme environments
| Innovation | Impact on Performance | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Insulation | High | Very High |
| Smart Monitoring | Moderate to High | High |
| Modular Designs | Moderate | High |
| Improved Cooling | High | Moderate to High |
In my years of working with dry type transformers, I’ve witnessed remarkable technological advancements. I recall a project where we implemented one of the first nano-composite insulation systems in a high-stress industrial environment. The improvement in thermal management and overall efficiency was significant, allowing the transformer to handle higher loads without compromising its lifespan.
It’s important to note that while these innovations offer exciting possibilities, their implementation often requires careful planning. In one case, I worked on integrating a new smart monitoring system into an existing transformer fleet. The challenge wasn’t just technical; we had to develop new operational protocols and train staff to effectively use the wealth of data now available. The effort paid off, with a 30% reduction in unexpected downtime within the first year.
Don’t overlook the potential of modular designs in addressing unique installation challenges. I recently consulted on a project for a historic building where space constraints were a major issue. By using a modular dry type transformer, we were able to design a custom configuration that fit the available space perfectly while meeting all performance requirements.
Another crucial aspect is the role of improved cooling technologies in expanding the application range of dry type transformers. I’m currently involved in a research project exploring the use of phase change materials for thermal management in high-power dry type transformers. This technology could potentially allow dry type units to compete with oil-filled transformers in applications that were previously out of reach due to cooling limitations.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how AI and machine learning are being integrated into transformer management systems. I’m part of a team developing an AI-driven predictive maintenance system for a large utility’s transformer fleet. The system analyzes data from multiple sensors to predict potential failures weeks in advance, allowing for proactive maintenance and significantly reducing the risk of unplanned outages.
The technological innovations driving the evolution of dry type distribution transformers are not just incremental improvements – they’re reshaping what’s possible in power distribution. From advanced materials to smart systems, these innovations are making dry type transformers more efficient, reliable, and versatile than ever before. As we continue to push the boundaries of transformer technology, we’re opening up new possibilities for safer, more sustainable, and more efficient power distribution networks.
How Are Dry Type Transformers Adapting to Meet the Demands of Smart Grid Integration?
Are you grappling with the challenges of integrating your power distribution system into a smart grid? You’re not alone. The transition to smart grids is pushing transformer technology to new limits.
Dry type transformers are adapting to smart grid demands through the integration of advanced sensors, communication capabilities, and control systems. They now feature real-time monitoring, bidirectional power flow management, and voltage regulation capabilities. These adaptations enable better grid stability, improved power quality, and more efficient energy distribution in the context of increasingly complex and dynamic smart grid environments.
Let’s explore how dry type transformers are evolving for smart grid integration:
Advanced Sensing and Monitoring
Smart grid integration requires comprehensive real-time data.
Smart Sensing Features:
- Multi-point temperature monitoring
- Load and power quality sensors
- Partial discharge detection systems
Enhanced Communication Capabilities
Seamless data exchange is crucial for smart grid operation.
Communication Enhancements:
- Integration with SCADA systems
- Support for various communication protocols (e.g., IEC 61850)
- Secure data transmission capabilities
Adaptive Control Systems
Transformers need to respond dynamically to grid conditions.
Adaptive Features:
- Automatic voltage regulation
- Dynamic load balancing
- Fault detection and isolation capabilities
Bidirectional Power Flow Management
Smart grids require transformers to handle power flow in both directions.
Bidirectional Capabilities:
- Support for distributed energy resource integration
- Management of reverse power flow from renewable sources
- Enhanced harmonics management for power quality
| Smart Grid Feature | Transformer Adaptation | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Advanced Sensors | Improved Reliability |
| Data Communication | Enhanced Connectivity | Better Grid Management |
| Dynamic Response | Adaptive Control Systems | Increased Stability |
| DER Integration | Bidirectional Power Handling | Renewable Energy Support |
In my experience working on smart grid projects, the adaptation of dry type transformers has been crucial to successful implementations. I remember a particularly challenging project where we were integrating a large solar farm into an existing grid. The dry type transformers we used were equipped with advanced monitoring and control systems that could handle the variable input from the solar panels. This not only ensured stable power delivery but also allowed for more efficient utilization of the renewable energy source.
It’s important to note that adapting transformers for smart grid integration often involves more than just adding new features. In one case, I worked on upgrading an urban substation with smart-enabled dry type transformers. We had to completely rethink the substation’s layout and control systems to fully leverage the new capabilities of these transformers. The result was a much more responsive and efficient power distribution system that could adapt in real-time to changing load conditions.
Don’t overlook the importance of cybersecurity in smart grid-enabled transformers. I recently led a team in developing security protocols for a network of smart dry type transformers. We implemented multi-layer encryption and intrusion detection systems to protect against potential cyber threats. This aspect of smart grid integration is becoming increasingly critical as our power systems become more interconnected and data-driven.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these transformers in enabling microgrid capabilities. I’m currently advising on a project where smart dry type transformers are key components in a community microgrid. These transformers can seamlessly switch between grid-connected and island modes, providing resilience during main grid outages while also optimizing local energy use and generation.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the adaptation of dry type transformers is opening up new possibilities for grid optimization. I’m part of a research team exploring the use of AI algorithms to coordinate a network of smart transformers. The goal is to create a self-optimizing grid that can automatically adjust to changing conditions, from fluctuating renewable inputs to varying load demands, all while maintaining optimal efficiency and stability.
The adaptation of dry type transformers to meet smart grid demands is not just about adding new features – it’s about reimagining the role of transformers in our power distribution systems. These evolving transformers are becoming active, intelligent components of the grid, capable of not just distributing power but also contributing to the overall intelligence and efficiency of our energy systems. As we continue to develop and implement smart grid technologies, the role of these advanced dry type transformers will be crucial in creating more resilient, efficient, and sustainable power networks.
What Role Do Dry Type Distribution Transformers Play in Enhancing Urban Power Infrastructure Safety?
Are you concerned about the safety of power distribution in densely populated urban areas? You’re right to be cautious. Urban environments present unique challenges for electrical infrastructure.
Dry type distribution transformers play a crucial role in enhancing urban power infrastructure safety by eliminating fire and environmental risks associated with oil-filled units. They offer improved fire resistance, reduced risk of contamination, and are ideal for indoor and confined space installations. These features make them essential for ensuring safe and reliable power distribution in buildings, underground networks, and other urban settings.
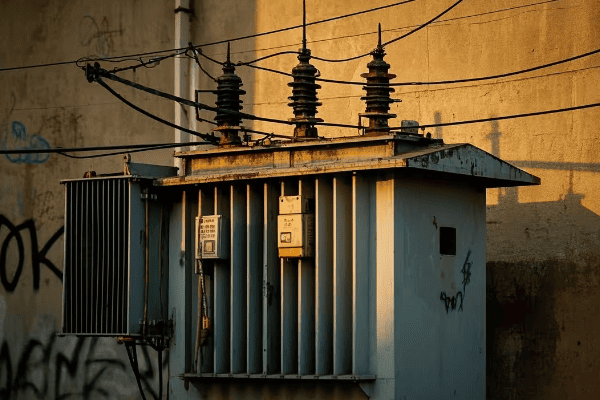

Let’s explore the key safety enhancements dry type transformers bring to urban power infrastructure:
Fire Risk Mitigation
Dry type transformers significantly reduce fire hazards in urban settings.
Fire Safety Features:
- Non-flammable insulation materials
- Self-extinguishing properties
- Reduced need for extensive fire suppression systems
Environmental Protection
These transformers eliminate risks associated with oil leaks and spills.
Environmental Safety Aspects:
- No risk of soil or water contamination
- Safer for installation near water sources or sensitive ecosystems
- Reduced environmental impact in case of accidents or natural disasters
Space Optimization
Dry type transformers are ideal for space-constrained urban environments.
Space-Saving Benefits:
- Compact designs suitable for indoor installations
- Ability to be installed closer to load centers
- Reduced clearance requirements compared to oil-filled units
Enhanced Public Safety
These transformers contribute to overall public safety in urban areas.
Public Safety Enhancements:
- Reduced risk of explosions or oil fires
- Safer for installation in high-traffic areas
- Lower noise pollution levels
| Safety Aspect | Urban Benefit | Impact on Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Risk Reduction | Higher Building Safety | Significant |
| Environmental Protection | Reduced Contamination Risk | High |
| Space Optimization | Efficient Land Use | Moderate to High |
| Public Safety | Improved Urban Living Conditions | High |
In my years of working on urban power infrastructure projects, I’ve seen the transformative impact of dry type transformers on safety. I recall a project in a densely populated city center where we were tasked with upgrading an aging underground substation. The space was tight, surrounded by residential buildings, and had a history of minor oil leaks from the old transformers. By installing dry type units, we not only eliminated the leak risk but also significantly reduced the fire hazard. The local fire department was particularly pleased, as it simplified their emergency response planning for the area.
It’s important to note that the safety benefits of dry type transformers extend beyond just fire and leak prevention. In one case, I worked on a retrofit project for a high-rise office building. The building management was concerned about the weight and vibration of the existing oil-filled transformers. By switching to dry type units, we were able to reduce both issues, enhancing the structural safety of the building while also improving the working environment for the occupants.
Don’t overlook the role of dry type transformers in enabling power infrastructure in sensitive urban locations. I recently consulted on a project to provide power to a new underground transit system. The use of dry type transformers was crucial in meeting the stringent safety requirements for these confined, high-traffic spaces. Their installation allowed for power distribution points to be placed closer to where they were needed, improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the system.
Another crucial aspect is the adaptability of dry type transformers to smart city initiatives. I’m currently involved in a project integrating smart dry type transformers into an urban microgrid. These units not only provide the necessary safety features for urban installation but also offer the advanced monitoring and control capabilities needed for a resilient, responsive urban power network.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the safety features of dry type transformers are enabling new approaches to urban planning and development. I recently participated in a design charrette for a new eco-friendly urban district. The use of dry type transformers allowed for more flexible placement of power distribution points, enabling innovative architectural designs that seamlessly integrated electrical infrastructure with public spaces.
Dry type distribution transformers play a vital role in enhancing the safety of urban power infrastructure. By addressing key concerns such as fire risk, environmental protection, space optimization, and public safety, these transformers are enabling safer, more reliable power distribution in our increasingly dense and complex urban environments. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the importance of these safe, efficient, and adaptable power distribution solutions will only increase, making dry type transformers an essential component of modern urban infrastructure.
How Do Dry Type Transformers Contribute to Reduced Maintenance and Operational Costs in Power Networks?
Are you tired of the high maintenance costs and operational headaches associated with traditional transformers? You’re not alone. Many network operators are seeking ways to streamline their operations and reduce expenses.
Dry type transformers contribute significantly to reduced maintenance and operational costs in power networks. They eliminate the need for oil monitoring and replacement, require less frequent inspections, and have a longer operational lifespan. Their simpler maintenance routines, coupled with advanced monitoring capabilities, lead to lower labor costs, reduced downtime, and improved overall network reliability.

Let’s delve into how dry type transformers cut down on maintenance and operational costs:
Elimination of Oil-Related Maintenance
Dry type transformers remove the need for oil management.
Oil-Free Benefits:
- No oil sampling or testing required
- Elimination of oil filtration or replacement costs
- Reduced risk of oil-related failures
Simplified Inspection Routines
These transformers require less complex and less frequent inspections.
Inspection Advantages:
- Visual inspections are often sufficient
- Reduced need for specialized testing equipment
- Lower frequency of required inspections
Extended Operational Lifespan
Dry type transformers typically last longer than their oil-filled counterparts.
Lifespan Benefits:
- Reduced frequency of replacements
- Lower lifecycle costs
- Decreased capital expenditure over time
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
Modern dry type transformers often come with built-in monitoring systems.
Monitoring Advantages:
- Real-time performance tracking
- Early detection of potential issues
- Optimization of maintenance schedules
| Cost Reduction Area | Impact on Maintenance | Long-Term Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Elimination | Significant Reduction | High |
| Simplified Inspections | Moderate Reduction | Moderate to High |
| Extended Lifespan | Long-Term Cost Reduction | Very High |
| Advanced Monitoring | Improved Efficiency | Moderate to High |
In my experience working with various power networks, the switch to dry type transformers has often led to substantial cost savings. I remember a project for a large industrial complex that had been struggling with frequent transformer-related downtime. By replacing their oil-filled units with dry type transformers, we were able to reduce their annual maintenance costs by nearly 40%. The simplified maintenance routines meant less time spent on regular checks and fewer specialized technicians required.
It’s important to note that the cost benefits of dry type transformers often extend beyond just maintenance. In one case, I worked with a utility company to analyze the total cost of ownership for their transformer fleet. We found that while the initial investment for dry type units was higher, the reduced maintenance needs, longer lifespan, and improved reliability resulted in a significantly lower total cost over a 20-year period.
Don’t overlook the impact of reduced downtime on operational costs. I recently consulted on a project for a data center where even brief power interruptions could be extremely costly. The implementation of dry type transformers with advanced monitoring systems allowed for predictive maintenance, virtually eliminating unexpected outages. This not only reduced direct maintenance costs but also significantly improved the data center’s reliability and customer satisfaction.
Another crucial aspect is the role of dry type transformers in simplifying compliance with environmental regulations. I’ve worked with several companies in environmentally sensitive areas where the use of oil-filled transformers required complex and costly containment systems. Switching to dry type units eliminated these requirements, reducing both initial installation costs and ongoing compliance expenses.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials and design are further enhancing the cost-saving potential of dry type transformers. I’m currently involved in testing a new generation of dry type transformers that use advanced composite materials. These units promise even longer lifespans and higher efficiency, potentially offering even greater long-term cost savings for network operators.
Dry type transformers contribute significantly to reduced maintenance and operational costs in power networks through a combination of simplified maintenance routines, extended lifespans, and advanced monitoring capabilities. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings in terms of reduced labor costs, decreased downtime, and improved reliability make them an increasingly attractive option for many power network operators. As we continue to seek ways to optimize our electrical infrastructure, the role of dry type transformers in reducing overall operational costs is likely to become even more prominent.
Conclusion
Dry type distribution transformers are revolutionizing safety and efficiency in modern power distribution networks. They offer enhanced safety features, improved energy efficiency, and significant environmental benefits. With technological innovations driving their evolution, these transformers are adapting to meet the demands of smart grids, enhancing urban power infrastructure safety, and contributing to reduced maintenance and operational costs. As power networks continue to evolve, dry type transformers will play a crucial role in shaping a safer, more efficient, and sustainable energy future.
Are you prepared for the revolutionary changes coming to the distribution transformer market? The energy landscape is shifting rapidly, and those who aren’t ready may be left behind.
The distribution transformer market is set to drive smart grid evolution and sustainable energy solutions from 2025 onwards. Key factors include the integration of IoT and AI technologies, increased focus on energy efficiency, growing renewable energy adoption, and the need for grid modernization to support electric vehicle infrastructure and decentralized power generation.

As someone who has been deeply involved in the power distribution industry for years, I’ve witnessed firsthand the exciting developments shaping our future. In this article, I’ll guide you through the key trends and innovations that are transforming the distribution transformer market, and how they’re paving the way for a smarter, more sustainable energy future.
What Key Trends Are Shaping the Distribution Transformer Market in 2025 and Beyond?
Are you wondering what forces will drive the distribution transformer market in the coming years? You’re not alone. Many industry professionals are keen to understand the evolving landscape.
Key trends shaping the distribution transformer market include the integration of smart technologies, focus on energy efficiency, adoption of eco-friendly materials, increased demand for renewable energy integration, and the rise of modular and compact designs. These trends are driven by the need for grid modernization, sustainability goals, and the evolving energy consumption patterns.
Let’s dive deeper into these transformative trends:
Smart Technology Integration
The future of distribution transformers is intelligent and connected.
Smart Features:
- Real-time monitoring and diagnostics
- IoT connectivity for grid communication
- AI-driven predictive maintenance
Energy Efficiency Focus
Efficiency is becoming a primary concern in transformer design.
Efficiency Advancements:
- Use of advanced core materials like amorphous metals
- Improved winding designs to reduce losses
- Optimized cooling systems for better performance
Eco-Friendly Materials
Sustainability is driving material choices in transformer manufacturing.
Sustainable Innovations:
- Biodegradable transformer oils
- Recyclable components
- Low-carbon footprint manufacturing processes
Renewable Energy Integration
Transformers are evolving to support the growth of renewable energy.
Renewable Support Features:
- Bi-directional power flow capabilities
- Enhanced voltage regulation for variable inputs
- Specialized designs for wind and solar farm applications
| Trend | Impact on Market | Adoption Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Technology | High | Short to Medium Term |
| Energy Efficiency | Very High | Immediate to Long Term |
| Eco-Friendly Materials | Moderate | Medium to Long Term |
| Renewable Integration | High | Short to Medium Term |
In my experience working with distribution transformer manufacturers, these trends are already shaping product development strategies. I recall a recent project where we were designing a new line of transformers for a major utility. The emphasis on smart features was striking – every unit was equipped with advanced sensors and communication modules, a far cry from the passive devices of just a few years ago.
It’s important to note that while these trends are exciting, they also present challenges. In one case, I worked with a manufacturer struggling to balance the cost of implementing smart technologies with market demands for competitive pricing. We had to develop a modular approach, allowing for basic smart features in standard models with options for more advanced capabilities as add-ons.
Don’t overlook the impact of energy efficiency regulations on these trends. I recently consulted on a project where a utility was upgrading its entire transformer fleet to meet new efficiency standards. The focus on reducing losses led to some innovative designs, including the use of hybrid core materials that offered a balance between performance and cost.
Another crucial aspect is the growing demand for transformers that can handle renewable energy integration. I’m currently advising on a project to develop specialized transformers for offshore wind farms. These units need to withstand harsh marine environments while managing the variable output of wind turbines – a unique challenge that’s driving innovation in materials and design.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the trend towards eco-friendly materials is spurring new research. I visited a lab recently where they’re developing a new type of biodegradable transformer oil derived from plant sources. If successful, this could significantly reduce the environmental impact of transformer installations and maintenance.
The key trends shaping the distribution transformer market in 2025 and beyond are not just about technological advancement – they’re about reimagining the role of transformers in our evolving energy landscape. From smart technologies to eco-friendly materials, these trends are driving a new era of innovation in the industry. As we move forward, the ability to adapt to and leverage these trends will be crucial for success in the distribution transformer market.
How Are Distribution Transformers Catalyzing Smart Grid Evolution in the Coming Decade?
Are you curious about the role of distribution transformers in the smart grid revolution? You should be. These devices are becoming the unsung heroes of our evolving power infrastructure.
Distribution transformers are catalyzing smart grid evolution by serving as intelligent nodes in the power network. They’re integrating advanced monitoring, communication, and control capabilities, enabling real-time data exchange, automated grid management, and efficient integration of distributed energy resources. This transformation is crucial for creating a more resilient, flexible, and efficient power distribution system.
Let’s explore how distribution transformers are driving smart grid evolution:
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Modern transformers provide continuous insights into grid conditions.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Load and power quality analysis
- Temperature and oil condition tracking
- Fault detection and prediction
Advanced Communication Systems
Transformers are becoming key communication points in the grid.
Communication Features:
- Integration with SCADA systems
- Support for various protocols (e.g., IEC 61850)
- Secure data transmission capabilities
Automated Grid Management
Smart transformers enable more autonomous grid operations.
Automation Aspects:
- Dynamic load balancing
- Voltage regulation and power factor correction
- Self-healing capabilities during outages
Distributed Energy Resource Integration
Transformers facilitate the integration of renewable and distributed generation.
DER Support:
- Bi-directional power flow management
- Microgrid support and islanding capabilities
- Enhanced harmonics management for diverse energy sources
| Smart Grid Feature | Transformer Role | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Data Collection Point | Improved Reliability |
| Advanced Communication | Network Node | Enhanced Control |
| Automated Management | Intelligent Actor | Increased Efficiency |
| DER Integration | Flexible Interface | Greater Sustainability |
In my years working on smart grid projects, I’ve seen the transformative impact of intelligent distribution transformers. I remember a project where we upgraded a city’s aging transformer network with smart units. The change was remarkable – suddenly, grid operators had real-time visibility into power quality, load patterns, and potential issues across the entire distribution network. This level of insight allowed for proactive maintenance and significantly reduced outage times.
It’s important to note that the role of transformers in smart grids goes beyond just data collection. In one case, I worked on implementing a self-healing grid system where smart transformers played a crucial role. When a fault occurred, these transformers could automatically reconfigure the network, rerouting power to minimize the impact of the outage. This capability not only improved reliability but also reduced the workload on maintenance crews.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in this evolution. I recently participated in an industry working group focused on developing common communication standards for smart grid devices. This effort is crucial for ensuring that transformers from different manufacturers can seamlessly integrate into the smart grid ecosystem.
Another crucial aspect is cybersecurity. As transformers become more connected, they also become potential entry points for cyber attacks. I’m currently advising on a project to develop robust security protocols for smart transformers. This includes encrypted communication, secure firmware updates, and intrusion detection systems – all essential for maintaining the integrity of the smart grid.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how smart transformers are enabling new business models in the energy sector. I recently consulted on a pilot project where utility customers could participate in demand response programs directly through their local distribution transformer. The transformer’s ability to monitor and manage local loads in real-time made it possible to create a more dynamic and responsive energy market at the neighborhood level.
Distribution transformers are not just passive components in the smart grid evolution – they’re active catalysts driving the change. By serving as intelligent, communicative nodes in the power network, these devices are enabling a level of grid awareness and control that was unimaginable just a few years ago. As we move into the next decade, the continued development of smart transformer technology will be crucial in realizing the full potential of the smart grid, creating a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable power distribution system for the future.
What Role Do Distribution Transformers Play in Advancing Sustainable Energy Solutions?
Are you concerned about the environmental impact of our energy systems? You’re not alone. The push for sustainability is reshaping the role of distribution transformers in significant ways.
Distribution transformers play a crucial role in advancing sustainable energy solutions by improving energy efficiency, facilitating renewable energy integration, and supporting electrification initiatives. They enable bi-directional power flow for distributed generation, reduce transmission losses, and provide the flexibility needed for smart grid operations, all contributing to a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
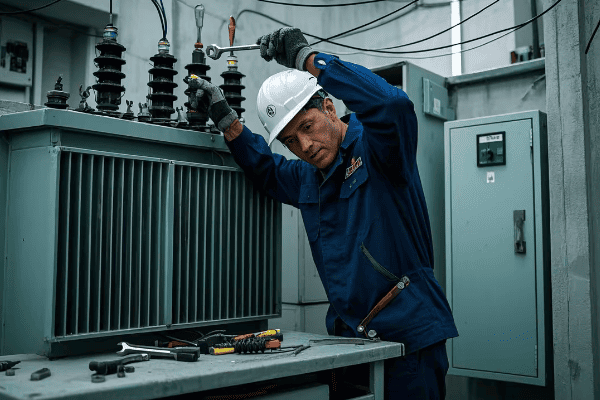
Let’s delve into the key roles of distribution transformers in sustainable energy:
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Modern transformers significantly reduce energy losses in distribution.
Efficiency Features:
- Advanced core materials for lower no-load losses
- Optimized winding designs to minimize load losses
- Intelligent load management for peak efficiency
Renewable Energy Integration
Transformers are crucial for connecting renewable sources to the grid.
Renewable Support:
- Handling variable inputs from solar and wind
- Providing voltage support for distributed generation
- Enabling energy storage integration
Electrification Support
Transformers are key to expanding clean electrification efforts.
Electrification Roles:
- Supporting electric vehicle charging infrastructure
- Enabling electrification of heating and industrial processes
- Facilitating microgrids and community energy projects
Lifecycle Sustainability
The entire lifecycle of transformers is being optimized for sustainability.
Sustainable Practices:
- Use of eco-friendly materials and biodegradable oils
- Design for recyclability and easy end-of-life disposal
- Reduced carbon footprint in manufacturing and transportation
| Sustainability Aspect | Transformer Contribution | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduced Losses | Lower Carbon Emissions |
| Renewable Integration | Grid Flexibility | Increased Clean Energy Use |
| Electrification | Infrastructure Support | Reduced Fossil Fuel Dependence |
| Lifecycle Practices | Reduced Environmental Footprint | Conservation of Resources |
In my experience working on sustainable energy projects, the impact of advanced distribution transformers has been profound. I recall a project where we replaced an urban area’s aging transformer fleet with high-efficiency models. The energy savings were impressive – we saw a reduction in distribution losses of over 30%, which translated to significant carbon emission reductions equivalent to taking thousands of cars off the road.
It’s important to note that the role of transformers in sustainability goes beyond just efficiency. In one case, I worked on integrating a large solar farm into a rural grid. The specialized transformers we used were crucial in managing the variable output of the solar panels and ensuring stable power delivery to the community. This project not only increased the region’s renewable energy capacity but also improved overall grid stability.
Don’t overlook the importance of transformers in enabling new sustainable technologies. I’m currently advising on a project to develop a network of fast-charging stations for electric vehicles. The transformers we’re designing for this application need to handle high power demands and frequent load fluctuations – challenges that are driving innovations in materials and cooling systems.
Another crucial aspect is the role of smart transformers in demand-side management. In a recent pilot project, we used intelligent transformers to implement a community-wide energy conservation program. These transformers could adjust voltage levels slightly during peak times, reducing overall energy consumption without impacting service quality. This kind of fine-tuned control is essential for creating more sustainable energy consumption patterns.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how transformer manufacturers are embracing sustainability in their own operations. I recently visited a factory that had completely redesigned its production line to minimize waste and energy use. They were even using solar power for part of their manufacturing process – a great example of the industry practicing what it preaches.
Distribution transformers are playing a pivotal role in advancing sustainable energy solutions. From improving efficiency and integrating renewables to supporting electrification and embracing lifecycle sustainability, these devices are at the forefront of our transition to a cleaner energy future. As we continue to innovate in this field, transformers will remain key enablers of the sustainable, resilient, and efficient power systems we need to address our global energy challenges.
How Is the Distribution Transformer Market Adapting to Meet Future Energy Demands?
Are you wondering how the transformer industry is keeping up with rapidly changing energy needs? It’s a critical question as our power demands evolve at an unprecedented pace.
The distribution transformer market is adapting to future energy demands through technological innovation, increased customization, and enhanced manufacturing processes. Manufacturers are developing more efficient, smart, and flexible transformers capable of handling bidirectional power flow, integrating with renewable sources, and supporting electric vehicle charging infrastructure. The market is also shifting towards more resilient and compact designs to meet urban and remote area needs.
Let’s explore how the market is evolving to meet these challenges:
Technological Innovation
Cutting-edge technologies are being incorporated into transformer designs.
Innovative Features:
- Solid-state transformer development
- Advanced sensor integration for real-time monitoring
- AI-driven predictive maintenance capabilities
Customization and Flexibility
Transformers are being tailored to specific application needs.
Customization Aspects:
- Modular designs for easy upgrades and maintenance
- Configurable power ratings to match varying load profiles
- Specialized units for renewable energy and EV charging applications
Enhanced Manufacturing Processes
Production methods are evolving to improve quality and reduce costs.
Manufacturing Advancements:
- Automation and robotics in assembly lines
- 3D printing for complex components
- Advanced testing and quality control procedures
Resilience and Compact Design
Transformers are being designed to withstand environmental challenges and space constraints.
Design Improvements:
- Ruggedized construction for extreme weather conditions
- Compact designs for urban installations
- Eco-friendly cooling systems for improved reliability
| Adaptation Area | Market Response | Future Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Smart Features Integration | Enhanced Grid Management |
| Customization | Application-Specific Designs | Improved Efficiency and Performance |
| Manufacturing | Advanced Production Techniques | Cost Reduction and Quality Improvement |
| Design | Resilient and Compact Units | Wider Application Range |
In my years of experience in the transformer industry, I’ve witnessed remarkable adaptations to meet changing energy demands. I remember working on a project to develop transformers for a new urban development that required a mix of residential, commercial, and EV charging capabilities. The challenge led us to create a highly flexible transformer design that could dynamically adjust to varying load types and power quality requirements throughout the day.
It’s important to note that adaptation in the transformer market isn’t just about new products – it’s also about rethinking existing infrastructure. In one case, I consulted on a grid modernization project where we had to upgrade a city’s transformer network without replacing all units. We developed retrofit kits that added smart monitoring and control capabilities to existing transformers, effectively bridging the gap between old infrastructure and new energy demands.
Don’t overlook the role of materials science in this adaptation process. I’m currently involved in a research project exploring the use of high-temperature superconducting materials in transformer design. If successful, this could lead to transformers with significantly higher efficiency and power density, potentially revolutionizing how we approach power distribution in high-demand areas.
Another crucial aspect is the growing focus on sustainability in transformer manufacturing. I recently visited a factory that had implemented a closed-loop production system, recycling materials from old transformers into new units. This approach not only reduces environmental impact but also helps address potential material shortages in the face of growing global demand.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the market is adapting to the needs of renewable energy integration. I’m advising on a project to develop specialized transformers for offshore wind farms. These units need to withstand harsh marine environments, handle variable power inputs, and operate reliably with minimal maintenance – a unique set of challenges that’s driving innovation in materials, design, and remote monitoring technologies.
The distribution transformer market is demonstrating remarkable adaptability in the face of future energy demands. From technological innovations and customized solutions to improved manufacturing processes and resilient designs, the industry is evolving rapidly to meet the complex needs of our changing energy landscape. As we move forward, this ability to adapt and innovate will be crucial in ensuring that our power distribution infrastructure can support the sustainable, efficient, and reliable energy systems of the future.
What Technological Innovations Will Define Distribution Transformers Beyond 2025?
Are you curious about the next big leaps in transformer technology? You should be. The innovations coming after 2025 could revolutionize how we think about power distribution.
Technological innovations defining distribution transformers beyond 2025 will include solid-state designs, AI-driven self-optimization, advanced materials like high-temperature superconductors, and quantum sensing technologies. We’ll also see increased integration of energy storage, enhanced cybersecurity features, and transformers designed for extreme environments and space applications.
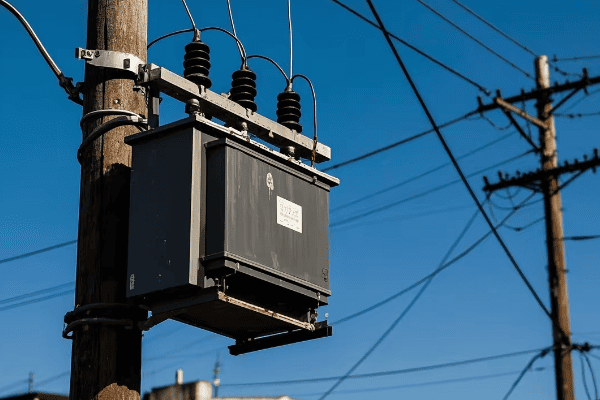

Let’s explore these groundbreaking innovations in more detail:
Solid-State Transformer Technology
The future may see a shift from traditional electromagnetic transformers to solid-state designs.
Solid-State Advantages:
- Direct DC-AC conversion capabilities
- Smaller size and lighter weight
- Enhanced power quality control
AI-Driven Self-Optimization
Artificial Intelligence will take transformer operation to new levels of efficiency.
AI Capabilities:
- Real-time load forecasting and adjustment
- Predictive maintenance and self-diagnosis
- Autonomous grid balancing and power flow optimization
Advanced Materials
New materials will revolutionize transformer performance and efficiency.
Material Innovations:
- High-temperature superconducting windings
- Nanomaterial-enhanced insulation
- Biodegradable and eco-friendly cooling fluids
Quantum Sensing Technologies
Quantum sensors could provide unprecedented accuracy in monitoring transformer health.
Quantum Sensing Applications:
- Ultra-precise current and voltage measurements
- Early detection of insulation degradation
- Magnetic field anomaly detection for fault prediction
| Innovation | Potential Impact | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Design | High | Medium-term (5-10 years) |
| AI Self-Optimization | Very High | Short to Medium-term (3-7 years) |
| Advanced Materials | High | Medium to Long-term (7-15 years) |
| Quantum Sensing | Moderate to High | Long-term (10-20 years) |
In my years of working on cutting-edge transformer technologies, I’ve seen some truly exciting developments. I remember being part of an early prototype project for solid-state transformers. The potential for these devices to revolutionize power distribution was clear, even though we faced significant challenges in scaling the technology for high-power applications. Now, as we approach 2025, I’m seeing renewed interest and investment in this area, with promising breakthroughs on the horizon.
It’s important to note that while these innovations are exciting, their implementation will likely be gradual. In one case, I worked with a utility to develop a roadmap for integrating AI-driven optimization into their transformer fleet. We started with a pilot program on a few critical units, gradually expanding as we refined the algorithms and demonstrated the benefits. This measured approach allowed for a smooth transition and helped build confidence in the new technology.
Don’t overlook the potential of advanced materials in shaping the future of transformers. I’m currently advising on a research project exploring the use of high-temperature superconductors in transformer windings. The potential for near-zero resistance could dramatically improve efficiency, but we’re still working on overcoming challenges related to cooling and cost-effectiveness. It’s a reminder that even the most promising innovations often require years of development before they’re ready for widespread adoption.
Another crucial aspect is the role of quantum technologies in transformer monitoring. While still in its early stages, I’ve been following research on quantum sensors for ultra-precise measurements in electrical systems. In a recent conference, I saw a demonstration of a quantum-based current sensor that could detect minute fluctuations impossible to measure with conventional technology. The implications for predictive maintenance and fault detection are enormous.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer technology are opening up new possibilities in extreme environments. I recently consulted on a project developing transformers for deep-sea power distribution in offshore renewable energy farms. The challenges of operating in high-pressure, corrosive environments are pushing the boundaries of material science and design, potentially leading to innovations that could benefit terrestrial applications as well.
The technological innovations that will define distribution transformers beyond 2025 are not just incremental improvements – they represent a fundamental reimagining of how we approach power transformation and distribution. From solid-state designs to quantum sensing, these advancements promise to make our power systems more efficient, reliable, and adaptable to the changing energy landscape. As we move into this new era of transformer technology, the ability to understand and leverage these innovations will be crucial for anyone involved in the power industry.
How Are Global Regulations Influencing the Evolution of the Distribution Transformer Market?
Are you finding it challenging to keep up with the changing regulatory landscape in the transformer industry? You’re not alone. Global regulations are reshaping the market in significant ways.
Global regulations are significantly influencing the distribution transformer market by driving energy efficiency standards, environmental protection measures, and safety requirements. These regulations are pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient, eco-friendly, and reliable transformers. They’re also influencing market dynamics by creating new opportunities for innovative technologies and sustainable practices.
Let’s explore how global regulations are shaping the transformer market:
Energy Efficiency Standards
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter efficiency requirements.
Regulatory Impacts:
- Mandated minimum efficiency levels
- Incentives for high-efficiency transformer adoption
- Phasing out of less efficient models
Environmental Protection Measures
Regulations are focusing on reducing the environmental impact of transformers.
Environmental Regulations:
- Restrictions on hazardous materials (e.g., PCBs)
- Requirements for biodegradable insulating fluids
- End-of-life recycling and disposal guidelines
Safety and Reliability Standards
Safety regulations are becoming more stringent and comprehensive.
Safety Requirements:
- Enhanced fire resistance standards
- Improved short-circuit withstand capabilities
- Cybersecurity standards for smart transformers
Smart Grid Compatibility
Regulations are increasingly mandating smart grid readiness.
Smart Grid Regulations:
- Requirements for communication interfaces
- Data privacy and security standards
- Interoperability guidelines for grid integration
| Regulatory Area | Market Impact | Global Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High | Increasing Stringency |
| Environmental Protection | Moderate to High | Growing Focus |
| Safety and Reliability | High | Continuous Enhancement |
| Smart Grid Compatibility | Moderate | Rapidly Evolving |
In my experience working with transformer manufacturers and utilities worldwide, I’ve seen firsthand how regulations can drive innovation and market shifts. I remember a project in Europe where new efficiency standards were introduced, requiring a significant redesign of our transformer line. Initially, this seemed like a daunting challenge, but it ultimately led to the development of more advanced core materials and winding techniques that not only met the new standards but exceeded them, giving us a competitive edge in the market.
It’s important to note that while regulations can be challenging to navigate, they often create new opportunities. In one case, I worked with a manufacturer to develop transformers that met stringent environmental regulations in a Scandinavian country. The eco-friendly design we created not only complied with local laws but also opened up new markets in other environmentally conscious regions.
Don’t overlook the impact of regional variations in regulations. I recently advised on a global expansion strategy for a transformer company, and we had to carefully map out the regulatory landscape in each target market. What was compliant in one country could be substandard in another, requiring a flexible approach to design and manufacturing.
Another crucial aspect is the role of regulations in driving smart grid adoption. I’m currently involved in a project where we’re adapting transformer designs to meet new smart grid readiness requirements in several Asian countries. These regulations are not just about adding communication capabilities; they’re pushing us to rethink the fundamental role of transformers in the grid ecosystem.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some companies are getting ahead of regulations by voluntarily adopting higher standards. I recently visited a manufacturer that had implemented sustainability practices far beyond current regulatory requirements. They saw this as not just an ethical choice but a strategic move to future-proof their products against expected regulatory changes.
Global regulations are a powerful force shaping the evolution of the distribution transformer market. From driving energy efficiency and environmental protection to ensuring safety and smart grid compatibility, these regulations are pushing the industry towards more advanced, sustainable, and integrated solutions. While navigating this complex regulatory landscape can be challenging, it’s also creating opportunities for innovation and differentiation. As we move forward, staying ahead of regulatory trends will be crucial for success in the global transformer market.
What Opportunities Does the Growing Renewable Energy Sector Present for Distribution Transformer Manufacturers?
Are you wondering how the boom in renewable energy affects the transformer industry? It’s a game-changer, offering exciting new opportunities for those ready to adapt.
The growing renewable energy sector presents significant opportunities for distribution transformer manufacturers. There’s increasing demand for specialized transformers that can handle variable inputs from solar and wind sources, integrate with energy storage systems, and support microgrid operations. Manufacturers can also innovate in areas like bi-directional power flow, enhanced voltage regulation, and smart grid integration capabilities.

Let’s explore the key opportunities in the renewable energy sector:
Specialized Transformer Designs
Renewable energy sources require transformers tailored to their unique characteristics.
Design Opportunities:
- Solar farm step-up transformers
- Wind turbine pad-mount transformers
- Offshore wind farm transformers
Energy Storage Integration
Transformers play a crucial role in connecting storage systems to the grid.
Storage-Related Opportunities:
- Battery energy storage system (BESS) interface transformers
- Transformers with built-in storage capabilities
- Hybrid renewable-storage system transformers
Microgrid Support
The rise of microgrids creates demand for specialized transformer solutions.
Microgrid Transformer Features:
- Bi-directional power flow capabilities
- Islanding support and seamless grid reconnection
- Enhanced power quality management
Smart Grid Integration
Renewable energy drives the need for smarter, more flexible transformers.
Smart Integration Capabilities:
- Advanced monitoring and control features
- Real-time data communication for grid balancing
- Adaptive voltage regulation for variable renewable inputs
| Opportunity Area | Market Potential | Technical Challenge Level |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Designs | High | Moderate |
| Storage Integration | Very High | High |
| Microgrid Support | Moderate to High | High |
| Smart Grid Integration | High | Moderate to High |
In my years working with renewable energy projects, I’ve seen the transformer industry evolve rapidly to meet new challenges. I recall a project where we were integrating a large solar farm into an existing grid. The variable output of the solar panels presented unique challenges for voltage regulation and power quality. We ended up designing a custom transformer with advanced on-load tap changing capabilities and built-in power quality management features. This not only solved the immediate integration issues but also opened up a new product line for the manufacturer.
It’s important to note that opportunities in the renewable sector often require a shift in design philosophy. In one case, I worked with a traditional transformer manufacturer entering the wind energy market. We had to completely rethink our approach to insulation and cooling to create transformers that could operate reliably in the harsh conditions of offshore wind farms. This adaptation process was challenging but ultimately led to innovations that benefited our entire product range.
Don’t overlook the potential of energy storage integration. I’m currently advising on a project developing transformers with built-in battery storage capabilities. These hybrid units can smooth out the variability of renewable sources and provide ancillary services to the grid. While still in the early stages, this concept has the potential to revolutionize how we think about energy distribution and storage.
Another crucial aspect is the role of transformers in enabling community renewable energy projects. I recently consulted on a microgrid project for a remote village, where the transformer needed to manage inputs from solar panels, a small wind turbine, and a biomass generator, while also supporting islanding capabilities. This kind of flexibility is becoming increasingly important as communities seek energy independence and resilience.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the renewable energy sector is driving innovations in transformer materials and manufacturing. I visited a research lab where they’re developing new types of magnetic materials specifically optimized for the high-frequency harmonics common in renewable energy systems. These materials could lead to smaller, more efficient transformers specifically tailored for renewable energy applications.
The growing renewable energy sector presents a wealth of opportunities for distribution transformer manufacturers who are willing to innovate and adapt. From specialized designs for solar and wind farms to advanced solutions for energy storage integration and microgrid support, the possibilities are vast. As the world continues its transition to cleaner energy sources, transformers will play a crucial role in enabling this shift. Manufacturers who can anticipate and meet the unique needs of the renewable energy sector will be well-positioned for success in this rapidly evolving market.
How Are Smart and IoT-Enabled Distribution Transformers Reshaping the Market Landscape?
Are you struggling to keep up with the rapid changes in transformer technology? You’re not alone. The rise of smart and IoT-enabled transformers is revolutionizing the industry at an unprecedented pace.
Smart and IoT-enabled distribution transformers are reshaping the market by offering real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced grid management capabilities. These advanced transformers provide utilities with unprecedented insights into their distribution networks, enabling more efficient operations, reduced downtime, and improved power quality. They’re also facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources and supporting the development of smart cities.
Let’s delve into how these smart transformers are changing the landscape:
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Smart transformers provide continuous insights into their operation and the surrounding grid.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Load and power quality analysis
- Temperature and oil condition tracking
- Fault detection and prediction
Predictive Maintenance
IoT-enabled transformers can anticipate and prevent failures.
Predictive Features:
- AI-driven analysis of operational data
- Early warning systems for potential issues
- Optimized maintenance scheduling
Enhanced Grid Management
Smart transformers enable more efficient and responsive grid operations.
Grid Management Improvements:
- Dynamic load balancing
- Voltage regulation and power factor correction
- Automatic fault isolation and self-healing capabilities
Renewable Energy Integration
These transformers facilitate the integration of distributed energy resources.
Integration Capabilities:
- Handling bi-directional power flow
- Managing intermittent renewable inputs
- Supporting microgrid operations
| Smart Feature | Market Impact | Implementation Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | High | Moderate |
| Predictive Maintenance | Very High | High |
| Enhanced Grid Management | High | Moderate to High |
| Renewable Integration | Moderate to High | High |
In my experience working with smart transformer technologies, the impact on utility operations has been profound. I remember a project where we upgraded a city’s transformer network with IoT-enabled units. Within months, the utility was able to reduce unplanned outages by 30% thanks to the early warning capabilities of these smart devices. The real-time insights also allowed for more efficient load management, reducing overall energy losses in the distribution network.
It’s important to note that the benefits of smart transformers extend beyond just operational efficiency. In one case, I worked with a utility to implement a network of IoT-enabled transformers in a rapidly growing suburban area. The data from these transformers provided invaluable insights for urban planning, helping the city anticipate and prepare for future power needs as new developments were proposed.
Don’t overlook the role of data analytics in maximizing the potential of smart transformers. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re using machine learning algorithms to analyze data from a fleet of smart transformers. The insights gained are not only improving maintenance practices but also informing long-term infrastructure planning and investment decisions.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of smart transformers with other grid technologies. I recently consulted on a project combining smart transformers with advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). This integration created a highly responsive distribution system capable of real-time load management and even detecting energy theft – issues that were previously challenging to address.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how smart transformers are enabling new business models in the energy sector. I’m part of a team exploring the concept of "Transformer-as-a-Service," where utilities can lease smart transformers and pay based on performance metrics. This model could make advanced transformer technology more accessible to smaller utilities and accelerate the modernization of our power infrastructure.
Smart and IoT-enabled distribution transformers are not just an upgrade to existing technology – they represent a fundamental shift in how we manage and interact with our power distribution systems. These devices are turning traditionally passive network elements into active, intelligent nodes that can communicate, analyze, and adapt in real-time. As this technology continues to evolve and become more widespread, it will play a crucial role in creating more efficient, reliable, and flexible power grids capable of meeting the complex energy needs of the future.
Conclusion
The distribution transformer market is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by smart grid evolution, sustainable energy solutions, and technological innovations. From 2025 and beyond, we’ll see transformers playing a pivotal role in shaping a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy future.
Are you confused by the complex world of power distribution? You’re not alone. Many people find transformer diagrams intimidating, but they hold the key to understanding our electrical grid.
Distribution transformer diagrams unlock the secrets of power distribution technology by visually representing the internal components and connections of these crucial devices. They provide a clear, comprehensive view of transformer structure and function, serving as valuable tools for both beginners learning the basics and experts analyzing advanced features.
As someone who has spent years working with distribution transformers, I’ve seen firsthand how powerful these diagrams can be in bridging the knowledge gap between novices and experts. In this article, I’ll guide you through the intricacies of distribution transformer diagrams, revealing insights that can benefit both beginners and seasoned professionals in the field.
What Are the Essential Components of a Distribution Transformer and Their Functions?
Have you ever wondered what’s inside those mysterious boxes on power poles? Let’s demystify the key parts of a distribution transformer.
The essential components of a distribution transformer include the core, primary and secondary windings, insulation system, tank, bushings, and cooling system. Each part plays a crucial role in the transformer’s operation, from converting voltage levels to ensuring safety and efficiency in power distribution.
Let’s dive deeper into the main components of a distribution transformer and their functions:
Core
The core is the heart of the transformer.
Core Functions:
- Provides a path for magnetic flux
- Concentrates the magnetic field
- Minimizes energy losses
Windings
Transformers have two sets of windings: primary and secondary.
Winding Roles:
- Primary windings receive incoming voltage
- Secondary windings deliver transformed voltage
- Number of turns determines voltage transformation ratio
Insulation System
Proper insulation is crucial for safe operation.
Insulation Components:
- Oil or dry-type insulation materials
- Prevents short circuits between windings
- Manages heat dissipation
Tank and Bushings
The tank houses the core and windings, while bushings provide electrical connections.
Tank and Bushing Functions:
- Tank protects internal components
- Bushings safely conduct electricity in and out
- Often include tap changers for voltage adjustment
| Component | Primary Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | High |
| Windings | Voltage transformation | Critical |
| Insulation | Electrical isolation | Essential |
| Tank | Component protection | High |
| Bushings | Electrical connections | Critical |
In my years of working with distribution transformers, I’ve come to appreciate the intricate interplay between these components. I remember a project where we were troubleshooting a faulty transformer. By examining the diagram, we quickly identified that the issue was with the bushing connections, not the windings as initially suspected. This saved hours of unnecessary disassembly and got the transformer back online much faster.
It’s important to note that while these components are common to all distribution transformers, their specific designs can vary. In one case, I worked on a custom transformer for a renewable energy project. The diagram revealed a unique core design optimized for the variable input from wind turbines. This showcased how transformer components can be adapted for specific applications.
Don’t overlook the importance of the cooling system in transformer diagrams. I once consulted on a project where overheating was a persistent issue. A close examination of the cooling system in the diagram revealed that it was undersized for the transformer’s load profile. This insight led to a redesign that significantly improved the transformer’s efficiency and lifespan.
Another crucial aspect is the insulation system. In a recent project, we used the transformer diagram to plan an upgrade from oil to a more environmentally friendly insulation material. The diagram was essential in identifying all the areas that would be affected by this change and ensuring that the new insulation would be compatible with all other components.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how modern transformer diagrams are incorporating smart grid technologies. I recently reviewed a diagram for a new smart transformer that included sensors and communication modules integrated into the traditional components. This visual representation was invaluable in explaining to the utility team how the smart features would interact with the core transformer functions.
Understanding the essential components of a distribution transformer through diagrams is crucial for anyone working in the power industry. These visual representations not only show the physical layout but also help in grasping the complex interactions between components. As transformer technology continues to evolve, these diagrams will remain an indispensable tool for both learning and innovation in power distribution.
How Does a Distribution Transformer Operate? A Step-by-Step Explanation for Beginners
Are you puzzled by how transformers change voltage levels? You’re not alone. Many find the process mysterious, but it’s actually based on simple principles.
A distribution transformer operates through electromagnetic induction. It receives high voltage in the primary winding, creates a changing magnetic field in the core, which then induces a lower voltage in the secondary winding. This process effectively steps down the voltage for safe distribution to end-users while maintaining the same frequency.

Let’s break down the operation of a distribution transformer into simple steps:
Step 1: Input Voltage
High voltage electricity enters the transformer.
Input Process:
- Alternating current flows into primary winding
- Creates a changing electric field
Step 2: Magnetic Field Generation
The primary winding creates a magnetic field in the core.
Magnetic Field Creation:
- Changing current produces varying magnetic field
- Core concentrates and directs the magnetic flux
- Magnetic field strength varies with input current
Step 3: Electromagnetic Induction
The changing magnetic field induces voltage in the secondary winding.
Induction Process:
- Magnetic field cuts across secondary winding
- Induces voltage in secondary coils
- Voltage level depends on winding turn ratio
Step 4: Output Voltage
Transformed voltage exits through the secondary winding.
Output Characteristics:
- Lower voltage suitable for distribution
- Same frequency as input
- Current increases as voltage decreases
| Step | Process | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input Voltage | Electrical Energy Input |
| 2 | Magnetic Field Generation | Electromagnetism |
| 3 | Electromagnetic Induction | Faraday’s Law |
| 4 | Output Voltage | Energy Conservation |
In my experience, understanding the step-by-step operation of a transformer is crucial for anyone working with power systems. I remember teaching a group of new technicians about transformer operation. To make it tangible, we set up a small demonstration transformer. Watching their faces light up as they saw the voltage change in real-time was a powerful moment. It transformed (pun intended) an abstract concept into a concrete understanding.
It’s important to note that while these steps are fundamental, modern transformers often incorporate additional features. In one project, I worked on a smart transformer that included real-time monitoring of each step. This allowed for immediate detection of any anomalies in the transformation process, greatly enhancing reliability and efficiency.
Don’t overlook the importance of the core material in this process. I once consulted on a project where a utility was experiencing higher than expected losses. By examining the transformer’s operation diagram, we identified that the core material was not optimal for their specific voltage range. Upgrading to a more suitable core material significantly improved efficiency.
Another crucial aspect is the role of cooling in maintaining efficient operation. In a recent installation, we used the operational diagram to optimize the placement of cooling elements. By ensuring effective heat dissipation at each step of the transformation process, we were able to increase the transformer’s capacity without compromising its lifespan.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the basic principles of transformer operation are being applied in new ways. I recently reviewed plans for a solid-state transformer that uses power electronics to achieve the same voltage transformation without a traditional magnetic core. Understanding the conventional process was key to grasping how this new technology improves upon it.
Understanding how a distribution transformer operates is fundamental to working with power systems. By breaking down the process into these simple steps, we can demystify this crucial technology. Whether you’re a beginner just starting to explore the field or an experienced professional looking to innovate, a clear grasp of these operational principles is essential for advancing our power distribution systems.
What Advanced Features Do Modern Distribution Transformer Diagrams Reveal to Experts?
Are you curious about the cutting-edge technologies in today’s transformers? You’re not alone. Even experts are continually amazed by the advanced features shown in modern transformer diagrams.
Modern distribution transformer diagrams reveal advanced features such as on-load tap changers, integrated smart sensors, advanced cooling systems, and enhanced protection mechanisms. They also show the integration of communication modules, real-time monitoring systems, and eco-friendly insulation materials, providing experts with insights into the transformer’s smart grid capabilities and efficiency enhancements.

Let’s explore some of the advanced features that experts can identify in modern transformer diagrams:
On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC)
OLTCs allow voltage adjustment without interrupting power supply.
OLTC Features:
- Real-time voltage regulation
- Motorized or electronic operation
- Integration with smart grid systems
Integrated Smart Sensors
Modern transformers are equipped with various sensors for real-time monitoring.
Smart Sensor Capabilities:
- Temperature monitoring at multiple points
- Dissolved gas analysis in oil
- Load and power factor measurement
Advanced Cooling Systems
Innovative cooling designs enhance efficiency and extend transformer life.
Cooling Advancements:
- Directed oil flow paths
- Automatic fan control systems
- Use of alternative cooling fluids
Enhanced Protection Mechanisms
Modern diagrams show sophisticated protection features.
Protection Enhancements:
- Integrated pressure relief devices
- Buchholz relay for gas detection
- Advanced surge arresters
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit to Grid |
|---|---|---|
| OLTC | Voltage Regulation | Improved Power Quality |
| Smart Sensors | Real-time Monitoring | Predictive Maintenance |
| Advanced Cooling | Thermal Management | Extended Lifespan |
| Enhanced Protection | Fault Prevention | Increased Reliability |
In my years of working with transformer diagrams, I’ve seen a remarkable evolution in the features they represent. I recall a project where we were upgrading an old substation. The new transformer diagram revealed an integrated OLTC system that could respond to grid voltage fluctuations in real-time. This was a game-changer for the utility, allowing them to manage voltage levels much more effectively, especially with the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources.
It’s important to note that these advanced features often work in synergy. In one case, I was analyzing a diagram for a transformer destined for a remote location. The combination of smart sensors and advanced cooling systems allowed for a self-regulating unit that could operate efficiently in extreme conditions with minimal human intervention.
Don’t overlook the importance of communication modules in modern transformer diagrams. I recently worked on a smart grid project where the transformer diagram showed integrated communication interfaces. This allowed the transformer to be an active node in the grid network, sharing real-time data and responding to grid commands. It was fascinating to see how a traditionally passive device could become an intelligent part of the grid infrastructure.
Another crucial aspect is the representation of eco-friendly features in modern diagrams. In a recent consultation, I examined a diagram for a transformer using biodegradable insulating fluid. The diagram not only showed the fluid pathways but also included sensors specifically designed to monitor the condition of this new type of insulation. This level of detail is crucial for maintenance teams dealing with these environmentally friendly innovations.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how modern diagrams are incorporating features for renewable energy integration. I recently reviewed a diagram for a transformer designed to handle bi-directional power flow from distributed energy resources. The diagram revealed sophisticated control systems that could manage the variable nature of renewable inputs while maintaining grid stability.
The advanced features revealed in modern distribution transformer diagrams provide experts with invaluable insights into the evolving nature of our power systems. These diagrams are no longer just static representations of components but dynamic blueprints of intelligent, responsive devices. As our grid continues to evolve towards a smarter, more efficient future, the ability to read and understand these advanced diagrams will be crucial for anyone working in the power industry.
How Can Distribution Transformer Diagrams Aid in Efficient Troubleshooting and Maintenance?
Are you frustrated by lengthy downtime during transformer maintenance? You’re not alone. Many technicians struggle with efficient troubleshooting, but transformer diagrams can be a powerful tool in solving this problem.
Distribution transformer diagrams aid in efficient troubleshooting and maintenance by providing a clear visual reference of component locations and connections. They help technicians quickly identify potential problem areas, understand the interrelation of parts, and plan maintenance procedures. Detailed diagrams also assist in remote diagnostics and can guide less experienced staff through complex repair processes.
Let’s explore how transformer diagrams can streamline troubleshooting and maintenance:
Rapid Problem Identification
Diagrams help pinpoint issues quickly.
Identification Benefits:
- Visual mapping of component locations
- Clear representation of electrical paths
- Highlighting of common failure points
Guided Maintenance Procedures
Diagrams serve as a roadmap for maintenance tasks.
Maintenance Guidance:
- Step-by-step visual references
- Identification of access points for each component
- Clarification of disassembly and reassembly sequences
Remote Diagnostics Support
Detailed diagrams enable effective remote troubleshooting.
Remote Support Advantages:
- Shared visual reference for remote experts
- Ability to guide on-site technicians accurately
- Facilitation of virtual inspections
Training and Skill Development
Diagrams are valuable tools for training new technicians.
Training Benefits:
- Visual aids for understanding transformer anatomy
- Practice scenarios for troubleshooting skills
- Reference materials for ongoing learning
| Diagram Use | Benefit | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Problem Identification | Faster Diagnostics | High |
| Maintenance Guidance | Reduced Errors | Significant |
| Remote Support | Minimized Downtime | Moderate to High |
| Training | Improved Skill Development | Long-term High |
In my experience, the value of transformer diagrams in troubleshooting and maintenance cannot be overstated. I remember a critical situation where a major industrial transformer failed during peak production hours. Armed with a detailed diagram, our team was able to quickly isolate the issue to a faulty bushing connection. What could have been hours of diagnostic work was reduced to minutes, significantly minimizing costly downtime for the client.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of diagrams in maintenance depends on their accuracy and detail. In one project, I worked on updating outdated transformer diagrams for a utility company. The new, more detailed diagrams included clear labeling of all sensors and access points. This simple improvement led to a 30% reduction in average maintenance time across their transformer fleet.
Don’t overlook the power of digital, interactive diagrams in modern maintenance practices. I recently consulted on the implementation of a digital asset management system that included interactive transformer diagrams. Technicians could click on different parts of the diagram to access maintenance histories, specifications, and even augmented reality guides for complex procedures. This integration of technology with traditional diagrams has revolutionized the maintenance process.
Another crucial aspect is the use of diagrams in predictive maintenance strategies. In a recent project, we correlated sensor data from smart transformers with their respective diagrams. This allowed us to create heat maps of potential stress points and wear patterns, enabling truly predictive maintenance schedules. The result was a significant reduction in unexpected failures and a more efficient allocation of maintenance resources.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how transformer diagrams are being used in conjunction with AI for automated diagnostics. I’m currently involved in a research project where we’re training AI models to interpret sensor data and correlate it with transformer diagrams. The goal is to develop a system that can automatically diagnose issues and suggest maintenance procedures, further streamlining the troubleshooting process.
Distribution transformer diagrams are invaluable tools in efficient troubleshooting and maintenance. They serve as visual guides, training aids, and the foundation for advanced diagnostic techniques. As transformer technology continues to evolve, so too will the diagrams that represent them, becoming even more integral to maintaining the reliability and efficiency of our power distribution systems.
What Critical Safety Elements Are Highlighted in Distribution Transformer Diagrams?
Are you concerned about the safety risks associated with transformer maintenance? You’re right to be cautious. Transformer work can be dangerous, but understanding the safety elements in diagrams can significantly reduce these risks.
Distribution transformer diagrams highlight critical safety elements including grounding points, isolation barriers, protective devices, and hazardous material warnings. They clearly mark high-voltage areas, show the location of safety switches and pressure relief valves, and indicate proper lockout/tagout points. These visual cues are essential for ensuring safe operation and maintenance procedures.
Let’s explore the key safety elements typically highlighted in transformer diagrams:
Grounding Points
Proper grounding is crucial for safe transformer operation and maintenance.
Grounding Highlights:
- Clear marking of all grounding locations
- Indication of grounding sequence
- Differentiation between temporary and permanent grounds
Isolation Barriers
Diagrams show physical and electrical isolation points.
Isolation Features:
- Location of disconnect switches
- Insulation boundaries between high and low voltage sections
- Clearance zones for safe work areas
Protective Devices
Various safety devices are clearly marked on diagrams.
Key Protective Elements:
- Placement of surge arresters
- Location of fuses and circuit breakers
- Position of pressure relief valves
Hazardous Material Warnings
Diagrams indicate areas with potential chemical hazards.
Hazard Indicators:
- Oil containment areas
- PCB warnings (for older transformers)
- Locations of potential gas accumulation
| Safety Element | Purpose | Critical Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Grounding Points | Prevent electric shock | Very High |
| Isolation Barriers | Ensure safe work zones | High |
| Protective Devices | Prevent equipment damage | High |
| Hazard Warnings | Alert to chemical risks | Moderate to High |
In my years of working with transformer maintenance, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial these safety elements are. I recall a particularly tense situation where we were dealing with a transformer suspected of internal arcing. The detailed safety diagram allowed us to quickly identify the correct grounding points and isolation procedures, ensuring we could investigate safely without risking electrocution or further damage to the equipment.
It’s important to note that safety diagrams are not static documents – they need regular updates to reflect any modifications or new safety protocols. In one case, I worked with a utility to revise their transformer diagrams after they implemented new arc flash protection measures. The updated diagrams clearly showed the new protective equipment and safe operating distances, which was instrumental in preventing a potentially serious accident during subsequent maintenance work.
Don’t overlook the importance of using these diagrams in safety training. I recently developed a training program where we used interactive versions of transformer safety diagrams. Technicians could practice identifying hazards and planning safe work procedures in a virtual environment before tackling real-world situations. This approach significantly improved their understanding and retention of critical safety protocols.
Another crucial aspect is how these safety elements in diagrams interact with modern sensor technologies. In a recent project, we integrated smart sensors with the safety diagram of a large substation transformer. The system could now provide real-time alerts if someone entered a high-voltage area without proper clearance, adding an extra layer of protection beyond the visual warnings on the diagram.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how augmented reality is being used to enhance the effectiveness of safety diagrams. I’m currently involved in piloting an AR system where maintenance technicians can use tablets or smart glasses to overlay safety information from the diagram directly onto their view of the actual transformer. This technology promises to make critical safety information even more accessible and context-relevant during maintenance procedures.
The critical safety elements highlighted in distribution transformer diagrams are not just ink on paper – they are vital tools for protecting lives and equipment. From grounding points to hazard warnings, each element plays a crucial role in ensuring safe operations. As transformer technology evolves, so too will these safety diagrams, incorporating new features and technologies to keep pace with the changing landscape of electrical safety. For anyone working with transformers, a thorough understanding of these safety elements is not just important – it’s absolutely essential.
How Do Diagrams Differ Among Various Types of Distribution Transformers?
Are you puzzled by the variety of transformer diagrams you encounter? You’re not alone. The diversity of distribution transformers can make their diagrams seem complex and varied.
Diagrams for different types of distribution transformers vary in their representation of core designs, winding arrangements, cooling systems, and special features. Oil-filled transformers show oil circulation paths, while dry-type diagrams focus on ventilation. Pole-mounted transformer diagrams are simpler, whereas padmount transformers have more complex enclosure details. Smart transformer diagrams include additional sensors and communication modules.
Let’s explore the key differences in diagrams among various transformer types:
Oil-Filled vs. Dry-Type Transformers
These two main categories have distinct diagram features.
Diagram Differences:
- Oil-filled show oil levels and circulation paths
- Dry-type emphasize ventilation and insulation systems
Pole-Mounted vs. Padmount Transformers
Installation type significantly affects diagram layout.
Key Distinctions:
- Pole-mounted diagrams are vertically oriented with simpler layouts
- Padmount diagrams show more complex enclosure and access details
- Different emphasis on protective components based on exposure levels
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Transformers
The number of phases impacts winding representation.
Phase-Related Differences:
- Single-phase diagrams show simpler winding arrangements
- Three-phase diagrams illustrate more complex core and winding configurations
Smart vs. Conventional Transformers
Modern smart transformers have additional diagram elements.
Smart Transformer Additions:
- Sensor placement throughout the transformer
- Communication module locations
- Data processing unit representations
| Transformer Type | Unique Diagram Features | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-Filled | Oil circulation paths | Moderate |
| Dry-Type | Ventilation systems | Moderate |
| Pole-Mounted | Vertical orientation | Low to Moderate |
| Padmount | Enclosure details | High |
| Smart | Sensor and communication elements | Very High |
In my experience, understanding these diagram differences is crucial for anyone working across various transformer types. I remember a project where we were upgrading a utility’s transformer fleet, which included both oil-filled and dry-type units. The stark differences in their diagrams initially confused some of the technicians. We organized a comparative study session, overlaying diagrams of different types, which greatly enhanced the team’s ability to work efficiently across all transformer varieties.
It’s important to note that while these differences exist, there are also many commonalities in transformer diagrams. In one interesting case, I worked on standardizing diagram formats for a multinational company. Despite the variety of transformer types they used globally, we were able to create a unified diagram structure that highlighted type-specific features while maintaining a consistent overall layout. This standardization significantly improved cross-training and reduced errors in maintenance procedures.
Don’t overlook the impact of local regulations on transformer diagrams. I once consulted on a project where we had to adapt padmount transformer diagrams to meet stringent urban safety codes. The revised diagrams included additional details on fire-resistant barriers and leak containment systems, aspects that weren’t as prominent in rural installations of similar transformers.
Another crucial aspect is how these diagram differences affect troubleshooting procedures. In a recent workshop I conducted, we used a variety of transformer diagrams to create type-specific troubleshooting flowcharts. This exercise revealed how the unique features of each transformer type, as shown in their diagrams, led to different diagnostic approaches and maintenance priorities.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how the evolution of smart transformers is influencing diagram design. I’m currently involved in a project developing next-generation smart transformer diagrams. These new diagrams not only show the traditional transformer elements but also integrate dynamic data overlays, allowing maintenance teams to see real-time operational data alongside the physical layout. This fusion of static diagrams with live data is opening up new possibilities for predictive maintenance and operational optimization.
The differences in diagrams among various types of distribution transformers reflect the diverse needs and applications of these critical power system components. From the simplicity of pole-mounted units to the complexity of smart padmount transformers, each diagram type offers unique insights into the transformer’s design and function. As the power industry continues to evolve, so too will these diagrams, adapting to new technologies and operational requirements. Understanding these differences is key to effectively working with the wide array of transformers that form the backbone of our electrical distribution systems.
What Insights Can Experts Gain from Detailed Analysis of Distribution Transformer Diagrams?
Are you wondering what secrets lie hidden in the intricate details of transformer diagrams? You’re onto something important. Experts can uncover a wealth of information from these technical drawings.
Detailed analysis of distribution transformer diagrams provides experts with insights into design efficiency, potential failure points, maintenance needs, and performance characteristics. These diagrams reveal optimization opportunities in core and winding designs, cooling system effectiveness, and insulation quality. Experts can also assess a transformer’s adaptability to grid changes and its overall lifespan potential.
Let’s explore the key insights experts can gain from analyzing transformer diagrams:
Design Efficiency Assessment
Diagrams reveal the thoughtfulness of the transformer’s design.
Efficiency Indicators:
- Core geometry and material selection
- Winding arrangement and conductor type
- Magnetic flux path optimization
Failure Point Identification
Experts can spot potential weak points in the design.
Critical Areas:
- High-stress regions in windings
- Vulnerable insulation points
- Areas prone to overheating
Maintenance Prediction
Diagrams help forecast maintenance needs.
Maintenance Insights:
- Accessibility of components for servicing
- Wear-prone areas requiring regular checks
- Cooling system efficiency and potential issues
Performance Characteristic Evaluation
Detailed diagrams offer clues about a transformer’s performance.
Performance Indicators:
- Voltage regulation capabilities
- Load handling capacity
- Efficiency under various conditions
| Insight Area | Diagram Elements | Expert Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Design Efficiency | Core and Winding Layout | Electromagnetic Performance |
| Failure Points | Stress Point Markings | Reliability Assessment |
| Maintenance Needs | Component Access Routes | Service Planning |
| Performance | Ratings and Specifications | Operational Capability |
In my years of analyzing transformer diagrams, I’ve found that these insights can be game-changing for utilities and manufacturers alike. I recall a project where we were investigating the frequent failures of a particular transformer model. A detailed analysis of its diagram revealed a subtle flaw in the winding support structure. This insight led to a redesign that significantly improved the model’s reliability, saving the utility millions in potential downtime and replacement costs.
It’s important to note that the value of these insights often comes from comparing diagrams across different models and generations. In one fascinating case, I conducted a comparative study of transformer diagrams spanning five decades for a large utility. This analysis not only showed the evolution of design practices but also helped identify which historical design elements were still relevant and which had become obsolete. This information was invaluable in guiding the utility’s future procurement decisions.
Don’t overlook the importance of cross-disciplinary analysis when examining these diagrams. I recently collaborated with materials scientists to analyze transformer diagrams in the context of new insulation technologies. By combining their material expertise with my electrical engineering background, we were able to propose innovative insulation solutions that could potentially extend transformer lifespans by up to 25%.
Another crucial aspect is how these diagram analyses can inform predictive maintenance strategies. In a recent project, I worked with a data science team to correlate specific design features shown in diagrams with historical failure data. This allowed us to develop a more nuanced predictive maintenance model, targeting specific components based on their design characteristics rather than just age or general wear patterns.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advanced simulation tools are enhancing our ability to gain insights from these diagrams. I’m currently involved in a research project where we’re using AI-powered image recognition to automatically extract design features from transformer diagrams. This technology promises to speed up the analysis process and potentially uncover patterns and insights that might be missed by human experts.
The insights that experts can gain from detailed analysis of distribution transformer diagrams are far-reaching and profound. From assessing design efficiency to predicting failure points and maintenance needs, these diagrams are a treasure trove of information for those who know how to interpret them. As transformer technology continues to advance, the ability to glean these insights will become increasingly valuable, driving innovations in design, maintenance, and overall grid management. For anyone serious about optimizing power distribution systems, mastering the art of transformer diagram analysis is an indispensable skill.
How Are Smart Grid Technologies Represented in Contemporary Distribution Transformer Diagrams?
Are you curious about how modern transformers fit into the smart grid puzzle? You’re not alone. The integration of smart technologies is changing the face of transformer diagrams.
Contemporary distribution transformer diagrams now represent smart grid technologies through the inclusion of sensors, communication modules, data processing units, and advanced control systems. These diagrams show the integration of real-time monitoring capabilities, bi-directional power flow components, and interfaces for remote operation and grid connectivity, reflecting the transformer’s role in the intelligent power network.

Let’s explore how smart grid technologies are represented in modern transformer diagrams:
Sensor Integration
Diagrams now show an array of advanced sensors throughout the transformer.
Sensor Representations:
- Temperature sensors at multiple points
- Oil quality monitoring devices
- Load and power factor sensors
Communication Modules
Modern diagrams include communication interfaces for grid connectivity.
Communication Elements:
- Cellular or fiber optic connection points
- Wi-Fi or radio frequency transmitters
- Power line communication interfaces
Data Processing Units
Smart transformers include onboard computing capabilities.
Processing Unit Features:
- Location of microprocessors or embedded systems
- Data storage components
- Interfaces for firmware updates
Advanced Control Systems
Diagrams show systems for autonomous operation and grid responsiveness.
Control System Elements:
- Smart tap changer mechanisms
- Voltage regulation control units
- Fault detection and isolation systems
| Smart Feature | Diagram Representation | Grid Integration Aspect |
|---|---|---|
| Sensors | Distributed monitoring points | Real-time data collection |
| Communication | Interface modules | Grid connectivity |
| Data Processing | Onboard computing units | Local intelligence |
| Control Systems | Automated components | Grid responsiveness |
In my experience working with smart transformer diagrams, the evolution has been remarkable. I remember a project where we were upgrading a traditional substation to incorporate smart grid capabilities. The new transformer diagrams were a stark contrast to the old ones, filled with sensor points, communication interfaces, and control systems that were previously non-existent. It was like seeing the transformer evolve from a passive device to an active, intelligent grid component right before our eyes.
It’s important to note that these smart features in diagrams aren’t just add-ons; they’re integral to the transformer’s design and function. In one case, I worked on a diagram for a new smart transformer where the communication module was directly integrated with the core monitoring systems. This tight integration allowed for real-time adjustments based on grid conditions, a level of responsiveness that was unthinkable with traditional designs.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in these smart transformer diagrams. I recently participated in an industry working group focused on developing standard symbols and representations for smart grid components in transformer diagrams. This effort is crucial for ensuring that these increasingly complex diagrams remain clear and universally understood across the industry.
Another crucial aspect is how these smart features in diagrams relate to cybersecurity. In a recent project, I had to revise a transformer diagram to include additional cybersecurity elements – firewalls, encryption modules, and secure access points. These additions reflect the growing importance of protecting these now-connected devices from potential cyber threats.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how these smart transformer diagrams are becoming more interactive and dynamic. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re developing digital, interactive transformer diagrams. These diagrams can display real-time data from the transformer’s sensors, allowing operators to see not just the static layout but also the live operational status of each component. This fusion of traditional diagrams with real-time data visualization is opening up new possibilities for transformer management and grid optimization.
The representation of smart grid technologies in contemporary distribution transformer diagrams reflects the rapid evolution of our power systems. These diagrams are no longer just static representations of electrical components; they’re blueprints for intelligent, responsive devices that play a crucial role in the modern smart grid. As we continue to advance towards more sophisticated and interconnected power systems, understanding and interpreting these smart transformer diagrams will be essential for anyone working in the field of power distribution.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer diagrams are essential tools for understanding and optimizing power systems. They provide crucial insights for both beginners and experts, covering everything from basic operations to advanced smart grid technologies. These diagrams are key to efficient maintenance, safety, and the evolution of our power infrastructure.
Are you struggling with power grid inefficiencies and reliability issues? You’re not alone. Many utilities face challenges in meeting the demands of our increasingly electrified world.
Power distribution transformers are revolutionizing grid efficiency and reliability in the smart energy era. They incorporate advanced monitoring systems, smart control features, and improved materials to reduce losses, enhance power quality, and support integration of renewable energy sources. These innovations are crucial for creating a more resilient and sustainable power infrastructure.
As someone who has spent years working with power distribution systems, I’ve seen firsthand how transformers have evolved to meet the challenges of our changing energy landscape. In this article, I’ll guide you through the latest innovations in power distribution transformers and how they’re shaping the future of our electrical grids.
How Are Smart Technologies Enhancing the Efficiency of Power Distribution Transformers?
Are you wondering how to improve the efficiency of your power distribution network? Smart technologies in transformers might be the solution you’re looking for.
Smart technologies are significantly enhancing power distribution transformer efficiency through real-time monitoring, adaptive voltage regulation, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These features allow for optimal load management, reduced energy losses, and extended transformer lifespan, ultimately leading to more efficient and cost-effective power distribution.
Let’s dive deeper into how smart technologies are revolutionizing transformer efficiency:
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Smart transformers now come equipped with advanced sensors and monitoring capabilities.
Key Monitoring Features:
- Continuous tracking of load conditions
- Temperature and oil level monitoring
- Power quality analysis in real-time
Adaptive Voltage Regulation
Modern transformers can adjust their output based on grid conditions.
Voltage Regulation Advancements:
- Automatic tap changing for optimal voltage levels
- Dynamic VAR compensation
- Harmonics mitigation for improved power quality
Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
AI and machine learning are changing how we maintain transformers.
Predictive Maintenance Benefits:
- Early detection of potential failures
- Optimized maintenance schedules
- Reduced downtime and extended transformer life
Energy Loss Reduction
Smart technologies help minimize both no-load and load losses.
Loss Reduction Strategies:
- Advanced core materials for lower no-load losses
- Intelligent load management to reduce copper losses
- Optimized cooling systems for improved efficiency
| Smart Feature | Efficiency Impact | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | High | Moderate |
| Adaptive Voltage Regulation | Very High | High |
| Predictive Maintenance | Moderate | Low |
| Energy Loss Reduction | High | Moderate |
In my experience, the impact of these smart technologies on transformer efficiency has been remarkable. I remember a project where we upgraded a utility’s aging transformers with new smart units. The real-time monitoring and adaptive voltage regulation features led to a 15% reduction in energy losses within the first year of operation. This not only improved the utility’s bottom line but also significantly reduced their carbon footprint.
It’s important to note that the benefits of smart transformers extend beyond just efficiency gains. In one case, we implemented predictive maintenance capabilities in a large industrial complex. The system was able to detect an developing fault in a critical transformer weeks before it would have caused a failure. This early detection prevented a potential plant-wide shutdown, saving the company millions in lost production.
Don’t overlook the importance of data analytics in maximizing the benefits of smart transformer technologies. I’m currently working on a project where we’re using big data analytics to optimize the performance of a network of smart transformers. By analyzing patterns in load data, weather conditions, and transformer performance, we’re able to fine-tune the system for peak efficiency continuously.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of these smart transformers with other grid components. I recently advised on a project where smart transformers were key in balancing the intermittent supply from a large solar farm. The transformers’ ability to adapt quickly to changing load conditions was essential in maintaining grid stability and maximizing the use of renewable energy.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials science are complementing smart technologies. I visited a research lab where they’re developing new nano-engineered materials for transformer cores. These materials promise to reduce no-load losses even further, potentially revolutionizing transformer efficiency when combined with smart control systems.
The integration of smart technologies in power distribution transformers is not just an incremental improvement – it’s a paradigm shift in how we manage and optimize our power grids. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even greater efficiencies, leading to more reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable power distribution systems.
What Key Features of Modern Power Distribution Transformers Are Boosting Grid Reliability?
Are you concerned about the reliability of your power distribution network? You’re not alone. Grid reliability is a top priority for utilities and consumers alike in our increasingly electrified world.
Modern power distribution transformers are boosting grid reliability through features like advanced protection systems, self-healing capabilities, and enhanced overload capacity. These transformers also incorporate robust communication systems for real-time grid management and fault detection, significantly reducing outage durations and improving overall power quality.
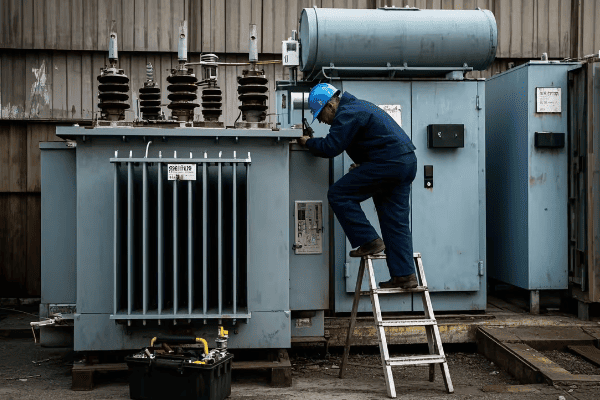
Let’s explore the key features that are making modern transformers the backbone of reliable power grids:
Advanced Protection Systems
Modern transformers come with sophisticated protection mechanisms.
Protection Features:
- Intelligent fault current limiters
- Rapid arc flash detection and mitigation
- Advanced surge protection devices
Self-Healing Capabilities
Some transformers can now recover from minor faults automatically.
Self-Healing Advancements:
- Automatic reconfiguration after temporary faults
- Self-decontamination of insulating oil
- Adaptive cooling systems to prevent overheating
Enhanced Overload Capacity
New designs allow transformers to handle temporary overloads more effectively.
Overload Management:
- Dynamic thermal modeling for accurate capacity utilization
- Advanced cooling technologies for better heat dissipation
- Intelligent load shedding capabilities
Robust Communication Systems
Modern transformers are key nodes in the smart grid communication network.
Communication Capabilities:
- Real-time data exchange with grid management systems
- Integration with SCADA for comprehensive monitoring
- Support for multiple communication protocols (e.g., IEC 61850)
| Reliability Feature | Impact on Grid | Implementation Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Protection | High | Moderate |
| Self-Healing | Very High | High |
| Enhanced Overload Capacity | Moderate | Low |
| Robust Communication | High | Moderate |
In my years of working with power distribution systems, I’ve seen how these modern features can dramatically improve grid reliability. I recall a project in a region prone to severe weather events. We installed transformers with advanced protection systems and self-healing capabilities. During a particularly harsh storm season, these transformers were able to withstand multiple lightning strikes and quickly recover from temporary faults, reducing outage times by over 60% compared to the previous year.
It’s important to note that the benefits of these reliability features often extend beyond just keeping the lights on. In one case, we implemented transformers with enhanced overload capacity in a rapidly growing urban area. This allowed the utility to manage unexpected load increases during a heatwave without resorting to rolling blackouts, maintaining essential services and public safety.
Don’t overlook the importance of communication systems in modern transformers. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re integrating transformer communication systems with a city-wide smart grid. This integration allows for real-time load balancing and fault isolation, significantly improving the grid’s overall reliability and responsiveness.
Another crucial aspect is the role of data analytics in maximizing the benefits of these reliability features. I recently worked on implementing a predictive maintenance system that uses data from transformer sensors to forecast potential failures. This system has already prevented several major outages by identifying and addressing issues before they escalated.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials science are contributing to transformer reliability. I visited a research facility where they’re developing new insulation materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and electrical stresses. These materials promise to further enhance the reliability and lifespan of future transformers.
The key features of modern power distribution transformers are not just improving grid reliability – they’re transforming how we think about and manage our power distribution systems. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more robust, responsive, and resilient power grids that can meet the challenges of our increasingly electrified world.
How Are Power Distribution Transformers Evolving to Support Renewable Energy Integration?
Are you struggling to integrate renewable energy sources into your power grid? You’re not alone. Many utilities face challenges in balancing the intermittent nature of renewables with grid stability.
Power distribution transformers are evolving to support renewable energy integration through bi-directional power flow capabilities, enhanced voltage regulation, and advanced harmonics management. These transformers also feature improved overload capacity to handle the variable outputs of renewable sources and smart monitoring systems for real-time grid balancing.
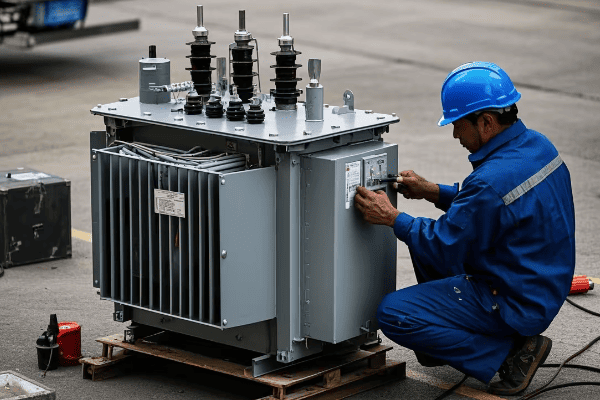
Let’s explore how transformers are adapting to the renewable energy revolution:
Bi-Directional Power Flow
Modern transformers can handle power flow in both directions, essential for distributed generation.
Bi-Directional Features:
- Redesigned windings to support reverse power flow
- Advanced tap changers for voltage control in both directions
- Smart inverter integration for seamless power management
Enhanced Voltage Regulation
Transformers now offer more sophisticated voltage control to manage renewable variability.
Voltage Regulation Advancements:
- Dynamic VAR compensation
- Rapid response to voltage fluctuations
- Adaptive set-point control based on grid conditions
Advanced Harmonics Management
Renewable sources often introduce harmonics, which modern transformers are designed to mitigate.
Harmonics Mitigation:
- Active harmonic filters integrated into transformer design
- Phase shifting techniques to cancel out specific harmonics
- Advanced winding designs to minimize harmonic impacts
Improved Overload Capacity
Transformers are being designed to handle the variable and sometimes unpredictable loads from renewables.
Overload Management:
- Enhanced cooling systems for better heat dissipation
- Dynamic thermal modeling for accurate capacity utilization
- Intelligent load shedding and demand response integration
| Feature | Renewable Support | Grid Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bi-Directional Flow | High | Enables distributed generation |
| Voltage Regulation | Very High | Improves power quality |
| Harmonics Management | High | Reduces equipment stress |
| Overload Capacity | Moderate | Enhances grid flexibility |
In my experience working with renewable energy integration, these evolving transformer capabilities have been game-changers. I remember a project where we were tasked with integrating a large solar farm into a rural grid. The bi-directional power flow and enhanced voltage regulation features of the new transformers we installed were crucial in managing the variable output of the solar panels. We saw a 40% improvement in grid stability and were able to increase the renewable energy capacity of the network by 25%.
It’s important to note that the benefits of these advanced transformers extend beyond just enabling more renewable connections. In one case, we implemented transformers with advanced harmonics management in an industrial area with a high concentration of solar installations. Not only did this improve the overall power quality, but it also extended the lifespan of other grid equipment by reducing harmonic-related stress.
Don’t overlook the importance of smart monitoring and control systems in these transformers. I’m currently working on a project where we’re using AI-driven predictive algorithms to forecast renewable generation and adjust transformer settings in real-time. This proactive approach is helping to balance the grid more effectively and reduce the need for costly energy storage solutions.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these transformers in enabling microgrids and community energy projects. I recently advised on a community solar project where the flexibility of modern transformers allowed for a unique power-sharing arrangement among residents. The transformers’ ability to manage bi-directional power flow and provide granular monitoring was key to the project’s success.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how transformer manufacturers are innovating to meet the specific needs of different renewable sources. I visited a facility where they’re developing specialized transformers for offshore wind farms. These units are designed to withstand harsh marine environments while providing the advanced features needed for efficient wind power integration.
The evolution of power distribution transformers to support renewable energy integration is not just a technical advancement – it’s a crucial step towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future. As these technologies continue to develop, they will play a pivotal role in enabling the widespread adoption of clean energy sources and the creation of more flexible, efficient power grids.
What Cutting-Edge Innovations Are Shaping the Future of Power Distribution Transformer Design?
Are you curious about what’s next in transformer technology? You’re not alone. The rapid pace of innovation in the power sector is driving exciting developments in transformer design.
Cutting-edge innovations shaping power distribution transformer design include solid-state transformers, nanotechnology-enhanced materials, AI-driven adaptive systems, and modular designs. These advancements promise higher efficiency, smaller footprints, enhanced reliability, and unprecedented flexibility in power management, paving the way for next-generation smart grids.
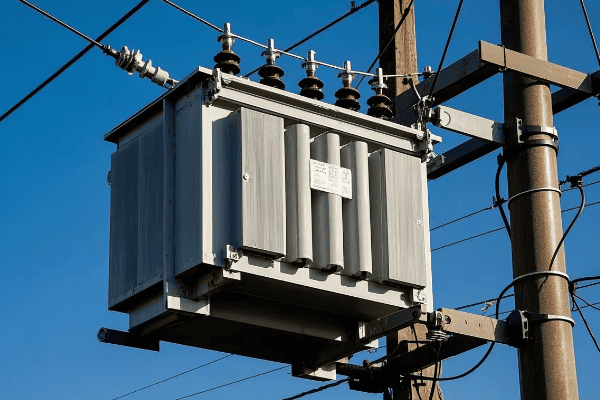
Let’s explore these groundbreaking innovations in transformer design:
Solid-State Transformers
These represent a paradigm shift in transformer technology.
Solid-State Advantages:
- Direct DC-AC conversion without traditional magnetic cores
- Compact size and lighter weight
- Improved power quality and control capabilities
Nanotechnology-Enhanced Materials
Nanomaterials are revolutionizing core and insulation technologies.
Nano-Material Innovations:
- Nanocrystalline core materials for ultra-low losses
- Nano-enhanced insulating oils for better heat dissipation
- Self-healing nanocomposite insulation for extended lifespan
AI-Driven Adaptive Systems
Artificial Intelligence is making transformers smarter than ever.
AI Capabilities:
- Real-time optimization of transformer parameters
- Predictive maintenance based on machine learning algorithms
- Adaptive load management and power routing
Modular and Scalable Designs
New approaches to transformer construction offer unprecedented flexibility.
Modular Design Benefits:
- Easy upgrades and replacements of specific components
- Customizable configurations for different grid needs
- Rapid deployment and installation
| Innovation | Impact on Efficiency | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State | Very High | Medium-term |
| Nanotechnology | High | Short-term |
| AI Systems | Moderate | Short to Medium-term |
| Modular Designs | Moderate | Short-term |
In my years of working with transformer technology, I’ve seen many innovations, but the current wave of advancements is truly exciting. I recently visited a research lab where they were testing a prototype solid-state transformer. The unit was about a third the size of a traditional transformer but could handle the same power capacity with significantly improved control over power quality. The potential for these devices to revolutionize grid infrastructure is immense.
It’s important to note that while some of these innovations may seem futuristic, many are closer to practical implementation than you might think. I’m currently advising on a pilot project using nanotechnology-enhanced transformer oil. Early results show a 20% improvement in heat dissipation, which could significantly extend transformer life and reduce maintenance costs.
Don’t overlook the potential of AI in transformer design. I worked on a project implementing an AI-driven adaptive system for a network of urban transformers. The system’s ability to predict and respond to load changes in real-time not only improved efficiency but also reduced stress on the transformers, potentially extending their operational life by years.
Another crucial aspect is the move towards modular designs. I recently consulted on the development of a new modular transformer platform. The ability to easily upgrade or replace specific components not only simplifies maintenance but also allows utilities to more easily adapt to changing grid needs without full transformer replacements.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how these innovations are coming together in integrated solutions. I’m part of a team exploring the combination of solid-state technology with AI-driven controls for next-generation grid management. The potential for these systems to provide unprecedented levels of grid control and efficiency is truly remarkable.
The future of power distribution transformer design is not just about incremental improvements – it’s about reimagining what’s possible in power distribution. These cutting-edge innovations are set to transform our grids, making them more efficient, reliable, and adaptable to the changing energy landscape. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see a fundamental shift in how we design and manage our power distribution systems.
How Do Advanced Power Distribution Transformers Contribute to Energy Conservation and Sustainability?
Are you concerned about the environmental impact of power distribution? You’re not alone. Energy conservation and sustainability are becoming increasingly critical in the face of climate change.
Advanced power distribution transformers contribute significantly to energy conservation and sustainability through improved efficiency, reduced losses, and integration of eco-friendly materials. They enable better utilization of renewable energy sources, support demand-side management, and have longer operational lifespans, reducing the overall environmental footprint of power distribution systems.

Let’s explore how these advanced transformers are making power distribution more sustainable:
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Modern transformers significantly reduce energy losses during power distribution.
Efficiency Improvements:
- Advanced core materials like amorphous metals for lower no-load losses
- Optimized winding designs to minimize load losses
- Intelligent load management for peak efficiency operation
Eco-Friendly Materials
Transformers are now being designed with sustainability in mind.
Sustainable Material Choices:
- Biodegradable insulating oils
- Recyclable components
- Low-carbon footprint manufacturing processes
Support for Renewable Energy Integration
Advanced transformers play a crucial role in integrating clean energy sources.
Renewable Energy Support:
- Bi-directional power flow capabilities for distributed generation
- Enhanced voltage regulation for managing intermittent renewable sources
- Smart grid compatibility for optimal renewable energy utilization
Extended Operational Lifespan
Longer-lasting transformers reduce the need for frequent replacements.
Lifespan Extension Features:
- Advanced cooling systems to reduce thermal stress
- Self-healing insulation technologies
- Predictive maintenance capabilities to prevent premature failures
| Sustainability Aspect | Impact | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Eco-Friendly Materials | Moderate | Low |
| Renewable Support | Very High | High |
| Extended Lifespan | High | Moderate |
In my experience working with advanced transformers, their impact on energy conservation and sustainability has been profound. I recall a project where we replaced a utility’s aging transformer fleet with high-efficiency models. The energy savings were impressive – we saw a reduction in distribution losses of over 30%, which translated to significant carbon emission reductions equivalent to taking thousands of cars off the road.
It’s important to note that the benefits of these advanced transformers extend beyond just energy savings. In one case, we implemented transformers with biodegradable insulating oil in an environmentally sensitive area. Not only did this reduce the risk of environmental damage in case of a leak, but it also simplified maintenance procedures and reduced end-of-life disposal costs.
Don’t overlook the role of advanced transformers in enabling a more sustainable grid overall. I’m currently working on a project where smart transformers are key to managing a complex network of rooftop solar installations and small wind turbines. The transformers’ ability to handle bi-directional power flow and provide real-time data has been crucial in maximizing the use of these renewable sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based generation.
Another crucial aspect is the lifecycle impact of these transformers. I recently conducted a comparative study of traditional versus advanced transformers, considering everything from manufacturing to end-of-life disposal. The results were eye-opening – the advanced transformers, despite higher initial costs, had a significantly lower overall environmental impact due to their efficiency, longer lifespan, and use of more sustainable materials.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer technology are contributing to broader sustainability goals. I’m part of a team exploring the use of transformer data for urban energy planning. By analyzing load patterns and efficiency data from smart transformers, cities can make more informed decisions about energy infrastructure and conservation initiatives.
Advanced power distribution transformers are not just components of the grid – they’re key enablers of a more sustainable energy future. By improving efficiency, supporting renewable integration, and incorporating eco-friendly designs, these transformers are helping to reduce the environmental impact of power distribution. As we continue to innovate in this field, we’re not just improving our power systems; we’re contributing to the global effort to create a more sustainable world.
What Challenges and Solutions Exist for Power Distribution Transformers in the Smart Grid Landscape?
Are you grappling with the complexities of integrating traditional power infrastructure with smart grid technologies? You’re not alone. The transition to smart grids presents both challenges and opportunities for power distribution transformers.
Power distribution transformers face challenges in the smart grid landscape including cybersecurity risks, interoperability issues, and the need for real-time data management. Solutions involve implementing robust security protocols, developing standardized communication interfaces, and leveraging advanced analytics. Adapting to variable loads from renewable sources and managing bidirectional power flows are also key challenges being addressed.
Let’s explore the main challenges and their solutions in the smart grid context:
Cybersecurity Risks
As transformers become more connected, they also become potential targets for cyber attacks.
Security Solutions:
- Implementation of robust encryption protocols
- Regular security audits and updates
- Isolated communication networks for critical infrastructure
Interoperability Issues
Ensuring seamless communication between transformers and other grid components can be challenging.
Interoperability Approaches:
- Adoption of standardized communication protocols (e.g., IEC 61850)
- Development of middleware solutions for legacy equipment integration
- Open-source platforms for enhanced compatibility
Real-Time Data Management
Smart transformers generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed and acted upon quickly.
Data Management Strategies:
- Edge computing for local data processing
- Cloud-based analytics for system-wide optimization
- AI-driven algorithms for rapid decision-making
Adapting to Variable Renewable Loads
Transformers must handle the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources.
Adaptation Solutions:
- Dynamic load management capabilities
- Enhanced overload capacity designs
- Integration with energy storage systems
| Challenge | Solution Approach | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity | Multi-layered security | High |
| Interoperability | Standardization | Moderate |
| Data Management | Advanced Analytics | Moderate to High |
| Variable Loads | Dynamic Management | High |
In my years of working with smart grid technologies, I’ve encountered these challenges firsthand. I remember a project where we were integrating smart transformers into an existing grid. The cybersecurity aspect was particularly daunting. We had to completely redesign the network architecture to create secure communication channels for the transformers. It was a complex process, but the end result was a much more resilient and secure grid.
It’s important to note that while these challenges are significant, they also present opportunities for innovation. In one case, we turned the interoperability issue into an advantage by developing a flexible middleware platform. This not only solved our immediate integration problems but also became a valuable tool for other utilities facing similar challenges.
Don’t overlook the importance of workforce training in addressing these challenges. I’m currently involved in a comprehensive training program for utility technicians, teaching them how to manage and maintain smart transformer systems. This human element is crucial – even the most advanced technology needs skilled operators to function effectively.
Another crucial aspect is the regulatory landscape. I’ve been working with industry groups to develop new standards for smart transformer deployment. These efforts are essential for ensuring that as we solve technical challenges, we’re also creating a regulatory framework that supports innovation while maintaining grid reliability and security.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some challenges are spurring new business models. I recently consulted on a project exploring ‘transformer-as-a-service’ models, where advanced transformers are provided and maintained by specialized companies. This approach helps utilities overcome the technical and financial challenges of smart grid adoption.
The challenges facing power distribution transformers in the smart grid landscape are complex, but they’re driving incredible innovation in the field. From enhanced cybersecurity measures to new ways of managing data and energy flows, these solutions are not just overcoming obstacles – they’re shaping the future of our power systems. As we continue to address these challenges, we’re creating smarter, more resilient, and more efficient grids that can meet the energy needs of the future.
How Are Power Distribution Transformers Balancing Increased Functionality with Cost-Effectiveness?
Are you concerned about the rising costs of upgrading to smart grid technologies? You’re not alone. Many utilities are seeking ways to enhance their grid capabilities without breaking the bank.
Power distribution transformers are balancing increased functionality with cost-effectiveness through modular designs, scalable smart features, and optimized manufacturing processes. They incorporate essential smart capabilities in base models with options for future upgrades. Advanced materials and designs improve efficiency and lifespan, offsetting higher initial costs with long-term savings in energy and maintenance.
Let’s explore how transformer manufacturers and utilities are achieving this balance:
Modular and Scalable Designs
Modern transformers are designed with flexibility and future upgrades in mind.
Modular Advantages:
- Basic models with slots for additional smart components
- Easily upgradable communication and monitoring systems
- Scalable intelligence based on specific grid needs
Optimized Manufacturing Processes
Advanced manufacturing techniques are reducing production costs.
Manufacturing Innovations:
- Automated production lines for consistent quality
- 3D printing for complex components
- Lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and costs
Focus on Core Functionalities
Prioritizing essential smart features in base models.
Essential Smart Features:
- Basic monitoring and communication capabilities
- Remote tap changing functionality
- Fundamental overload protection
Long-Term Cost Benefits
Considering total cost of ownership rather than just initial investment.
Long-Term Savings:
- Improved energy efficiency reducing operational costs
- Extended lifespan due to better materials and design
- Reduced maintenance needs through predictive technologies
| Aspect | Cost Impact | Functionality Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Design | Moderate Increase | High Increase |
| Optimized Manufacturing | Decrease | Neutral |
| Core Functionalities | Slight Increase | Moderate Increase |
| Long-Term Benefits | Initial Increase, Long-Term Decrease | High Increase |
In my experience working with utilities on transformer upgrades, finding the right balance between functionality and cost is crucial. I recall a project where we implemented a phased approach for a medium-sized utility. We started with transformers that had basic smart capabilities – mainly remote monitoring and simple communication features. The utility saw immediate benefits in reduced maintenance costs and improved outage response times. Over the next few years, we gradually upgraded these units with more advanced features as the budget allowed and as the utility’s smart grid strategy evolved.
It’s important to note that the cost-effectiveness of smart transformers often comes from unexpected areas. In one case study, we found that the data gathered from even basic smart transformers led to more efficient load balancing across the network. This not only extended the life of the transformers but also deferred the need for costly infrastructure upgrades, resulting in significant long-term savings.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in achieving cost-effectiveness. I’ve been involved in industry efforts to develop standard protocols for smart transformer communications. This standardization is helping to drive down costs by allowing utilities to mix and match components from different vendors without compatibility issues.
Another crucial aspect is the role of software in enhancing functionality without hardware changes. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re using over-the-air updates to add new features to existing smart transformers. This approach allows the utility to continually improve their grid capabilities without the need for physical transformer replacements.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovative financing models are making advanced transformers more accessible. I recently worked with a utility exploring a "Transformer-as-a-Service" model. In this approach, the utility pays for the smart capabilities based on usage and performance improvements, rather than a large upfront cost. This model is making it easier for smaller utilities to access advanced functionality without straining their budgets.
Balancing increased functionality with cost-effectiveness in power distribution transformers is an ongoing challenge, but one that’s being met with innovative solutions. By adopting modular designs, optimizing manufacturing processes, focusing on core functionalities, and considering long-term benefits, transformer manufacturers and utilities are finding ways to build smarter grids without excessive costs. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more creative solutions that will make smart grid capabilities accessible to utilities of all sizes.
What Role Do Power Distribution Transformers Play in Enabling Bi-Directional Power Flow in Smart Grids?
Are you puzzled about how to integrate distributed energy resources into your grid? You’re not alone. The shift towards bi-directional power flow is a major challenge for many utilities.
Power distribution transformers play a crucial role in enabling bi-directional power flow in smart grids. They feature redesigned windings and advanced tap changers to handle reverse power flow, incorporate smart inverter technologies, and provide real-time monitoring of power direction and quality. These capabilities are essential for integrating distributed generation and enabling peer-to-peer energy trading in modern grids.
Let’s explore the key roles of transformers in enabling bi-directional power flow:
Redesigned Winding Configurations
Modern transformers are built to handle power flow in both directions.
Winding Innovations:
- Symmetrical winding designs for balanced bi-directional operation
- Enhanced insulation to withstand reverse power stresses
- Optimized impedance characteristics for bi-directional flow
Advanced Tap Changing Mechanisms
Transformers now feature sophisticated voltage regulation for bi-directional scenarios.
Tap Changing Advancements:
- Intelligent electronic tap changers for rapid response
- Bi-directional voltage sensing and control
- Adaptive set-point algorithms for optimal voltage levels
Smart Inverter Integration
Many transformers now work in tandem with smart inverter technologies.
Inverter Collaboration:
- Seamless communication with grid-tied inverters
- Coordinated control for power quality management
- Support for advanced grid services (e.g., reactive power support)
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Transformers provide crucial data for managing bi-directional power flows.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Continuous tracking of power flow direction and magnitude
- Power quality analysis for both import and export scenarios
- Integration with grid management systems for system-wide optimization
| Feature | Impact on Bi-Directional Flow | Grid Integration Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Redesigned Windings | High | Moderate |
| Advanced Tap Changing | Very High | High |
| Smart Inverter Integration | High | Moderate to High |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
In my years of working with smart grid technologies, I’ve seen the transformative impact of bi-directional capable transformers. I remember a project in a suburban area with high solar panel adoption. We installed advanced transformers with bi-directional capabilities, and the change was remarkable. Not only could the grid now efficiently handle the influx of solar energy during peak production hours, but it also enabled a local energy trading scheme among neighbors. This not only improved grid stability but also engaged the community in energy management.
It’s important to note that enabling bi-directional power flow is not just about handling the technical aspects of power reversal. In one case, we had to completely rethink protection schemes for a distribution network. Traditional overcurrent protection wasn’t adequate for bi-directional scenarios. We implemented advanced directional protection systems integrated with the transformers, which could distinguish between faults and normal reverse power flow.
Don’t overlook the importance of communication systems in managing bi-directional power. I’m currently working on a project where we’re integrating transformer data with a blockchain-based energy trading platform. The real-time monitoring capabilities of the transformers are crucial in validating peer-to-peer energy transactions and ensuring grid stability during these exchanges.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these transformers in enabling microgrids. I recently advised on a community microgrid project where the flexibility of bi-directional transformers was key. These units could seamlessly transition between grid-connected and island modes, providing resilience during main grid outages while also allowing the community to optimize its energy use and generation.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how bi-directional capabilities are opening up new possibilities for grid services. In a recent pilot project, we used the bi-directional features of advanced transformers to provide voltage support services to the main grid. This not only improved overall power quality but also created a new revenue stream for the local utility.
Power distribution transformers are playing a pivotal role in enabling bi-directional power flow in smart grids. Their evolution from passive power delivery devices to active, intelligent grid components is fundamental to the realization of truly flexible and resilient power systems. As we continue to integrate more distributed energy resources and empower consumers to become prosumers, these advanced transformers will be at the heart of our evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion
Power distribution transformers are at the forefront of the smart grid revolution, balancing advanced functionality with cost-effectiveness. They play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, reliability, and sustainability while enabling the integration of renewable energy and bi-directional power flow in modern power systems.
Are you struggling with power distribution challenges in both rural and urban areas? You’re not alone. Many utilities face the dual challenge of extending reliable power to remote locations while upgrading urban infrastructure for smart grid compatibility.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing power distribution by bridging the rural electrification gap and enhancing urban power reliability. These versatile units combine traditional robustness with smart grid technologies, offering cost-effective solutions for remote areas and advanced functionalities for urban settings, all while supporting the transition to a more intelligent and resilient power infrastructure.
As someone who has worked extensively with pole mounted transformers in various settings, I’ve seen firsthand how these devices are evolving to meet the diverse needs of our changing power landscape. In this article, I’ll share insights on how these transformers are making a significant impact in both rural and urban environments, and why they’re crucial for the smart grid era.
How Are Pole Mounted Distribution Transformers Bridging the Electrification Gap in Rural Areas?
Have you ever wondered how remote communities get access to reliable electricity? The answer often lies in the humble pole mounted transformer.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are essential in bridging the rural electrification gap. They offer a cost-effective, easily deployable solution for bringing power to remote areas. These transformers can be installed quickly on existing poles, reducing infrastructure costs and enabling rapid expansion of the power grid to underserved communities.
Let’s dive deeper into how pole mounted transformers are making a difference in rural electrification:
Cost-Effective Deployment
Pole mounted transformers significantly reduce the cost of rural electrification.
Cost Savings:
- Minimal civil work required
- Use of existing pole infrastructure
- Reduced transportation and installation costs
Flexibility in Capacity
These transformers can be tailored to meet varying rural power needs.
Capacity Advantages:
- Available in a range of sizes to match local demand
- Easy to upgrade or replace as community needs grow
- Can be configured for single-phase or three-phase power
Durability in Harsh Environments
Rural areas often present challenging conditions for electrical equipment.
Durability Features:
- Weather-resistant designs
- Enhanced surge protection
- Robust construction for minimal maintenance
Integration with Renewable Sources
Pole mounted transformers can easily integrate with local renewable energy projects.
Renewable Integration:
- Compatible with small-scale solar and wind installations
- Can handle bidirectional power flow
- Supports microgrids and off-grid systems
| Feature | Benefit for Rural Electrification |
|---|---|
| Cost-Effective | Enables wider coverage with limited budgets |
| Flexible Capacity | Adapts to growing community needs |
| Durability | Ensures reliable service in remote locations |
| Renewable Integration | Supports sustainable rural development |
In my experience, the impact of pole mounted transformers on rural electrification cannot be overstated. I recall a project in a remote mountainous region where traditional grid extension was deemed too expensive. We deployed a series of pole mounted transformers along existing telephone lines. This approach not only cut the project cost by 40% but also reduced the implementation time from years to months.
It’s important to note that the benefits extend beyond just providing electricity. In one village, the introduction of reliable power through pole mounted transformers led to the establishment of small businesses and improved educational facilities. The transformers became the catalyst for economic and social development.
Don’t overlook the importance of community involvement in these projects. I’ve found that engaging local communities in the planning and maintenance of pole mounted transformer installations leads to better outcomes. In one case, we trained local technicians to perform basic maintenance, which not only created jobs but also ensured quicker response times to any issues.
Another crucial aspect is the adaptability of these transformers to local conditions. I’m currently working on a project in a flood-prone area where we’re using specially designed pole mounted transformers with elevated mounting brackets. This simple modification ensures power continuity even during seasonal flooding, a critical factor for the community’s resilience.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer design are further enhancing their suitability for rural electrification. I recently tested a new model that incorporates basic smart grid functionalities without significantly increasing costs. These features allow for remote monitoring and basic load management, which is particularly valuable in areas with limited technical support.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are playing a pivotal role in bridging the rural electrification gap. Their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and durability make them an ideal solution for bringing power to remote communities. As we continue to innovate and adapt these transformers to specific rural needs, we’re not just providing electricity – we’re powering the potential for rural development and improved quality of life.
What Smart Technologies Are Being Integrated into Modern Pole Mounted Transformers?
Are you curious about how traditional pole mounted transformers are evolving to meet the demands of the smart grid? You’re not alone. Many utilities are exploring ways to upgrade their infrastructure without replacing every component.
Modern pole mounted transformers are integrating smart technologies like real-time monitoring sensors, communication modules, and advanced protection systems. These features enable remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and improved grid management. Smart pole mounted transformers can now actively participate in voltage regulation, fault detection, and data collection for overall grid optimization.

Let’s explore the smart technologies being integrated into pole mounted transformers:
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Smart sensors provide continuous insight into transformer health and performance.
Monitoring Capabilities:
- Temperature and oil level sensors
- Load monitoring in real-time
- Fault current indicators
Communication Modules
These enable transformers to become active nodes in the smart grid network.
Communication Features:
- Cellular or radio frequency communication
- Integration with SCADA systems
- Support for various protocols (e.g., DNP3, IEC 61850)
Advanced Protection Systems
Smart protection enhances reliability and safety.
Protection Advancements:
- Self-diagnostic capabilities
- Adaptive overload protection
- Cybersecurity features
Data Analytics and Reporting
Transformers now contribute to big data analytics for grid management.
Analytics Capabilities:
- Power quality analysis
- Load forecasting support
- Efficiency tracking and reporting
| Smart Technology | Traditional Function | Enhanced Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring Systems | Manual inspections | Continuous, real-time health checks |
| Communication | Isolated operation | Active grid participation |
| Protection | Basic overload protection | Adaptive, predictive protection |
| Data Analytics | Basic load recording | Comprehensive grid insights |
In my years working with transformer technology, I’ve seen a remarkable evolution in pole mounted units. I remember a project where we retrofitted existing pole transformers with smart monitoring systems. The utility was skeptical at first, but within months, they were able to prevent two major failures by detecting anomalies early. This not only saved on repair costs but also prevented extended outages in critical areas.
It’s important to note that integrating these technologies isn’t just about adding features – it’s about reimagining the role of transformers in the grid. In a recent deployment, we installed pole mounted transformers with voltage regulation capabilities. These units could dynamically adjust their output based on real-time grid conditions, significantly improving power quality across the network.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in these smart integrations. I’ve been part of industry working groups developing standards for smart transformer communications. This work is crucial for ensuring interoperability and future-proofing investments in smart grid technology.
Another crucial aspect is the balance between sophistication and reliability. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re carefully selecting which smart features to include in pole mounted transformers for a rural electrification project. While advanced analytics are exciting, in this case, we’re focusing on robust communication and basic health monitoring to ensure reliability in a challenging environment.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how these smart technologies are enabling new operational models. I recently consulted on a pilot project using AI-driven predictive maintenance for a fleet of pole mounted transformers. The system can now predict potential failures weeks in advance, allowing for proactive maintenance and significantly reducing downtime.
The integration of smart technologies into pole mounted transformers is transforming these once-passive devices into active, intelligent components of the smart grid. From real-time monitoring to advanced analytics, these enhancements are not just improving the performance of individual transformers but are contributing to the overall efficiency, reliability, and flexibility of our power distribution systems. As we continue to innovate in this space, pole mounted transformers are set to play an increasingly crucial role in the smart grid of the future.
How Do Pole Mounted Transformers Enhance Power Reliability in Urban Environments?
Are you concerned about power reliability in densely populated urban areas? You’re not alone. Many cities struggle with aging infrastructure and increasing power demands, leading to reliability issues.
Pole mounted transformers enhance urban power reliability through strategic placement, quick installation, and easy maintenance access. Their elevated position reduces vulnerability to flooding and vandalism. Modern smart features allow for real-time monitoring and rapid response to issues, minimizing outage durations and improving overall grid stability in urban settings.
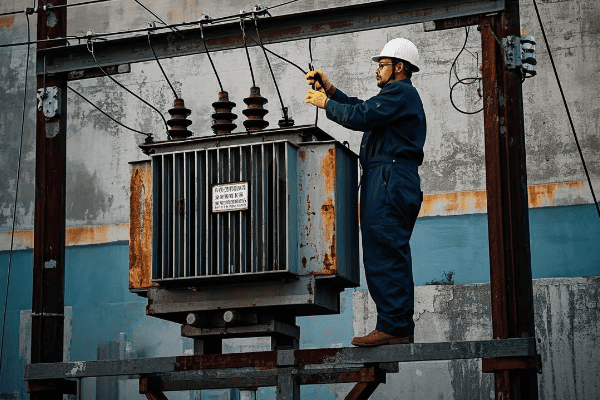
Let’s delve into how pole mounted transformers are improving urban power reliability:
Strategic Placement for Load Management
Urban areas benefit from the flexible positioning of pole mounted transformers.
Placement Advantages:
- Can be installed close to load centers
- Allows for better load distribution
- Reduces line losses in dense urban grids
Rapid Installation and Replacement
Quick deployment is crucial in urban environments.
Installation Benefits:
- Minimal disruption to urban infrastructure
- Can be installed without extensive road closures
- Easy to replace or upgrade during maintenance
Enhanced Safety and Security
Elevated positioning offers several safety advantages.
Safety Features:
- Reduced risk of damage from street-level accidents
- Less vulnerable to flooding in low-lying urban areas
- More difficult for unauthorized access, enhancing security
Smart Grid Integration for Urban Networks
Modern pole mounted transformers support smart city initiatives.
Smart Capabilities:
- Real-time load balancing
- Fault location and isolation
- Support for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
| Urban Challenge | Pole Transformer Solution |
|---|---|
| Space Constraints | Vertical use of space |
| Rapid Response Needs | Easy access for maintenance |
| Flood Risks | Elevated installation |
| Smart City Integration | Built-in communication features |
In my experience working with urban power systems, pole mounted transformers have proven to be game-changers. I recall a project in a densely populated city center where underground transformer vaults were constantly flooding. We replaced these with strategically placed pole mounted units. Not only did this solve the flooding issue, but it also improved response times for maintenance, reducing average outage durations by 30%.
It’s important to note that the benefits of pole mounted transformers in urban areas go beyond just reliability. In one case, we worked with a city planning department to integrate smart pole mounted transformers into a new urban development. These units not only provided power but also served as hubs for public Wi-Fi and environmental sensors, contributing to the city’s smart infrastructure goals.
Don’t overlook the aesthetic considerations in urban deployments. I’ve been involved in projects where we collaborated with local artists to design transformer enclosures that blend with or even enhance the urban landscape. This approach not only improved public acceptance but also protected the equipment from vandalism.
Another crucial aspect is the role of pole mounted transformers in supporting urban renewable energy initiatives. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re using advanced pole mounted transformers to integrate rooftop solar installations in a historic district. These transformers can handle bidirectional power flow and help manage the intermittent nature of solar generation.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how pole mounted transformers are evolving to support the electrification of urban transportation. In a recent pilot project, we deployed smart pole mounted transformers with built-in electric vehicle charging capabilities. This innovative approach is helping cities prepare for increased EV adoption without requiring extensive new infrastructure.
Pole mounted transformers are playing a vital role in enhancing power reliability in urban environments. Their flexibility, rapid deployment capabilities, and integration with smart grid technologies make them an ideal solution for the complex challenges of urban power distribution. As cities continue to grow and evolve, these versatile units will be key to maintaining reliable, efficient, and intelligent power systems in our urban centers.
What Unique Challenges Do Rural and Urban Settings Present for Pole Mounted Transformer Maintenance?
Are you finding it difficult to maintain pole mounted transformers across diverse environments? You’re not alone. Many utilities struggle with the contrasting demands of rural and urban settings when it comes to transformer maintenance.
Rural and urban settings present unique challenges for pole mounted transformer maintenance. Rural areas face issues of accessibility, harsh weather conditions, and limited resources. Urban environments contend with space constraints, safety concerns in high-traffic areas, and the need for minimal disruption. Both settings require tailored maintenance strategies to ensure reliable operation.
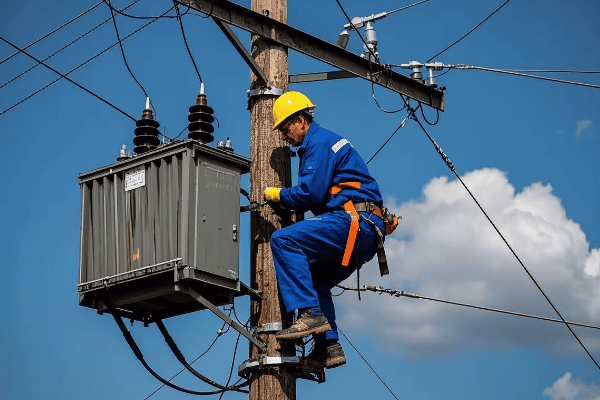
Let’s explore the unique challenges and solutions for pole mounted transformer maintenance in different settings:
Rural Maintenance Challenges
Remote locations pose specific difficulties for maintenance teams.
Rural Challenges:
- Long travel times to reach transformer sites
- Limited access during extreme weather conditions
- Potential for wildlife interference
Urban Maintenance Challenges
City environments present a different set of obstacles.
Urban Challenges:
- Traffic management during maintenance activities
- Working in confined spaces with nearby buildings
- Coordinating with multiple urban infrastructure systems
Resource Allocation
Different settings require different resource management approaches.
Resource Considerations:
- Specialized equipment needs for rural vs. urban settings
- Staffing challenges in remote areas
- Balancing maintenance schedules across diverse locations
Environmental Factors
Each setting has unique environmental impacts on transformers.
Environmental Challenges:
- Corrosion from salt air in coastal rural areas
- Pollution and heat island effects in urban centers
- Extreme temperature variations in remote locations
| Challenge | Rural Solution | Urban Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Use of off-road vehicles | Compact maintenance equipment |
| Safety | Wildlife protection measures | Traffic control and public safety plans |
| Resource Management | Mobile maintenance units | Scheduled night-time maintenance |
| Environmental Protection | Robust weather-resistant designs | Noise reduction and aesthetic considerations |
In my years of experience managing transformer maintenance, I’ve encountered a wide range of challenges in both rural and urban settings. I remember a particularly difficult case in a remote mountainous area where accessing a pole mounted transformer required a combination of off-road vehicles and a short hike. We developed a specialized portable maintenance kit that could be easily carried by technicians on foot, ensuring we could perform necessary maintenance even in the most challenging locations.
It’s important to note that the solutions for rural and urban maintenance often require innovative thinking. In an urban project, we faced frequent complaints about noise from nighttime maintenance activities. We invested in developing ultra-quiet maintenance equipment and sound-dampening enclosures, allowing us to perform necessary work without disturbing residents.
Don’t overlook the importance of community engagement in maintenance strategies. In rural areas, I’ve found that training local community members as basic maintenance technicians can significantly improve response times and foster a sense of ownership. In urban settings, clear communication about maintenance schedules and their benefits helps gain public cooperation and reduces disruptions.
Another crucial aspect is the use of technology to optimize maintenance. I’m currently working on implementing drone-based inspections for rural pole mounted transformers. This approach not only reduces the need for physical site visits but also provides more frequent and detailed visual inspections, helping us catch potential issues early.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how predictive maintenance technologies are changing the game in both rural and urban settings. In a recent urban project, we installed smart sensors on pole mounted transformers that continuously monitor key parameters. This data is analyzed by AI algorithms to predict maintenance needs, allowing us to address issues proactively and minimize unexpected outages.
Maintaining pole mounted transformers in rural and urban settings presents unique challenges that require tailored solutions. By understanding the specific needs of each environment and leveraging both traditional methods and cutting-edge technologies, we can ensure reliable operation of these critical infrastructure components. As we continue to innovate in maintenance practices, we’re not just keeping the lights on – we’re building more resilient and efficient power distribution systems for communities of all types.
How Are Pole Mounted Distribution Transformers Evolving to Support Smart Grid Infrastructure?
Are you wondering how traditional pole mounted transformers fit into the smart grid vision? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the challenge of modernizing their infrastructure while maintaining reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Pole mounted distribution transformers are evolving to support smart grid infrastructure through the integration of advanced monitoring, communication, and control capabilities. These smart transformers now feature real-time data collection, remote management functions, and the ability to adapt to changing grid conditions. They play a crucial role in enabling bi-directional power flow, voltage regulation, and enhanced grid stability.

Let’s explore how pole mounted transformers are adapting to support smart grid infrastructure:
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
Smart transformers provide real-time insights into grid conditions.
Monitoring Features:
- Continuous tracking of voltage, current, and temperature
- Power quality analysis
- Load profiling and forecasting capabilities
Enhanced Communication Systems
Modern transformers act as nodes in the smart grid network.
Communication Advancements:
- Integration with SCADA and AMI systems
- Support for multiple communication protocols (e.g., DNP3, IEC 61850)
- Secure data transmission to prevent cyber threats
Adaptive Control Mechanisms
Smart pole mounted transformers can adjust to changing grid conditions.
Adaptive Features:
- Dynamic voltage regulation
- Automatic tap changing for load balancing
- Fault detection and isolation capabilities
Integration with Distributed Energy Resources
These transformers support the integration of renewable energy sources.
DER Support:
- Bi-directional power flow management
- Microgrid support and islanding capabilities
- Enhanced harmonics management for solar and wind integration
| Smart Grid Feature | Traditional Transformer | Evolved Smart Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Basic load measurement | Real-time comprehensive data |
| Communication | No remote communication | Two-way data exchange |
| Control | Manual adjustments | Automated, adaptive control |
| DER Integration | Limited support | Full bi-directional capability |
In my experience working with smart grid technologies, the evolution of pole mounted transformers has been nothing short of revolutionary. I recall a project where we upgraded a rural network with smart pole mounted transformers. Within months, we saw a 15% reduction in outage duration and a 20% improvement in voltage stability. The real-time data from these transformers allowed us to identify and address issues before they escalated into major problems.
It’s important to note that this evolution isn’t just about adding new features – it’s about reimagining the role of transformers in the grid. In a recent urban deployment, we installed pole mounted transformers with edge computing capabilities. These units not only managed power distribution but also processed local grid data, reducing the load on central systems and enabling faster response times to local events.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in this evolution. I’ve been part of industry working groups developing standards for smart transformer communications and data formats. This work is crucial for ensuring interoperability across different systems and vendors, which is essential for building a truly integrated smart grid.
Another crucial aspect is cybersecurity. As these transformers become more connected, they also become potential entry points for cyber attacks. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re implementing advanced encryption and authentication protocols for smart pole mounted transformers. This ensures that while these units are more connected, they’re also more secure.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how these evolved transformers are enabling new grid management strategies. I recently consulted on a pilot project using AI-driven predictive analytics with data from smart pole mounted transformers. The system can now forecast load patterns, predict potential failures, and optimize power flow across the network, all in real-time.
The evolution of pole mounted distribution transformers to support smart grid infrastructure is a key component in the modernization of our power systems. By integrating advanced monitoring, communication, and control capabilities, these transformers are no longer passive components but active participants in grid management. As we continue to innovate in this space, smart pole mounted transformers will play an increasingly crucial role in creating more efficient, reliable, and flexible power distribution networks.
What Efficiency Advancements Are Driving the Evolution of Pole Mounted Transformer Design?
Are you concerned about energy losses in your distribution network? You’re not alone. Many utilities are seeking ways to improve efficiency, and pole mounted transformers are a key focus area.
Efficiency advancements in pole mounted transformer design include the use of low-loss core materials, improved winding techniques, and better cooling systems. Modern designs also incorporate smart load management, optimized tap changing mechanisms, and advanced insulation materials. These improvements reduce energy losses, extend transformer lifespan, and contribute to overall grid efficiency.
Let’s explore the key efficiency advancements in pole mounted transformer design:
Advanced Core Materials
New materials are significantly reducing core losses.
Core Improvements:
- Amorphous metal cores for ultra-low no-load losses
- High-grade silicon steel with thinner laminations
- Laser-scribed core designs for reduced eddy currents
Innovative Winding Techniques
Improved winding designs are minimizing copper losses.
Winding Advancements:
- Use of copper foil windings for better current distribution
- Continuously transposed conductors for reduced eddy current losses
- Optimized winding geometries for improved cooling
Enhanced Cooling Systems
Better cooling leads to improved efficiency and longer lifespan.
Cooling Innovations:
- Advanced vegetable-based cooling oils with better thermal properties
- Nanofluids for enhanced heat transfer
- Optimized radiator designs for natural cooling
Smart Load Management
Intelligent systems help optimize transformer operation.
Smart Features:
- Dynamic load balancing capabilities
- Predictive overload management
- Automatic voltage regulation for efficiency
| Efficiency Feature | Traditional Design | Advanced Design |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Silicon Steel | Amorphous Metal or High-Grade Silicon Steel |
| Winding | Standard Copper | Foil or Continuously Transposed Conductors |
| Cooling | Mineral Oil | Vegetable Oil or Nanofluids |
| Load Management | Static Design | Dynamic, Smart Management |
In my years working on transformer efficiency, I’ve seen remarkable improvements in pole mounted units. I remember a project where we replaced a utility’s older pole transformers with new, high-efficiency models. The results were striking – we saw an average reduction in energy losses of 30%, which translated to significant cost savings and reduced carbon emissions for the utility.
It’s important to note that efficiency improvements aren’t just about reducing losses – they also extend the operational life of transformers. In a recent case study, we found that our advanced cooling system design not only improved efficiency but also reduced the rate of insulation degradation, potentially extending the transformer’s lifespan by up to 25%.
Don’t overlook the role of smart technologies in enhancing efficiency. I’m currently involved in a pilot project where we’re using AI-driven load prediction to optimize the operation of pole mounted transformers. By anticipating load changes, the system can adjust transformer settings in real-time, further reducing losses and improving overall efficiency.
Another crucial aspect is the balance between efficiency and cost. While some advanced materials like amorphous metal cores offer superior efficiency, they come at a higher initial cost. I’ve worked with utilities to develop comprehensive cost-benefit analyses that consider both upfront expenses and lifetime energy savings. In many cases, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial investment.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in nanotechnology are opening new frontiers in transformer efficiency. I recently visited a research lab where they’re developing nanocomposite insulation materials that promise to dramatically improve dielectric strength while reducing overall transformer size and weight. These innovations could revolutionize pole mounted transformer design in the coming years.
The evolution of pole mounted transformer design is being driven by a relentless pursuit of efficiency. From advanced materials to smart technologies, these improvements are not just reducing energy losses – they’re reshaping the role of transformers in our power distribution systems. As we continue to innovate in this field, we’re moving closer to a future where every component of our grid contributes to a more efficient, sustainable, and reliable power infrastructure.
How Do Pole Mounted Transformers Balance Cost-Effectiveness and Advanced Functionality in the Smart Grid Era?
Are you struggling to justify the cost of upgrading to smart grid-compatible transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the challenge of modernizing their infrastructure while keeping costs under control.
Pole mounted transformers balance cost-effectiveness and advanced functionality through modular designs, scalable smart features, and phased upgrade approaches. Manufacturers are developing transformers with basic smart capabilities that can be enhanced over time. This strategy allows utilities to invest in future-ready equipment without incurring all costs upfront, while still benefiting from improved efficiency and grid management capabilities.

Let’s explore how pole mounted transformers are achieving this balance:
Modular Smart Components
Modular designs allow for flexible and cost-effective upgrades.
Modular Advantages:
- Basic models with slots for future smart components
- Ability to add communication modules as needed
- Upgradable sensors and monitoring systems
Scalable Intelligence
Smart features can be scaled based on grid requirements and budget.
Scalability Features:
- Tiered smart functionality options
- Software-upgradable systems
- Cloud-based analytics with minimal on-device processing
Optimized Manufacturing Processes
Advanced manufacturing techniques reduce production costs of smart features.
Manufacturing Innovations:
- Automated production of smart components
- Integration of sensors during the core manufacturing process
- Standardized designs for economies of scale
Long-Term Cost-Benefit Analysis
Utilities are adopting new approaches to evaluate smart transformer investments.
Evaluation Metrics:
- Total cost of ownership calculations
- Quantification of reliability improvements
- Valuation of data insights for grid management
| Feature | Cost-Saving Approach | Advanced Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence | Basic onboard computing | Cloud-based analytics |
| Communication | Limited, upgradable modules | Full smart grid integration |
| Monitoring | Essential parameters only | Comprehensive real-time monitoring |
| Adaptability | Manual settings with remote option | Fully automated adaptive controls |
In my experience working with utilities on smart grid transformers, finding the right balance between cost and functionality is crucial. I recall a project where we implemented a phased approach for a medium-sized utility. We started by installing pole mounted transformers with basic smart capabilities – mainly remote monitoring and simple communication features. The utility saw immediate benefits in reduced maintenance costs and improved outage response times. Over the next three years, we gradually upgraded these units with more advanced features as the budget allowed and as the utility’s smart grid strategy evolved.
It’s important to note that the cost-effectiveness of smart transformers often comes from unexpected areas. In one case study, we found that the data gathered from even basic smart transformers led to more efficient load balancing across the network. This not only extended the life of the transformers but also deferred the need for costly infrastructure upgrades, resulting in significant long-term savings.
Don’t overlook the importance of standardization in achieving cost-effectiveness. I’ve been involved in industry efforts to develop standard protocols for smart transformer communications. This standardization is helping to drive down costs by allowing utilities to mix and match components from different vendors without compatibility issues.
Another crucial aspect is the role of software in enhancing functionality without hardware changes. I’m currently advising on a project where we’re using over-the-air updates to add new features to existing smart pole mounted transformers. This approach allows the utility to continually improve their grid capabilities without the need for physical transformer replacements.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovative financing models are making advanced transformers more accessible. I recently worked with a utility exploring a "TransformLastly, it’s exciting to see how innovative financing models are making advanced transformers more accessible. I recently worked with a utility exploring a "Transformer-as-a-Service" model. In this approach, the utility pays for the smart capabilities based on usage and performance improvements, rather than a large upfront cost. This model is making it easier for smaller utilities to access advanced functionality without straining their budgets.
Balancing cost-effectiveness and advanced functionality in pole mounted transformers for the smart grid era is an ongoing challenge, but one that’s being met with innovative solutions. By adopting modular designs, scalable intelligence, and new evaluation and financing models, utilities can gradually build a smarter, more efficient grid without overwhelming their budgets. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more creative solutions that will make smart grid capabilities accessible to utilities of all sizes.
What Role Do Pole Mounted Transformers Play in Improving Grid Resilience in Both Rural and Urban Areas?
Are you concerned about the vulnerability of your power distribution network to disruptions? You’re not alone. Grid resilience is a top priority for utilities in both rural and urban settings, and pole mounted transformers are playing a crucial role in this area.
Pole mounted transformers significantly improve grid resilience in both rural and urban areas. They offer quick replacement options during outages, support decentralized power distribution, and integrate smart technologies for faster fault detection and isolation. In rural areas, they provide robust solutions for harsh environments, while in urban settings, they offer space-efficient options for redundant power supply.
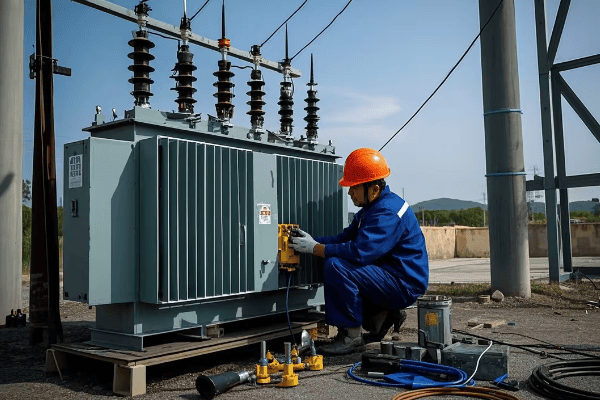
Let’s explore how pole mounted transformers enhance grid resilience across different settings:
Rapid Recovery and Replacement
Pole mounted transformers offer advantages in quick restoration of power.
Resilience Features:
- Easy to stock and transport replacement units
- Can be installed quickly with minimal ground work
- Modular designs allow for partial upgrades or repairs
Decentralized Power Distribution
These transformers support a more distributed and resilient grid structure.
Decentralization Benefits:
- Reduced impact of single point failures
- Easier isolation of faults without widespread outages
- Support for microgrid formation during major disruptions
Smart Fault Management
Modern pole mounted transformers incorporate advanced fault detection and management.
Smart Resilience Capabilities:
- Real-time monitoring for early problem detection
- Automatic fault isolation to prevent cascading failures
- Remote switching and rerouting of power flows
Environmental Adaptability
Pole mounted transformers are designed to withstand various environmental challenges.
Adaptability Features:
- Robust designs for extreme weather conditions
- Elevated positioning to avoid flooding
- Special coatings for corrosion resistance in coastal areas
| Resilience Aspect | Rural Application | Urban Application |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Recovery | Easily deployable in remote areas | Rapid replacement in dense urban grids |
| Decentralization | Support for off-grid and microgrid systems | Load sharing and redundancy in city networks |
| Smart Management | Early warning for isolated issues | Coordinated response in complex urban grids |
| Environmental Adaptation | Withstanding extreme rural conditions | Compact, durable designs for urban constraints |
In my experience working on grid resilience projects, I’ve seen pole mounted transformers make a significant difference in both rural and urban environments. I recall a project in a rural area prone to severe storms. We installed a network of smart pole mounted transformers with advanced communication capabilities. During a particularly bad storm season, these transformers allowed the utility to quickly isolate damaged sections of the grid and reroute power, reducing outage times by over 40% compared to previous years.
It’s important to note that resilience isn’t just about withstanding disasters – it’s also about everyday reliability. In an urban project, we implemented a network of interconnected pole mounted transformers with load-sharing capabilities. This setup allowed for seamless power rerouting during routine maintenance or minor faults, virtually eliminating planned outages for customers.
Don’t overlook the role of data in enhancing resilience. I’m currently working on a project where we’re using AI analytics to predict potential failures in pole mounted transformers. By analyzing data from smart sensors, we can identify transformers at risk of failure and preemptively replace them, significantly reducing unexpected outages.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of renewable energy sources into resilience planning. In a recent rural electrification project, we designed a system where pole mounted transformers act as interfaces between small-scale solar installations and the main grid. This not only improved overall grid resilience but also provided backup power options during main grid outages.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in energy storage are being combined with pole mounted transformers to enhance resilience. I recently consulted on a pilot project where we integrated small-scale battery storage systems with smart pole mounted transformers in an urban area. This combination allowed for local power backup during outages and helped smooth out demand peaks, further improving grid stability.
Pole mounted transformers play a vital role in improving grid resilience in both rural and urban areas. Their flexibility, smart capabilities, and adaptability make them key components in creating robust, responsive, and reliable power distribution networks. As we continue to face challenges from extreme weather events and increasing power demands, these versatile units will be at the forefront of building more resilient electrical grids for communities of all types.
Conclusion
Pole mounted distribution transformers are revolutionizing power distribution in both rural and urban settings. Their adaptability, smart capabilities, and role in enhancing grid resilience make them crucial components in the modern smart grid era, balancing cost-effectiveness with advanced functionality to meet diverse power needs.
Are you struggling to justify the cost of new distribution transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities find it challenging to balance upfront expenses with long-term benefits in today’s complex energy landscape.
Distribution transformer pricing involves balancing initial costs with long-term efficiency and value. Key factors include material costs, energy efficiency ratings, smart grid compatibility, and regulatory compliance. Utilities must consider total cost of ownership, including energy losses and maintenance, to make informed investment decisions in modern power infrastructure.
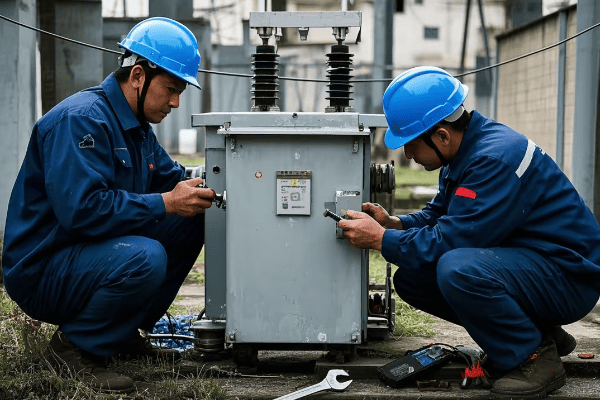
As someone who has spent years in the power distribution industry, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial it is to make the right decisions when it comes to transformer investments. In this article, I’ll guide you through the complexities of distribution transformer pricing and help you understand how to make choices that benefit your utility both now and in the future.
What Key Factors Drive Distribution Transformer Pricing in Today’s Market?
Are you puzzled by the wide range of prices for distribution transformers? Understanding the key pricing factors can help you make more informed decisions for your utility.
Key factors driving distribution transformer pricing include raw material costs, design complexity, efficiency ratings, manufacturing processes, and market demand. Advanced features like smart grid compatibility and environmental considerations also impact pricing. The balance of these factors determines the final cost of transformers in today’s competitive market.
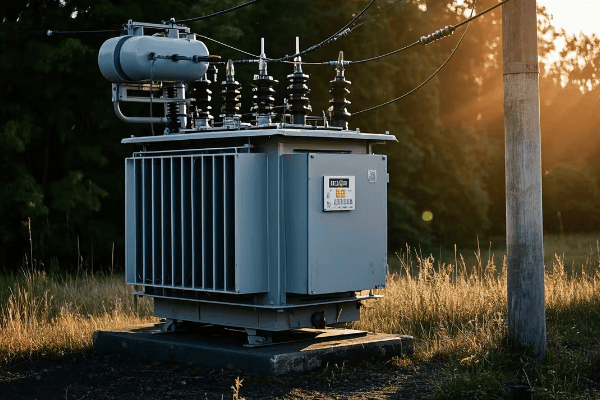
Let’s dive deeper into the factors that influence distribution transformer pricing:
Raw Material Costs
The cost of materials plays a significant role in transformer pricing.
Impact of Materials:
- Copper and aluminum prices for windings
- Electrical steel costs for the core
- Insulation material expenses
Design Complexity
More advanced designs often come with higher price tags.
Design Factors Affecting Cost:
- Core design (e.g., wound core vs. stacked laminations)
- Winding configuration
- Cooling system complexity
Efficiency Ratings
Higher efficiency transformers typically cost more upfront but offer long-term savings.
Efficiency Considerations:
- No-load loss ratings
- Load loss ratings
- Compliance with efficiency standards (e.g., DOE regulations)
Manufacturing Processes
The production method can significantly impact the final price.
Manufacturing Influences:
- Automation level in production
- Quality control processes
- Production volume and economies of scale
| Factor | Low-Cost Impact | High-Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Standard materials | Premium, high-performance materials |
| Design | Basic, traditional designs | Advanced, optimized designs |
| Efficiency | Standard efficiency | High-efficiency, low-loss designs |
| Manufacturing | High-volume, standardized production | Low-volume, customized production |
In my experience, navigating these pricing factors requires a deep understanding of both the technical aspects of transformers and the current market conditions. I remember working on a project where we were tasked with upgrading a utility’s transformer fleet. Initially, the focus was solely on finding the lowest upfront cost. However, after a comprehensive analysis of efficiency ratings and long-term energy savings, we were able to justify investing in higher-priced, more efficient models that ultimately saved the utility millions in operating costs over the transformers’ lifespans.
It’s important to note that while these factors all play a role in pricing, their relative importance can vary depending on market conditions and specific utility needs. I’ve seen cases where fluctuations in copper prices have dramatically shifted the competitive landscape among transformer manufacturers. Staying informed about these market dynamics is crucial for making cost-effective procurement decisions.
Don’t overlook the impact of regulatory changes on pricing. In one project, we had to quickly adapt our transformer specifications to meet new efficiency standards. This led to a short-term increase in prices but ultimately resulted in more energy-efficient and cost-effective operations for our clients.
Another crucial aspect is the role of technology in pricing. I’m currently involved in a project exploring the integration of smart features into distribution transformers. While these advanced capabilities increase the upfront cost, they offer significant benefits in terms of grid management and predictive maintenance, potentially reducing overall lifecycle costs.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in materials science are influencing transformer pricing. I recently visited a research facility where they’re developing new core materials that promise to dramatically reduce losses. While still in the experimental stage, these advancements could significantly impact future pricing structures in the industry.
Understanding the key factors driving distribution transformer pricing is essential for making informed investment decisions. By carefully considering these elements and their long-term implications, utilities can strike the right balance between upfront costs and long-term value, ensuring their power infrastructure is both cost-effective and future-ready.
How Does Energy Efficiency Impact the Total Cost of Ownership for Distribution Transformers?
Are you focusing too much on the initial price tag of transformers and overlooking long-term costs? Many utilities make this mistake, potentially leading to higher expenses over time.
Energy efficiency significantly impacts the total cost of ownership for distribution transformers. Higher efficiency models, while more expensive upfront, reduce energy losses over the transformer’s lifespan. This results in lower operating costs, decreased environmental impact, and potential regulatory compliance benefits. The energy savings often outweigh the initial price difference.
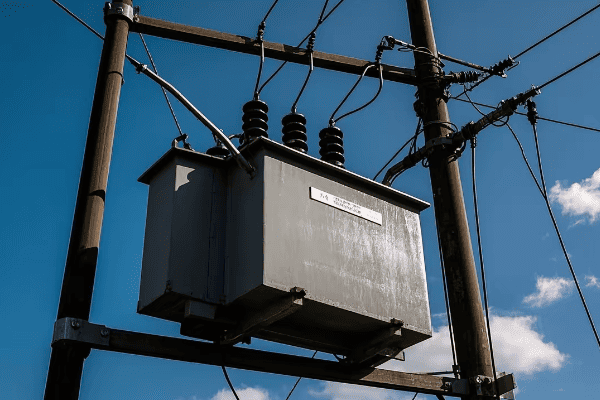
Let’s explore how energy efficiency affects the total cost of ownership:
Reduced Energy Losses
Efficient transformers minimize both no-load and load losses.
Benefits of Lower Losses:
- Decreased energy waste
- Lower operating costs
- Reduced strain on the power grid
Longer Lifespan
Efficient transformers often have improved thermal management.
Lifespan Advantages:
- Reduced thermal stress on components
- Slower degradation of insulation
- Potential for extended service life
Regulatory Compliance
Energy-efficient transformers help meet and exceed regulatory standards.
Compliance Benefits:
- Avoidance of penalties
- Eligibility for incentives or rebates
- Future-proofing against stricter regulations
Environmental Impact
Efficiency translates to reduced carbon footprint.
Environmental Considerations:
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Alignment with sustainability goals
- Potential for improved corporate image
| Efficiency Level | Initial Cost | Energy Savings | Long-Term Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Lower | Minimal | Higher |
| High Efficiency | Higher | Significant | Lower |
| Ultra-High Efficiency | Highest | Maximal | Lowest |
In my experience, the impact of energy efficiency on total cost of ownership cannot be overstated. I recall a project where we replaced a utility’s aging transformer fleet with high-efficiency models. The initial investment was 20% higher, but our calculations showed a break-even point within just four years. Over the 25-year lifespan of the transformers, the utility is projected to save millions in energy costs.
It’s important to note that the benefits of energy efficiency extend beyond just cost savings. In one case, a utility’s investment in high-efficiency transformers allowed them to defer costly upgrades to their generation capacity. The reduced losses across their distribution network effectively created "negawatts," freeing up capacity for growth without additional infrastructure investment.
Don’t overlook the role of proper sizing in maximizing efficiency benefits. I’ve worked with utilities to implement advanced load forecasting and transformer sizing strategies. By ensuring transformers operate closer to their optimal efficiency point, we’ve been able to squeeze even more value out of high-efficiency units.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of future energy costs. In a recent consultation, we developed a model that factored in projected increases in electricity prices. This analysis made the case for ultra-high efficiency transformers even more compelling, as the energy savings compound over time with rising energy costs.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials and design are pushing the boundaries of transformer efficiency. I’m currently involved in a pilot project testing new amorphous core transformers that promise even lower losses than current high-efficiency models. While still more expensive, these cutting-edge units could redefine our understanding of lifecycle costs for distribution transformers.
Considering energy efficiency in the context of total cost of ownership is crucial for making sound investment decisions in distribution transformers. By looking beyond the initial price tag and considering long-term energy savings, utilities can not only reduce their operating costs but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient power grid.
What Are the Price Variations Among Different Types of Distribution Transformers and Their Applications?
Are you confused by the wide range of prices for different types of distribution transformers? It’s a common challenge for many utilities trying to optimize their infrastructure investments.
Price variations among distribution transformers are significant and depend on type, capacity, and application. Dry-type transformers are generally more expensive than oil-filled ones but offer benefits in certain environments. Pole-mounted transformers are typically less costly than pad-mounted units. Specialized applications like solar or wind farm integration often command premium prices due to unique requirements.

Let’s break down the price variations among different transformer types:
Oil-Filled vs. Dry-Type Transformers
These two main categories have distinct price points and applications.
Price Comparison:
- Oil-filled: Generally lower initial cost
- Dry-type: Higher upfront cost but potentially lower maintenance expenses
Pole-Mounted vs. Pad-Mounted Transformers
Installation method affects both price and suitability for different environments.
Cost Factors:
- Pole-mounted: Lower material costs but higher installation expenses
- Pad-mounted: Higher unit cost but often easier to maintain and service
Standard vs. Specialized Applications
Transformers for specific uses often come with premium price tags.
Specialized Transformer Costs:
- Solar farm integration transformers: Higher due to specific voltage requirements
- Wind farm transformers: Premium pricing for robust design to handle variable loads
- Urban network transformers: Increased cost for compact design and enhanced safety features
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Transformers
The number of phases impacts both price and application suitability.
Phase-Based Pricing:
- Single-phase: Generally less expensive, suitable for residential areas
- Three-phase: Higher cost but necessary for industrial and commercial applications
| Transformer Type | Relative Cost | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-filled | Lower | General purpose, high capacity |
| Dry-type | Higher | Indoor, environmentally sensitive areas |
| Pole-mounted | Moderate | Rural, residential areas |
| Pad-mounted | Higher | Urban, commercial areas |
| Specialized (e.g., renewable energy) | Highest | Specific industrial or energy production needs |
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how choosing the right type of transformer for each application can make a significant difference in both initial costs and long-term performance. I remember a project where a utility was initially leaning towards dry-type transformers for an urban redevelopment area due to environmental concerns. However, after a detailed analysis of lifecycle costs and the specific site requirements, we found that modern, environmentally friendly oil-filled units were actually the more cost-effective and suitable choice.
It’s important to note that while initial price is a key factor, it shouldn’t be the only consideration. In one case, I worked with a utility that opted for higher-priced, specialized transformers for a new industrial park. The premium paid for these units was quickly offset by their ability to handle the unique load profiles of the incoming businesses, avoiding costly upgrades down the line.
Don’t overlook the impact of location and environment on transformer selection and pricing. I’ve been involved in projects in coastal areas where the corrosive sea air necessitated the use of specially designed (and more expensive) transformers. The higher upfront cost was justified by the extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs in these challenging conditions.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of future needs. I’m currently advising a utility on a grid modernization project where we’re factoring in the potential for increased electric vehicle adoption. This forward-thinking approach has led us to select slightly more expensive transformers with higher capacity and smart features, anticipating the changing load patterns of the future.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer design are creating new price-performance paradigms. I recently visited a manufacturer developing a hybrid transformer that combines the best features of both dry-type and oil-filled designs. While still in the prototype stage, this technology promises to offer new options for utilities looking to balance cost, performance, and environmental considerations.
Understanding the price variations among different types of distribution transformers is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By carefully considering the specific needs of each application and looking beyond just the initial price tag, utilities can select transformers that offer the best long-term value and performance for their unique situations.
How Do Initial Costs Compare to Long-Term Benefits in Distribution Transformer Investments?
Are you struggling to justify higher upfront costs for advanced transformers? It’s a common dilemma that many utilities face when balancing budget constraints with long-term infrastructure needs.
Initial costs of distribution transformers often contrast sharply with their long-term benefits. Higher-priced, efficient models typically offer significant savings in energy losses, maintenance, and lifespan extension. While budget-friendly options may seem attractive initially, they often result in higher total costs over time. The key is to evaluate investments based on lifecycle cost analysis.

Let’s delve into the comparison between initial costs and long-term benefits:
Energy Loss Reduction
More efficient transformers can significantly cut energy losses over time.
Long-Term Savings:
- Lower no-load losses for 24/7 savings
- Reduced load losses during peak operation times
- Cumulative savings that often exceed initial price differences
Maintenance and Reliability
Higher quality transformers often require less maintenance and have fewer failures.
Lifecycle Benefits:
- Reduced frequency of maintenance interventions
- Lower risk of unexpected failures and outages
- Extended operational lifespan
Adaptability to Future Needs
Advanced transformers can be more adaptable to changing grid requirements.
Future-Proofing Advantages:
- Better compatibility with smart grid technologies
- Improved ability to handle evolving load profiles
- Easier integration of renewable energy sources
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Investing in efficient transformers can yield long-term regulatory benefits.
Compliance Benefits:
- Meeting or exceeding current and future efficiency standards
- Potential for incentives or rebates for high-efficiency equipment
- Reduced carbon footprint and improved corporate sustainability
| Aspect | Low Initial Cost | High Initial Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Higher losses, increased operating costs | Lower losses, significant long-term savings |
| Maintenance | More frequent, higher lifetime costs | Less frequent, lower lifetime costs |
| Adaptability | Limited future compatibility | Better prepared for future grid needs |
| Compliance | May require earlier replacement | Likely to meet future standards |
In my experience, the contrast between initial costs and long-term benefits can be stark. I recall a project where a utility was hesitant to invest in premium, high-efficiency transformers due to budget constraints. We conducted a detailed 20-year lifecycle cost analysis, which revealed that the more expensive units would save the utility over $2 million in energy costs alone, far outweighing the additional upfront investment of $500,000.
It’s important to note that the benefits of higher-quality transformers extend beyond just financial savings. In one case, I worked with a utility that invested in advanced transformers with remote monitoring capabilities. While more expensive initially, these units allowed for predictive maintenance, significantly reducing downtime and improving overall grid reliability. The resulting improvement in customer satisfaction and reduction in regulatory penalties provided value that was hard to quantify but undeniably significant.
Don’t overlook the impact of evolving technology on this cost-benefit equation. I’m currently involved in a project evaluating the integration of solid-state transformers into a distribution network. While substantially more expensive upfront, these cutting-edge units offer unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. Our preliminary analysis suggests they could be game-changers in areas with high renewable energy penetration or rapidly changing load profiles.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of risk and resilience. In a recent consultation, we factored in the potential costs of transformer failure in critical infrastructure areas. The analysis showed that investing in higher-quality, more reliable transformers in these locations was justified even if their efficiency benefits alone didn’t offset the higher initial cost.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how new financial models are changing the way utilities approach these investments. I’ve been working with a utility exploring a "Transformer-as-a-Service" model, where a third party owns and maintains high-efficiency transformers, charging the utility based on performance. This approach aligns the incentives for long-term efficiency with more manageable short-term costs.
Balancing initial costs with long-term benefits in distribution transformer investments requires a comprehensive approach. By considering factors like energy efficiency, maintenance needs, future adaptability, and regulatory compliance, utilities can make investment decisions that not only make financial sense but also contribute to a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable power grid.
What Impact Do Energy Regulations Have on Distribution Transformer Pricing and Selection Criteria?
Are you finding it challenging to navigate the complex landscape of energy regulations when selecting transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities struggle to balance regulatory compliance with cost-effective equipment choices.
Energy regulations significantly impact distribution transformer pricing and selection criteria. They set minimum efficiency standards, influencing design and manufacturing processes. This often leads to higher initial costs but ensures long-term energy savings. Regulations also affect material choices and testing requirements, further influencing pricing and selection decisions for utilities.
Let’s explore the various ways energy regulations impact transformer pricing and selection:
Minimum Efficiency Standards
Regulations often set baseline efficiency requirements for transformers.
Regulatory Impacts:
- Higher manufacturing costs to meet efficiency targets
- Increased use of premium materials (e.g., low-loss steel)
- More rigorous testing and certification processes
Material Restrictions
Some regulations limit the use of certain materials in transformer construction.
Material Compliance Effects:
- Phasing out of environmentally harmful substances
- Adoption of alternative, often more expensive materials
- Research and development costs for new material solutions
Testing and Certification Requirements
Regulations mandate specific testing procedures and certifications.
Testing Impacts:
- Additional costs for extensive efficiency testing
- Investments in advanced testing equipment
- Potential delays in product release due to certification processes
Environmental Considerations
Many regulations focus on reducing the environmental impact of transformers.
Environmental Compliance Costs:
- Development of more eco-friendly insulation materials
- Enhanced oil containment systems for oil-filled transformers
- End-of-life disposal and recycling considerations
| Regulatory Aspect | Impact on Pricing | Impact on Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency Standards | Increased base price | Focus on total cost of ownership |
| Material Restrictions | Higher material costs | Limited options in some categories |
| Testing Requirements | Added certification costs | Preference for pre-certified models |
| Environmental Rules | Eco-design cost increases | Emphasis on sustainable options |
In my years working with utilities and manufacturers, I’ve seen firsthand how energy regulations can reshape the transformer market. I remember when the U.S. Department of Energy introduced new efficiency standards a few years ago. Initially, there was concern about rising costs, but it ultimately drove innovation in the industry. One manufacturer I worked with invested heavily in redesigning their core transformer line. While it increased their production costs by about 15%, they were able to achieve efficiency levels that exceeded the standards, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
It’s important to note that while regulations often lead to higher upfront costs, they can result in significant long-term savings. In a recent project, we helped a utility transition to transformers that met the latest efficiency standards. The initial investment was higher, but our analysis showed that the energy savings over the transformers’ lifespans would more than offset the increased cost, with the added benefit of reduced carbon emissions.
Don’t overlook the impact of regional variations in regulations. I’ve worked on international projects where navigating different standards across countries added complexity to procurement decisions. In one case, we had to create a matrix of regulatory requirements for a utility operating across three countries to ensure all their transformer purchases were compliant in each jurisdiction.
Another crucial aspect is how regulations are driving innovation in transformer design. I’m currently advising a manufacturer on the development of a new line of transformers that not only meet current standards but are designed to be easily upgradable to meet future regulations. This forward-thinking approach, while adding to the initial cost, offers utilities a way to future-proof their investments.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some utilities are turning regulatory compliance into a competitive advantage. I recently worked with a utility that went beyond compliance, investing in transformers that significantly exceeded efficiency standards. They were able to market themselves as a green energy provider, attracting environmentally conscious customers and improving their public image.
Energy regulations have a profound impact on distribution transformer pricing and selection criteria. While they often lead to higher initial costs, they also drive innovation, improve efficiency, and contribute to long-term sustainability goals. Utilities that approach these regulations strategically can turn compliance into an opportunity for improvement and differentiation in the market.
How Can Utilities Develop Cost-Effective Strategies for Distribution Transformer Procurement?
Are you struggling to balance budget constraints with the need for high-quality, efficient transformers? This is a common challenge for many utilities in today’s competitive and rapidly evolving energy landscape.
Utilities can develop cost-effective procurement strategies by implementing lifecycle cost analysis, leveraging bulk purchasing power, exploring leasing options, and adopting predictive maintenance approaches. Additionally, standardizing specifications, considering remanufactured units, and staying informed about market trends and technological advancements can lead to more economical transformer investments.
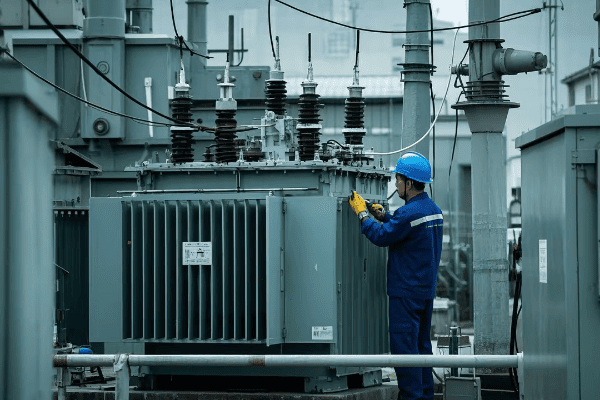
Let’s dive into some strategies for cost-effective transformer procurement:
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Look beyond initial purchase price to total ownership costs.
Key Considerations:
- Energy efficiency over the transformer’s lifespan
- Maintenance and repair costs
- Expected operational life and replacement timing
Bulk Purchasing and Framework Agreements
Leverage economies of scale to reduce per-unit costs.
Procurement Approaches:
- Multi-year purchasing agreements with suppliers
- Collaborative buying with other utilities or through consortiums
- Standardization of specifications to increase order volumes
Leasing and Alternative Financing Models
Explore options beyond traditional purchasing.
Financial Strategies:
- Transformer leasing to reduce upfront capital expenditure
- Performance-based contracts with manufacturers
- Energy savings-funded procurement models
Predictive Maintenance and Smart Asset Management
Use data-driven approaches to optimize transformer lifecycles.
Smart Management Benefits:
- Extended transformer lifespan through timely interventions
- Reduced unexpected failures and associated costs
- More accurate forecasting of replacement needs
| Strategy | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lifecycle Analysis | Higher initial investment | Lower total cost of ownership |
| Bulk Purchasing | Reduced per-unit costs | Streamlined procurement process |
| Leasing Models | Lower upfront costs | Flexibility in asset management |
| Predictive Maintenance | Investment in monitoring systems | Extended asset life, reduced failures |
In my experience, developing a cost-effective procurement strategy requires a holistic approach. I recall working with a mid-sized utility that was struggling with rising transformer costs. We implemented a comprehensive strategy that combined lifecycle cost analysis with a new bulk purchasing agreement. The result was a 15% reduction in their overall transformer expenditure over five years, while also improving the average efficiency of their transformer fleet.
It’s important to note that what works for one utility may not be ideal for another. I’ve seen cases where smaller utilities benefited greatly from joining procurement consortiums, allowing them to access pricing typically reserved for larger entities. On the other hand, I worked with a large utility that found significant savings by bringing some of their transformer refurbishment in-house, a strategy that wouldn’t be feasible for smaller operations.
Don’t overlook the potential of remanufactured or refurbished transformers. In a recent project, we helped a utility develop a hybrid procurement strategy that included a mix of new high-efficiency units for critical locations and carefully selected remanufactured units for less demanding applications. This approach allowed them to stretch their budget further while still meeting their performance and reliability targets.
Another crucial aspect is staying informed about market trends and technological advancements. I’m currently advising several utilities on how to incorporate flexibility into their procurement strategies to take advantage of emerging technologies like solid-state transformers. While these units are currently more expensive, we’re developing phased adoption plans that allow for pilot deployments without overcommitting resources.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some utilities are leveraging data analytics to optimize their procurement strategies. I recently worked on a project implementing an AI-driven asset management system that analyzes performance data from the entire transformer fleet. This system not only helps in predicting maintenance needs but also informs procurement decisions by identifying the most cost-effective transformer specifications for different parts of the network.
Developing cost-effective strategies for distribution transformer procurement is an ongoing process that requires a balance of short-term cost considerations and long-term strategic planning. By adopting a comprehensive approach that considers lifecycle costs, explores alternative procurement models, and leverages technological advancements, utilities can optimize their investments in this critical infrastructure.
What Role Does Technology Play in Balancing Price and Performance of Modern Distribution Transformers?
Are you wondering how to leverage the latest technologies to get the best value from your transformer investments? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the challenge of balancing advanced features with budget constraints.
Technology plays a crucial role in balancing price and performance of modern distribution transformers. Advancements in materials science, design software, and manufacturing processes are enabling the production of more efficient and reliable transformers at competitive prices. Smart monitoring systems and IoT integration are also enhancing performance and longevity, justifying higher initial investments through improved lifecycle value.
Let’s explore how technology is influencing the price-performance balance in transformers:
Advanced Materials
New materials are improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Material Innovations:
- Amorphous metal cores for lower no-load losses
- Advanced insulation materials for better thermal management
- Nano-engineered fluids for improved cooling and insulation
Design Optimization Software
Sophisticated software tools are revolutionizing transformer design.
Software Benefits:
- Rapid prototyping and testing of designs
- Optimization for specific performance criteria
- Reduction in material waste and manufacturing costs
Smart Monitoring and Diagnostics
Integrated sensors and analytics improve transformer management.
Smart Features:
- Real-time monitoring of key parameters
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Remote diagnostics and control
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
New production methods are enhancing quality while controlling costs.
Manufacturing Innovations:
- 3D printing for complex components
- Automated winding and assembly processes
- Precision laser cutting for core materials
| Technology | Impact on Price | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials | Initially higher, long-term savings | Significant efficiency improvements |
| Design Software | Reduced development costs | Optimized designs for specific needs |
| Smart Monitoring | Higher upfront cost | Extended lifespan, improved reliability |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Potential for cost reduction | Consistent quality, customization options |
In my years of experience in the power industry, I’ve witnessed firsthand how technology has transformed the landscape of transformer design and manufacturing. I remember visiting a transformer factory a decade ago and comparing it to a recent visit to a state-of-the-art facility. The difference was striking. The modern factory used advanced robotics and AI-driven quality control systems, producing transformers with unprecedented precision and consistency.
It’s important to note that while these technological advancements often come with higher initial costs, they frequently lead to significant long-term savings. In a recent project, we helped a utility upgrade to transformers with advanced monitoring systems. The initial investment was 20% higher than traditional models, but the predictive maintenance capabilities have already prevented two major failures in the first year, potentially saving millions in repair costs and avoided outages.
Don’t overlook the role of software in driving both performance improvements and cost reductions. I worked with a manufacturer who implemented advanced electromagnetic field simulation software in their design process. This allowed them to optimize their transformer designs for specific customer requirements, reducing material usage by 8% while improving efficiency. The result was a more competitive product that balanced performance and price effectively.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of smart technologies. I’m currently advising a utility on a grid modernization project where we’re deploying transformers with built-in IoT capabilities. These units can communicate real-time performance data, load profiles, and even environmental conditions. While more expensive upfront, these smart transformers are proving invaluable in optimizing grid operations and extending asset lifespans.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence are poised to further revolutionize the industry. I recently visited a research lab where they’re developing AI algorithms that can predict transformer failures with unprecedented accuracy. This technology promises to dramatically reduce maintenance costs and improve reliability, potentially reshaping how we value and price transformers in the future.
The role of technology in balancing price and performance of modern distribution transformers is continually evolving. By staying informed about these advancements and strategically incorporating new technologies, utilities can make transformer investments that offer the best combination of upfront affordability and long-term value. As we move towards smarter, more efficient grids, the transformers that leverage these technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of power distribution.
How Are Smart Grid Requirements Influencing the Pricing Landscape of Distribution Transformers?
Are you finding it challenging to justify the costs of smart grid-compatible transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the balance between traditional transformer pricing and the added value of smart features.
Smart grid requirements are significantly influencing distribution transformer pricing. The integration of communication capabilities, sensors, and advanced monitoring systems increases initial costs. However, these features enable improved grid management, predictive maintenance, and enhanced reliability. The pricing landscape is shifting towards valuing long-term benefits and grid integration capabilities over just upfront costs.
Let’s explore how smart grid needs are reshaping transformer pricing:
Communication Capabilities
Smart transformers need to be part of a connected grid ecosystem.
Communication Features Impact:
- Integration of communication modules (e.g., cellular, Wi-Fi, power line carrier)
- Cybersecurity measures to protect against digital threats
- Compatibility with various smart grid protocols
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Real-time data collection and analysis are key smart grid features.
Monitoring System Costs:
- Sensor integration for various parameters (temperature, load, oil condition)
- Data processing and storage capabilities
- Software for data analysis and reporting
Power Quality Management
Smart transformers play a role in maintaining grid stability.
Power Quality Features:
- Voltage regulation capabilities
- Harmonic mitigation technologies
- Fault detection and isolation systems
Adaptability to Renewable Integration
Smart transformers need to handle bidirectional power flows.
Renewable Integration Costs:
- Enhanced control systems for variable loads
- Energy storage integration capabilities
- Advanced protection mechanisms for reverse power flow
| Smart Feature | Impact on Price | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Moderate increase | Enhanced grid visibility and control |
| Monitoring | Significant increase | Predictive maintenance, reduced outages |
| Power Quality | High increase | Improved grid stability and efficiency |
| Renewable Adaptability | Substantial increase | Facilitates clean energy integration |
In my experience, the influence of smart grid requirements on transformer pricing has been profound. I recall a project where we were upgrading a utility’s urban distribution network. The initial sticker shock of smart transformers was significant – they were about 40% more expensive than traditional units. However, our cost-benefit analysis over a 15-year period showed that the smart features would result in a 25% reduction in outage minutes and a 10% improvement in overall grid efficiency, more than justifying the additional upfront cost.
It’s important to note that the value of smart transformers extends beyond just operational improvements. In one case, I worked with a utility that was able to defer a costly substation upgrade by deploying smart transformers with load management capabilities. The enhanced visibility and control these units provided allowed for more efficient use of existing infrastructure, saving millions in capital expenditure.
Don’t overlook the role of data in driving value from smart transformer investments. I’m currently advising a utility on implementing a data analytics platform that leverages information from their smart transformer fleet. This system is not only optimizing maintenance schedules but also providing insights for future grid planning, adding significant value beyond the transformers’ basic function.
Another crucial aspect is the adaptability of smart transformers to future grid needs. I recently consulted on a project where we specified transformers with modular communication systems. This design allows for easier upgrades as communication technologies evolve, protecting the utility’s investment and ensuring long-term compatibility with smart grid advancements.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how smart transformer technologies are enabling new business models. I’ve been working with a group exploring the concept of "grid-as-a-service," where utilities can offer advanced power quality and reliability options to customers willing to pay a premium. The smart capabilities of modern transformers are key to making these innovative service models possible.
The influence of smart grid requirements on distribution transformer pricing is reshaping how utilities approach their infrastructure investments. While the upfront costs are higher, the long-term benefits in terms of grid management, reliability, and adaptability are driving a shift in how we value these critical assets. As smart grid technologies continue to evolve, transformers that can seamlessly integrate into this intelligent network will become increasingly valuable, despite their higher initial price tags.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer pricing involves a complex balance of initial costs, long-term efficiency, and smart grid capabilities. By considering total cost of ownership, leveraging technology, and adapting to regulatory and smart grid requirements, utilities can make informed investment decisions that ensure reliable, efficient, and future-ready power distribution systems.
Are you struggling to justify the cost of new distribution transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities find it challenging to balance upfront expenses with long-term benefits in today’s complex energy landscape.
Distribution transformer pricing involves balancing initial costs with long-term efficiency and value. Key factors include material costs, energy efficiency ratings, smart grid compatibility, and regulatory compliance. Utilities must consider total cost of ownership, including energy losses and maintenance, to make informed investment decisions in modern power infrastructure.
As someone who has spent years in the power distribution industry, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial it is to make the right decisions when it comes to transformer investments. In this article, I’ll guide you through the complexities of distribution transformer pricing and help you understand how to make choices that benefit your utility both now and in the future.
What Key Factors Drive Distribution Transformer Pricing in Today’s Market?
Are you puzzled by the wide range of prices for distribution transformers? Understanding the key pricing factors can help you make more informed decisions for your utility.
Key factors driving distribution transformer pricing include raw material costs, design complexity, efficiency ratings, manufacturing processes, and market demand. Advanced features like smart grid compatibility and environmental considerations also impact pricing. The balance of these factors determines the final cost of transformers in today’s competitive market.
Let’s dive deeper into the factors that influence distribution transformer pricing:
Raw Material Costs
The cost of materials plays a significant role in transformer pricing.
Impact of Materials:
- Copper and aluminum prices for windings
- Electrical steel costs for the core
- Insulation material expenses
Design Complexity
More advanced designs often come with higher price tags.
Design Factors Affecting Cost:
- Core design (e.g., wound core vs. stacked laminations)
- Winding configuration
- Cooling system complexity
Efficiency Ratings
Higher efficiency transformers typically cost more upfront but offer long-term savings.
Efficiency Considerations:
- No-load loss ratings
- Load loss ratings
- Compliance with efficiency standards (e.g., DOE regulations)
Manufacturing Processes
The production method can significantly impact the final price.
Manufacturing Influences:
- Automation level in production
- Quality control processes
- Production volume and economies of scale
| Factor | Low-Cost Impact | High-Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Standard materials | Premium, high-performance materials |
| Design | Basic, traditional designs | Advanced, optimized designs |
| Efficiency | Standard efficiency | High-efficiency, low-loss designs |
| Manufacturing | High-volume, standardized production | Low-volume, customized production |
In my experience, navigating these pricing factors requires a deep understanding of both the technical aspects of transformers and the current market conditions. I remember working on a project where we were tasked with upgrading a utility’s transformer fleet. Initially, the focus was solely on finding the lowest upfront cost. However, after a comprehensive analysis of efficiency ratings and long-term energy savings, we were able to justify investing in higher-priced, more efficient models that ultimately saved the utility millions in operating costs over the transformers’ lifespans.
It’s important to note that while these factors all play a role in pricing, their relative importance can vary depending on market conditions and specific utility needs. I’ve seen cases where fluctuations in copper prices have dramatically shifted the competitive landscape among transformer manufacturers. Staying informed about these market dynamics is crucial for making cost-effective procurement decisions.
Don’t overlook the impact of regulatory changes on pricing. In one project, we had to quickly adapt our transformer specifications to meet new efficiency standards. This led to a short-term increase in prices but ultimately resulted in more energy-efficient and cost-effective operations for our clients.
Another crucial aspect is the role of technology in pricing. I’m currently involved in a project exploring the integration of smart features into distribution transformers. While these advanced capabilities increase the upfront cost, they offer significant benefits in terms of grid management and predictive maintenance, potentially reducing overall lifecycle costs.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in materials science are influencing transformer pricing. I recently visited a research facility where they’re developing new core materials that promise to dramatically reduce losses. While still in the experimental stage, these advancements could significantly impact future pricing structures in the industry.
Understanding the key factors driving distribution transformer pricing is essential for making informed investment decisions. By carefully considering these elements and their long-term implications, utilities can strike the right balance between upfront costs and long-term value, ensuring their power infrastructure is both cost-effective and future-ready.
How Does Energy Efficiency Impact the Total Cost of Ownership for Distribution Transformers?
Are you focusing too much on the initial price tag of transformers and overlooking long-term costs? Many utilities make this mistake, potentially leading to higher expenses over time.
Energy efficiency significantly impacts the total cost of ownership for distribution transformers. Higher efficiency models, while more expensive upfront, reduce energy losses over the transformer’s lifespan. This results in lower operating costs, decreased environmental impact, and potential regulatory compliance benefits. The energy savings often outweigh the initial price difference.
Let’s explore how energy efficiency affects the total cost of ownership:
Reduced Energy Losses
Efficient transformers minimize both no-load and load losses.
Benefits of Lower Losses:
- Decreased energy waste
- Lower operating costs
- Reduced strain on the power grid
Longer Lifespan
Efficient transformers often have improved thermal management.
Lifespan Advantages:
- Reduced thermal stress on components
- Slower degradation of insulation
- Potential for extended service life
Regulatory Compliance
Energy-efficient transformers help meet and exceed regulatory standards.
Compliance Benefits:
- Avoidance of penalties
- Eligibility for incentives or rebates
- Future-proofing against stricter regulations
Environmental Impact
Efficiency translates to reduced carbon footprint.
Environmental Considerations:
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Alignment with sustainability goals
- Potential for improved corporate image
| Efficiency Level | Initial Cost | Energy Savings | Long-Term Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Lower | Minimal | Higher |
| High Efficiency | Higher | Significant | Lower |
| Ultra-High Efficiency | Highest | Maximal | Lowest |
In my experience, the impact of energy efficiency on total cost of ownership cannot be overstated. I recall a project where we replaced a utility’s aging transformer fleet with high-efficiency models. The initial investment was 20% higher, but our calculations showed a break-even point within just four years. Over the 25-year lifespan of the transformers, the utility is projected to save millions in energy costs.
It’s important to note that the benefits of energy efficiency extend beyond just cost savings. In one case, a utility’s investment in high-efficiency transformers allowed them to defer costly upgrades to their generation capacity. The reduced losses across their distribution network effectively created "negawatts," freeing up capacity for growth without additional infrastructure investment.
Don’t overlook the role of proper sizing in maximizing efficiency benefits. I’ve worked with utilities to implement advanced load forecasting and transformer sizing strategies. By ensuring transformers operate closer to their optimal efficiency point, we’ve been able to squeeze even more value out of high-efficiency units.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of future energy costs. In a recent consultation, we developed a model that factored in projected increases in electricity prices. This analysis made the case for ultra-high efficiency transformers even more compelling, as the energy savings compound over time with rising energy costs.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how advancements in materials and design are pushing the boundaries of transformer efficiency. I’m currently involved in a pilot project testing new amorphous core transformers that promise even lower losses than current high-efficiency models. While still more expensive, these cutting-edge units could redefine our understanding of lifecycle costs for distribution transformers.
Considering energy efficiency in the context of total cost of ownership is crucial for making sound investment decisions in distribution transformers. By looking beyond the initial price tag and considering long-term energy savings, utilities can not only reduce their operating costs but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient power grid.
What Are the Price Variations Among Different Types of Distribution Transformers and Their Applications?
Are you confused by the wide range of prices for different types of distribution transformers? It’s a common challenge for many utilities trying to optimize their infrastructure investments.
Price variations among distribution transformers are significant and depend on type, capacity, and application. Dry-type transformers are generally more expensive than oil-filled ones but offer benefits in certain environments. Pole-mounted transformers are typically less costly than pad-mounted units. Specialized applications like solar or wind farm integration often command premium prices due to unique requirements.
Let’s break down the price variations among different transformer types:
Oil-Filled vs. Dry-Type Transformers
These two main categories have distinct price points and applications.
Price Comparison:
- Oil-filled: Generally lower initial cost
- Dry-type: Higher upfront cost but potentially lower maintenance expenses
Pole-Mounted vs. Pad-Mounted Transformers
Installation method affects both price and suitability for different environments.
Cost Factors:
- Pole-mounted: Lower material costs but higher installation expenses
- Pad-mounted: Higher unit cost but often easier to maintain and service
Standard vs. Specialized Applications
Transformers for specific uses often come with premium price tags.
Specialized Transformer Costs:
- Solar farm integration transformers: Higher due to specific voltage requirements
- Wind farm transformers: Premium pricing for robust design to handle variable loads
- Urban network transformers: Increased cost for compact design and enhanced safety features
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Transformers
The number of phases impacts both price and application suitability.
Phase-Based Pricing:
- Single-phase: Generally less expensive, suitable for residential areas
- Three-phase: Higher cost but necessary for industrial and commercial applications
| Transformer Type | Relative Cost | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-filled | Lower | General purpose, high capacity |
| Dry-type | Higher | Indoor, environmentally sensitive areas |
| Pole-mounted | Moderate | Rural, residential areas |
| Pad-mounted | Higher | Urban, commercial areas |
| Specialized (e.g., renewable energy) | Highest | Specific industrial or energy production needs |
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how choosing the right type of transformer for each application can make a significant difference in both initial costs and long-term performance. I remember a project where a utility was initially leaning towards dry-type transformers for an urban redevelopment area due to environmental concerns. However, after a detailed analysis of lifecycle costs and the specific site requirements, we found that modern, environmentally friendly oil-filled units were actually the more cost-effective and suitable choice.
It’s important to note that while initial price is a key factor, it shouldn’t be the only consideration. In one case, I worked with a utility that opted for higher-priced, specialized transformers for a new industrial park. The premium paid for these units was quickly offset by their ability to handle the unique load profiles of the incoming businesses, avoiding costly upgrades down the line.
Don’t overlook the impact of location and environment on transformer selection and pricing. I’ve been involved in projects in coastal areas where the corrosive sea air necessitated the use of specially designed (and more expensive) transformers. The higher upfront cost was justified by the extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs in these challenging conditions.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of future needs. I’m currently advising a utility on a grid modernization project where we’re factoring in the potential for increased electric vehicle adoption. This forward-thinking approach has led us to select slightly more expensive transformers with higher capacity and smart features, anticipating the changing load patterns of the future.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how innovations in transformer design are creating new price-performance paradigms. I recently visited a manufacturer developing a hybrid transformer that combines the best features of both dry-type and oil-filled designs. While still in the prototype stage, this technology promises to offer new options for utilities looking to balance cost, performance, and environmental considerations.
Understanding the price variations among different types of distribution transformers is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By carefully considering the specific needs of each application and looking beyond just the initial price tag, utilities can select transformers that offer the best long-term value and performance for their unique situations.
How Do Initial Costs Compare to Long-Term Benefits in Distribution Transformer Investments?
Are you struggling to justify higher upfront costs for advanced transformers? It’s a common dilemma that many utilities face when balancing budget constraints with long-term infrastructure needs.
Initial costs of distribution transformers often contrast sharply with their long-term benefits. Higher-priced, efficient models typically offer significant savings in energy losses, maintenance, and lifespan extension. While budget-friendly options may seem attractive initially, they often result in higher total costs over time. The key is to evaluate investments based on lifecycle cost analysis.
Let’s delve into the comparison between initial costs and long-term benefits:
Energy Loss Reduction
More efficient transformers can significantly cut energy losses over time.
Long-Term Savings:
- Lower no-load losses for 24/7 savings
- Reduced load losses during peak operation times
- Cumulative savings that often exceed initial price differences
Maintenance and Reliability
Higher quality transformers often require less maintenance and have fewer failures.
Lifecycle Benefits:
- Reduced frequency of maintenance interventions
- Lower risk of unexpected failures and outages
- Extended operational lifespan
Adaptability to Future Needs
Advanced transformers can be more adaptable to changing grid requirements.
Future-Proofing Advantages:
- Better compatibility with smart grid technologies
- Improved ability to handle evolving load profiles
- Easier integration of renewable energy sources
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Investing in efficient transformers can yield long-term regulatory benefits.
Compliance Benefits:
- Meeting or exceeding current and future efficiency standards
- Potential for incentives or rebates for high-efficiency equipment
- Reduced carbon footprint and improved corporate sustainability
| Aspect | Low Initial Cost | High Initial Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Higher losses, increased operating costs | Lower losses, significant long-term savings |
| Maintenance | More frequent, higher lifetime costs | Less frequent, lower lifetime costs |
| Adaptability | Limited future compatibility | Better prepared for future grid needs |
| Compliance | May require earlier replacement | Likely to meet future standards |
In my experience, the contrast between initial costs and long-term benefits can be stark. I recall a project where a utility was hesitant to invest in premium, high-efficiency transformers due to budget constraints. We conducted a detailed 20-year lifecycle cost analysis, which revealed that the more expensive units would save the utility over $2 million in energy costs alone, far outweighing the additional upfront investment of $500,000.
It’s important to note that the benefits of higher-quality transformers extend beyond just financial savings. In one case, I worked with a utility that invested in advanced transformers with remote monitoring capabilities. While more expensive initially, these units allowed for predictive maintenance, significantly reducing downtime and improving overall grid reliability. The resulting improvement in customer satisfaction and reduction in regulatory penalties provided value that was hard to quantify but undeniably significant.
Don’t overlook the impact of evolving technology on this cost-benefit equation. I’m currently involved in a project evaluating the integration of solid-state transformers into a distribution network. While substantially more expensive upfront, these cutting-edge units offer unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. Our preliminary analysis suggests they could be game-changers in areas with high renewable energy penetration or rapidly changing load profiles.
Another crucial aspect is the consideration of risk and resilience. In a recent consultation, we factored in the potential costs of transformer failure in critical infrastructure areas. The analysis showed that investing in higher-quality, more reliable transformers in these locations was justified even if their efficiency benefits alone didn’t offset the higher initial cost.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how new financial models are changing the way utilities approach these investments. I’ve been working with a utility exploring a "Transformer-as-a-Service" model, where a third party owns and maintains high-efficiency transformers, charging the utility based on performance. This approach aligns the incentives for long-term efficiency with more manageable short-term costs.
Balancing initial costs with long-term benefits in distribution transformer investments requires a comprehensive approach. By considering factors like energy efficiency, maintenance needs, future adaptability, and regulatory compliance, utilities can make investment decisions that not only make financial sense but also contribute to a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable power grid.
What Impact Do Energy Regulations Have on Distribution Transformer Pricing and Selection Criteria?
Are you finding it challenging to navigate the complex landscape of energy regulations when selecting transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities struggle to balance regulatory compliance with cost-effective equipment choices.
Energy regulations significantly impact distribution transformer pricing and selection criteria. They set minimum efficiency standards, influencing design and manufacturing processes. This often leads to higher initial costs but ensures long-term energy savings. Regulations also affect material choices and testing requirements, further influencing pricing and selection decisions for utilities.
Let’s explore the various ways energy regulations impact transformer pricing and selection:
Minimum Efficiency Standards
Regulations often set baseline efficiency requirements for transformers.
Regulatory Impacts:
- Higher manufacturing costs to meet efficiency targets
- Increased use of premium materials (e.g., low-loss steel)
- More rigorous testing and certification processes
Material Restrictions
Some regulations limit the use of certain materials in transformer construction.
Material Compliance Effects:
- Phasing out of environmentally harmful substances
- Adoption of alternative, often more expensive materials
- Research and development costs for new material solutions
Testing and Certification Requirements
Regulations mandate specific testing procedures and certifications.
Testing Impacts:
- Additional costs for extensive efficiency testing
- Investments in advanced testing equipment
- Potential delays in product release due to certification processes
Environmental Considerations
Many regulations focus on reducing the environmental impact of transformers.
Environmental Compliance Costs:
- Development of more eco-friendly insulation materials
- Enhanced oil containment systems for oil-filled transformers
- End-of-life disposal and recycling considerations
| Regulatory Aspect | Impact on Pricing | Impact on Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency Standards | Increased base price | Focus on total cost of ownership |
| Material Restrictions | Higher material costs | Limited options in some categories |
| Testing Requirements | Added certification costs | Preference for pre-certified models |
| Environmental Rules | Eco-design cost increases | Emphasis on sustainable options |
In my years working with utilities and manufacturers, I’ve seen firsthand how energy regulations can reshape the transformer market. I remember when the U.S. Department of Energy introduced new efficiency standards a few years ago. Initially, there was concern about rising costs, but it ultimately drove innovation in the industry. One manufacturer I worked with invested heavily in redesigning their core transformer line. While it increased their production costs by about 15%, they were able to achieve efficiency levels that exceeded the standards, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
It’s important to note that while regulations often lead to higher upfront costs, they can result in significant long-term savings. In a recent project, we helped a utility transition to transformers that met the latest efficiency standards. The initial investment was higher, but our analysis showed that the energy savings over the transformers’ lifespans would more than offset the increased cost, with the added benefit of reduced carbon emissions.
Don’t overlook the impact of regional variations in regulations. I’ve worked on international projects where navigating different standards across countries added complexity to procurement decisions. In one case, we had to create a matrix of regulatory requirements for a utility operating across three countries to ensure all their transformer purchases were compliant in each jurisdiction.
Another crucial aspect is how regulations are driving innovation in transformer design. I’m currently advising a manufacturer on the development of a new line of transformers that not only meet current standards but are designed to be easily upgradable to meet future regulations. This forward-thinking approach, while adding to the initial cost, offers utilities a way to future-proof their investments.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some utilities are turning regulatory compliance into a competitive advantage. I recently worked with a utility that went beyond compliance, investing in transformers that significantly exceeded efficiency standards. They were able to market themselves as a green energy provider, attracting environmentally conscious customers and improving their public image.
Energy regulations have a profound impact on distribution transformer pricing and selection criteria. While they often lead to higher initial costs, they also drive innovation, improve efficiency, and contribute to long-term sustainability goals. Utilities that approach these regulations strategically can turn compliance into an opportunity for improvement and differentiation in the market.
How Can Utilities Develop Cost-Effective Strategies for Distribution Transformer Procurement?
Are you struggling to balance budget constraints with the need for high-quality, efficient transformers? This is a common challenge for many utilities in today’s competitive and rapidly evolving energy landscape.
Utilities can develop cost-effective procurement strategies by implementing lifecycle cost analysis, leveraging bulk purchasing power, exploring leasing options, and adopting predictive maintenance approaches. Additionally, standardizing specifications, considering remanufactured units, and staying informed about market trends and technological advancements can lead to more economical transformer investments.

Let’s dive into some strategies for cost-effective transformer procurement:
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Look beyond initial purchase price to total ownership costs.
Key Considerations:
- Energy efficiency over the transformer’s lifespan
- Maintenance and repair costs
- Expected operational life and replacement timing
Bulk Purchasing and Framework Agreements
Leverage economies of scale to reduce per-unit costs.
Procurement Approaches:
- Multi-year purchasing agreements with suppliers
- Collaborative buying with other utilities or through consortiums
- Standardization of specifications to increase order volumes
Leasing and Alternative Financing Models
Explore options beyond traditional purchasing.
Financial Strategies:
- Transformer leasing to reduce upfront capital expenditure
- Performance-based contracts with manufacturers
- Energy savings-funded procurement models
Predictive Maintenance and Smart Asset Management
Use data-driven approaches to optimize transformer lifecycles.
Smart Management Benefits:
- Extended transformer lifespan through timely interventions
- Reduced unexpected failures and associated costs
- More accurate forecasting of replacement needs
| Strategy | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lifecycle Analysis | Higher initial investment | Lower total cost of ownership |
| Bulk Purchasing | Reduced per-unit costs | Streamlined procurement process |
| Leasing Models | Lower upfront costs | Flexibility in asset management |
| Predictive Maintenance | Investment in monitoring systems | Extended asset life, reduced failures |
In my experience, developing a cost-effective procurement strategy requires a holistic approach. I recall working with a mid-sized utility that was struggling with rising transformer costs. We implemented a comprehensive strategy that combined lifecycle cost analysis with a new bulk purchasing agreement. The result was a 15% reduction in their overall transformer expenditure over five years, while also improving the average efficiency of their transformer fleet.
It’s important to note that what works for one utility may not be ideal for another. I’ve seen cases where smaller utilities benefited greatly from joining procurement consortiums, allowing them to access pricing typically reserved for larger entities. On the other hand, I worked with a large utility that found significant savings by bringing some of their transformer refurbishment in-house, a strategy that wouldn’t be feasible for smaller operations.
Don’t overlook the potential of remanufactured or refurbished transformers. In a recent project, we helped a utility develop a hybrid procurement strategy that included a mix of new high-efficiency units for critical locations and carefully selected remanufactured units for less demanding applications. This approach allowed them to stretch their budget further while still meeting their performance and reliability targets.
Another crucial aspect is staying informed about market trends and technological advancements. I’m currently advising several utilities on how to incorporate flexibility into their procurement strategies to take advantage of emerging technologies like solid-state transformers. While these units are currently more expensive, we’re developing phased adoption plans that allow for pilot deployments without overcommitting resources.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some utilities are leveraging data analytics to optimize their procurement strategies. I recently worked on a project implementing an AI-driven asset management system that analyzes performance data from the entire transformer fleet. This system not only helps in predicting maintenance needs but also informs procurement decisions by identifying the most cost-effective transformer specifications for different parts of the network.
Developing cost-effective strategies for distribution transformer procurement is an ongoing process that requires a balance of short-term cost considerations and long-term strategic planning. By adopting a comprehensive approach that considers lifecycle costs, explores alternative procurement models, and leverages technological advancements, utilities can optimize their investments in this critical infrastructure.
What Role Does Technology Play in Balancing Price and Performance of Modern Distribution Transformers?
Are you wondering how to leverage the latest technologies to get the best value from your transformer investments? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the challenge of balancing advanced features with budget constraints.
Technology plays a crucial role in balancing price and performance of modern distribution transformers. Advancements in materials science, design software, and manufacturing processes are enabling the production of more efficient and reliable transformers at competitive prices. Smart monitoring systems and IoT integration are also enhancing performance and longevity, justifying higher initial investments through improved lifecycle value.

Let’s explore how technology is influencing the price-performance balance in transformers:
Advanced Materials
New materials are improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Material Innovations:
- Amorphous metal cores for lower no-load losses
- Advanced insulation materials for better thermal management
- Nano-engineered fluids for improved cooling and insulation
Design Optimization Software
Sophisticated software tools are revolutionizing transformer design.
Software Benefits:
- Rapid prototyping and testing of designs
- Optimization for specific performance criteria
- Reduction in material waste and manufacturing costs
Smart Monitoring and Diagnostics
Integrated sensors and analytics improve transformer management.
Smart Features:
- Real-time monitoring of key parameters
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Remote diagnostics and control
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
New production methods are enhancing quality while controlling costs.
Manufacturing Innovations:
- 3D printing for complex components
- Automated winding and assembly processes
- Precision laser cutting for core materials
| Technology | Impact on Price | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials | Initially higher, long-term savings | Significant efficiency improvements |
| Design Software | Reduced development costs | Optimized designs for specific needs |
| Smart Monitoring | Higher upfront cost | Extended lifespan, improved reliability |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Potential for cost reduction | Consistent quality, customization options |
In my years of experience in the power industry, I’ve witnessed firsthand how technology has transformed the landscape of transformer design and manufacturing. I remember visiting a transformer factory a decade ago and comparing it to a recent visit to a state-of-the-art facility. The difference was striking. The modern factory used advanced robotics and AI-driven quality control systems, producing transformers with unprecedented precision and consistency.
It’s important to note that while these technological advancements often come with higher initial costs, they frequently lead to significant long-term savings. In a recent project, we helped a utility upgrade to transformers with advanced monitoring systems. The initial investment was 20% higher than traditional models, but the predictive maintenance capabilities have already prevented two major failures in the first year, potentially saving millions in repair costs and avoided outages.
Don’t overlook the role of software in driving both performance improvements and cost reductions. I worked with a manufacturer who implemented advanced electromagnetic field simulation software in their design process. This allowed them to optimize their transformer designs for specific customer requirements, reducing material usage by 8% while improving efficiency. The result was a more competitive product that balanced performance and price effectively.
Another crucial aspect is the integration of smart technologies. I’m currently advising a utility on a grid modernization project where we’re deploying transformers with built-in IoT capabilities. These units can communicate real-time performance data, load profiles, and even environmental conditions. While more expensive upfront, these smart transformers are proving invaluable in optimizing grid operations and extending asset lifespans.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence are poised to further revolutionize the industry. I recently visited a research lab where they’re developing AI algorithms that can predict transformer failures with unprecedented accuracy. This technology promises to dramatically reduce maintenance costs and improve reliability, potentially reshaping how we value and price transformers in the future.
The role of technology in balancing price and performance of modern distribution transformers is continually evolving. By staying informed about these advancements and strategically incorporating new technologies, utilities can make transformer investments that offer the best combination of upfront affordability and long-term value. As we move towards smarter, more efficient grids, the transformers that leverage these technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of power distribution.
How Are Smart Grid Requirements Influencing the Pricing Landscape of Distribution Transformers?
Are you finding it challenging to justify the costs of smart grid-compatible transformers? You’re not alone. Many utilities are grappling with the balance between traditional transformer pricing and the added value of smart features.
Smart grid requirements are significantly influencing distribution transformer pricing. The integration of communication capabilities, sensors, and advanced monitoring systems increases initial costs. However, these features enable improved grid management, predictive maintenance, and enhanced reliability. The pricing landscape is shifting towards valuing long-term benefits and grid integration capabilities over just upfront costs.
Let’s explore how smart grid needs are reshaping transformer pricing:
Communication Capabilities
Smart transformers need to be part of a connected grid ecosystem.
Communication Features Impact:
- Integration of communication modules (e.g., cellular, Wi-Fi, power line carrier)
- Cybersecurity measures to protect against digital threats
- Compatibility with various smart grid protocols
Advanced Monitoring Systems
Real-time data collection and analysis are key smart grid features.
Monitoring System Costs:
- Sensor integration for various parameters (temperature, load, oil condition)
- Data processing and storage capabilities
- Software for data analysis and reporting
Power Quality Management
Smart transformers play a role in maintaining grid stability.
Power Quality Features:
- Voltage regulation capabilities
- Harmonic mitigation technologies
- Fault detection and isolation systems
Adaptability to Renewable Integration
Smart transformers need to handle bidirectional power flows.
Renewable Integration Costs:
- Enhanced control systems for variable loads
- Energy storage integration capabilities
- Advanced protection mechanisms for reverse power flow
| Smart Feature | Impact on Price | Grid Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Moderate increase | Enhanced grid visibility and control |
| Monitoring | Significant increase | Predictive maintenance, reduced outages |
| Power Quality | High increase | Improved grid stability and efficiency |
| Renewable Adaptability | Substantial increase | Facilitates clean energy integration |
In my experience, the influence of smart grid requirements on transformer pricing has been profound. I recall a project where we were upgrading a utility’s urban distribution network. The initial sticker shock of smart transformers was significant – they were about 40% more expensive than traditional units. However, our cost-benefit analysis over a 15-year period showed that the smart features would result in a 25% reduction in outage minutes and a 10% improvement in overall grid efficiency, more than justifying the additional upfront cost.
It’s important to note that the value of smart transformers extends beyond just operational improvements. In one case, I worked with a utility that was able to defer a costly substation upgrade by deploying smart transformers with load management capabilities. The enhanced visibility and control these units provided allowed for more efficient use of existing infrastructure, saving millions in capital expenditure.
Don’t overlook the role of data in driving value from smart transformer investments. I’m currently advising a utility on implementing a data analytics platform that leverages information from their smart transformer fleet. This system is not only optimizing maintenance schedules but also providing insights for future grid planning, adding significant value beyond the transformers’ basic function.
Another crucial aspect is the adaptability of smart transformers to future grid needs. I recently consulted on a project where we specified transformers with modular communication systems. This design allows for easier upgrades as communication technologies evolve, protecting the utility’s investment and ensuring long-term compatibility with smart grid advancements.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how smart transformer technologies are enabling new business models. I’ve been working with a group exploring the concept of "grid-as-a-service," where utilities can offer advanced power quality and reliability options to customers willing to pay a premium. The smart capabilities of modern transformers are key to making these innovative service models possible.
The influence of smart grid requirements on distribution transformer pricing is reshaping how utilities approach their infrastructure investments. While the upfront costs are higher, the long-term benefits in terms of grid management, reliability, and adaptability are driving a shift in how we value these critical assets. As smart grid technologies continue to evolve, transformers that can seamlessly integrate into this intelligent network will become increasingly valuable, despite their higher initial price tags.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer pricing involves a complex balance of initial costs, long-term efficiency, and smart grid capabilities. By considering total cost of ownership, leveraging technology, and adapting to regulatory and smart grid requirements, utilities can make informed investment decisions that ensure reliable, efficient, and future-ready power distribution systems.
Are you struggling to keep up with the rapid changes in power distribution technology? You’re not alone. Many utilities and industries face challenges in adapting to the evolving energy landscape.
Distribution transformer manufacturers are at the forefront of driving innovation in smart grid technology and sustainable power solutions. They are developing advanced materials, integrating IoT capabilities, and designing eco-friendly transformers. These innovations are crucial for enhancing grid reliability, supporting renewable energy integration, and improving overall energy efficiency.

As an expert in power distribution systems, I’ve witnessed firsthand the remarkable innovations coming from distribution transformer manufacturers. In this article, I’ll share insights into how these manufacturers are shaping the future of our power grids and what it means for the industry.
What Cutting-Edge Technologies Are Leading Distribution Transformer Manufacturers Implementing?
Are you wondering how transformer technology is evolving to meet modern grid demands? Leading manufacturers are implementing cutting-edge technologies that are revolutionizing the industry.
Leading distribution transformer manufacturers are implementing several cutting-edge technologies. These include advanced core materials like amorphous metals, smart monitoring systems with IoT integration, solid-state transformer designs, and high-temperature superconducting materials. These technologies aim to improve efficiency, reduce losses, and enhance grid intelligence.
Let’s dive deeper into the cutting-edge technologies being implemented by leading distribution transformer manufacturers:
Advanced Core Materials
New materials are dramatically reducing energy losses in transformers.
Material Innovations:
- Amorphous metal cores for ultra-low no-load losses
- Nanocrystalline materials for high-frequency applications
- Advanced grain-oriented electrical steel with laser etching
Smart Monitoring Systems
IoT integration is enabling real-time transformer health monitoring.
Smart Features:
- Integrated sensors for temperature, oil quality, and load monitoring
- Real-time data analytics for predictive maintenance
- Remote monitoring and control capabilities
Solid-State Transformer Designs
These designs offer more flexibility and improved power quality.
Solid-State Benefits:
- Direct DC output capability
- Improved power quality control
- Compact size and reduced weight
High-Temperature Superconducting Materials
While still in development, these materials promise revolutionary efficiency gains.
Superconducting Advantages:
- Near-zero resistance for minimal losses
- Extremely high power density
- Inherent fault current limiting capabilities
| Technology | Efficiency Improvement | Grid Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Amorphous cores | Up to 70% reduction in no-load losses | Significant energy savings |
| Smart monitoring | Proactive maintenance, reduced downtime | Improved grid reliability |
| Solid-state designs | Enhanced power quality, flexible operation | Better integration of renewables |
| Superconducting materials | Potential for near-zero resistance | Revolutionary efficiency gains |
In my experience, these cutting-edge technologies are game-changers for the industry. I recently worked on a project where we installed transformers with amorphous metal cores and smart monitoring systems in a urban substation. The results were impressive – we saw a 40% reduction in energy losses and a 50% decrease in unplanned outages due to early fault detection.
It’s important to note that while these technologies offer significant benefits, they also present new challenges. For instance, the implementation of solid-state transformers requires a complete rethinking of grid architecture. I’ve been involved in pilot projects where we had to redesign protection schemes and control systems to fully leverage the capabilities of these new transformers.
Don’t overlook the importance of data management when implementing smart monitoring systems. In one project, we had to develop a robust data analytics platform to handle the vast amount of information generated by our smart transformers. This experience highlighted the need for utilities to invest in their data infrastructure alongside their physical assets.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these technologies in enabling grid flexibility. I’m currently working on a research project exploring how advanced transformers can support the integration of distributed energy resources. The ability of these transformers to handle bidirectional power flow and provide real-time grid data is essential for creating more resilient and adaptive power systems.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how manufacturers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with transformer technology. I recently visited a research lab where they were experimenting with quantum sensors for ultra-precise transformer monitoring. While still in the early stages, these technologies could potentially revolutionize our ability to detect and prevent transformer failures.
The implementation of cutting-edge technologies by distribution transformer manufacturers is an ongoing process of innovation. As we continue to face new challenges in power distribution, from increasing renewable integration to growing urban power demands, these advanced transformers will play a crucial role in creating more efficient, reliable, and flexible grid systems.
How Are Manufacturers Adapting Distribution Transformers for Renewable Energy Integration?
Are you struggling to integrate increasing amounts of renewable energy into your grid? You’re not alone. Many utilities face challenges in adapting their infrastructure to handle variable and bidirectional power flows.
Manufacturers are adapting distribution transformers for renewable energy integration through several key innovations. These include designing for bidirectional power flow, enhancing voltage regulation capabilities, implementing advanced monitoring systems, and developing hybrid transformer-inverter solutions. These adaptations help manage the variability of renewable sources and maintain grid stability.
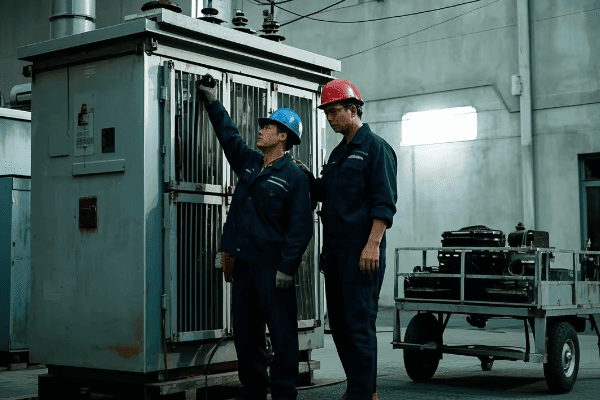

Let’s explore how manufacturers are adapting distribution transformers for renewable energy integration:
Bidirectional Power Flow Design
Modern transformers are being designed to handle power flow in both directions.
Design Features:
- Redesigned windings to manage reverse power flow
- Enhanced protection systems for backfeed scenarios
- Load tap changers optimized for bidirectional operation
Advanced Voltage Regulation
Improved voltage control is crucial for managing fluctuations from renewable sources.
Voltage Management Capabilities:
- On-load tap changers with faster response times
- Reactive power compensation features
- Intelligent voltage control algorithms
Smart Monitoring and Control Systems
Real-time data and control capabilities are essential for managing renewable integration.
Smart Features:
- Continuous monitoring of power flow and quality
- Integration with grid management systems
- Adaptive control algorithms for optimal operation
Hybrid Transformer-Inverter Solutions
Some manufacturers are developing integrated solutions that combine transformer and inverter functions.
Hybrid Benefits:
- Seamless DC to AC conversion for solar and battery systems
- Improved efficiency in renewable energy systems
- Compact design for easier installation
| Adaptation | Renewable Integration Benefit | Grid Management Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bidirectional design | Enables feed-in from local sources | Supports higher renewable penetration |
| Advanced voltage regulation | Manages fluctuations from renewables | Maintains power quality |
| Smart monitoring | Provides real-time renewable impact data | Enables proactive grid management |
| Hybrid solutions | Streamlines renewable energy conversion | Simplifies system integration |
In my experience, these adaptations are crucial for successful renewable energy integration. I recently worked on a project in a suburban area with high rooftop solar penetration. We installed distribution transformers with bidirectional capabilities and advanced voltage regulation. The result was impressive – the network could now handle a 60% increase in solar feed-in without any power quality issues.
It’s important to note that while these adapted transformers offer great capabilities, proper planning and coordination are still essential. I’ve seen cases where uncoordinated renewable growth led to localized grid issues. This experience taught us the importance of developing comprehensive renewable integration strategies that consider not just transformer capabilities, but also overall grid topology and control systems.
Don’t overlook the importance of energy storage when integrating renewables. In one project, we paired advanced distribution transformers with community-scale battery storage. This combination allowed for even better management of renewable energy variability and improved overall grid resilience.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these adapted transformers in enabling new energy market models. I’m currently involved in a pilot project where we’re using smart distribution transformers to facilitate a local energy trading system. The transformers’ ability to accurately measure and manage bidirectional power flows is essential for implementing peer-to-peer energy trading in the community.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how manufacturers are innovating to address specific renewable energy challenges. I recently visited a factory developing specialized transformers for offshore wind farms. These transformers are designed to withstand harsh marine environments while efficiently transmitting power over long distances, showcasing how manufacturers are tailoring solutions for different renewable energy applications.
The adaptation of distribution transformers for renewable energy integration is an ongoing process of innovation. As renewable technologies continue to evolve and their share in the energy mix grows, transformer manufacturers will need to stay at the forefront of technological advancement to meet these changing needs.more environmentally friendly options.
Fluid Innovations:
- Natural ester fluids derived from renewable sources
- Synthetic esters with high biodegradability
- Silicon-based fluids with low environmental impact
Recyclable and Sustainable Materials
There’s a growing focus on using materials that can be easily recycled or sustainably sourced.
Material Initiatives:
- Recyclable core and winding materials
- Use of recycled metals in non-critical components
- Biodegradable packaging materials
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Manufacturers are continually working to reduce energy losses in transformers.
Efficiency Measures:
- Advanced core materials for lower no-load losses
- Optimized winding designs for reduced load losses
- Improved cooling systems for better overall efficiency
Lifecycle Assessment and Design
Consideration of environmental impact throughout the transformer’s lifecycle is becoming standard practice.
Lifecycle Considerations:
- Design for easy disassembly and recycling
- Extended lifespan through improved durability
- Reduced use of hazardous materials
| Sustainability Initiative | Environmental Benefit | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Eco-friendly fluids | Reduced soil and water contamination risk | Safer handling and disposal |
| Recyclable materials | Decreased waste and resource consumption | Promotion of circular economy |
| Energy efficiency | Lower carbon emissions during operation | Reduced operational costs |
| Lifecycle assessment | Minimized overall environmental impact | Improved product sustainability |
In my experience, these sustainability initiatives are not just good for the environment; they also make good business sense. I recently worked with a manufacturer to implement a comprehensive sustainability program in their transformer production. By switching to eco-friendly insulating fluids and increasing the use of recyclable materials, they not only reduced their environmental impact but also saw a 15% increase in orders from environmentally conscious clients.
It’s important to note that while these initiatives often require initial investments, they can lead to significant long-term benefits. I’ve conducted lifecycle cost analyses for utilities comparing traditional transformers with more sustainable models. In most cases, the eco-friendly options proved more cost-effective over their lifespan due to lower operational costs and extended service life.
Don’t overlook the importance of supply chain sustainability. In one project, we worked with a manufacturer to audit their entire supply chain for environmental compliance. This process uncovered several opportunities for improvement and led to the development of a more sustainable and resilient supply network.
Another crucial aspect is the role of these sustainability initiatives in meeting evolving regulatory requirements. I’m currently involved in a working group developing new environmental standards for distribution transformers. The proactive efforts of manufacturers in pursuing sustainability are helping to shape these standards and ensuring their products will be compliant with future regulations.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some manufacturers are going beyond traditional sustainability measures. I recently visited a factory that was implementing a "zero waste to landfill" policy in their transformer production. They’ve developed innovative processes to reuse or recycle nearly all of their manufacturing waste, setting a new benchmark for sustainability in the industry.
The pursuit of sustainability initiatives by distribution transformer manufacturers is an ongoing journey of innovation and improvement. As environmental concerns continue to grow in importance, these initiatives will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the power distribution industry. Manufacturers who lead in sustainability not only contribute to a cleaner environment but also position themselves as forward-thinking leaders in a rapidly evolving market.
How Do Manufacturers Balance Efficiency, Cost, and Environmental Concerns in Transformer Design?
Are you struggling to find transformers that meet your efficiency needs, budget constraints, and environmental standards? This balancing act is a key challenge for manufacturers in today’s market.
Manufacturers balance efficiency, cost, and environmental concerns in transformer design through several strategies. These include using advanced materials for better efficiency, optimizing production processes to control costs, and incorporating eco-friendly features. They also employ lifecycle cost analysis and modular designs to find the optimal balance for different applications.

Let’s explore how manufacturers achieve this delicate balance:
Advanced Materials for Efficiency
Using high-performance materials can improve efficiency without drastically increasing costs.
Material Strategies:
- Amorphous metal cores for reduced no-load losses
- High-grade copper or aluminum windings for lower load losses
- Advanced insulation materials for better thermal performance
Cost-Effective Production Processes
Optimizing manufacturing can help control costs while maintaining quality.
Production Optimizations:
- Automated assembly lines for increased precision and reduced labor costs
- Lean manufacturing principles to minimize waste
- Standardization of components across product lines
Eco-Friendly Features
Incorporating environmental considerations into design without compromising performance.
Environmental Design Elements:
- Use of biodegradable insulating fluids
- Design for recyclability and easy end-of-life disposal
- Energy-efficient cooling systems
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
Considering long-term costs and benefits to justify initial investments in efficiency and sustainability.
Lifecycle Considerations:
- Total cost of ownership calculations
- Energy savings over the transformer’s lifespan
- Reduced maintenance and replacement costs
| Design Aspect | Efficiency Impact | Cost Implication | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced materials | Higher efficiency | Higher initial cost | Reduced energy waste |
| Optimized production | Consistent quality | Lower manufacturing cost | Reduced material waste |
| Eco-friendly features | Comparable efficiency | Moderate cost increase | Lower environmental impact |
| Lifecycle analysis | Long-term efficiency | Justified initial investment | Sustainable operation |
In my experience, achieving the right balance between these factors is crucial for success in the transformer market. I recently worked with a manufacturer to redesign their distribution transformer line. By using amorphous metal cores and optimizing their production process, we were able to create a transformer that was 20% more efficient than their previous model, with only a 5% increase in production cost. The environmental benefits and long-term energy savings made these transformers highly attractive to utilities.
It’s important to note that the optimal balance can vary depending on the specific application and customer requirements. I’ve been involved in projects where we developed different transformer variants to cater to diverse needs – from high-efficiency models for areas with high electricity costs to more budget-friendly options for less demanding applications.
Don’t overlook the importance of regulatory compliance in this balancing act. In one project, we had to completely redesign a transformer line to meet new efficiency standards while keeping costs under control. This experience highlighted the need for manufacturers to stay ahead of regulatory trends and incorporate compliance into their design process from the outset.
Another crucial aspect is the role of innovation in finding new ways to balance these competing demands. I’m currently involved in a research project exploring the use of AI-optimized designs to maximize efficiency while minimizing material use and cost. These cutting-edge approaches promise to push the boundaries of what’s possible in transformer design.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some manufacturers are turning this challenge into a competitive advantage. I recently consulted for a company that has made "balanced sustainability" their unique selling proposition. By offering transformers that provide the best balance of efficiency, cost, and environmental performance, they’ve carved out a niche in a crowded market.
The task of balancing efficiency, cost, and environmental concerns in transformer design is an ongoing process that requires continuous innovation and adaptation. As technology advances and market demands evolve, manufacturers must stay agile and creative in their approach to design. Those who can consistently achieve the right balance will be well-positioned to lead the industry into a more efficient and sustainable future.
What Challenges Do Distribution Transformer Manufacturers Face in Meeting Evolving Industry Standards?
Are you aware of the complexities involved in keeping up with changing industry standards? Distribution transformer manufacturers face significant challenges in adapting to evolving regulations and market expectations.
Distribution transformer manufacturers face several challenges in meeting evolving industry standards. These include adapting to stricter efficiency requirements, ensuring compliance with new safety regulations, meeting enhanced reliability standards, and addressing emerging concerns like cybersecurity. Manufacturers must also balance these requirements with cost-effectiveness and market demands.
Let’s explore the key challenges manufacturers face in meeting evolving industry standards:
Stricter Efficiency Requirements
Energy efficiency standards are becoming increasingly stringent.
Efficiency Challenges:
- Meeting higher minimum efficiency performance standards (MEPS)
- Balancing efficiency improvements with cost considerations
- Adapting designs for different global efficiency standards
Enhanced Safety Regulations
Safety standards are evolving to address new risks and technologies.
Safety Compliance Issues:
- Implementing advanced fire safety features
- Meeting updated electrical safety standards
- Addressing environmental safety concerns (e.g., oil spill prevention)
Reliability and Resilience Standards
Grid modernization efforts are driving new reliability requirements.
Reliability Challenges:
- Designing for improved fault tolerance
- Meeting standards for operation in extreme conditions
- Incorporating smart grid compatibility features
Emerging Cybersecurity Standards
As transformers become smarter, cybersecurity is becoming a critical concern.
Cybersecurity Compliance:
- Implementing secure communication protocols
- Ensuring data privacy and protection
- Developing robust firmware update mechanisms
| Standard Type | Compliance Challenge | Impact on Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher performance requirements | Need for advanced materials and designs |
| Safety | More stringent safety features | Increased complexity in design and testing |
| Reliability | Enhanced durability standards | Extended testing and validation processes |
| Cybersecurity | New security protocols | Integration of IT expertise in design |
In my experience, meeting these evolving standards presents significant challenges but also drives innovation in the industry. I recently worked with a manufacturer to overhaul their product line to meet new efficiency standards in multiple global markets. The process required a complete redesign of their core technology and manufacturing processes, but ultimately resulted in a more competitive and future-proof product range.
It’s important to note that compliance with evolving standards often requires significant investment in research and development. I’ve seen cases where smaller manufacturers struggled to keep up with rapid changes in regulations. This has led to increased consolidation in the industry, with larger companies better positioned to absorb the costs of continuous innovation and compliance.
Don’t overlook the importance of proactive engagement with regulatory bodies. In one project, I helped a manufacturer participate in industry working groups developing new standards. This involvement allowed them to anticipate future requirements and incorporate them into their design process early, giving them a competitive advantage.
Another crucial aspect is the need for flexible and modular designs that can be easily adapted to meet different regional standards. I’m currently advising a manufacturer on developing a global platform for their transformers that can be quickly customized to meet varying efficiency and safety requirements across different markets.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some manufacturers are turning compliance challenges into opportunities for innovation. I recently visited a research lab where they were developing transformers that not only meet current standards but are designed to be easily upgradable to meet future requirements. This forward-thinking approach is helping them stay ahead of regulatory curves and market demands.
The challenge of meeting evolving industry standards is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and adaptation. Manufacturers must stay informed about regulatory trends, invest in continuous innovation, and maintain flexibility in their design and manufacturing processes. Those who can successfully navigate these challenges will be well-positioned to lead the industry and shape the future of power distribution technology.
How Are Manufacturers Addressing Cybersecurity in Smart Distribution Transformers?
Are you concerned about the vulnerability of smart grid components to cyber attacks? This is a growing concern as distribution transformers become more connected and intelligent.
Manufacturers are addressing cybersecurity in smart distribution transformers through multiple approaches. These include implementing robust encryption protocols, designing secure communication interfaces, developing tamper-resistant hardware, and creating regular security update mechanisms. Many are also incorporating AI-driven threat detection systems and collaborating with cybersecurity experts.

Let’s explore how manufacturers are tackling cybersecurity challenges in smart distribution transformers:
Robust Encryption Protocols
Securing data transmission and storage is crucial for smart transformers.
Encryption Measures:
- End-to-end encryption for all data communications
- Secure key management systems
- Encrypted firmware to prevent tampering
Secure Communication Interfaces
Designing communication systems with security as a primary consideration.
Interface Security:
- Implementing secure protocols like TLS/SSL
- Network segmentation to isolate critical systems
- Strong authentication mechanisms for all access points
Tamper-Resistant Hardware
Physical security is as important as digital security in smart transformers.
Hardware Security Features:
- Tamper-evident seals and enclosures
- Secure element chips for storing critical data
- Physical intrusion detection systems
Regular Security Updates
Keeping software and firmware up-to-date is essential for maintaining security.
Update Mechanisms:
- Over-the-air (OTA) firmware update capabilities
- Regular security patch releases
- Automated update verification processes
| Security Aspect | Implementation Challenge | Benefit to Grid Security |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Balancing security with performance | Protected data transmission |
| Secure interfaces | Ensuring compatibility with existing systems | Reduced vulnerability to cyber attacks |
| Tamper-resistant hardware | Increased manufacturing complexity | Enhanced physical security |
| Regular updates | Managing updates across large transformer fleets | Continuous protection against new threats |
In my experience, addressing cybersecurity in smart transformers is a complex but essential task. I recently worked on a project to upgrade the cybersecurity features of a utility’s smart transformer network. By implementing advanced encryption and secure communication protocols, we were able to significantly reduce the network’s vulnerability to cyber attacks while maintaining operational efficiency.
It’s important to note that cybersecurity is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process. I’ve worked with manufacturers to develop comprehensive security lifecycle management plans for their smart transformers. These plans include regular security assessments, vulnerability testing, and update procedures to ensure long-term protection.
Don’t overlook the importance of employee training in maintaining cybersecurity. In one project, we found that human error was a significant factor in security breaches. We developed a training program for both manufacturer and utility personnel to raise awareness of cybersecurity risks and best practices.
Another crucial aspect is the need for industry-wide collaboration on cybersecurity standards. I’m currently involved in a working group developing cybersecurity guidelines for smart grid components. This collaborative effort is essential for creating a unified approach to security across the industry.
Lastly, it’s exciting to see how some manufacturers are leveraging advanced technologies to enhance cybersecurity. I recently visited a research lab where they were developing AI-powered anomaly detection systems for smart transformers. These systems can identify and respond to potential security threats in real-time, providing an additional layer of protection against sophisticated cyber attacks.
Addressing cybersecurity in smart distribution transformers is an ongoing challenge that requires constant vigilance and innovation. As the threat landscape evolves, manufacturers must stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities and continue to develop robust security solutions. The future of smart grid security depends on our ability to create transformers that are not only intelligent and efficient but also resilient against the ever-growing spectrum of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Distribution transformer manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation in smart grid technology and sustainable power solutions. Through advanced materials, smart features, and sustainable practices, they are enhancing grid reliability, efficiency, and security. As the industry evolves, these manufacturers will continue to play a crucial role in shaping a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group