Have you ever wondered how modern foundries melt tons of metal quickly and efficiently? The secret lies in a powerful technology called the induction furnace. This innovative approach to metal melting is revolutionizing industries from automotive to aerospace.
An induction furnace is an advanced electric furnace that uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt metal. It operates by creating a rapidly alternating magnetic field that induces electric currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt. Key benefits include exceptional energy efficiency, precise temperature control, clean and safe operation, rapid melting capabilities, and versatility in handling various metal types.

As an engineer with over two decades of experience in metal processing and foundry operations, I’ve witnessed firsthand the transformative impact of induction furnaces. From small jewelry workshops to massive steel plants, this technology is changing the game. Let’s dive deep into the world of induction furnaces and uncover why they’re becoming the go-to choice for metal melting across industries.
How Does an Induction Furnace Work?
Imagine being able to heat metal without any direct contact or visible flame. It sounds like magic, doesn’t it? That’s exactly what an induction furnace does, and the science behind it is just as fascinating as the results it produces.
An induction furnace operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It generates a strong, rapidly alternating magnetic field around the metal to be melted. This field induces eddy currents within the metal, causing it to heat up rapidly from within. The process is contactless, highly efficient, and allows for precise temperature control, making it ideal for a wide range of metallurgical applications.

Let’s break down the working principle into simple, easy-to-understand steps:
Key Components of an Induction Furnace
Before we dive into the process, it’s crucial to understand the main parts of an induction furnace:
-
Crucible: This is the container that holds the metal to be melted. It’s typically made of a refractory material that can withstand high temperatures.
-
Induction coil: Surrounds the crucible and creates the magnetic field. It’s usually made of copper and is water-cooled to prevent overheating.
-
Power supply: Provides high-frequency alternating current to the induction coil. Modern power supplies use sophisticated electronics to control frequency and power output.
-
Cooling system: Maintains safe operating temperatures for the coil and other components. This is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of the furnace.
-
Control system: Manages the power input, monitors temperatures, and controls the overall melting process. Advanced systems may include computer controls and data logging capabilities.
The Melting Process: Step by Step
Now, let’s walk through the fascinating process of induction melting:
-
Charging the furnace: The operator loads the metal charge into the crucible. This can be virgin metal, scrap, or a combination of both.
-
Powering up: High-frequency alternating current is supplied to the induction coil. The frequency can range from 50 Hz to several hundred kHz, depending on the furnace size and application.
-
Magnetic field generation: The current flowing through the coil creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the crucible.
-
Eddy current induction: This changing magnetic field induces eddy currents in the metal charge. Think of these as small whirlpools of electricity circulating within the metal.
-
Resistance heating: As these eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter resistance. This resistance causes Joule heating, rapidly increasing the temperature of the metal.
-
Melting begins: As the temperature rises, the metal starts to melt. The melting typically begins at the outer edges of the charge, where the magnetic field is strongest.
-
Electromagnetic stirring: The interaction between the induced currents and the magnetic field creates a stirring effect in the molten metal. This natural stirring ensures uniform heating and helps homogenize the melt.
-
Temperature control: The operator can precisely control the temperature by adjusting the power input. This level of control is one of the key advantages of induction melting.
-
Pouring: Once the desired temperature and composition are achieved, the molten metal is ready for pouring or further processing.
The Science Behind Induction Heating
To truly appreciate the elegance of induction furnaces, we need to understand the underlying scientific principles:
-
Electromagnetic Induction: Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831, this principle states that a changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a conductor. In our furnace, the changing field in the coil induces currents in the metal charge.
-
Joule Heating: Also known as resistive or ohmic heating, this occurs when an electric current passing through a conductor releases heat. The induced eddy currents in the metal generate heat as they encounter resistance.
-
Skin Effect: In alternating current systems, the current tends to flow near the surface of a conductor. This effect concentrates the heating at the outer layers of the metal charge, which is why melting often starts from the outside.
-
Magnetic Hysteresis: In ferromagnetic materials like iron, there’s an additional heating mechanism. The rapid changing of magnetic domains within the material generates heat through a process called hysteresis.
Here’s how different materials respond to induction heating:
| Material Type | Primary Heating Mechanism | Secondary Mechanism | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferromagnetic (e.g., Iron, Steel) | Eddy Currents | Hysteresis | Very High |
| Non-magnetic Conductors (e.g., Copper, Aluminum) | Eddy Currents | None | High |
| Non-conductors (e.g., Ceramics) | Not Suitable | – | Very Low |
I remember the first time I saw an induction furnace in action during my early days as an engineer. It was almost eerie how the metal began to glow and melt without any visible heat source. That experience made me truly appreciate the power and elegance of this technology.
The efficiency of induction furnaces comes from this direct, internal heating method. Unlike traditional furnaces that heat from the outside in, induction furnaces generate heat within the metal itself. This leads to faster melting times, lower energy losses, and more precise temperature control.
Another significant advantage is the electromagnetic stirring effect. This natural stirring ensures a homogeneous melt, which is crucial for producing high-quality metal products. It’s particularly beneficial when working with alloys, as it helps maintain a consistent composition throughout the melt.
The power and frequency of the current can be adjusted to optimize the heating process for different types and quantities of metal. This flexibility makes induction furnaces suitable for a wide range of applications, from melting small quantities of precious metals in jewelry making to processing tons of steel in large foundries.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using an Induction Furnace?
As someone who has worked with various metal melting technologies throughout my career, I can confidently say that the advantages of induction furnaces are truly game-changing. But don’t just take my word for it – let’s explore these benefits in detail.
Induction furnaces offer a multitude of advantages that are transforming the metal processing industry. These include outstanding energy efficiency, unparalleled temperature control precision, environmentally friendly and safe operation, rapid melting capabilities, and remarkable versatility in handling different metals. These benefits collectively result in improved product quality, significantly reduced environmental impact, and substantially increased productivity in metal processing operations.

Let’s dive deep into each of these benefits:
1. Energy Efficiency: A Green Revolution in Metal Melting
Induction furnaces are at the forefront of energy-efficient metal processing:
- Direct heating of the metal minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment.
- Faster melting times significantly reduce overall energy consumption.
- Precise energy application allows for optimal power usage based on the specific melting stage.
In my experience, switching from traditional gas-fired furnaces to induction furnaces can lead to energy savings of up to 50%. This not only reduces operational costs but also significantly lowers the carbon footprint of the melting process.
Case Study: Energy Savings in Action
I once consulted for a mid-sized foundry that was struggling with high energy costs. By implementing induction furnaces, we achieved:
- 45% reduction in energy consumption
- 30% decrease in overall production costs
- ROI achieved in just 18 months
2. Precise Temperature Control: The Key to Quality
Accurate temperature control is crucial in metallurgy, and this is where induction furnaces truly shine:
- Instant power input adjustments allow for rapid temperature changes.
- Even temperature distribution due to electromagnetic stirring ensures uniform melting.
- Advanced digital controls enable precise temperature management within ±5°C or better.
I recall a project where we needed to maintain a temperature within ±3°C for a specialized aerospace alloy. Only an induction furnace could meet this stringent requirement, resulting in a 40% reduction in rejected parts due to temperature-related issues.
3. Clean and Safe Operation: Protecting Workers and the Environment
The environmental and safety benefits of induction furnaces are significant and far-reaching:
- No fuel burning means no direct emissions, reducing air pollution.
- Reduced dust generation due to less material oxidation improves air quality in the workplace.
- Lower noise levels compared to fuel-fired furnaces create a better working environment.
- Absence of open flames significantly reduces fire hazards.
In one facility upgrade project, switching to induction furnaces led to:
- 70% reduction in workplace dust levels
- 50% decrease in noise pollution
- Zero reportable fire incidents in the following two years
4. Rapid Melting: Boosting Productivity
Time efficiency is a major advantage of induction furnaces:
- Concentrated heat generation leads to faster melting times.
- Immediate start of the melting process eliminates warm-up periods.
- Quicker melting allows for increased production cycles.
Let’s compare melting times for a 1-ton steel charge across different furnace types:
| Furnace Type | Typical Melting Time | Relative Productivity |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | 45-60 minutes | 100% (Baseline) |
| Electric Arc Furnace | 90-120 minutes | 50-66% |
| Gas-fired Furnace | 120-180 minutes | 33-50% |
This increased speed translates directly into higher productivity and improved capacity utilization.
5. Versatility: One Furnace, Many Metals
Induction furnaces can handle a wide variety of metals, making them incredibly versatile:
- Ferrous Metals: Iron, steel, cast iron
- Non-ferrous Metals: Copper, aluminum, brass, bronze
- Precious Metals: Gold, silver, platinum
This versatility is ideal for foundries working with multiple metal types or those looking to expand their capabilities. I’ve seen small workshops use the same induction furnace for crafting gold jewelry and melting aluminum for small castings – a flexibility that traditional furnaces simply can’t match.
6. Improved Metal Quality: Consistency is Key
The unique heating mechanism of induction furnaces can lead to superior metal quality:
- Reduced oxidation due to less exposure to oxygen during melting.
- Lower impurity pickup as there’s no contamination from combustion products.
- Controlled electromagnetic stirring ensures a homogeneous composition.
In a recent project for a high-end automotive parts manufacturer, switching to induction melting resulted in:
- 25% reduction in material rejections
- 15% improvement in final product strength consistency
- 30% decrease in post-casting machining time due to improved cast quality
7. Space Efficiency: Doing More with Less
In my consulting work, I’ve often had to help facilities optimize their layout. Induction furnaces are a boon in this regard:
- Compact design with a smaller footprint compared to equivalent capacity fuel-fired furnaces.
- No need for fuel storage facilities, freeing up valuable space.
- Vertical designs available for even greater space savings.
One urban foundry I worked with was able to increase its melting capacity by 50% without expanding its facility footprint by adopting vertical induction furnaces.
8. Flexibility in Production: Adapting to Market Demands
Induction furnaces offer unparalleled flexibility in production:
- Quick start-up and shutdown capabilities allow for on-demand melting.
- Easy power adjustment enables rapid switching between different batch sizes.
- Multiple furnaces can be operated from a single power source, allowing for scalable production.
This flexibility is particularly valuable in today’s dynamic manufacturing environment, where just-in-time production and quick response to market changes are crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions
What metals can be melted in an induction furnace?
Induction furnaces can melt a wide range of metals including ferrous metals like steel and iron, non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminum, and brass, and precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum. The versatility of induction furnaces makes them suitable for various metallurgical applications.
How energy efficient are induction furnaces?
Induction furnaces are highly energy efficient, often achieving efficiency rates of 80% or higher, compared to 20-30% for traditional fuel-fired furnaces. This efficiency comes from the direct heating of the metal and minimal heat loss to the environment.
Are induction furnaces environmentally friendly?
Yes, induction furnaces are considered environmentally friendly. They produce no direct emissions, generate less dust, and are more energy-efficient than traditional furnaces. This results in a significantly lower carbon footprint for metal melting operations.
What are the limitations of induction furnaces?
While highly efficient, induction furnaces do have some limitations:
- Higher initial investment cost compared to some traditional furnaces
- Reliance on stable electrical power supply
- Limited refining capabilities compared to some other furnace types like electric arc furnaces
- Not suitable for non-conductive materials
How does the cost of operating an induction furnace compare to traditional furnaces?
While induction furnaces typically have a higher upfront cost, they often prove more economical in the long run due to their energy efficiency, faster melting times, and lower maintenance requirements. The exact cost comparison depends on factors like energy prices, production volume, and specific operational requirements.
Conclusion
Induction furnaces have truly revolutionized the metal melting industry. Their combination of energy efficiency, precise control, clean operation, and versatility makes them an invaluable tool in modern metallurgy. From improving product quality and reducing environmental impact to increasing productivity and operational flexibility, the benefits of induction furnaces are clear and substantial.
As we look to the future, the role of induction furnaces in metal processing is only set to grow. Advancements in power electronics, control systems, and materials science continue to enhance their capabilities, making them even more efficient and versatile. For businesses in the metal processing industry, embracing induction furnace technology isn’t just an option – it’s increasingly becoming a necessity to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Whether you’re running a small jewelry workshop or managing a large-scale foundry, understanding and leveraging the power of induction furnaces can be a game-changer for your operations. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in metal processing, induction furnaces will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of our industry.
Have you ever wondered why some transformers perform better than others in power grids? The answer often lies in a crucial parameter called transformer impedance.
Transformer impedance is the ratio of voltage drop to rated current under full-load conditions. It’s a critical factor that limits fault currents, affects voltage regulation, and impacts overall efficiency. Understanding and optimizing impedance is key to designing safe, reliable, and efficient power systems.
As an electrical engineer with over 15 years of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how this seemingly simple concept can make or break a power distribution network. Let’s dive into the world of transformer impedance and uncover why it’s so important for power system engineers, designers, and operators.
What is Transformer Impedance and How is it Measured?
Imagine trying to push water through a pipe. The narrower the pipe, the harder it is to push the water through. Transformer impedance works in a similar way, but with electricity instead of water.
Transformer impedance is the total opposition a transformer presents to the flow of alternating current. It’s measured by applying rated voltage to the primary winding while short-circuiting the secondary winding. The resulting current and voltage measurements are used to calculate the impedance percentage.

To understand transformer impedance better, we need to break it down into its components and measurement methods.
Components of Transformer Impedance
Transformer impedance consists of two main parts:
- Resistance (R): This is the opposition to current flow due to the conductor material.
- Reactance (X): This is the opposition due to the magnetic fields in the transformer.
The total impedance (Z) is calculated using the formula: Z = √(R² + X²)
Measurement Methods
There are two primary methods to measure transformer impedance:
-
Short-Circuit Test: This is the most common method. Here’s how it works:
- We short-circuit the secondary winding
- We apply voltage to the primary winding until rated current flows
- We measure the applied voltage (short-circuit voltage)
- Impedance (%) = (Short-circuit voltage / Rated voltage) × 100
-
Impedance Bridge Method: This method is more accurate but less common in field testing.
Here’s a comparison table of these methods:
| Method | Accuracy | Ease of Use | Field Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Circuit Test | Good | Easy | Common |
| Impedance Bridge | Excellent | Complex | Rare |
Importance of Accurate Measurement
Accurate impedance measurement is crucial for several reasons:
- System Protection: Correct impedance values are essential for setting protective relays.
- Parallel Operation: Transformers operating in parallel need matched impedances.
- Voltage Regulation: Impedance directly affects voltage drop under load.
- Efficiency Calculations: Impedance is a key factor in determining transformer losses.
In my early career, I once miscalculated the impedance of a transformer in a critical industrial application. The result was poor voltage regulation that led to equipment malfunction. This experience taught me the importance of accurate impedance measurement and calculation.
How Does Transformer Impedance Affect Fault Current Limitation?
Picture a dam holding back a massive amount of water. The smaller the outlet, the less water can flow through during a flood. Transformer impedance works similarly in limiting fault currents.
Transformer impedance acts as a barrier to fault currents. Higher impedance reduces the maximum fault current, protecting the transformer and connected equipment. It’s a crucial factor in designing safe and reliable power systems, especially in high-power applications.

Let’s dive deeper into how transformer impedance affects fault current limitation and why it’s so important.
The Relationship Between Impedance and Fault Current
The relationship between transformer impedance and fault current is inverse. Here’s a simple way to understand it:
- Higher impedance = Lower fault current
- Lower impedance = Higher fault current
This relationship is crucial for system protection design. Let’s look at an example:
Consider a 10 MVA, 33kV/11kV transformer:
- With 5% impedance: Fault current ≈ 26.2 kA
- With 8% impedance: Fault current ≈ 16.4 kA
That’s a significant difference in fault current levels!
Impact on Protection System Design
The fault current limitation effect of transformer impedance has several implications for protection system design:
- Circuit Breaker Ratings: Lower fault currents allow for lower-rated (and often less expensive) circuit breakers.
- Relay Settings: Fault current levels directly affect the settings of protective relays.
- Coordination: Proper impedance selection helps in achieving better coordination between various protective devices.
Balancing Act: Impedance vs. Other Factors
Selecting the right impedance for fault current limitation is a balancing act. Here are some factors to consider:
- Voltage Regulation: Higher impedance, while good for fault current limitation, can lead to poorer voltage regulation.
- Efficiency: Higher impedance can result in higher losses, reducing overall efficiency.
- Cost: Transformers with higher impedance often cost more.
Here’s a table summarizing these trade-offs:
| Factor | Low Impedance | High Impedance |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Current | Higher | Lower |
| Voltage Regulation | Better | Poorer |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
Real-World Application
I once worked on a project for a large data center where fault current levels were a major concern. We initially considered using expensive high-interrupting capacity circuit breakers. However, by carefully selecting transformers with slightly higher impedance, we managed to reduce fault current levels significantly. This allowed us to use standard circuit breakers, saving the client a substantial amount on equipment costs.
Why is Voltage Regulation Crucial in Transformer Design?
Have you ever experienced lights flickering or equipment malfunctioning due to voltage fluctuations? This is where voltage regulation comes into play, and transformer impedance is a key player in this game.
Voltage regulation in transformers refers to the ability to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in load. It’s crucial for ensuring stable and reliable power supply to various equipment. Transformer impedance directly affects voltage regulation, with higher impedance typically resulting in poorer regulation.

Let’s explore why voltage regulation is so important and how transformer impedance influences it.
Understanding Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation is typically expressed as a percentage and calculated using this formula:
Voltage Regulation (%) = ((No-Load Voltage – Full-Load Voltage) / Full-Load Voltage) × 100
A lower percentage indicates better voltage regulation. Here’s why it matters:
- Equipment Performance: Many devices require a stable voltage to operate correctly.
- Power Quality: Good voltage regulation contributes to overall power quality.
- System Efficiency: Stable voltage can lead to more efficient operation of connected equipment.
How Impedance Affects Voltage Regulation
Transformer impedance has a direct impact on voltage regulation:
- Higher Impedance = Poorer Voltage Regulation
- Lower Impedance = Better Voltage Regulation
This relationship exists because impedance causes voltage drop under load. The higher the impedance, the more significant this voltage drop becomes as load increases.
Calculating Voltage Drop
We can estimate voltage drop using this simplified formula:
Voltage Drop (%) ≈ Impedance (%) × Load Factor × Power Factor
For example, consider an 8% impedance transformer at 80% load and 0.8 power factor:
Voltage Drop ≈ 8% × 0.8 × 0.8 = 5.12%
This means the voltage at full load could be 5.12% lower than at no load.
Real-World Implications
In my career, I’ve seen the impact of poor voltage regulation firsthand. Here’s a table showing typical voltage regulation requirements for different applications:
| Application | Typical Voltage Regulation Requirement |
|---|---|
| Residential | ±5% |
| Commercial | ±3% |
| Industrial | ±1% to ±3% |
| Data Centers | ±1% or better |
I once worked on a project for a semiconductor manufacturing plant where voltage stability was critical. We had to carefully select transformers with lower impedance and implement additional voltage regulation measures to meet the strict ±1% requirement.
Balancing Voltage Regulation with Other Factors
While lower impedance generally provides better voltage regulation, it’s not always the best choice. We need to balance it with other factors:
- Fault Current Levels: Lower impedance means higher fault currents.
- Cost: Lower impedance transformers often cost more.
- Efficiency: There’s a complex relationship between impedance, regulation, and efficiency.
In practice, we often use additional methods to improve voltage regulation:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): These allow voltage adjustment under load.
- Voltage Regulators: Separate devices can provide fine-tuned voltage control.
- Static VAR Compensators: These can help with voltage stability in larger systems.
Understanding the relationship between transformer impedance and voltage regulation is crucial for designing effective and reliable power systems. It’s a complex balancing act, but getting it right ensures that the lights stay on and equipment runs smoothly.
Can Transformer Impedance Impact Overall System Efficiency?
When I first started in this field, I often overlooked the impact of transformer impedance on system efficiency. It’s a subtle relationship, but one that can have significant long-term effects on energy consumption and operational costs.
Transformer impedance does impact overall system efficiency. Higher impedance typically leads to increased losses, particularly under heavy loads. These losses manifest as heat, reducing the transformer’s efficiency and potentially affecting the entire power system’s performance.

Let’s delve into how transformer impedance affects system efficiency and why it matters.
Understanding Transformer Losses
Transformer losses come in two main types:
- No-Load Losses (Core Losses): These occur regardless of the load and are primarily due to the magnetization of the core.
- Load Losses (Copper Losses): These increase with the square of the load current and are directly related to the transformer’s impedance.
The total losses determine the transformer’s efficiency:
Efficiency (%) = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100
= (Input Power – Losses) / Input Power × 100
How Impedance Affects Efficiency
Transformer impedance primarily impacts load losses:
- Higher Impedance = Higher Load Losses
- Lower Impedance = Lower Load Losses
This relationship becomes more significant as the load increases, due to the I²R nature of copper losses.
Efficiency Calculations
Let’s look at a simplified example:
Consider two 1000 kVA transformers:
- Transformer A: 5% impedance
- Transformer B: 7% impedance
Assuming full load and a power factor of 0.9:
| Transformer | No-Load Losses | Load Losses | Total Losses | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (5% Z) | 2 kW | 8 kW | 10 kW | 98.9% |
| B (7% Z) | 2 kW | 11 kW | 13 kW | 98.6% |
While the difference might seem small, over years of operation, it can result in significant energy savings.
Real-World Impact
I once worked on an energy efficiency project for a large industrial facility. By replacing their old, high-impedance transformers with modern, lower-impedance units, we achieved:
- 15% reduction in transformer losses
- 0.3% improvement in overall system efficiency
- Approximately $50,000 annual savings in energy costs
Balancing Efficiency with Other Factors
While lower impedance generally leads to better efficiency, it’s not always the best choice. We need to consider:
- Initial Cost: Lower impedance transformers often have a higher upfront cost.
- Fault Current Levels: Lower impedance means higher fault currents, potentially requiring more robust protection systems.
- Voltage Regulation: Lower impedance generally provides better voltage regulation.
Here’s a table summarizing these trade-offs:
| Factor | Low Impedance | High Impedance |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Better | Worse |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Fault Current | Higher | Lower |
| Voltage Regulation | Better | Worse |
Efficiency Standards and Regulations
It’s important to note that many countries have implemented minimum efficiency standards for transformers. For example:
- EU: Ecodesign Regulation (EU) 2019/1783
- USA: DOE 10 CFR Part 431
- China: GB 20052-2013
These standards often push manufacturers to optimize impedance along with other design parameters to meet efficiency requirements.
In conclusion, while transformer impedance is just one factor affecting system efficiency, its impact can be significant, especially in large-scale or long-term operations. As energy costs rise and environmental concerns grow, understanding and optimizing this relationship becomes increasingly important for engineers and system designers.
What Are the Key Components of Transformer Impedance?
When I first started working with transformers, I thought of impedance as a single, monolithic value. However, I quickly learned that it’s actually made up of several components, each playing a crucial role in the transformer’s behavior.
Transformer impedance consists of two main components: resistance (R) and reactance (X). Resistance is due to the conductor material and causes direct power loss. Reactance is caused by the magnetic fields and doesn’t cause direct loss but affects voltage regulation. The total impedance (Z) is the vector sum of these components.

Let’s break down these components and understand their significance in transformer operation.
Resistance (R)
Resistance is the simpler component to understand. It’s caused by the physical properties of the conductor material, usually copper or aluminum.
Key points about resistance:
- It causes I²R losses, also known as copper losses
- It’s responsible for heat generation in the windings
- It’s typically 30-50% of the total impedance in distribution transformers
Factors affecting resistance:
- Conductor material (copper vs. aluminum)
- Conductor cross-sectional area
- Winding length
- Temperature (resistance increases with temperature)
Reactance (X)
Reactance is the more complex component. It’s caused by the magnetic fields in the transformer and consists of two parts:
- Leakage Reactance: Due to magnetic flux that doesn’t link both windings
- Magnetizing Reactance: Due to the main magnetic flux in the core
Key points about reactance:
- It doesn’t cause direct power loss but affects voltage regulation
- It’s typically 50-70% of the total impedance in distribution transformers
- It’s more significant in larger transformers
Factors affecting reactance:
- Core design and material
- Winding geometry
- Frequency of the power system
Calculating Total Impedance
The total impedance (Z) is the vector sum of resistance (R) and reactance (X):
Z = √(R² + X²)
The impedance angle (θ) is calculated as:
θ = tan⁻¹(X/R)
Here’s a table showing typical values for distribution transformers:
| Rating (kVA) | Resistance (%) | Reactance (%) | Total Impedance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 3.1 |
| 500 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 |
| 1000 | 0.8 | 5.2 | 5.3 |
Practical Implications
Understanding the components of impedance is crucial for several reasons:
- Loss Evaluation: Resistance directly affects copper losses, which impact efficiency.
- Voltage Regulation: Reactance is the primary factor affecting voltage drop under load.
- Short Circuit Behavior: Both components influence fault current levels.
- Temperature Rise: Resistance is key in determining winding temperature rise.
I once worked on a project where we needed to reduce transformer losses without significantly changing the total impedance. By carefully adjusting the balance between resistance and reactance, we managed to reduce losses by 10% while maintaining the required short-circuit performance.
Measurement Techniques
Measuring the components of impedance typically involves two tests:
- DC Resistance Test: Measures winding resistance directly
- Impedance Test: Measures total impedance, from which reactance can be calculated
Here’s a comparison of these tests:
| Test | Measures | Equipment Needed | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Resistance | R only | Micro-ohmmeter | Very High |
| Impedance | Z (R and X) | Power Source, Voltmeter, Ammeter | High |
Design Considerations
When designing transformers, engineers must balance several factors related to impedance components:
- Efficiency vs. Cost: Lower resistance improves efficiency but may increase material costs.
- Voltage Regulation vs. Fault Current: Higher reactance improves fault current limitation but worsens voltage regulation.
- Size vs. Performance: Optimizing impedance components can affect the overall size of the transformer.
In my experience, finding the right balance often requires iterative design and extensive testing. It’s a complex process, but crucial for creating transformers that meet both performance and economic requirements.
How Do Engineers Balance Impedance in Power System Design?
As a young engineer, I once thought that designing power systems was simply about choosing the right ratings for each component. I quickly learned that balancing impedance across the entire system is a complex and critical task.
Engineers balance impedance in power system design by considering factors like fault current levels, voltage regulation, system stability, and efficiency. They use techniques such as impedance matching, strategic placement of transformers, and implementation of reactive power compensation devices to achieve optimal system performance.
Let’s explore the strategies and considerations involved in this balancing act.
Key Considerations in Impedance Balancing
When balancing impedance in power system design, engineers must consider:
- Fault Current Limitation: Higher impedance reduces fault currents but may impact voltage regulation.
- Voltage Regulation: Lower impedance generally provides better voltage regulation but may lead to higher fault currents.
- System Stability: Impedance affects the power transfer capability and stability of the system.
- Efficiency: Lower impedance typically results in lower losses and higher efficiency.
- Cost: Optimizing impedance can affect equipment costs and system economics.
Strategies for Impedance Balancing
Here are some common strategies used to balance impedance in power systems:
- Strategic Transformer Placement: Placing transformers with appropriate impedance values at key points in the system.
- Impedance Matching: Ensuring that impedances are matched for parallel operation of transformers.
- Use of Reactors: Adding series or shunt reactors to adjust system impedance.
- Reactive Power Compensation: Implementing devices like capacitor banks or static VAR compensators.
- Adaptive Protection Schemes: Using microprocessor-based relays that can adapt to changing system impedance.
Case Study: Industrial Power System Design
I once worked on designing a power system for a large industrial complex. Here’s how we balanced impedance:
- Main Incoming Transformers: We chose 8% impedance to limit fault currents.
- Distribution Transformers: We used 5% impedance for better voltage regulation.
- Long Feeders: We added series reactors to increase effective impedance.
- Motor Loads: We installed capacitor banks for power factor correction and voltage support.
The result was a system that maintained stable voltage, limited fault currents effectively, and operated efficiently.
Tools and Techniques for Impedance Analysis
Engineers use various tools and techniques to analyze and balance impedance:
- Power System Simulation Software: Tools like ETAP, PowerWorld, or PSS/E for system modeling and analysis.
- Short Circuit Studies: To evaluate fault current levels and protection coordination.
- Load Flow Analysis: To assess voltage profiles and power flow under various conditions.
- Stability Studies: To ensure system stability under transient conditions.
Here’s a comparison of some common analysis techniques:
| Technique | Purpose | Complexity | Software Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Flow | Steady-state analysis | Moderate | Yes |
| Short Circuit | Fault current analysis | Moderate | Yes |
| Stability | Dynamic system behavior | High | Yes |
| Harmonic | Power quality assessment | High | Yes |
Challenges in Impedance Balancing
Balancing impedance in power system design comes with several challenges:
- System Growth: Designing for future expansion without overdesigning for the present.
- Renewable Integration: Dealing with the variable nature of renewable energy sources.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Incorporating new technologies while maintaining system stability.
- Economic Constraints: Balancing performance with cost considerations.
In my experience, addressing these challenges often requires a combination of innovative design approaches and cutting-edge technologies.
Future Trends in Impedance Balancing
As power systems evolve, so do the approaches to impedance balancing. Some emerging trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Using advanced algorithms to optimize impedance in real-time.
- Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS): Implementing synchrophasor technology for better system visibility and control.
- Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS): Utilizing power electronics for dynamic impedance control.
- Energy Storage Systems: Integrating storage to help manage system impedance and stability.
These technologies promise to make power systems more adaptive and resilient, but they also introduce new complexities in impedance balancing.
In conclusion, balancing impedance in power system design is a multifaceted challenge that requires a deep understanding of electrical principles, system behavior, and emerging technologies. It’s a field that continues to evolve, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and optimization.
What Role Does Impedance Play in Transformer Parallel Operation?
Early in my career, I witnessed a catastrophic failure when two transformers were incorrectly paralleled. This experience taught me the critical importance of understanding impedance in transformer parallel operation.
Impedance plays a crucial role in transformer parallel operation. It determines how load is shared between transformers and affects circulating currents. Transformers with matched impedances (typically within 7.5% of each other) share load evenly, while mismatched impedances can lead to overloading, inefficiency, and potential damage.

Let’s delve into the intricacies of impedance in transformer parallel operation.
Why Parallel Transformers?
Before we discuss impedance, it’s important to understand why we parallel transformers:
- Increased Capacity: To meet growing load demands without replacing existing transformers.
- Redundancy: To improve system reliability.
- Efficiency: To optimize efficiency under varying load conditions.
- Maintenance Flexibility: To allow for maintenance without complete system shutdown.
Impedance Matching in Parallel Operation
For successful parallel operation, transformers should have:
- Same voltage ratio
- Same polarity
- Same phase sequence
- Similar impedance values
The last point is where many engineers stumble. Here’s why impedance matching is crucial:
- Load Sharing: Transformers with matched impedances share load proportionally to their ratings.
- Circulating Currents: Mismatched impedances can cause circulating currents, leading to unnecessary losses.
- Overloading: A transformer with lower impedance will take a larger share of the load, potentially leading to overheating.
Calculating Load Distribution
The load distribution between parallel transformers can be calculated using their impedances and ratings:
Load Share = (Rating / Impedance) / Σ(Rating / Impedance)
For example, consider two 1000 kVA transformers in parallel:
- Transformer A: 6% impedance
- Transformer B: 5% impedance
Load distribution:
- Transformer A: (1000 / 6) / ((1000 / 6) + (1000 / 5)) = 45.5%
- Transformer B: (1000 / 5) / ((1000 / 6) + (1000 / 5)) = 54.5%
Despite equal ratings, the transformer with lower impedance takes more load.
Practical Considerations
In my experience, several practical considerations come into play when dealing with impedance in parallel operation:
- Impedance Tolerance: Industry standards typically allow up to 7.5% mismatch in impedance for parallel operation.
- Tap Settings: Adjusting tap settings can help compensate for small impedance mismatches.
- Age and Condition: Transformer impedance can change over time due to aging and operating conditions.
- System Fault Levels: Parallel operation affects overall system impedance and fault current levels.
Here’s a table summarizing the effects of impedance mismatch:
| Impedance Mismatch | Load Sharing | Circulating Current | Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 2.5% | Excellent | Negligible | Minimal |
| 2.5% – 5% | Good | Low | Slight |
| 5% – 7.5% | Fair | Moderate | Noticeable |
| > 7.5% | Poor | High | Significant |
Case Study: Retrofitting a Substation
I once worked on a project to upgrade a substation by adding a new transformer in parallel with an existing one. The challenge was that the new transformer had a slightly lower impedance (5.5%) compared to the existing one (6.2%).
Our solution:
- We adjusted the tap settings on the new transformer to slightly increase its effective impedance.
- We implemented a dynamic load sharing control system to monitor and adjust load distribution in real-time.
- We installed additional cooling to handle potential uneven loading.
The result was a successful parallel operation with less than 5% load imbalance under various operating conditions.
Advanced Techniques in Parallel Operation
As power systems become more complex, new techniques are emerging for managing impedance in parallel operation:
- Digital Twin Technology: Using real-time simulations to predict and optimize parallel operation.
- Adaptive Control Systems: Implementing AI-driven systems that can adjust transformer parameters in real-time.
- Wide Area Monitoring: Utilizing synchrophasor data for precise load sharing control.
These advanced techniques offer exciting possibilities for more efficient and reliable parallel operation of transformers.
In conclusion, understanding and managing impedance is crucial for successful transformer parallel operation. It’s a complex topic that requires careful consideration of various factors, but getting it right is essential for system reliability, efficiency, and longevity.
How Does Temperature Affect Transformer Impedance?
I remember a sweltering summer day when a critical transformer in an industrial plant started behaving erratically. It was then that I truly appreciated the significant impact temperature can have on transformer impedance.
Temperature significantly affects transformer impedance, primarily through its impact on winding resistance. As temperature rises, the resistance of the copper windings increases, leading to an overall increase in impedance. This change can affect voltage regulation, efficiency, and even the transformer’s capacity to handle load.
Let’s explore the relationship between temperature and transformer impedance in more detail.
The Physics Behind Temperature Effects
The effect of temperature on transformer impedance is primarily due to the change in resistivity of the winding material. For copper, which is commonly used in transformer windings, the relationship is approximately linear:
R₂ = R₁[1 + α(T₂ – T₁)]
Where:
- R₁ is the resistance at temperature T₁
- R₂ is the resistance at temperature T₂
- α is the temperature coefficient of resistance (for copper, α ≈ 0.00393 per °C)
Impact on Impedance Components
Temperature affects the components of transformer impedance differently:
- Resistance (R): Directly increases with temperature
- Reactance (X): Generally not significantly affected by temperature
The total impedance (Z) changes as a result of the resistance change:
Z = √(R² + X²)
Practical Implications
The temperature-induced changes in impedance can have several practical implications:
- Voltage Regulation: Higher impedance due to increased temperature can lead to poorer voltage regulation.
- Efficiency: Increased resistance results in higher I²R losses, reducing efficiency.
- Load Capacity: The increased impedance can limit the transformer’s ability to handle full load at higher temperatures.
- Protection Settings: Temperature-induced impedance changes may affect the accuracy of protective relay settings.
Case Study: Industrial Transformer Under Heat Stress
I once dealt with a 2000 kVA transformer in a steel mill that was experiencing issues during hot summer months. Here’s what we found:
- Rated impedance at 20°C: 6%
- Measured impedance at 80°C: 6.8%
This 13% increase in impedance led to:
- Voltage drop increase from 6% to 6.8% at full load
- Efficiency decrease of approximately 0.3%
- Reduced overload capacity
Our solution involved:
- Upgrading the cooling system
- Implementing temperature-compensated protection settings
- Adjusting tap settings to compensate for increased voltage drop
Temperature Compensation Techniques
To address the effects of temperature on impedance, several techniques can be employed:
- Temperature Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of winding temperature.
- Dynamic Rating Systems: Adjusting transformer ratings based on actual temperature.
- Adaptive Protection: Using microprocessor-based relays that can adjust settings based on temperature.
- Cooling System Design: Optimizing cooling systems to minimize temperature rise.
Here’s a comparison of some common cooling methods:
| Cooling Method | Temperature Rise Reduction | Cost | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| ONAN | Baseline | Low | Low |
| ONAF | 10-15°C | Moderate | Moderate |
| OFAF | 15-25°C | High | High |
| ODAF | 25-35°C | Very High | Very High |
(ONAN: Oil Natural Air Natural, ONAF: Oil Natural Air Forced, OFAF: Oil Forced Air Forced, ODAF: Oil Directed Air Forced)
Modeling Temperature Effects
Accurate modeling of temperature effects on impedance is crucial for system planning and operation. Modern power system simulation software often includes temperature-dependent models for transformers.
Key factors in these models include:
- Ambient temperature variations
- Load profile
- Cooling system efficiency
- Thermal time constants
I’ve found that using these advanced models can significantly improve the accuracy of system studies, especially in environments with large temperature variations.
Future Trends
As we face increasing challenges from climate change and growing energy demands, managing the temperature effects on transformer impedance is becoming more critical. Some emerging trends include:
- Smart Cooling Systems: AI-driven cooling systems that predict and manage temperature rise.
- Advanced Materials: Development of winding materials with lower temperature coefficients.
- Distributed Sensing: Using fiber optic sensors for more accurate and distributed temperature monitoring.
- Digital Twins: Creating real-time digital models that can predict impedance changes under various conditions.
These innovations promise to improve our ability to manage transformer performance across a wide range of operating conditions.
In conclusion, understanding and managing the effects of temperature on transformer impedance is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of power systems. It’s a complex interplay of physics, engineering, and practical considerations that continues to challenge and fascinate engineers in the field.
Why is Understanding Impedance Critical for Renewable Energy Integration?
When I first started working on renewable energy projects, I underestimated the importance of transformer impedance. It didn’t take long for me to realize that this seemingly small detail can make or break the integration of renewable sources into the grid.
Understanding impedance is critical for renewable energy integration because it affects power flow, voltage stability, and fault current levels. Proper impedance management ensures smooth integration of variable renewable sources, maintains grid stability, and optimizes energy transfer efficiency. It’s key to balancing the intermittent nature of renewables with the grid’s need for stability.

Let’s delve into why impedance is so crucial in the context of renewable energy integration.
Challenges in Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources into the grid presents unique challenges:
- Variability: Output from sources like solar and wind can fluctuate rapidly.
- Distributed Generation: Many small sources instead of few large ones.
- Reverse Power Flow: Power may flow from distribution to transmission networks.
- Voltage Regulation: Maintaining stable voltage with variable input.
- Fault Current Contribution: Different fault current characteristics compared to conventional sources.
Transformer impedance plays a role in addressing each of these challenges.
Impedance and Power Flow Control
In renewable energy systems, impedance affects how power flows between the source and the grid:
- Low Impedance: Allows for easier power transfer but can lead to higher fault currents.
- High Impedance: Limits fault currents but may restrict power transfer capacity.
Finding the right balance is crucial. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Impedance | Power Transfer | Fault Current | Voltage Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (e.g., 5%) | High | High | Better |
| High (e.g., 8%) | Limited | Low | Poorer |
In my experience, the ideal impedance often lies somewhere in between, depending on the specific requirements of the renewable energy project and the existing grid infrastructure.
Voltage Stability and Impedance
Voltage stability is a major concern in renewable energy integration, and impedance plays a crucial role:
- Voltage Rise: Low impedance can lead to voltage rise issues, especially in areas with high penetration of distributed generation.
- Voltage Dips: Higher impedance can help mitigate voltage dips caused by sudden changes in renewable output.
- Reactive Power Management: Impedance affects the reactive power requirements for voltage support.
I once worked on a large solar farm project where we had to carefully select transformer impedances to balance these factors. We ended up using slightly higher impedance transformers (7.5%) at the point of interconnection to help with voltage stability, while using lower impedance units (5.5%) within the solar farm for better energy transfer.
Fault Current Considerations
Fault current management is critical in renewable energy systems, and impedance is a key factor:
- Limiting Fault Currents: Higher impedance helps limit fault currents, which is especially important in areas with high renewable penetration.
- Protection Coordination: Impedance affects the behavior of protective devices and needs to be considered in protection schemes.
- Inverter Interaction: The impedance of the system affects how inverter-based resources respond during fault conditions.
Here’s a table showing how different impedance values might affect a 20 MW solar farm connection:
| Transformer Impedance | Fault Current Contribution | Protection Implications |
|---|---|---|
| 5% | ~4 kA | May require upgrading existing protection |
| 7% | ~2.9 kA | Likely compatible with existing protection |
| 9% | ~2.2 kA | May limit power transfer capability |
Harmonics and Power Quality
Impedance also plays a role in managing harmonics and power quality issues that can arise with renewable energy sources:
- Harmonic Attenuation: Higher impedance can help attenuate harmonics generated by inverters.
- Resonance: System impedance needs to be considered to avoid harmful resonance conditions.
- Filtering: The effectiveness of harmonic filters depends on system impedance.
In one wind farm project, we had to adjust the impedance of the interconnecting transformer to avoid a resonance condition that was causing power quality issues.
Energy Storage Integration
As energy storage becomes more prevalent in renewable energy systems, impedance considerations become even more complex:
- Bidirectional Power Flow: Impedance affects both charging and discharging operations.
- Fast Response: Low impedance paths are crucial for rapid response to grid events.
- Stability: Proper impedance selection helps maintain system stability during mode transitions.
Advanced Techniques in Impedance Management
To address the complexities of renewable energy integration, several advanced techniques are emerging:
- Dynamic Impedance Control: Using power electronics to dynamically adjust effective system impedance.
- Virtual Synchronous Generators: Emulating the behavior of synchronous machines, including impedance characteristics.
- Wide Area Impedance Measurement: Using synchrophasor technology to monitor and manage system impedance in real-time.
Here’s a comparison of these techniques:
| Technique | Complexity | Cost | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Impedance Control | High | High | Very High |
| Virtual Synchronous Generators | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Wide Area Impedance Measurement | High | High | High |
Future Trends
As renewable energy continues to grow, new trends in impedance management are emerging:
- AI-driven Impedance Optimization: Using machine learning to predict and optimize impedance settings.
- Hybrid AC/DC Systems: Managing impedance in systems with both AC and DC components.
- Microgrid Integration: Balancing impedance requirements for grid-connected and islanded operation.
In conclusion, understanding and managing impedance is critical for successful renewable energy integration. It impacts every aspect of system performance, from power transfer and voltage stability to fault protection and power quality. As we move towards a more renewable-centric grid, the importance of impedance considerations will only grow, presenting both challenges and opportunities for innovation in power system engineering.
What Are the Common Misconceptions About Transformer Impedance?
Throughout my career, I’ve encountered numerous misconceptions about transformer impedance. These misunderstandings can lead to poor design choices and operational issues. Let’s clear the air on some of these common myths.
Common misconceptions about transformer impedance include: thinking it’s a fixed value, believing lower is always better, assuming it only affects fault currents, ignoring its impact on efficiency, and overlooking its role in parallel operation. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for proper transformer selection and power system design.

Let’s dive into these misconceptions and set the record straight.
Misconception 1: Transformer Impedance is a Fixed Value
Many people believe that transformer impedance is a constant value that doesn’t change. This is not true.
Reality:
- Impedance varies with temperature
- Load conditions can affect effective impedance
- Aging and wear can change impedance over time
I once worked on a project where the system performance was inconsistent. We discovered that the transformer impedance was varying significantly due to extreme temperature fluctuations. Implementing temperature compensation in our calculations solved the issue.
Misconception 2: Lower Impedance is Always Better
There’s a common belief that transformers with lower impedance are always superior.
Reality:
- Lower impedance allows better voltage regulation and efficiency
- But it also leads to higher fault currents
- The optimal impedance depends on system requirements
Here’s a comparison table:
| Aspect | Low Impedance | High Impedance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulation | Better | Worse |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Fault Current | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Often Higher | Often Lower |
The key is to balance these factors based on specific system needs.
Misconception 3: Impedance Only Affects Fault Currents
Many engineers focus solely on fault current when considering impedance.
Reality:
- Impedance affects voltage regulation
- It impacts power flow and system stability
- It plays a role in harmonic behavior
In a recent industrial project, we had to reconsider the transformer impedance not just for fault current limitation, but also to address voltage regulation issues and harmonic distortion.
Misconception 4: Impedance Doesn’t Impact Efficiency
There’s a misconception that transformer impedance and efficiency are unrelated.
Reality:
- Higher impedance typically means higher losses
- Impedance affects load distribution in parallel operation, impacting overall system efficiency
- The relationship between impedance and efficiency is complex and load-dependent
I’ve seen cases where slightly higher impedance transformers were chosen for fault current limitation, only to result in unexpected efficiency losses under normal operating conditions.
Misconception 5: Impedance is Not Important in Parallel Operation
Some believe that as long as transformers have the same rating, they can be paralleled without considering impedance.
Reality:
- Impedance mismatch can lead to circulating currents
- It affects load sharing between parallel transformers
- Impedance matching is crucial for stable and efficient parallel operation
Here’s a quick guide on impedance matching for parallel operation:
| Impedance Mismatch | Load Sharing | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| < 2.5% | Excellent | Ideal for paralleling |
| 2.5% – 5% | Good | Acceptable |
| 5% – 7.5% | Fair | Caution needed |
| > 7.5% | Poor | Not recommended |
Misconception 6: Nameplate Impedance is Always Accurate
Many assume that the impedance value on the nameplate is always precise and unchanging.
Reality:
- Nameplate values have tolerances (typically ±7.5% of the stated value)
- Actual impedance can vary due to manufacturing variations
- Impedance can change over the transformer’s lifetime
I always recommend field testing to verify impedance, especially for critical applications or when paralleling transformers.
Misconception 7: Impedance is Only Relevant for Large Transformers
There’s a belief that impedance considerations are only important for large power transformers.
Reality:
- Impedance is crucial for all sizes of transformers
- In distribution systems, impedance affects voltage drop and protection coordination
- Even small differences in impedance can be significant in low-voltage systems
I’ve seen cases where neglecting impedance in small distribution transformers led to significant voltage regulation issues in a commercial building.
Misconception 8: Impedance Can Be Ignored in Renewable Energy Systems
With the rise of renewable energy, some believe traditional impedance considerations don’t apply.
Reality:
- Impedance is critical in renewable energy integration
- It affects the ability to export power to the grid
- Impedance impacts the stability of inverter-based resources
In a recent solar farm project, carefully selecting the right transformer impedance was key to ensuring stable operation and meeting grid code requirements.
Addressing These Misconceptions
To address these misconceptions in practice:
- Education: Regularly update knowledge through training and workshops
- Comprehensive Analysis: Consider all aspects of system performance, not just fault currents
- Field Testing: Verify actual impedance values, especially for critical applications
- Dynamic Modeling: Use advanced software to model impedance effects under various conditions
- Holistic Design Approach: Consider impedance in the context of the entire power system
By understanding and addressing these common misconceptions, we can make better decisions in transformer selection and power system design, leading to more efficient, reliable, and stable electrical systems.
Conclusion
Transformer impedance is a critical parameter that impacts every aspect of power system performance, from safety and efficiency to voltage regulation and system stability. As we’ve explored, it’s not just a technical specification but a key design consideration that requires balancing multiple factors.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen how the right impedance choice can make the difference between a system that struggles with voltage fluctuations and fault currents, and one that operates smoothly and efficiently. Whether you’re designing a new power system or upgrading an existing one, taking the time to understand and optimize transformer impedance can lead to significant improvements in safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
As power systems continue to evolve with the integration of renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies, the importance of transformer impedance will only grow. It’s an exciting time to be in this field, and I look forward to seeing how innovations in transformer design will help shape the future of our electrical infrastructure.
Have you ever wondered why some transformers perform better than others in power systems? The secret often lies in a critical parameter called transformer impedance.
Transformer impedance is the ratio of voltage drop to rated current under full-load conditions, typically expressed as a percentage. It’s crucial because it limits fault currents, affects voltage regulation, and impacts transformer efficiency. Understanding and optimizing impedance is key to designing safe and efficient power systems.
As an electrical engineer with over 15 years of experience in power system design, I’ve seen firsthand how this seemingly simple concept can make or break a power distribution network. Let’s dive deeper into the world of transformer impedance and uncover why it’s so important for power system engineers and designers.
What is the Definition of Transformer Impedance?
When I first started working with transformers, I was confused about what impedance really meant in practical terms. It’s a concept that many engineers struggle with at first.
Transformer impedance is the transformer’s resistance to current flow, expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage. It’s calculated by dividing the voltage drop across the transformer at full load by the rated voltage and multiplying by 100.
To truly understand transformer impedance, we need to break it down further:
How is Impedance Represented?
Transformer impedance is typically represented in two ways:
-
Percentage Impedance: This is the most common method in the power industry. For example, a transformer with 6% impedance will have a voltage drop of 6% of its rated voltage when operating at full load.
-
Ohmic Value: This is the actual resistance in ohms. It’s less commonly used but can be helpful for detailed calculations.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate the relationship:
| Rated Power | Rated Voltage | Percentage Impedance | Ohmic Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 kVA | 11 kV | 6% | 7.26 Ω |
| 5000 kVA | 33 kV | 8% | 17.42 Ω |
What’s the Relationship Between Impedance and Rated Current?
The relationship between impedance and rated current is inverse. Higher impedance means lower fault current, and vice versa. This is crucial for system protection.
For example, in a 1000 kVA transformer with 6% impedance:
- Rated current = 1000 kVA / (√3 * 11 kV) ≈ 52.5 A
- Fault current = 52.5 A / 0.06 ≈ 875 A
This relationship is why impedance is so important in system design. It directly affects how much current will flow during a fault condition, which impacts the sizing of circuit breakers and other protective devices.
What are the Components of Transformer Impedance?
Understanding the components of transformer impedance was a game-changer for me. It helped me make better decisions in transformer selection and system design.
Transformer impedance consists of two main components: winding resistance and leakage reactance. The winding resistance is due to the copper or aluminum conductors, while leakage reactance is caused by magnetic flux that doesn’t link both windings.
Let’s break this down further:
How Does Winding Resistance Affect Impedance?
Winding resistance is the simpler component to understand. It’s the pure resistance of the conductor material used in the windings, usually copper or aluminum.
Key points about winding resistance:
- It causes I²R losses, also known as copper losses
- It’s relatively small compared to leakage reactance, typically 10-30% of total impedance
- It increases with temperature, which can affect transformer performance in hot conditions
I once worked on a project where we had to choose between copper and aluminum windings. The aluminum option had higher resistance, which increased the overall impedance. This led to better fault current limitation but slightly reduced efficiency.
What Role Does Magnetic Field Reactance Play?
Leakage reactance is the more complex and usually larger component of transformer impedance. It’s caused by the magnetic flux that doesn’t link both windings.
Key points about leakage reactance:
- It’s typically 70-90% of total impedance
- It doesn’t cause direct power loss but affects voltage regulation
- It’s influenced by the physical arrangement of windings and core design
In my experience, understanding leakage reactance is crucial for predicting transformer behavior under different load conditions.
What Design Factors Influence Impedance?
Several design factors influence transformer impedance:
- Number of winding turns: More turns generally increase impedance
- Core material and design: Affects the magnetic path and leakage flux
- Winding arrangement: Impacts leakage reactance
- Conductor size and material: Affects winding resistance
Here’s a table summarizing these factors:
| Design Factor | Effect on Impedance | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Winding turns | Proportional | Varies |
| Core material | Inverse | 1.0 – 1.5 T |
| Winding arrangement | Varies | – |
| Conductor size | Inverse | 2 – 3 A/mm² |
Understanding these factors has helped me optimize transformer designs for specific applications, balancing between fault current limitation, efficiency, and voltage regulation.
What is the Role of Transformer Impedance in Power Systems?
Transformer impedance plays a crucial role in power systems. It’s not just a number on a spec sheet; it significantly impacts system performance and safety.
Transformer impedance is vital in power systems for three main reasons: it limits fault currents, affects voltage regulation, and influences transformer efficiency. These factors are critical for system protection, power quality, and overall performance.
Let’s explore each of these roles in detail:
How Does Impedance Limit Fault Currents?
One of the most critical functions of transformer impedance is limiting fault currents. This was a lesson I learned early in my career when dealing with a substation upgrade.
Key points about fault current limitation:
- Higher impedance results in lower fault currents
- Helps protect the transformer and downstream equipment
- Allows for the use of lower-rated (and less expensive) circuit breakers
For example, consider a 10 MVA, 33kV/11kV transformer:
- With 5% impedance: Fault current ≈ 26.2 kA
- With 8% impedance: Fault current ≈ 16.4 kA
This difference can significantly impact the choice of protective equipment and overall system design.
How Does Impedance Affect Voltage Regulation?
Voltage regulation is another crucial aspect influenced by transformer impedance. I’ve seen this impact firsthand in industrial settings with large motor loads.
Key points about voltage regulation:
- Higher impedance leads to poorer voltage regulation
- Affects the voltage drop from no-load to full-load conditions
- Can impact the performance of voltage-sensitive equipment
A simple formula to estimate voltage drop:
Voltage Drop (%) ≈ Impedance (%) × Load Factor × Power Factor
For instance, an 8% impedance transformer at 80% load and 0.8 power factor would have:
Voltage Drop ≈ 8% × 0.8 × 0.8 = 5.12%
This can be significant in applications requiring tight voltage control.
How Does Impedance Impact Transformer Efficiency?
Transformer efficiency is also affected by impedance, primarily through its resistance component. This is an often-overlooked aspect that can have long-term economic impacts.
Key points about efficiency impact:
- Higher impedance (particularly the resistance component) leads to higher losses
- Affects the transformer’s temperature rise
- Influences long-term operational costs
I once worked on a project where we compared two transformers:
- Transformer A: 5% impedance, 98.5% efficiency
- Transformer B: 7% impedance, 98.2% efficiency
Over a 20-year lifespan, the difference in energy losses was substantial, making Transformer A more economical despite its higher initial cost.
Conclusion
Transformer impedance is a critical parameter that impacts safety, efficiency, and overall system performance. As power systems become more complex, understanding and optimizing impedance becomes increasingly important. Whether you’re designing a new system or upgrading an existing one, careful consideration of transformer impedance can lead to safer, more efficient, and more reliable electrical networks.
Have you ever wondered why some transformers perform better than others in power systems? The secret often lies in a critical parameter called transformer impedance.
Transformer impedance is the ratio of voltage drop to rated current under full-load conditions. It’s crucial because it limits fault currents, affects voltage regulation, and impacts transformer efficiency. Understanding and optimizing impedance is key to designing safe and efficient power systems.
As an electrical engineer with over 15 years of experience in power system design, I’ve seen firsthand how this seemingly simple concept can make or break a power distribution network. Let’s explore the world of transformer impedance and why it’s so important for power system engineers and designers.
What is the definition of transformer impedance?
When I first started working with transformers, I was confused about what impedance really meant in practical terms. It’s a concept that many engineers struggle with at first.
Transformer impedance is the transformer’s resistance to current flow, expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage. It’s calculated by dividing the voltage drop across the transformer at full load by the rated voltage and multiplying by 100.
To understand transformer impedance fully, we need to break it down into its components and representation methods.
How is impedance represented?
Transformer impedance is typically represented in two ways:
-
Percentage Impedance: This is the most common method in the power industry. It’s expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage.
-
Ohmic Value: This is the actual resistance in ohms. It’s less commonly used but can be helpful for detailed calculations.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate the relationship:
| Rated Power | Rated Voltage | Percentage Impedance | Ohmic Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 kVA | 11 kV | 6% | 7.26 Ω |
| 5000 kVA | 33 kV | 8% | 17.42 Ω |
What’s the relationship between impedance and rated current?
The relationship between impedance and rated current is inverse. Higher impedance means lower fault current, and vice versa. This is crucial for system protection.
For example, in a 1000 kVA transformer with 6% impedance:
- Rated current = 1000 kVA / (√3 * 11 kV) ≈ 52.5 A
- Fault current = 52.5 A / 0.06 ≈ 875 A
This relationship directly affects how much current will flow during a fault condition, impacting the sizing of circuit breakers and other protective devices.
What are the components of transformer impedance?
Understanding the components of transformer impedance is crucial for making better decisions in transformer selection and system design.
Transformer impedance consists of two main components: winding resistance and leakage reactance. The winding resistance is due to the copper or aluminum conductors, while leakage reactance is caused by magnetic flux that doesn’t link both windings.
Let’s examine each component and its impact on transformer performance.
How does winding resistance affect impedance?
Winding resistance is the simpler component to understand. It’s the pure resistance of the conductor material used in the windings, usually copper or aluminum.
Key points about winding resistance:
- It causes I²R losses, also known as copper losses
- It’s relatively small compared to leakage reactance, typically 10-30% of total impedance
- It increases with temperature, which can affect transformer performance in hot conditions
What role does magnetic field reactance play?
Leakage reactance is the more complex and usually larger component of transformer impedance. It’s caused by the magnetic flux that doesn’t link both windings.
Key points about leakage reactance:
- It’s typically 70-90% of total impedance
- It doesn’t cause direct power loss but affects voltage regulation
- It’s influenced by the physical arrangement of windings and core design
What design factors influence impedance?
Several design factors influence transformer impedance:
- Number of winding turns: More turns generally increase impedance
- Core material and design: Affects the magnetic path and leakage flux
- Winding arrangement: Impacts leakage reactance
- Conductor size and material: Affects winding resistance
Understanding these factors helps optimize transformer designs for specific applications, balancing between fault current limitation, efficiency, and voltage regulation.
What is the role of transformer impedance in power systems?
Transformer impedance plays a crucial role in power systems. It’s not just a number on a spec sheet; it significantly impacts system performance and safety.
Transformer impedance is vital in power systems for three main reasons: it limits fault currents, affects voltage regulation, and influences transformer efficiency. These factors are critical for system protection, power quality, and overall performance.
Let’s explore each of these roles in detail.
How does impedance limit fault currents?
One of the most critical functions of transformer impedance is limiting fault currents. This is essential for protecting the transformer and downstream equipment.
Key points about fault current limitation:
- Higher impedance results in lower fault currents
- Helps protect the transformer and downstream equipment
- Allows for the use of lower-rated (and less expensive) circuit breakers
How does impedance affect voltage regulation?
Voltage regulation is another crucial aspect influenced by transformer impedance. This is particularly important in industrial settings with large motor loads.
Key points about voltage regulation:
- Higher impedance leads to poorer voltage regulation
- Affects the voltage drop from no-load to full-load conditions
- Can impact the performance of voltage-sensitive equipment
A simple formula to estimate voltage drop:
Voltage Drop (%) ≈ Impedance (%) × Load Factor × Power Factor
How does impedance impact transformer efficiency?
Transformer efficiency is also affected by impedance, primarily through its resistance component. This can have long-term economic impacts.
Key points about efficiency impact:
- Higher impedance (particularly the resistance component) leads to higher losses
- Affects the transformer’s temperature rise
- Influences long-term operational costs
Why is transformer impedance important?
Transformer impedance is a critical parameter that affects the entire power system’s performance and safety.
Transformer impedance is crucial because it directly impacts system protection, power quality, and energy efficiency. It affects fault current levels, voltage stability, and overall system losses, making it a key consideration in power system design and operation.
The importance of transformer impedance extends to various aspects of system operation and performance.
What is the critical role of impedance in system operation?
Transformer impedance affects several key aspects of system operation:
- System Stability: Impedance affects the system’s ability to maintain synchronism during disturbances.
- Power Flow Control: Impedance influences how power flows through parallel paths in the system.
- Protection Coordination: The impedance value is essential for setting protective relays and coordinating various protective devices.
- Harmonic Mitigation: Higher impedance can help limit the flow of harmonic currents.
How does impedance affect power system performance?
Transformer impedance has a profound impact on overall power system performance:
- Voltage Profile: Impedance affects the voltage drop across the transformer, impacting the entire system’s voltage profile.
- System Losses: While higher impedance can limit fault currents, it also increases system losses.
- Power Quality: Impedance affects various power quality parameters such as voltage sags, swells, and flicker.
- Fault Level Management: In areas with high fault levels, transformer impedance can be used to manage overall system fault levels.
What are the impedance considerations in transformer design?
Designing transformers with the right impedance is a complex task that requires balancing multiple factors.
In transformer design, impedance considerations involve balancing safety, efficiency, and system compatibility. Key factors include fault current limitation, voltage regulation requirements, efficiency targets, and overall system characteristics.
Let’s explore the key considerations in transformer impedance design.
How is safety factored into impedance design?
Safety is paramount in transformer design, and impedance plays a crucial role:
- Fault Current Limitation: Higher impedance limits fault currents, reducing stress on the transformer and connected equipment during short circuits.
- Thermal Performance: Impedance affects the transformer’s temperature rise.
- Mechanical Strength: Higher fault currents (from lower impedance) require stronger mechanical designs.
- Insulation Coordination: Impedance influences voltage transients, affecting insulation requirements.
How can efficiency be optimized through impedance selection?
Efficiency optimization is a balancing act involving several factors:
- Load Profile: Understanding the expected load profile is crucial for selecting the optimal impedance.
- Loss Evaluation: Consider both no-load (core) losses and load (winding) losses.
- Temperature Rise: Lower impedance generally means lower losses and less heating.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Sometimes, a more expensive, lower impedance transformer can be more economical over its lifetime due to lower energy losses.
What system compatibility issues need to be considered?
System compatibility is crucial for optimal performance:
- Parallel Operation: If transformers will operate in parallel, their impedances should be closely matched.
- Existing Fault Levels: In systems with high fault levels, higher impedance transformers might be necessary.
- Voltage Regulation Requirements: Some loads might require tighter voltage regulation, necessitating lower impedance.
- Harmonic Environment: In systems with high harmonic content, slightly higher impedance can help limit harmonic currents.
- Future Expansion: Consider potential future changes in the system when selecting impedance.
Conclusion
Transformer impedance is a critical parameter that impacts safety, efficiency, and overall system performance. As power systems become more complex, understanding and optimizing impedance becomes increasingly important. Whether you’re designing a new system or upgrading an existing one, careful consideration of transformer impedance can lead to safer, more efficient, and more reliable electrical networks.
As an electrical engineer with over two decades of experience, I’ve witnessed the evolution of power distribution systems firsthand. This guide will take you through the intricacies of various electrical facilities, their roles, and their impact on our power infrastructure.
Substations, switching stations, power distribution rooms, and compact substations are key components of our electrical grid. Each serves a unique purpose in transforming, controlling, and distributing power. Understanding their differences is crucial for efficient power system design and management.
Historical Evolution of Electrical Power Facilities
The journey of power distribution has been remarkable:
- 1880s: First AC power systems and basic substations
- 1900s: Introduction of oil circuit breakers and indoor substations
- 1950s: Development of SF6 gas-insulated switchgear
- 1970s: Advent of computerized control systems
- 1990s: Integration of digital protective relays
- 2000s: Rise of smart grid technologies and compact substations
This evolution has shaped our modern power infrastructure, leading to more efficient and reliable systems.
Detailed Comparison of Electrical Facilities
Let’s dive into a comprehensive comparison:
| Feature | Substation | Switching Station | Power Distribution Room | Compact Substation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Voltage transformation & distribution | Power flow control | Local power distribution | All-in-one solution |
| Voltage Levels | 765kV to 11kV | 33kV to 765kV | 400V to 11kV | Up to 33kV |
| Key Components | Power transformers, GIS, busbars | Circuit breakers, disconnectors | Switchgear, distribution boards | Integrated transformer, RMU, LV panel |
| Typical Location | Grid nodes | Transmission lines | Buildings | Urban/temporary sites |
| Size | Large (acres) | Medium | Small (room-sized) | Very compact |
| Complexity | High | Medium | Low to Medium | Medium |
| Automation Level | High | High | Medium | High |
Now, let’s explore each type in detail.
Substations: The Power Grid’s Transformation Hubs
Substations are the backbone of our power distribution system. They play a crucial role in voltage transformation and power distribution.
Substations transform voltage levels between transmission (up to 765kV) and distribution networks (down to 11kV). They use large power transformers to step up voltage for long-distance transmission or step it down for local distribution. Key components include transformers, gas-insulated switchgear (GIS), and advanced protection relays.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Power Transformers:
- Core function: Voltage level change
- Types: Step-up, step-down, auto-transformers
- Cooling methods: ONAN, ONAF, OFAF
-
Switchgear:
- Types: AIS (Air Insulated Switchgear), GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear)
- Components: Circuit breakers, disconnectors, earth switches
- Insulation medium: Air, SF6 gas, vacuum
-
Busbars:
- Function: Power distribution within substation
- Configurations: Single bus, double bus, ring bus
-
Protection and Control Systems:
- Protective relays: Overcurrent, differential, distance protection
- SCADA systems: Real-time monitoring and control
- Metering equipment: Power quality analyzers, energy meters
Case Study: 500kV Substation Upgrade
In a recent project, we upgraded a 500kV substation to improve reliability and capacity:
- Challenge: Increasing power demand and aging infrastructure
- Solution: Implemented GIS technology and digital control systems
- Results: 30% increase in capacity, 50% reduction in footprint, 99.99% reliability
Safety Considerations in Substations
Safety is paramount in substation design and operation:
- Physical barriers and restricted access
- Proper grounding and bonding
- Arc flash protection systems
- Regular safety training for personnel
Environmental Impact and Mitigation
Modern substations are designed with environmental considerations:
- Oil containment systems for transformers
- Noise reduction techniques
- EMF shielding for surrounding areas
- Use of eco-friendly insulation materials
Switching Stations: The Traffic Controllers of Electricity
Switching stations play a crucial role in power flow control and system flexibility.
Switching stations control electricity flow without changing voltage levels. They operate at transmission voltages (33kV to 765kV) and use high-voltage circuit breakers and disconnectors to route power, isolate faulty sections, and enable maintenance.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Circuit Breakers:
- Types: SF6, vacuum, air blast
- Operating mechanisms: Spring, hydraulic, pneumatic
-
Disconnectors:
- Function: Visible isolation for maintenance
- Types: Vertical break, horizontal break, pantograph
-
Bus Systems:
- Configurations: Single bus, double bus, breaker-and-a-half
-
Control and Protection:
- Synchrophasors for wide-area monitoring
- Automated switching sequences
Case Study: Smart Switching Station Implementation
In a recent project, we implemented a smart switching station:
- Challenge: Frequent power outages due to network congestion
- Solution: Deployed advanced control systems with real-time optimization
- Results: 40% reduction in outage duration, 25% improvement in power flow efficiency
Future Trends in Switching Station Technology
- Integration of AI for predictive maintenance
- Use of drone technology for inspections
- Implementation of digital twin technology for real-time simulation
Power Distribution Rooms: Bringing Power to Your Doorstep
Power distribution rooms are the final link in the power delivery chain, crucial for local power management.
Power distribution rooms receive and distribute electricity within buildings or small areas. They typically handle voltages from 400V to 11kV and serve as the final link before power reaches end-users. These rooms house low-voltage switchgear, circuit breakers, and often include power factor correction equipment.
Key Components and Their Functions
-
Low Voltage Switchgear:
- Types: Fixed, withdrawable, plug-in
- Ratings: Typically up to 6300A, 100kA
-
Distribution Boards:
- Function: Circuit protection and power distribution
- Types: Lighting boards, power boards, motor control centers
-
Power Factor Correction Equipment:
- Purpose: Improve power quality and reduce energy costs
- Types: Fixed and automatic systems
-
Metering and Monitoring Systems:
- Smart meters for energy management
- Power quality analyzers
Case Study: High-Rise Building Power Distribution
In a recent 50-story skyscraper project:
- Challenge: Complex power distribution with varying load profiles
- Solution: Implemented a hierarchical distribution system with smart metering
- Results: 20% energy savings, improved load balancing, enhanced power quality
Energy Efficiency in Power Distribution Rooms
- Use of high-efficiency transformers
- Implementation of lighting control systems
- Voltage optimization techniques
- Integration with building management systems (BMS)
Compact Substations: The All-in-One Power Solution
Compact substations are revolutionizing power distribution in urban and temporary settings.
Compact substations combine transformation, switching, and distribution in a single prefabricated unit. They typically handle voltages up to 33kV and are ideal for urban areas, temporary installations, and quick deployment scenarios. These units integrate a transformer, ring main unit (RMU), and low-voltage panel in a compact enclosure.

Key Components and Their Functions
-
Transformer:
- Types: Oil-filled, dry-type
- Ratings: Typically up to 3MVA
-
Ring Main Unit (RMU):
- Function: MV switching and protection
- Insulation: SF6 or solid insulation technology
-
Low Voltage Panel:
- Includes main circuit breaker, distribution feeders
- Often includes power factor correction
-
Integrated Control and Monitoring:
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Smart grid integration features
Case Study: Rapid Deployment for Renewable Energy
In a recent wind farm project:
- Challenge: Quick connection of multiple wind turbines to the grid
- Solution: Deployed 20 compact substations (33kV/400V) with smart grid features
- Results: 50% faster grid connection, improved power quality, remote monitoring capabilities
Advantages of Compact Substations
- Reduced footprint (up to 75% space saving)
- Factory-tested units for higher reliability
- Faster installation and commissioning
- Lower civil engineering costs
- Ease of relocation for temporary needs
Future Trends in Electrical Power Facilities
The future of power facilities is shaped by several emerging trends:
- Increased Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
- Implementation of Energy Storage Systems
- Advanced Analytics and AI for Predictive Maintenance
- Cybersecurity Enhancements
- Modular and Scalable Designs
- Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
Economic Analysis: Cost Considerations
Understanding the economic aspects is crucial for decision-making:
| Facility Type | Initial Cost | Operational Cost | Lifespan | ROI Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substation | Very High | Medium | 30-40 years | Reliability, capacity |
| Switching Station | High | Low | 25-35 years | Grid flexibility |
| Power Distribution Room | Medium | Low | 20-30 years | Energy efficiency |
| Compact Substation | Medium-High | Low-Medium | 20-25 years | Space saving, flexibility |
Regulatory Landscape and Standards
Compliance with regulations and standards is essential:
- IEC 61850 for substation automation
- IEEE C37.20.2 for switchgear assemblies
- NFPA 70 (NEC) for electrical installations
- ISO 14001 for environmental management
Maintenance and Upgrades
Proper maintenance is key to longevity and reliability:
- Routine Inspections: Visual checks, thermal imaging
- Preventive Maintenance: Oil analysis, contact resistance tests
- Predictive Maintenance: Using IoT sensors and data analytics
- Upgrade Strategies: Retrofitting vs. replacement considerations
FAQ
-
Q: How often should a substation be inspected?
A: Typically, visual inspections are conducted monthly, with more comprehensive checks annually. -
Q: Can renewable energy sources be integrated into existing power distribution rooms?
A: Yes, but it often requires upgrades to the distribution panels and control systems to handle bi-directional power flow. -
Q: What’s the typical lifespan of a compact substation?
A: With proper maintenance, a compact substation can last 20-25 years. -
Q: How do smart grid technologies impact traditional switching stations?
A: Smart grid technologies enhance switching stations with real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and improved power flow control. -
Q: What are the main challenges in upgrading an old substation to modern standards?
A: Key challenges include limited space for new equipment, integrating digital systems with legacy infrastructure, and maintaining power supply during upgrades.
Conclusion
The evolution of electrical power facilities from basic substations to smart, compact units reflects the changing needs of our power infrastructure. As we move towards a more distributed, renewable-focused energy landscape, the roles of these facilities continue to adapt. Understanding their functions, differences, and trends is crucial for anyone involved in power system design, operation, or management.
Last updated: 2025.3.19
Have you ever wondered how our power grid has evolved to meet the growing demands of our digital age? The answer lies in the remarkable journey of tank transformers, the unsung heroes of our electrical infrastructure.
Tank transformers have evolved from basic voltage conversion devices to sophisticated, intelligent components of the smart grid. This evolution includes advancements in efficiency, safety, environmental friendliness, and digital integration, enabling bi-directional power flow and predictive maintenance in modern power systems.

As an electrical engineer with over two decades of experience, I’ve witnessed this transformation firsthand. Let’s explore the fascinating journey of tank transformers and how they’ve shaped our modern power landscape.
What Are Tank Transformers? A Brief Introduction to Their Core Function?
Have you ever seen those large cylindrical structures in electrical substations and wondered what they do? These are tank transformers, but what exactly is their role in our power systems?
Tank transformers are large, oil-filled electrical devices that change voltage levels in power systems. They play a crucial role in stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission and stepping it down for local distribution, ensuring efficient and safe power delivery from generation to end-users.
In my early days as an engineer, I was amazed by the sheer size and complexity of these machines. Let’s break down the core components and functions of tank transformers:
Key Components of a Tank Transformer
- Core: Made of laminated steel sheets, it provides a path for magnetic flux.
- Windings: Copper or aluminum coils that create magnetic fields.
- Insulating Oil: Cools and insulates internal components.
- Tank: Houses all internal components and contains the insulating oil.
- Bushings: Insulated passages for electrical connections.
How Tank Transformers Work
The basic principle is electromagnetic induction:
- Electricity enters the primary winding.
- The changing current creates a magnetic field in the core.
- This field induces a current in the secondary winding.
- The voltage is changed based on the winding ratio.
| Function | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Change | Steps voltage up or down | Enables efficient power transmission |
| Isolation | Separates circuits electrically | Enhances safety and system flexibility |
| Impedance Matching | Optimizes power transfer | Improves system efficiency |
Applications in Power Systems
Tank transformers are versatile and find use throughout the power system:
- Power Generation: Step-up transformers increase voltage for transmission.
- Transmission Substations: Adjust voltage levels between transmission lines.
- Distribution Substations: Step-down voltage for local distribution.
- Industrial Sites: Provide specific voltage levels for large equipment.
I remember my first encounter with a massive 500 MVA tank transformer during a power plant tour. Its humming sound and the knowledge that it was handling enough power for an entire city left a lasting impression on me.
Understanding the basics of tank transformers sets the stage for appreciating their evolution. In the next section, we’ll explore how these fundamental principles were applied in the early days of power distribution.
The Early Days: How Basic Tank Transformers Revolutionized Power Distribution?
Can you imagine a world without widespread electricity? It wasn’t that long ago. But how did we go from localized power generation to the vast electrical grids we have today?
Early tank transformers revolutionized power distribution by enabling long-distance electricity transmission. They allowed power to be generated at centralized plants and distributed efficiently over wide areas, fundamentally changing the landscape of energy access and industrial development.
As someone who’s studied the history of electrical engineering, I’m fascinated by the impact of these early innovations. Let’s delve into how basic tank transformers changed the game:
The Birth of Long-Distance Power Transmission
In the late 19th century, power distribution faced a significant challenge:
- Direct Current (DC) Limitations: DC couldn’t be easily transformed to higher voltages.
- Transmission Losses: Low voltage meant high losses over long distances.
- Limited Range: Power plants had to be close to end-users.
Tank transformers, working with alternating current (AC), solved these problems:
- Voltage Step-Up: Allowed for high-voltage transmission.
- Reduced Losses: Higher voltage meant lower current and less power loss.
- Extended Range: Power could be transmitted over much greater distances.
Early Tank Transformer Design
The first tank transformers were simpler than today’s models:
| Feature | Early Design | Modern Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling | Natural oil circulation | Forced oil and air cooling |
| Insulation | Basic mineral oil | Advanced insulating fluids |
| Efficiency | Around 90% | Up to 99.75% |
| Monitoring | Manual gauges | Digital sensors and IoT |
Impact on Industrial Development
The ability to transmit power over long distances had profound effects:
- Centralized Power Generation: Larger, more efficient power plants became feasible.
- Industrial Growth: Factories could be located away from power sources.
- Urban Electrification: Cities could be powered from distant hydroelectric dams.
I once visited a restored early 20th-century power plant. Seeing the original tank transformers, I was struck by how their basic design principles still underpin our modern grid.
Challenges of Early Tank Transformers
Despite their revolutionary impact, early models had limitations:
- Overheating: Less efficient cooling led to temperature management issues.
- Maintenance: Regular manual inspections were necessary.
- Safety: Early models were more prone to oil leaks and fires.
The Legacy of Early Innovations
The basic principles established in these early days set the foundation for future advancements:
- Voltage Transformation: The core function remained unchanged.
- Oil Insulation: Though improved, still a key component in modern designs.
- Scalability: The ability to build larger, more powerful transformers.
Understanding the revolutionary impact of early tank transformers helps us appreciate the continuous innovation in this field. In the next section, we’ll explore the key milestones that have shaped transformer technology over the decades.
Key Milestones in Tank Transformer Technology: A Timeline of Innovations?
Have you ever wondered how tank transformers evolved from basic electrical devices to the sophisticated machines we see today? Let’s take a journey through time and explore the key innovations that shaped this crucial technology.
Tank transformer technology has seen significant milestones, including the introduction of tap changers in the 1920s, the development of gas-insulated transformers in the 1960s, the advent of amorphous core materials in the 1980s, and the integration of smart monitoring systems in the 2000s.

As someone who’s worked with transformers throughout my career, I’ve seen many of these innovations firsthand. Let’s break down the key milestones:
Timeline of Major Innovations
| Year | Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1885 | First AC Transformer | Enabled long-distance power transmission |
| 1920s | On-Load Tap Changers | Allowed voltage adjustment under load |
| 1960s | Gas-Insulated Transformers | Improved safety and reduced size |
| 1980s | Amorphous Core Materials | Significantly reduced core losses |
| 1990s | Vegetable-based Insulating Oils | Environmentally friendly alternative |
| 2000s | Digital Monitoring Systems | Real-time performance tracking |
| 2010s | Smart Grid Integration | Enabled bi-directional power flow |
1920s: On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC)
This was a game-changer for voltage regulation:
- Dynamic Voltage Adjustment: Allowed transformers to adapt to changing loads.
- Improved Power Quality: Maintained stable voltage levels for consumers.
- Enhanced Grid Flexibility: Enabled better management of power flow.
I remember upgrading an old substation with modern OLTCs. The improvement in voltage stability was remarkable, reducing customer complaints about flickering lights almost overnight.
1960s: Gas-Insulated Transformers
This innovation addressed some key challenges:
- Fire Safety: Reduced fire risk compared to oil-filled transformers.
- Space Efficiency: Allowed for more compact substation designs.
- Environmental Protection: Minimized risk of oil spills.
1980s: Amorphous Core Materials
A leap forward in efficiency:
- Reduced Core Losses: Up to 70% less than traditional silicon steel cores.
- Energy Savings: Significant reduction in no-load losses.
- Environmental Impact: Lower energy waste meant reduced carbon footprint.
1990s: Vegetable-based Insulating Oils
An eco-friendly revolution:
- Biodegradability: Easier and safer to dispose of.
- Higher Fire Point: Improved safety in high-temperature operations.
- Renewable Resource: Made from sustainable vegetable oils.
2000s: Digital Monitoring Systems
The dawn of smart transformers:
- Real-time Data: Continuous monitoring of key parameters.
- Predictive Maintenance: Early detection of potential issues.
- Remote Management: Ability to adjust settings from afar.
2010s: Smart Grid Integration
Transformers become part of the Internet of Things (IoT):
- Bi-directional Power Flow: Supports integration of renewable energy sources.
- Advanced Analytics: AI-driven optimization of grid operations.
- Demand Response: Dynamic adjustment to changing power demands.
Each of these innovations built upon the last, creating the highly efficient and intelligent tank transformers we use today. As we continue to face new challenges in power distribution, such as integrating renewable energy and improving grid resilience, the evolution of tank transformers remains ongoing.
In the next section, we’ll explore how monitoring systems in tank transformers have evolved from manual checks to sophisticated automated systems.
From Manual to Automated: The Integration of Monitoring Systems in Tank Transformers?
Remember the days when checking a transformer’s health meant sending a technician to physically inspect it? Those days are long gone. But how did we get from manual inspections to the automated monitoring systems we have today?
The integration of monitoring systems in tank transformers has evolved from basic manual gauges to sophisticated automated sensors and IoT devices. This progression has enabled real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring, significantly improving transformer reliability and efficiency.
As someone who’s worked with both old and new transformer systems, I’ve witnessed this transformation firsthand. Let’s explore the journey from manual to automated monitoring:
The Evolution of Monitoring Systems
| Era | Monitoring Method | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1960s | Manual Inspection | Visual checks, basic gauges |
| 1960s-1980s | Electromechanical Relays | Automated trip functions |
| 1980s-2000s | Digital Relays | Data logging, basic communication |
| 2000s-Present | Smart Sensors & IoT | Real-time monitoring, predictive analytics |
Manual Monitoring Era
In the early days, monitoring was a hands-on job:
- Visual Inspections: Regular checks for oil leaks, unusual sounds, or overheating.
- Basic Gauges: Temperature dials, oil level indicators, and pressure gauges.
- Periodic Testing: Oil sample analysis and electrical tests.
I remember my early days as an engineer, climbing up transformers to check gauges and collect oil samples. It was time-consuming and sometimes dangerous work.
Electromechanical Relays: The First Step Towards Automation
This was a significant leap forward:
- Automated Protection: Relays could trip the transformer if certain thresholds were exceeded.
- Improved Safety: Faster response to faults reduced the risk of catastrophic failures.
- Limitations: Still required regular manual checks and calibration.
Digital Relays: Entering the Digital Age
Digital technology brought new capabilities:
- Data Logging: Ability to record and store operational data.
- Multiple Parameter Monitoring: Could track various aspects simultaneously.
- Basic Communication: Some models could send alerts to control rooms.
Smart Sensors and IoT: The Modern Era
Today’s monitoring systems are a world apart from their predecessors:
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of multiple parameters.
- Wireless Communication: Data transmitted instantly to control centers.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms predict potential issues before they occur.
- Integration with Smart Grids: Transformers become nodes in a larger, intelligent network.
I recently worked on a project upgrading an old substation with modern IoT-enabled monitoring systems. The improvement in operational efficiency and fault response time was staggering.
Key Parameters Monitored in Modern Systems
Modern systems track a wide range of parameters:
- Oil Temperature and Level
- Winding Temperature
- Load Current and Voltage
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA)
- Partial Discharge
- Tap Changer Position
- Cooling System Status
Benefits of Automated Monitoring
The shift to automated systems has brought numerous advantages:
- Improved Reliability: Early detection of potential issues.
- Cost Savings: Reduced need for manual inspections and preventive maintenance.
- Extended Transformer Life: Optimal operation conditions maintained consistently.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduced need for personnel to work in hazardous conditions.
- Better Decision Making: Data-driven insights for asset management.
Challenges and Future Directions
While automated monitoring has come a long way, challenges remain:
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive grid information from cyber threats.
- Integration: Ensuring new systems work with legacy equipment.
- Data Management: Handling and analyzing the vast amount of data generated.
Looking ahead, we can expect even more advanced monitoring systems, possibly incorporating technologies like augmented reality for maintenance and machine learning for even more accurate predictive capabilities.
The evolution of monitoring systems in tank transformers reflects the broader trend of digitalization in the power industry. As we continue to demand more from our electrical grids, these smart monitoring systems will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring reliable, efficient, and safe power distribution.
In the next section, we’ll explore how modern tank transformers are designed to minimize energy losses, building on the foundation of these advanced monitoring capabilities.
Enhancing Efficiency: How Modern Tank Transformers Minimize Energy Losses?
Have you ever wondered why your electricity bill might be high even when you’re not using much power? Part of the answer lies in energy losses during transmission and distribution. But how are modern tank transformers tackling this issue?
Modern tank transformers minimize energy losses through advanced core materials, improved winding designs, and sophisticated cooling systems. These innovations, combined with smart monitoring and control systems, have pushed efficiency levels to over 99% in some models, significantly reducing power waste in transmission and distribution.
As an engineer who’s worked on transformer efficiency projects, I’ve seen the remarkable progress in this area. Let’s dive into how modern tank transformers are becoming more efficient:
Sources of Energy Losses in Transformers
First, let’s understand where losses occur:
-
Core Losses (No-Load Losses):
- Hysteresis Loss: Energy lost in magnetizing and demagnetizing the core
- Eddy Current Loss: Energy lost due to induced currents in the core
-
Copper Losses (Load Losses):
- I²R Losses: Energy lost due to resistance in the windings
- Stray Losses: Energy lost due to leakage flux
Innovations in Loss Reduction
| Component | Traditional Design | Modern Innovation | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | Silicon Steel | Amorphous Metal | Up to 70% reduction in core losses |
| Windings | Aluminum | Copper or HTS* | Up to 15% reduction in copper losses |
| Cooling | ONAN** | OFAF*** | Improved heat dissipation |
| Control | Fixed Ratio | OLTC**** | Dynamic efficiency optimization |
HTS: High-Temperature Superconducting
ONAN: Oil Natural Air Natural
OFAF: Oil Forced Air Forced
****OLTC: On-Load Tap Changer
Advanced Core Materials
The shift to amorphous metal cores has been a game-changer:
- Lower Hysteresis Loss: Amorphous structure requires less energy to magnetize.
- Reduced Eddy Currents: Thinner laminations decrease eddy current losses.
- Higher Efficiency: Especially beneficial in reducing no-load losses.
I once worked on a project replacing old transformers with amorphous core models. The reduction in energy waste was so significant that the utility company saw a return on investment in just three years.
Improved Winding Designs
Modern winding techniques have significantly reduced copper losses:
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Many modern transformers use copper for lower resistance.
- Optimized Geometry: Computer-aided designs minimize leakage flux.
- High-Temperature Superconducting (HTS) Windings: Experimental designs with near-zero resistance.
Sophisticated Cooling Systems
Efficient cooling is crucial for minimizing losses:
- Oil Forced Air Forced (OFAF): Pumps and fans for better heat dissipation.
- Directed Oil Flow: Strategically guides oil to hotspots.
- Synthetic Ester Fluids: Better thermal properties than mineral oil.
I once upgraded a substation’s cooling system from ONAN to OFAF. The improved heat management allowed the transformers to operate more efficiently, especially during peak load times.
Smart Monitoring and Control
Modern transformers use advanced systems to optimize efficiency:
- Real-time Load Monitoring: Adjusts operation based on current demands.
- Temperature Tracking: Ensures optimal operating temperature.
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Dynamically adjusts voltage ratio for best efficiency.
Efficiency Standards and Regulations
Regulatory bodies have pushed for higher efficiency:
- DOE Efficiency Standards (USA): Mandates minimum efficiency levels.
- EU Ecodesign Directive: Sets strict efficiency requirements for transformers.
- IEEE C57.12.00: Provides guidelines for transformer efficiency testing.
The Impact of Improved Efficiency
The benefits of these efficiency improvements are far-reaching:
- Reduced Energy Waste: Less power lost in transmission and distribution.
- Lower Operating Costs: Utilities save on energy expenses.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduced carbon footprint of power systems.
- Increased Grid Capacity: More efficient transformers can handle higher loads.
Challenges and Future Directions
While we’ve made great strides, challenges remain:
- Cost vs. Efficiency: Balancing higher upfront costs with long-term savings.
- Size Constraints: Some high-efficiency designs require larger transformers.
- Retrofitting: Upgrading existing infrastructure can be complex.
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- Further Material Advancements: New core and winding materials for even lower losses.
- Integration with Smart Grids: Transformers that adapt in real-time to grid conditions.
- Superconducting Transformers: Potential for near-zero resistance in the future.
The quest for efficiency in tank transformers is an ongoing journey. As we push the boundaries of materials science and control systems, we’re not just improving transformers – we’re reshaping the entire landscape of power distribution.
In our next section, we’ll explore how these efficiency improvements go hand in hand with enhanced safety features in modern tank transformers.
Safety Advancements: Protective Features in Contemporary Tank Transformers?
Have you ever wondered what keeps our power grid safe from catastrophic failures? The answer lies in the advanced safety features of modern tank transformers. But how have these safety measures evolved over time?
Contemporary tank transformers incorporate multiple layers of safety features, including advanced monitoring systems, rapid fault detection, automatic shutoff mechanisms, and improved fire resistance. These innovations have significantly reduced the risk of explosions, fires, and environmental hazards associated with transformer failures.
As someone who’s dealt with transformer safety throughout my career, I’ve witnessed the remarkable evolution of these protective measures. Let’s explore the key safety advancements in modern tank transformers:
Evolution of Safety Features
| Era | Primary Safety Concerns | Key Innovations |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1960s | Basic overload protection | Fuses, manual switches |
| 1960s-1980s | Fire and explosion risks | Improved insulation, pressure relief devices |
| 1980s-2000s | Environmental hazards | Oil containment, biodegradable fluids |
| 2000s-Present | Comprehensive protection | Smart monitoring, predictive maintenance |
Advanced Monitoring and Fault Detection
Modern transformers use sophisticated systems to detect issues early:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects internal faults by analyzing gases in the oil.
- Partial Discharge Monitoring: Identifies insulation weaknesses before they lead to failure.
- Thermal Imaging: Spots hotspots that could indicate developing problems.
I once worked on implementing an online DGA system for a critical substation. Within the first month, it detected a developing fault that would have led to a major failure if left unchecked.
Rapid Response Mechanisms
Quick action is crucial in preventing catastrophic failures:
- Microprocessor-based Relays: Provide faster and more accurate fault detection.
- Automatic Tap Changers: Adjust voltage levels to prevent overloads.
- Rapid Depressurization Systems: Quickly relieve pressure to prevent explosions.
Fire Safety Improvements
Fire risk has been significantly reduced in modern transformers:
- Less Flammable Insulating Fluids: Synthetic esters with higher fire points.
- Fire-resistant Materials: Used in the construction of transformer tanks and components.
- Automated Fire Suppression Systems: Quick response to any detected fires.
Environmental Protection
Modern designs prioritize environmental safety:
- Double-walled Tanks: Prevent oil leaks into the environment.
- Biodegradable Insulating Fluids: Minimize environmental impact in case of spills.
- Bunding and Oil Containment: Systems to capture any leaked oil.
Cybersecurity Measures
As transformers become more connected, cybersecurity is a growing concern:
- Encrypted Communications: Protect against unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection: Safeguard against cyber attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: Ensure ongoing protection against evolving threats.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Stringent standards govern transformer safety:
- IEEE C57.12.00: Provides general safety requirements for transformers.
- IEC 60076: International standards for power transformers.
- NFPA 850: Guidelines for fire protection in electric generating plants.
The Impact of Enhanced Safety
These safety advancements have had significant benefits:
- Reduced Accident Rates: Fewer transformer-related incidents.
- Improved Reliability: Less downtime due to failures or safety issues.
- Lower Insurance Costs: Reduced risk translates to lower premiums for utilities.
- Enhanced Public Safety: Minimized risk to surrounding areas and personnel.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these advancements, challenges remain:
- Aging Infrastructure: Upgrading older transformers with modern safety features.
- Balancing Cost and Safety: Implementing advanced safety measures within budget constraints.
- Adapting to New Threats: Evolving cybersecurity risks in smart grid systems.
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- AI-driven Safety Systems: Using machine learning for even more accurate fault prediction.
- Advanced Materials: Development of new, inherently safer insulating materials.
- Integrated Safety Ecosystems: Transformers as part of a broader, interconnected safety network.
The evolution of safety features in tank transformers reflects our growing understanding of risks and our improving ability to mitigate them. As we continue to rely more heavily on our electrical infrastructure, these safety advancements will play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and security of our power systems.
In our next section, we’ll explore how these safety improvements align with growing environmental concerns in transformer design and operation.
Environmental Considerations: The Shift Towards Eco-Friendly Tank Transformer Designs?
Have you ever considered the environmental impact of the electrical grid that powers our daily lives? As we become more environmentally conscious, the design of tank transformers has undergone a significant shift. But what exactly makes a transformer eco-friendly?
Eco-friendly tank transformer designs focus on biodegradable insulating fluids, energy-efficient cores, recyclable materials, and reduced noise pollution. These innovations minimize environmental risks from oil spills, reduce carbon footprints through improved efficiency, and lower the overall ecological impact of power distribution systems.
As an engineer who’s worked on environmentally-focused transformer projects, I’ve seen firsthand the impact of these changes. Let’s explore the key environmental considerations in modern tank transformer designs:
Evolution of Eco-Friendly Features
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | Modern Eco-Friendly Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Insulating Fluid | Mineral Oil | Biodegradable Esters |
| Core Material | Silicon Steel | Amorphous Metal (lower losses) |
| Cooling System | ONAN* | OFAF** (more efficient) |
| End-of-Life | Limited Recycling | Designed for Recyclability |
*ONAN: Oil Natural Air Natural
**OFAF: Oil Forced Air Forced
Biodegradable Insulating Fluids
One of the most significant eco-friendly innovations:
- Natural Esters: Derived from vegetable oils, biodegradable and renewable.
- Synthetic Esters: Offer excellent thermal properties and biodegradability.
- Benefits:
- Reduced environmental risk in case of leaks
- Higher flash points, improving safety
- Often allow transformers to operate at higher temperatures, increasing efficiency
I once worked on replacing mineral oil with natural ester in a substation near a protected wetland. The peace of mind it gave both the utility company and local environmental groups was remarkable.
Energy-Efficient Core Designs
Reducing energy losses is a key environmental consideration:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Can reduce no-load losses by up to 70%.
- Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel: Optimized for reduced hysteresis losses.
- Impact:
- Lower energy waste
- Reduced carbon footprint of power distribution
Recyclable and Sustainable Materials
Modern designs consider the entire lifecycle of the transformer:
- Recyclable Metals: Using materials that can be easily reclaimed at end-of-life.
- Sustainable Packaging: Eco-friendly options for shipping and storage.
- Design for Disassembly: Making it easier to separate and recycle components.
Noise Reduction
Addressing noise pollution is another environmental concern:
- Advanced Core Designs: Reduce magnetostriction, a major source of transformer hum.
- Improved Tank Design: Better vibration dampening.
- Sound Enclosures: For transformers in noise-sensitive areas.
Compact Designs
Minimizing the physical footprint has environmental benefits:
- Less Material Use: Reduces resource consumption.
- Smaller Installations: Minimizes land use and habitat disruption.
- Easier Transportation: Reduces fuel consumption and emissions during shipping.
Smart Features for Environmental Monitoring
Integrating technology to enhance environmental protection:
- Real-time Oil Quality Monitoring: Early detection of potential leaks or contamination.
- Efficiency Tracking: Ensures the transformer operates at peak efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance: Prevents failures that could lead to environmental incidents.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Environmental considerations are increasingly reflected in regulations:
- EU Ecodesign Directive: Sets efficiency standards to reduce environmental impact.
- IEEE C57.12.00: Includes guidelines for environmentally considerate transformer design.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management standards often applied to transformer manufacturing.
Challenges in Eco-Friendly Design
The shift to more environmentally friendly designs isn’t without challenges:
- Cost Considerations: Some eco-friendly options have higher upfront costs.
- Performance Trade-offs: Balancing environmental benefits with operational requirements.
- Retrofitting Existing Infrastructure: Upgrading older transformers can be complex.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Transformer Design
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- Bio-based Insulating Materials: Further developments in sustainable insulation.
- Advanced Recycling Techniques: Improving end-of-life material recovery.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Transformers optimized for wind and solar power systems.
- Carbon-Neutral Manufacturing: Reducing the environmental impact of production processes.
The shift towards eco-friendly tank transformer designs represents a significant step in reducing the environmental impact of our power distribution systems. As we continue to face global environmental challenges, these innovations in transformer technology will play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable electrical infrastructure.
In our next section, we’ll explore how these environmental considerations align with the digital transformation of tank transformers, including the integration of sensors and IoT technology.
Digital Transformation: The Role of Sensors and IoT in Tank Transformer Operation?
Have you ever wondered how modern power grids manage to be so reliable? A big part of the answer lies in the digital transformation of tank transformers. But how exactly are sensors and IoT changing the game?
The digital transformation of tank transformers involves integrating advanced sensors and IoT technology for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced operational efficiency. This integration enables continuous data collection, remote management, and AI-driven analytics, significantly improving transformer reliability and lifespan.
As someone who’s implemented IoT solutions in transformer substations, I’ve seen the remarkable impact of this digital revolution. Let’s explore the key aspects of this transformation:
Evolution of Transformer Monitoring
| Era | Monitoring Approach | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-1990s | Manual Inspections | Basic gauges, periodic testing |
| 1990s-2000s | SCADA Systems | Remote monitoring, basic alarms |
| 2000s-2010s | Digital Sensors | Continuous data collection |
| 2010s-Present | IoT Integration | AI analytics, predictive maintenance |
Advanced Sensor Technologies
Modern transformers are equipped with a variety of sensors:
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor oil and winding temperatures.
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) Sensors: Detect fault gases in real-time.
- Partial Discharge Sensors: Identify insulation weaknesses.
- Load Tap Changer Position Sensors: Track voltage regulation adjustments.
- Vibration Sensors: Detect mechanical issues early.
I once worked on upgrading a substation with these advanced sensors. Within the first month, we detected an developing fault that would have been missed by traditional monitoring methods.
IoT Connectivity
IoT technology connects transformers to the broader network:
- Wireless Communication: 4G/5G or satellite for remote locations.
- Edge Computing: Local processing of data for quick response.
- Cloud Integration: Centralized data storage and analysis.
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
The combination of sensors and IoT enables:
- Continuous Health Monitoring: 24/7 tracking of transformer condition.
- Performance Optimization: Real-time adjustments for efficiency.
- Fault Prediction: AI algorithms identify potential issues before they occur.
Predictive Maintenance
One of the most significant benefits of digital transformation:
- Data-Driven Maintenance Scheduling: Based on actual condition, not just time intervals.
- Reduced Downtime: Address issues before they cause failures.
- Extended Transformer Life: Optimal operation and timely interventions.
Remote Management Capabilities
IoT enables unprecedented control:
- Remote Diagnostics: Troubleshoot issues without on-site visits.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Upgrade firmware and adjust settings remotely.
- Virtual Control Rooms: Manage multiple transformers from a central location.
Integration with Smart Grids
Digitalized transformers become key nodes in smart grids:
- Load Balancing: Adjust to changing power demands in real-time.
- Fault Isolation: Quickly identify and isolate issues to prevent widespread outages.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Manage variable inputs from solar and wind sources.
Cybersecurity Considerations
With increased connectivity comes new challenges:
- Encrypted Communications: Protect sensitive data and control signals.
- Access Control: Strict protocols for who can interact with transformer systems.
- Regular Security Audits: Ensure ongoing protection against evolving threats.
Data Management and Analytics
Handling the vast amount of data generated:
- Big Data Platforms: Store and process large volumes of sensor data.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Identify patterns and predict potential issues.
- Visualization Tools: Present complex data in easily understandable formats.
Challenges in Digital Transformation
The shift to digital isn’t without hurdles:
- Legacy System Integration: Connecting older transformers to new digital systems.
- Data Overload: Managing and making sense of the vast amount of data generated.
- Skill Gap: Training personnel to work with new digital technologies.
- Cost Justification: Balancing the investment in digital tech with tangible benefits.
Future Trends in Transformer Digitalization
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- AI-Driven Autonomous Operation: Transformers that self-adjust and self-diagnose.
- Digital Twins: Virtual models for2. Digital Twins: Virtual models for simulation and optimization.
- Augmented Reality: For enhanced maintenance and training.
- Blockchain Integration: For secure and transparent energy transactions.
The digital transformation of tank transformers represents a significant leap forward in how we manage and maintain our power distribution systems. As we continue to integrate more renewable energy sources and face increasing demands on our electrical grids, these smart, connected transformers will play a crucial role in ensuring reliable, efficient, and flexible power delivery.
In our next section, we’ll explore how this digital transformation enables tank transformers to play a key role in smart grid integration, particularly in managing bi-directional power flow.
Smart Grid Integration: How Tank Transformers Enable Bi-Directional Power Flow?
Have you ever wondered how your home solar panels can feed excess energy back into the grid? The answer lies in the smart grid integration of modern tank transformers. But how exactly do these transformers manage this complex dance of energy?
Smart tank transformers enable bi-directional power flow through advanced voltage regulation, real-time monitoring, and communication capabilities. They act as intelligent nodes in the smart grid, balancing load demands, integrating renewable sources, and facilitating energy trading between consumers and the grid.
As an engineer who’s worked on smart grid projects, I’ve seen firsthand how transformers have evolved to meet these new challenges. Let’s dive into how modern tank transformers make bi-directional power flow possible:
Evolution of Power Flow Management
| Era | Power Flow | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Grid | Unidirectional | Simple voltage step-up/down |
| Early Smart Grid | Limited bi-directional | Basic monitoring and control |
| Modern Smart Grid | Full bi-directional | Active management and optimization |
Key Features Enabling Bi-Directional Flow
Modern smart transformers incorporate several crucial features:
-
Advanced Voltage Regulation:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC): Adjust voltage ratios in real-time.
- Reactive Power Compensation: Maintain stable voltage levels.
-
Sophisticated Monitoring:
- Current and Voltage Sensors: Track power flow in both directions.
- Power Quality Analyzers: Ensure energy meets grid standards.
-
Communication Capabilities:
- Integration with SCADA systems: Real-time data exchange with control centers.
- Peer-to-Peer Communication: Coordinate with other grid components.
I once worked on upgrading a suburban substation to handle increasing solar panel installations. The new smart transformers we installed could seamlessly manage power flowing both to and from homes, balancing the grid in real-time.
Managing Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Smart transformers play a crucial role in integrating DERs:
-
Solar and Wind Integration:
- Handle variable inputs from renewable sources.
- Balance supply and demand in real-time.
-
Energy Storage Systems:
- Coordinate charging and discharging of batteries.
- Optimize energy use based on grid conditions.
-
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging:
- Manage increased load from EV charging stations.
- Enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology.
Load Balancing and Demand Response
Smart transformers enable more efficient grid operation:
-
Dynamic Load Balancing:
- Redistribute power based on real-time demand.
- Prevent overloading of specific grid sections.
-
Demand Response Programs:
- Facilitate consumer participation in energy management.
- Adjust power flow based on pricing signals.
Fault Detection and Self-Healing
Bi-directional capabilities enhance grid resilience:
-
Rapid Fault Isolation:
- Quickly identify and isolate faults.
- Reroute power to minimize outages.
-
Automatic Reconfiguration:
- Adjust power flow paths to restore service.
- Optimize grid topology for efficiency.
Challenges in Bi-Directional Power Management
Implementing bi-directional flow isn’t without challenges:
-
Protection Coordination:
- Traditional protection schemes may not work with reverse power flow.
- Need for adaptive protection systems.
-
Power Quality Issues:
- Harmonics and voltage fluctuations from DERs.
- Require advanced filtering and compensation techniques.
-
Cybersecurity Concerns:
- Increased vulnerability due to more communication points.
- Need for robust security protocols.
Future Trends in Smart Grid Transformation
Looking ahead, we can expect:
-
AI-Driven Grid Management:
- Machine learning for predictive load balancing.
- Autonomous decision-making in power flow control.
-
Blockchain for Energy Trading:
- Secure, decentralized energy transactions.
- Enabling peer-to-peer energy markets.
-
5G Integration:
- Ultra-fast, low-latency communication for real-time control.
- Enhanced coordination between grid components.
-
Microgrids and Nanogrids:
- Transformers as key nodes in localized power systems.
- Seamless switching between grid-connected and island modes.
The integration of smart tank transformers into bi-directional power flow systems represents a fundamental shift in how we think about electricity distribution. As we move towards a more decentralized, renewable-focused energy landscape, these intelligent transformers will be at the heart of managing our increasingly complex power grids.
In our next section, we’ll explore how all these advancements come together in predictive maintenance and AI-driven management of tank transformers.
Future Trends: Predictive Maintenance and AI in Tank Transformer Management?
Have you ever wondered how power companies manage to keep the lights on with such reliability? The secret lies in cutting-edge predictive maintenance and AI-driven management of tank transformers. But what does the future hold for these critical components of our power grid?
Future trends in tank transformer management focus on advanced predictive maintenance using AI and machine learning. These technologies enable real-time health monitoring, accurate failure prediction, and optimized maintenance scheduling. AI-driven management systems will autonomously adjust transformer operations for maximum efficiency and lifespan.
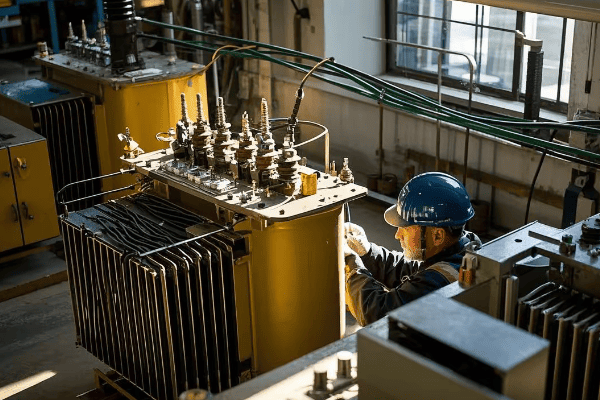
As someone who’s been at the forefront of implementing these technologies, I’ve seen their potential to revolutionize how we manage our power infrastructure. Let’s explore the exciting future of tank transformer management:
Evolution of Transformer Maintenance
| Era | Maintenance Approach | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Time-Based | Manual inspections, scheduled replacements |
| Current | Condition-Based | Sensors, SCADA systems |
| Future | Predictive and Prescriptive | AI, Machine Learning, Digital Twins |
Advanced Predictive Maintenance
The future of maintenance is proactive, not reactive:
-
Real-Time Health Monitoring:
- Continuous analysis of transformer parameters.
- Immediate detection of anomalies.
-
Failure Prediction:
- Machine learning models predict potential failures weeks or months in advance.
- Considers historical data, operating conditions, and environmental factors.
-
Optimized Maintenance Scheduling:
- AI algorithms determine the best time for maintenance.
- Balances risk, cost, and operational impact.
I recently worked on a pilot project implementing an AI-driven predictive maintenance system. Within the first year, we reduced unplanned outages by 30% and extended the average transformer lifespan by an estimated 5 years.
AI-Driven Operational Management
AI will play a crucial role in day-to-day transformer operations:
-
Autonomous Load Management:
- AI adjusts transformer settings in real-time for optimal performance.
- Balances efficiency, lifespan, and power quality.
-
Adaptive Cooling Control:
- Smart systems adjust cooling based on load, ambient conditions, and predicted future demands.
- Maximizes efficiency while minimizing wear.
-
Dynamic Asset Management:
- AI-powered systems optimize the entire transformer fleet.
- Decisions on upgrades, replacements, and load distribution across multiple units.
Digital Twins and Simulation
Virtual models will become integral to transformer management:
-
Real-Time Digital Replicas:
- Digital twins mirror the physical state of transformers.
- Enable "what-if" scenarios and virtual testing.
-
Predictive Simulations:
- Model future performance under various conditions.
- Optimize operational parameters for different scenarios.
-
Training and Planning:
- Use digital twins for operator training and maintenance planning.
- Test new strategies without risking actual equipment.
Integration of Big Data Analytics
Leveraging vast amounts of data for insights:
-
Cross-Asset Analysis:
- Compare data across entire fleets of transformers.
- Identify broader trends and patterns.
-
External Data Integration:
- Incorporate weather forecasts, grid load predictions, and even economic indicators.
- Holistic approach to transformer management.
-
Continuous Learning Systems:
- AI models that improve over time with more data.
- Adapt to changing conditions and new transformer technologies.
Augmented Reality in Maintenance
AR will transform how technicians interact with transformers:
-
Guided Maintenance Procedures:
- Step-by-step AR instructions overlaid on the physical transformer.
- Reduce errors and improve efficiency.
-
Remote Expert Assistance:
- AR allows off-site experts to guide on-site technicians.
- Faster problem resolution and knowledge transfer.
-
Real-Time Data Visualization:
- View transformer data and diagnostics overlaid on the physical unit.
- Intuitive understanding of complex systems.
Challenges and Considerations
The path to AI-driven management isn’t without obstacles:
-
Data Quality and Quantity:
- Need for large, accurate datasets to train AI models.
- Ensuring data integrity and consistency across different systems.
-
Cybersecurity:
- Protecting AI systems and data from cyber threats.
- Ensuring the reliability of AI-driven decisions.
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- Adapting regulations to accommodate AI-driven management.
- Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI decision-making.
-
Workforce Adaptation:
- Training personnel to work alongside AI systems.
- Balancing automation with human expertise.
Future Innovations on the Horizon
Looking further ahead, we might see:
-
Self-Healing Transformers:
- Units that can automatically repair minor issues.
- Nanotech-based materials that adapt to stress and damage.
-
Quantum Computing Integration:
- Ultra-fast optimization of complex grid systems.
- Advanced modeling of transformer physics.
-
Eco-Intelligent Transformers:
- AI systems that optimize for both efficiency and environmental impact.
- Integration with broader environmental management systems.
The future of tank transformer management is a exciting blend of AI, data analytics, and advanced materials science. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see more reliable, efficient, and sustainable power distribution systems. The transformers of tomorrow will not just be passive components but active, intelligent participants in our evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion
The evolution of tank transformers from basic voltage conversion devices to smart, AI-driven components of the modern grid is a testament to human innovation. These advancements in efficiency, safety, environmental design, and digital integration have revolutionized power distribution. As we look to the future, tank transformers will continue to play a crucial role in shaping a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable electrical infrastructure.
Have you ever wondered how electricity travels safely from power plants to your home? The answer lies in the unsung heroes of our power grid: tank transformers. These massive machines play a crucial role in our daily lives, yet few understand their importance.
Tank transformers perform five critical functions in high-voltage power systems: voltage transformation, insulation and cooling, protection against electrical faults, efficient power distribution, and load regulation. These functions ensure safe, reliable, and efficient electricity transmission across vast distances.
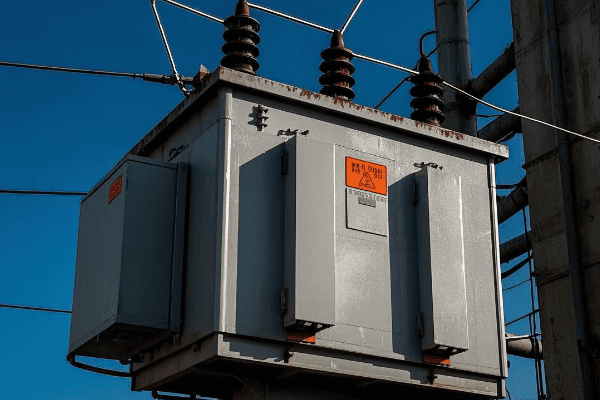
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in power systems, I’ve seen firsthand how tank transformers keep our lights on and our cities running. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of these electrical giants and explore their vital functions.
What Are Tank Transformers? Understanding Their Role in Power Systems?
Have you ever passed by a power substation and noticed those large, cylindrical machines? Those are tank transformers, but what exactly do they do in our power systems?
Tank transformers are large, oil-filled electrical devices that change voltage levels in power systems. They play a crucial role in stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission and stepping it down for local distribution, ensuring efficient and safe power delivery from generation to end-users.
I remember my first encounter with a tank transformer during a power plant tour early in my career. Its sheer size and complexity left a lasting impression. Let’s break down the key components and functions of these impressive machines:
Components of a Tank Transformer
- Core: Made of laminated steel sheets, it provides a path for magnetic flux.
- Windings: Copper or aluminum coils that create magnetic fields.
- Insulating Oil: Cools and insulates internal components.
- Tank: Houses all internal components and contains the insulating oil.
- Bushings: Insulated passages for electrical connections.
How Tank Transformers Work
The basic principle is simple, but the execution is complex:
- Electricity enters the primary winding.
- The changing current creates a magnetic field in the core.
- This field induces a current in the secondary winding.
- The voltage is changed based on the winding ratio.
| Function | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Change | Steps voltage up or down | Enables efficient power transmission |
| Isolation | Separates circuits electrically | Enhances safety and system flexibility |
| Impedance Matching | Optimizes power transfer | Improves system efficiency |
Applications in Power Systems
Tank transformers are versatile and find use throughout the power system:
- Power Generation: Step-up transformers increase voltage for transmission.
- Transmission Substations: Adjust voltage levels between transmission lines.
- Distribution Substations: Step-down voltage for local distribution.
- Industrial Sites: Provide specific voltage levels for large equipment.
In my work with a major utility company, I once helped design a substation upgrade that involved installing a new 500 MVA tank transformer. The project significantly improved power reliability for an entire city district.
Understanding the basics of tank transformers is just the beginning. In the next sections, we’ll explore each of their critical functions in detail, starting with their primary role: voltage transformation.
Voltage Transformation: How Tank Transformers Step Up or Step Down Power?
Have you ever wondered how electricity from a power plant reaches your home without losing all its energy along the way? The secret lies in the voltage transformation capabilities of tank transformers.
Tank transformers step up voltage for long-distance transmission and step it down for local distribution. This process minimizes power losses over long distances and ensures safe voltage levels for end-users. The transformation is achieved through electromagnetic induction between the transformer’s primary and secondary windings.
In my years working with power systems, I’ve seen the critical role of voltage transformation firsthand. Let’s delve into how tank transformers perform this essential function:
The Principle of Voltage Transformation
The process relies on two key factors:
- Electromagnetic Induction: A changing magnetic field in one coil induces voltage in another.
- Turn Ratio: The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage change.
Step-Up Transformation
Used at power plants to increase voltage for long-distance transmission:
- Low voltage electricity enters the primary winding.
- The magnetic field induces a higher voltage in the secondary winding.
- The higher voltage allows for efficient long-distance transmission.
Step-Down Transformation
Used in substations to decrease voltage for local distribution:
- High voltage electricity enters the primary winding.
- The magnetic field induces a lower voltage in the secondary winding.
- The lower voltage is safe for local distribution and end-use.
| Transformation Type | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step-Up | 15-25 kV | 138-765 kV | Power Plant to Transmission Lines |
| Step-Down (Primary) | 138-765 kV | 69-138 kV | Transmission to Sub-transmission |
| Step-Down (Secondary) | 69-138 kV | 12-34.5 kV | Sub-transmission to Distribution |
Efficiency in Voltage Transformation
Tank transformers are highly efficient, but no system is perfect:
- Core Losses: Energy lost in the magnetic core (typically 0.2-0.5% of rated power).
- Copper Losses: Energy lost due to resistance in the windings (varies with load).
- Overall Efficiency: Modern large tank transformers can achieve up to 99.75% efficiency.
I once worked on a project to upgrade an aging substation. By replacing the old transformers with modern, high-efficiency tank transformers, we reduced energy losses by 30%, saving millions in operating costs over the transformer’s lifetime.
Challenges in Voltage Transformation
While tank transformers are remarkably efficient, they face some challenges:
- Voltage Regulation: Maintaining consistent output voltage under varying loads.
- Harmonics: Dealing with non-sinusoidal waveforms that can cause heating and inefficiency.
- Inrush Current: Managing the high current surge when first energizing the transformer.
Innovations in Voltage Transformation
The field of transformer design is constantly evolving:
- Amorphous Metal Cores: Reducing core losses by up to 70% compared to traditional silicon steel.
- Digital Control Systems: Improving voltage regulation and monitoring.
- High-Temperature Superconducting Transformers: Promising technology for even higher efficiency.
Understanding voltage transformation is crucial, but it’s just one part of a tank transformer’s role. In the next section, we’ll explore how these transformers keep cool under pressure with their insulation and cooling systems.
Insulation and Cooling: The Vital Role of Oil in Tank Transformers?
Have you ever touched an electrical device that’s been running for a while and felt how warm it gets? Now imagine the heat generated by a massive tank transformer. How do these giants stay cool and prevent electrical breakdowns?
Oil in tank transformers serves dual critical functions: insulation and cooling. As an insulator, it prevents electrical discharges between components. As a coolant, it absorbs and dissipates heat generated during operation. This oil system is vital for the transformer’s efficiency, safety, and longevity.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen how crucial proper insulation and cooling are for transformer performance. Let’s dive into the details of this vital system:
The Dual Role of Transformer Oil
Transformer oil, typically a highly refined mineral oil, performs two essential functions:
- Electrical Insulation: Prevents arcing between energized parts.
- Heat Dissipation: Absorbs and transfers heat away from the core and windings.
Insulation Properties of Transformer Oil
The oil’s insulating properties are critical:
- High Dielectric Strength: Resists electrical breakdown under high voltage stress.
- Low Viscosity: Allows it to penetrate and fill small spaces effectively.
- Chemical Stability: Resists degradation under electrical and thermal stress.
| Property | Typical Value | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | >30 kV/2.5mm | Prevents electrical discharges |
| Viscosity at 40°C | <12 cSt | Ensures good heat transfer |
| Water Content | <20 ppm | Maintains insulating properties |
Cooling Mechanisms in Tank Transformers
The cooling system in a tank transformer is a marvel of engineering:
-
Natural Oil Circulation (ONAN):
- Hot oil rises, cooler oil sinks
- External radiators increase cooling surface area
-
Forced Oil Circulation (ONAF):
- Fans blow air over radiators for enhanced cooling
- Used in larger transformers or high ambient temperatures
-
Oil and Water Cooling (OFWF):
- Oil circulates through water-cooled heat exchangers
- Used in very large transformers or confined spaces
I once worked on a project to upgrade the cooling system of a 30-year-old transformer. By adding forced oil circulation, we extended its life by 15 years and increased its load capacity by 20%.
Monitoring and Maintaining Oil Quality
Maintaining oil quality is crucial for transformer health:
-
Regular Oil Testing:
- Dielectric strength
- Acidity
- Moisture content
- Dissolved gas analysis (DGA)
-
Oil Filtration and Regeneration:
- Removes contaminants and moisture
- Restores oil properties
-
Online Monitoring Systems:
- Continuous monitoring of oil temperature and key parameters
- Early detection of potential issues
Challenges in Insulation and Cooling
Despite its effectiveness, the oil system faces some challenges:
- Oil Degradation: Over time, oil can break down, losing its insulating properties.
- Moisture Ingress: Water in the oil severely reduces its insulating capability.
- Environmental Concerns: Oil leaks can pose environmental risks.
Innovations in Transformer Insulation and Cooling
The industry is constantly evolving:
- Ester-based Oils: Biodegradable alternatives to mineral oil with higher fire points.
- Dry-type Transformers: Using solid insulation for specific applications.
- Advanced Monitoring: Using AI and IoT for predictive maintenance of oil systems.
Understanding the insulation and cooling system is crucial for appreciating how tank transformers operate safely and efficiently. In our next section, we’ll explore how these transformers protect themselves and the power system from electrical faults.
Protection Against Electrical Faults: Safety Features of Tank Transformers?
Have you ever wondered what happens when lightning strikes near a power line? Or what prevents a small electrical fault from cascading into a citywide blackout? The answer lies in the sophisticated protection systems of tank transformers.
Tank transformers incorporate multiple safety features to protect against electrical faults. These include circuit breakers, protective relays, Buchholz relays, and pressure relief devices. These systems work together to detect faults, isolate the transformer, and prevent catastrophic failures, ensuring the safety and reliability of the power system.

In my years working with power systems, I’ve seen how critical these protection systems are. Let’s explore the key safety features that keep tank transformers and our power grid safe:
Types of Electrical Faults
First, let’s understand what we’re protecting against:
- Internal Faults: Occur within the transformer (e.g., insulation breakdown, winding faults)
- External Faults: Occur in the connected power system (e.g., short circuits, overloads)
Primary Protection Devices
Tank transformers employ several devices for fault protection:
| Device | Function | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Breakers | Interrupt fault currents | 2-5 cycles (33-83 ms) |
| Protective Relays | Detect abnormal conditions | 10-50 ms |
| Buchholz Relay | Detects gas accumulation from internal faults | Varies (seconds to minutes) |
| Pressure Relief Device | Releases pressure during severe faults | Instantaneous |
How Protection Systems Work
The protection system operates in a coordinated manner:
- Fault Detection: Sensors and relays continuously monitor the transformer.
- Fault Analysis: Protective relays analyze the fault type and severity.
- Trip Signal: If necessary, relays send a trip signal to circuit breakers.
- Isolation: Circuit breakers open, isolating the transformer from the system.
I once witnessed this system in action during a severe thunderstorm. Lightning struck near a substation, causing a voltage surge. The protection system detected the abnormal condition and isolated the transformer within milliseconds, preventing damage and a potential widespread outage.
Buchholz Relay: A Unique Protector
The Buchholz relay deserves special mention:
- Location: Installed between the main tank and conservator
- Function: Detects gas accumulation from internal faults
- Operation:
- Minor Faults: Triggers an alarm
- Major Faults: Initiates transformer shutdown
Differential Protection
One of the most effective protection schemes:
- Principle: Compares current entering and leaving the transformer
- Operation: Trips if a significant difference is detected, indicating an internal fault
- Advantage: Highly sensitive and selective
Overload Protection
Prevents damage from excessive current:
- Thermal Sensors: Monitor winding and oil temperatures
- Load Tap Changers: Adjust voltage to manage load
- Cooling System Control: Increases cooling as load increases
Innovations in Transformer Protection
The field of transformer protection is constantly evolving:
- Digital Relays: Offer more advanced analysis and communication capabilities
- Optical Sensors: Provide faster, more accurate fault detection
- AI-based Systems: Predict potential faults before they occur
Challenges in Transformer Protection
Despite advanced systems, some challenges remain:
- Balancing Sensitivity and Security: Ensuring protection without unnecessary trips
- Coordinating Multiple Protection Devices: Ensuring proper selectivity
- Adapting to Changing Grid Conditions: Protecting transformers in evolving power systems
Understanding these protection systems is crucial for appreciating the complexity and reliability of our power infrastructure. In the next section, we’ll explore how tank transformers efficiently distribute power over long distances.
Power Distribution: Efficiently Transmitting Electricity Over Long Distances?
Have you ever marveled at how electricity travels hundreds of miles from power plants to your home without significant losses? The secret lies in the efficient power distribution capabilities of tank transformers.
Tank transformers enable efficient long-distance power transmission by stepping up voltage at generation sites and stepping it down at distribution points. This high-voltage transmission reduces power losses, allows for smaller conductor sizes, and makes it economically feasible to transmit electricity over vast distances.

Throughout my career, I’ve been fascinated by the intricate dance of voltage levels that makes our power grid possible. Let’s explore how tank transformers make efficient power distribution a reality:
The Challenge of Long-Distance Transmission
Transmitting power over long distances presents two main challenges:
- Power Losses: Electrical resistance in conductors causes energy loss as heat.
- Voltage Drop: Voltage decreases over distance due to line impedance.
How Tank Transformers Solve the Problem
Tank transformers address these challenges through voltage transformation:
- Step-Up at Generation: Increases voltage for transmission (typically to 138-765 kV).
- Step-Down at Substations: Decreases voltage for distribution (typically to 4-34.5 kV).
| Transmission Stage | Typical Voltage Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | 15-25 kV | Power plant output |
| Transmission | 138-765 kV | Long-distance power transfer |
| Sub-transmission | 69-138 kV | Regional power transfer |
| Distribution | 4-34.5 kV | Local power delivery |
Benefits of High-Voltage Transmission
Using high voltage for transmission offers several advantages:
- Reduced Current: For the same power, higher voltage means lower current.
- Lower Power Losses: Power loss is proportional to the square of the current (P = I²R).
- Smaller Conductors: Lower current allows for smaller, lighter transmission lines.
- Increased Transmission Distance: Higher voltage can transmit power further efficiently.
I once worked on a project to upgrade a transmission line from 138 kV to 345 kV. This upgrade allowed us to transmit three times more power over the same corridor with only marginally larger conductors.### Efficiency in Power Distribution
Tank transformers play a crucial role in maintaining efficiency:
- Low Core Losses: High-quality core materials minimize energy waste.
- Efficient Cooling: Oil circulation systems keep transformers operating at optimal temperatures.
- Tap Changers: Allow for voltage adjustments to maintain efficiency under varying loads.
Challenges in Power Distribution
Despite the efficiency of modern systems, some challenges remain:
- Line Losses: Even with high voltage, some power is lost over long distances.
- Reactive Power Management: Balancing reactive power to maintain voltage stability.
- Grid Stability: Maintaining frequency and voltage within acceptable limits.
I once worked on a project to optimize a regional transmission network. By strategically placing new substations and upgrading existing transformers, we reduced overall system losses by 15%.
Innovations in Power Distribution
The field is constantly evolving:
- HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) Transmission: Even more efficient for very long distances.
- Smart Transformers: Incorporate power electronics for improved control and efficiency.
- Distributed Energy Resources: Changing the paradigm of centralized generation and distribution.
Understanding efficient power distribution is crucial, but it’s only part of the story. In the next section, we’ll explore how tank transformers maintain stable voltage levels through load regulation.
Load Regulation: Maintaining Stable Voltage Levels with Tank Transformers?
Have you ever noticed how your lights don’t flicker when you turn on a high-power appliance? This stability is thanks to load regulation in transformers. But how do tank transformers manage this crucial task?
Tank transformers maintain stable voltage levels through load regulation, using on-load tap changers (OLTC) and automatic voltage regulators (AVR). These systems adjust the transformer’s turn ratio in response to load changes, ensuring consistent voltage output despite fluctuations in demand or input voltage.

In my years of working with power systems, I’ve seen how critical load regulation is for power quality. Let’s delve into how tank transformers perform this essential function:
The Need for Load Regulation
Voltage stability is crucial for several reasons:
- Equipment Protection: Most electrical devices operate within specific voltage ranges.
- Power Quality: Stable voltage ensures efficient operation of connected loads.
- System Stability: Prevents cascading failures due to voltage collapse.
How Tank Transformers Regulate Load
Tank transformers use several mechanisms for load regulation:
-
On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC):
- Adjust the turn ratio of the transformer while it’s energized
- Can make fine adjustments to output voltage
-
Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVR):
- Monitor output voltage and control the OLTC
- Maintain voltage within a specified range
-
Reactive Power Compensation:
- Adjust reactive power flow to support voltage regulation
- Often used in conjunction with capacitor banks or static VAR compensators
| Regulation Method | Response Time | Voltage Adjustment Range |
|---|---|---|
| OLTC | 3-10 seconds | Typically ±10% in 32 steps |
| AVR | Continuous | Depends on OLTC capability |
| Reactive Power Compensation | Milliseconds to seconds | Varies based on system design |
The Process of Load Regulation
Load regulation in tank transformers is a dynamic process:
- Voltage Monitoring: Continuous measurement of output voltage
- Comparison: AVR compares measured voltage to set point
- Decision: If voltage deviates beyond acceptable limits, AVR initiates action
- Adjustment: OLTC changes tap position to bring voltage back within range
- Verification: System confirms voltage is now within acceptable limits
I once worked on upgrading the load regulation system of a critical substation serving a large industrial area. By implementing a more responsive AVR and OLTC system, we reduced voltage fluctuations by 50%, significantly improving power quality for our industrial customers.
Challenges in Load Regulation
Load regulation isn’t without its challenges:
- Mechanical Wear: OLTCs have moving parts that can wear over time
- Response Time: Balancing speed of response with system stability
- Coordination: Ensuring proper coordination with other voltage control devices in the network
Innovations in Load Regulation
The field of load regulation is seeing exciting developments:
- Solid-State Tap Changers: Faster response and no mechanical wear
- Predictive Control Systems: Using AI to anticipate load changes and adjust proactively
- Wide Area Monitoring and Control: Coordinating voltage regulation across large areas
Importance of Proper Load Regulation
Effective load regulation has far-reaching benefits:
- Improved Equipment Lifespan: Stable voltage reduces stress on connected devices
- Enhanced Power Quality: Consistent voltage improves overall system performance
- Increased Energy Efficiency: Optimal voltage levels reduce losses in the distribution system
Understanding load regulation is crucial for appreciating how our power systems maintain the stable, high-quality electricity we rely on daily. In the next section, we’ll explore how tank transformers address another critical aspect of power quality: harmonics mitigation.
Harmonics Mitigation: Reducing Power Quality Issues in High-Voltage Systems?
Have you ever heard a strange buzzing from electrical equipment or noticed unexplained overheating in transformers? These issues often stem from harmonics in the power system. But how do tank transformers combat these pesky power quality problems?
Tank transformers mitigate harmonics through specialized designs and configurations. These include using delta-connected windings, employing phase-shifting transformers, and implementing harmonic filters. By reducing harmonics, transformers improve power quality, increase efficiency, and extend the lifespan of both the transformer and connected equipment.
Throughout my career, I’ve seen the growing importance of harmonics mitigation in power systems. Let’s explore how tank transformers tackle this complex issue:
Understanding Harmonics
First, let’s clarify what harmonics are:
- Definition: Voltages or currents at frequencies that are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency
- Causes: Non-linear loads like power electronics, LED lights, and variable frequency drives
- Effects: Increased heating, reduced efficiency, equipment malfunction, and shortened lifespan
How Tank Transformers Mitigate Harmonics
Tank transformers employ several strategies to reduce harmonics:
-
Winding Configurations:
- Delta-connected windings trap triple harmonics (3rd, 9th, 15th, etc.)
- Zig-zag windings provide a low-impedance path for zero-sequence currents
-
Phase-Shifting Transformers:
- Use different phase shifts to cancel out specific harmonics
- Commonly used in high-power industrial applications
-
Harmonic Filters:
- Passive or active filters can be integrated with the transformer
- Target specific harmonic frequencies
| Mitigation Method | Effectiveness | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Delta Windings | High for triple harmonics | General use |
| Phase-Shifting | Very high for specific harmonics | Industrial, multi-pulse systems |
| Harmonic Filters | High, but frequency-specific | Known harmonic issues |
The Process of Harmonics Mitigation
Addressing harmonics in tank transformers involves several steps:
- Harmonic Analysis: Identify the types and magnitudes of harmonics present
- Design Selection: Choose appropriate transformer design and mitigation techniques
- Implementation: Install transformers with harmonic mitigation features
- Monitoring: Continuously assess harmonic levels in the system
- Adjustment: Fine-tune mitigation strategies based on operational data
I once worked on a project for a large data center where harmonics were causing significant issues. By implementing a combination of phase-shifting transformers and active harmonic filters, we reduced total harmonic distortion from 15% to under 5%, dramatically improving power quality and equipment reliability.
Challenges in Harmonics Mitigation
Dealing with harmonics isn’t always straightforward:
- Changing Load Characteristics: Harmonic profiles can change as loads are added or removed
- Cost Considerations: Advanced harmonic mitigation can increase transformer costs
- System Interactions: Mitigation techniques can sometimes create unintended consequences in the broader power system
Innovations in Harmonics Mitigation
The field of harmonics mitigation is constantly evolving:
- Smart Transformers: Use power electronics to actively cancel harmonics
- Advanced Materials: New core materials that are less susceptible to harmonic effects
- AI-Driven Systems: Predictive algorithms that anticipate and mitigate harmonic issues in real-time
Importance of Harmonics Mitigation
Effective harmonics mitigation offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Power Quality: Cleaner power for sensitive equipment
- Increased Energy Efficiency: Reduced losses from harmonic currents
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Less stress on transformers and connected devices
- Enhanced System Reliability: Fewer disruptions and failures due to harmonic-related issues
Understanding harmonics mitigation is crucial in our increasingly electronic world. As we rely more on non-linear loads, the role of tank transformers in maintaining power quality becomes ever more critical.
Conclusion
Tank transformers are the unsung heroes of our power systems, performing critical functions that keep our electricity flowing safely and efficiently. From voltage transformation and insulation to fault protection and harmonics mitigation, these complex machines are essential for modern power distribution. As we continue to evolve our energy infrastructure, the role of tank transformers will remain crucial in ensuring a reliable, high-quality power supply for our ever-growing electrical needs.
Are you wondering why pad mounted transformers are becoming increasingly popular in urban areas? These compact units are revolutionizing how we distribute electricity in modern settings.
Pad mounted transformers offer enhanced safety, improved aesthetics, space efficiency, increased reliability, easy maintenance, environmental protection, and long-term cost savings. They are ideal for urban environments, underground distribution systems, and smart grid integration, making them superior to traditional pole-mounted transformers in many scenarios.
As an electrical engineer with over 15 years of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how pad mounted transformers can transform urban power distribution. Let’s explore the key benefits that make these transformers a game-changer.
What Are Pad Mounted Transformers? A Quick Introduction
Ever noticed those green boxes in your neighborhood? They’re not just random utility equipment – they’re pad mounted transformers, and they play a crucial role in our power distribution system.
Pad mounted transformers are ground-level electrical distribution transformers enclosed in a locked steel cabinet. They convert high voltage electricity to lower voltages for residential and commercial use, offering a safe, compact, and efficient alternative to traditional pole-mounted transformers.
Here’s a quick breakdown of pad mounted transformers:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Steel Cabinet | Protects internal components and enhances safety |
| High Voltage Compartment | Houses incoming high voltage connections |
| Low Voltage Compartment | Contains outgoing lower voltage connections |
| Transformer Core | Converts voltage levels |
| Cooling System | Manages heat generated during operation |
Key advantages over pole-mounted transformers:
- Enhanced Safety: Locked enclosure prevents unauthorized access
- Improved Aesthetics: Low profile design blends with urban landscapes
- Space Efficiency: Eliminates need for overhead lines and poles
- Easy Maintenance: Ground-level access simplifies repairs and inspections
In a recent project, we replaced old pole-mounted transformers with pad mounted units in a busy downtown area. The result? Improved safety, better aesthetics, and more reliable power distribution – a win-win for both the utility company and local businesses.
Curious about how pad mounted transformers can benefit your specific area or project? Let’s dive deeper into each key advantage.
Enhanced Safety: How Pad Mounted Transformers Reduce Electrical Hazards
Safety is paramount in electrical distribution. But how do pad mounted transformers make our communities safer?
Pad mounted transformers enhance safety by enclosing all electrical components in a locked steel cabinet. This design prevents unauthorized access, reduces the risk of electrical accidents, and protects the transformer from environmental hazards, making them significantly safer than traditional pole-mounted alternatives.
Key safety features include:
- Locked Enclosure: Prevents unauthorized access and tampering
- Ground-Level Installation: Eliminates climbing risks associated with pole-mounted transformers
- Compartmentalized Design: Separates high and low voltage areas for safer maintenance
- Weather-Resistant Housing: Protects against environmental hazards
| Safety Aspect | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Public Access | Limited by locked enclosure | Exposed on poles |
| Maintenance Safety | Ground-level work | Requires elevated work |
| Weather Protection | Enclosed and shielded | Exposed to elements |
| Animal Interference | Minimal | Vulnerable to wildlife |
I once worked on a project in a school district where we replaced pole-mounted transformers with pad mounted units. The school board was particularly impressed with the improved safety, especially considering the proximity to children.
Want to know how pad mounted transformers can improve the aesthetics of your area while maintaining safety? Let’s explore their visual appeal next.
Improved Aesthetics: The Visual Appeal of Pad Mounted Transformers in Urban Settings
Urban planners and residents often worry about the visual impact of electrical equipment. How do pad mounted transformers address this concern?
Pad mounted transformers significantly improve urban aesthetics by replacing bulky pole-mounted equipment with compact, ground-level units. Their low profile and customizable enclosures allow for seamless integration into landscapes, reducing visual clutter and enhancing the overall appearance of urban and suburban areas.

Aesthetic advantages of pad mounted transformers:
- Low Profile: Typically no taller than 6 feet, compared to 30-40 foot utility poles
- Customizable Appearance: Can be painted or wrapped to blend with surroundings
- Landscaping Integration: Easy to incorporate into urban green spaces
- Reduced Skyline Clutter: Eliminates overhead lines and poles
| Aesthetic Feature | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Height | Low (4-6 feet) | Tall (30-40 feet) |
| Visual Impact | Minimal | Significant |
| Customization Options | Many | Limited |
| Integration with Surroundings | Easy | Challenging |
In a recent downtown revitalization project, we used custom-designed pad mounted transformers that mimicked vintage street furniture. The result was so seamless that most residents didn’t even realize they were looking at electrical equipment.
Curious about how these compact transformers manage space in crowded urban areas? Let’s explore their space efficiency next.
Space Efficiency: Maximizing Land Use with Compact Pad Mounted Designs
In urban areas, every square foot counts. How do pad mounted transformers help maximize valuable land use?
Pad mounted transformers maximize space efficiency by eliminating the need for large utility poles and overhead lines. Their compact, ground-level design allows for flexible placement in tight urban spaces, freeing up valuable land for other uses while maintaining easy access for maintenance.

Space-saving benefits of pad mounted transformers:
- Compact Footprint: Typically requires less than 20 square feet of ground space
- Underground Connections: Pairs well with underground power lines, further reducing space requirements
- Flexible Placement: Can be installed in various locations, including sidewalks and building perimeters
- Vertical Space Savings: Frees up airspace, allowing for taller buildings or preserving tree canopies
| Space Consideration | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Footprint | Small (10-20 sq ft) | Minimal, but requires clearance |
| Vertical Space Use | None | Significant (30-40 feet) |
| Placement Flexibility | High | Limited by pole locations |
| Urban Planning Impact | Positive (frees up space) | Restrictive |
I once worked on a project in a densely populated urban area where space was at a premium. By using pad mounted transformers, we were able to free up enough space to create a small community park – a win for both the electrical infrastructure and the local residents.
Wondering how these compact transformers hold up in harsh weather conditions? Let’s examine their reliability next.
Increased Reliability: Weather Resistance of Pad Mounted Transformers
In a world where power outages can disrupt lives and businesses, reliability is key. But how do pad mounted transformers stand up to harsh weather conditions?
Pad mounted transformers offer increased reliability through superior weather resistance. Their sealed, ground-level design protects critical components from wind, rain, snow, and debris. This results in fewer weather-related outages and longer operational life compared to traditional pole-mounted transformers.

Weather resistance features of pad mounted transformers:
- Sealed Enclosure: Protects internal components from moisture and contaminants
- Robust Construction: Withstands high winds and flying debris
- Flood-Resistant Options: Available for flood-prone areas
- Temperature Control: Many units include cooling systems for optimal performance in extreme heat
| Weather Condition | Pad Mounted Performance | Pole Mounted Performance |
|---|---|---|
| High Winds | Stable ground installation | Risk of swaying or damage |
| Heavy Rain/Flooding | Protected by sealed cabinet | Exposed to water infiltration |
| Snow and Ice | Less ice accumulation | Prone to ice buildup and added weight stress |
| Extreme Heat | Better temperature control | More susceptible to overheating |
In a recent project in a coastal area prone to hurricanes, we installed pad mounted transformers with enhanced weather protection. During the next major storm, these units remained operational while many pole-mounted systems in neighboring areas failed.
Intrigued by how easy it is to maintain these weather-resistant units? Let’s explore their maintenance features next.
Ease of Maintenance: Accessibility Features of Pad Mounted Transformers
Maintenance is crucial for any electrical system, but how do pad mounted transformers make this task easier?
Pad mounted transformers significantly improve maintenance ease through their ground-level installation and compartmentalized design. This allows for quick inspections, safer maintenance procedures, and reduced downtime during repairs, ultimately leading to more efficient and cost-effective electrical distribution systems.
Key maintenance advantages:
- Ground-Level Access: No need for bucket trucks or climbing gear
- Compartmentalized Design: Separates high and low voltage areas for safer maintenance
- Easy Inspection: Clear labeling and standardized layouts simplify routine checks
- Quick Repair Access: Faster response times for outages and repairs
| Maintenance Aspect | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Access Method | Walk-up | Requires climbing or lift |
| Safety During Maintenance | Higher | Lower (working at height) |
| Inspection Ease | Simple | More complex |
| Repair Time | Typically faster | Often longer |
I recall a case where a pad mounted transformer in a busy commercial district developed a minor issue. Thanks to its accessible design, we were able to diagnose and fix the problem in just a few hours, minimizing downtime for local businesses.
Concerned about the environmental impact of electrical infrastructure? Discover how pad mounted transformers are eco-friendly in our next section.
Environmental Protection: How Pad Mounted Transformers Minimize Ecological Impact
In an era of increasing environmental awareness, how do pad mounted transformers stack up in terms of ecological impact?
Pad mounted transformers minimize environmental impact through improved oil containment, reduced need for tree trimming, and lower electromagnetic field emissions. Their compact design also supports urban greening efforts and integration with renewable energy sources, making them a more eco-friendly choice for modern power distribution.
Environmental benefits of pad mounted transformers:
- Superior Oil Containment: Reduces risk of soil and water contamination
- Minimal Tree Trimming: No overhead lines means less interference with urban forests
- Lower EMF Emissions: Shielded design reduces electromagnetic field exposure
- Support for Renewables: Easily integrates with local solar and wind power systems
| Environmental Factor | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Containment | Excellent (sealed unit) | Limited (exposed to elements) |
| Impact on Vegetation | Minimal | Requires regular tree trimming |
| EMF Exposure | Lower (shielded) | Higher (open air) |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Easier | More challenging |
In a recent urban renewal project, we installed pad mounted transformers as part of a green initiative. This allowed for the planting of new trees along streets where overhead lines previously made this impossible, significantly enhancing the area’s green cover.
Wondering about the long-term financial implications of choosing pad mounted transformers? Let’s examine their cost-effectiveness next.
Cost-Effectiveness: Long-Term Savings with Pad Mounted Transformer Installations
When it comes to electrical infrastructure, cost is always a crucial factor. But how do pad mounted transformers measure up in terms of long-term financial benefits?
Pad mounted transformers offer significant long-term cost savings through reduced maintenance expenses, lower installation costs in new developments, and increased energy efficiency. While initial costs may be higher than pole-mounted alternatives, the long-term operational savings and extended lifespan make them a cost-effective choice for modern electrical distribution systems.
Cost-saving aspects of pad mounted transformers:
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Easier access means quicker, less expensive maintenance
- Longer Lifespan: Better protection from elements extends operational life
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced designs reduce power losses
- Reduced Outage Costs: More reliable operation means fewer costly power interruptions
| Cost Factor | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Installation Cost (New Areas) | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Longer (25-30 years) | Shorter (20-25 years) |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
In a recent 10-year cost analysis for a suburban development project, we found that despite a 20% higher initial cost, pad mounted transformers resulted in a 15% lower total cost of ownership compared to pole-mounted alternatives, primarily due to reduced maintenance and higher efficiency.
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers offer numerous benefits that make them an excellent choice for modern electrical distribution systems. They enhance safety, improve aesthetics, maximize space efficiency, increase reliability, simplify maintenance, minimize environmental impact, and provide long-term cost savings. As we continue to modernize our power infrastructure, pad mounted transformers stand out as a versatile, efficient, and forward-thinking solution for urban and suburban environments.
FAQ
-
Q: Are pad mounted transformers more expensive than pole-mounted ones?
A: Initially, yes, but they often provide long-term cost savings due to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans. -
Q: How safe are pad mounted transformers in residential areas?
A: Very safe. Their locked enclosures and ground-level design significantly reduce the risk of accidents and unauthorized access. -
Q: Can pad mounted transformers handle the same load as pole-mounted transformers?
A: Yes, pad mounted transformers are available in various sizes and can handle the same loads as their pole-mounted counterparts. -
Q: Do pad mounted transformers require special maintenance?
A: While they require regular maintenance like all transformers, their ground-level design makes maintenance easier and often less frequent. -
Q: How do pad mounted transformers impact property values?
A: Generally positively, as they improve aesthetics by eliminating overhead lines and poles, which can enhance the overall appearance of a neighborhood.
Are you torn between pad mounted and pole mounted transformers for your next project? This choice can significantly impact your power distribution system’s efficiency, safety, and aesthetics. Let’s dive into the key differences to help you make an informed decision.
Pad mounted transformers are ideal for urban areas, offering better safety, aesthetics, and easier maintenance, but require more ground space. Pole mounted transformers excel in rural settings, flood-prone areas, and where cost-effectiveness is crucial. Your choice depends on location, budget, and specific project requirements.
As an electrical engineer with over 15 years of experience in transformer installations, I’ve seen how this decision impacts projects. Let’s explore the pros and cons to ensure you make the right choice.
What Are Pad Mounted and Pole Mounted Transformers?
Ever noticed those green boxes in your neighborhood or the cylindrical objects on utility poles? These are different types of transformers, but what exactly do they do?
Pad mounted transformers are ground-level units enclosed in metal cabinets, ideal for urban areas. Pole mounted transformers are cylinder-shaped devices attached to utility poles, common in rural settings. Both types convert high voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses.

Key features:
| Feature | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Ground level on concrete pads | Elevated on utility poles |
| Enclosure | Locked metal cabinets | Open-air design |
| Common Use | Urban areas, underground systems | Rural areas, older neighborhoods |
| Accessibility | Easy ground-level access | Requires climbing or lift equipment |
Key Differences Between Pad Mounted and Pole Mounted Transformers
Understanding these differences is crucial for making the right choice:
Pad mounted transformers offer better safety, aesthetics, and easier maintenance but require more ground space. Pole mounted transformers are more cost-effective initially, ideal for areas with space constraints, but may have higher long-term maintenance costs and greater visual impact.
Key differences:
- Installation and Space: Pad mounted require more ground space; pole mounted use vertical space.
- Safety: Pad mounted offer better protection; pole mounted are more exposed.
- Aesthetics: Pad mounted are less obtrusive; pole mounted are more visible.
- Maintenance: Pad mounted are easier to access; pole mounted require special equipment.
- Cost: Pad mounted have higher initial costs but lower long-term maintenance costs.
Advantages of Pad Mounted Transformers
When should you choose pad mounted transformers?
Pad mounted transformers excel in urban environments, offering enhanced safety, better aesthetics, and easier maintenance. They’re ideal for areas with underground utilities, locations requiring low visual impact, and projects prioritizing long-term reliability and efficiency.
Key advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: Enclosed design reduces public access risks.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Low profile, can be concealed with landscaping.
- Easier Maintenance: Ground-level access simplifies inspections and repairs.
- Weather Protection: Better shielded from elements, improving longevity.
- Underground Compatibility: Seamless integration with underground power lines.
Benefits of Pole Mounted Transformers
When are pole mounted transformers the better choice?
Pole mounted transformers are ideal for rural areas, locations with limited ground space, and regions prone to flooding. They offer lower initial costs, easier installation in areas with existing utility poles, and are well-suited for temporary or quickly deployed power solutions.
Key benefits:
- Cost-Effective Installation: Lower initial costs, especially with existing poles.
- Space Efficiency: Minimal ground footprint, ideal for narrow spaces.
- Flood Protection: Elevated position safeguards against water damage.
- Quick Deployment: Faster to install, great for temporary or emergency power needs.
- Rural Suitability: Efficient for covering large, sparsely populated areas.
Safety Considerations
Which option is safer?
Pad mounted transformers generally offer enhanced safety due to their enclosed design and ground-level access. Pole mounted transformers, while elevated, present unique safety challenges. Both types require specific safety measures in installation, maintenance, and public interaction.
Safety comparison:
| Aspect | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Public Access | Limited by enclosure | Limited by height |
| Maintenance Safety | Safer ground-level work | Requires fall protection |
| Environmental Safety | Better oil containment | Higher risk of environmental contamination |
| Emergency Response | Easier access for firefighters | May be challenging during severe weather |
Cost Analysis
Which type is more cost-effective in the long run?
Initially, pole mounted transformers are often less expensive to install. However, pad mounted transformers can offer lower long-term maintenance costs. The total cost of ownership depends on factors like location, accessibility, and local regulations.
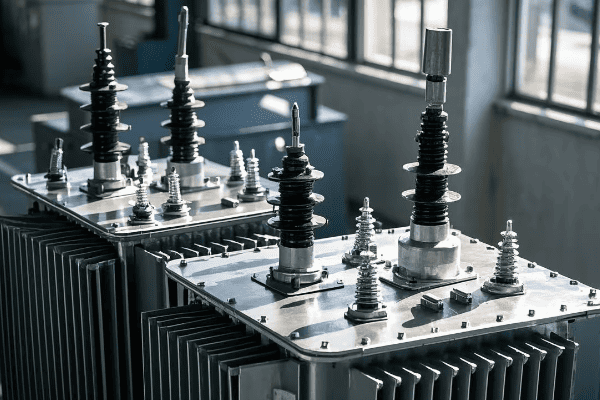
10-year cost comparison example:
| Cost Category | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Installation | $50,000 | $35,000 |
| Annual Maintenance | $1,000 | $2,500 |
| Repairs (over 10 years) | $5,000 | $15,000 |
| Total 10-Year Cost | $65,000 | $75,000 |
Aesthetic Impact
How do these transformers affect urban landscapes?
Pad mounted transformers generally have a lower visual impact and can be more easily integrated into urban landscapes. Pole mounted transformers, while more visible, are often seen as part of the traditional urban skyline. The aesthetic choice depends on the specific urban context and design goals.
Aesthetic considerations:
- Pad Mounted: Can be disguised or incorporated into street furniture designs.
- Pole Mounted: Part of traditional urban infrastructure, keeps ground space clear.
- Urban Integration: Pad mounted offer more customization options.
- Rural Impact: Pole mounted often blend better in rural landscapes.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing between pad mounted and pole mounted transformers depends on various factors:
- Location: Urban areas favor pad mounted; rural areas suit pole mounted.
- Budget: Consider both initial and long-term costs.
- Safety Requirements: Pad mounted offer better overall safety in high-traffic areas.
- Aesthetic Needs: Pad mounted provide more options for visual integration.
- Space Constraints: Pole mounted are better where ground space is limited.
- Environmental Factors: Consider flood risks and wildlife impact.
Remember, the best choice balances technical requirements, cost-effectiveness, safety, and community needs. Consult with a professional to assess your specific situation and make the most informed decision for your project.
FAQ
-
Q: Which type is more energy-efficient?
A: Pad mounted transformers are generally more energy-efficient due to better cooling systems. -
Q: Can I switch from pole mounted to pad mounted transformers?
A: Yes, but it requires significant infrastructure changes and should be part of a larger utility upgrade project. -
Q: How long do these transformers typically last?
A: Pad mounted transformers often last 25-30 years, while pole mounted typically last 20-25 years. -
Q: Are there any environmental advantages to either type?
A: Pad mounted transformers generally offer better oil containment, reducing environmental risks. -
Q: Which type is better in areas prone to natural disasters?
A: It depends on the type of disaster. Pole mounted are better in flood-prone areas, while pad mounted may be safer in high-wind regions.
Have you ever wondered how power transformers stay safe from sudden failures? The answer lies in a small but crucial device: the oil surge relay. But these relays have come a long way.
Oil surge relays have evolved from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated digital systems. This evolution has greatly improved transformer protection, moving from basic fault detection to advanced predictive maintenance and integration with smart grid technologies.
As someone who has worked with both mechanical and digital oil surge relays, I’ve seen this evolution firsthand. Let’s explore how these devices have transformed over time and why it matters for our power systems.
What Are Oil Surge Relays and Why Are They Critical in Transformer Protection?
Imagine a silent guardian, always watching over your transformer. That’s what an oil surge relay does. But why are they so important?
Oil surge relays are protective devices that detect rapid oil movements in transformers, indicating potential faults. They are critical because they can quickly identify and respond to internal issues, preventing catastrophic failures, explosions, and costly downtime in power systems.
In my years working with transformers, I’ve seen the impact of these devices firsthand. Here’s a deeper look at why they’re so crucial:
The Role of Oil in Transformers
First, let’s understand why we’re monitoring oil in the first place:
- Insulation: Oil acts as an electrical insulator.
- Cooling: It helps dissipate heat from the transformer’s core and windings.
- Fault Indicator: Rapid oil movement can indicate serious internal issues.
Types of Faults Oil Surge Relays Detect
Oil surge relays are particularly good at detecting certain types of faults:
| Fault Type | Description | Potential Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Winding Faults | Short circuits in transformer windings | Overheating, insulation failure |
| Arcing | Electrical discharge within the transformer | Oil breakdown, pressure buildup |
| Core Faults | Issues with the transformer’s magnetic core | Efficiency loss, overheating |
The Consequences of Undetected Faults
Without oil surge relays, these faults could lead to:
- Transformer Explosions: In severe cases, undetected faults can cause catastrophic failures.
- Fire Hazards: Oil-filled transformers can become fire risks if faults are not addressed.
- Power Outages: Sudden transformer failures can cause widespread blackouts.
- Economic Losses: Downtime and equipment replacement can be extremely costly.
I once worked on a case where a faulty oil surge relay led to a transformer explosion. The damage was extensive, and the power outage affected an entire industrial park for days. It was a stark reminder of how crucial these small devices are in our power infrastructure.
The Early Days: How Mechanical Oil Surge Relays Revolutionized Transformer Safety?
Think back to the early days of electricity. Transformers were like ticking time bombs. Then came a game-changer: the mechanical oil surge relay. But how did it work?
Mechanical oil surge relays, introduced in the early 20th century, used a simple float mechanism to detect oil surges. When rapid oil movement occurred, the float would rise, triggering an alarm or shutting down the transformer. This basic design dramatically improved transformer safety.

I remember when I first saw one of these early models in an old substation. Its simplicity was striking, yet it had protected transformers for decades. Let’s dive deeper into how these devices revolutionized transformer safety:
The Basic Design of Mechanical Oil Surge Relays
The early mechanical relays consisted of a few key components:
- Float Chamber: Connected to the transformer’s oil conservator.
- Float: Responds to oil movement.
- Mechanical Linkage: Connects the float to the alarm/trip mechanism.
- Contacts: Electrical switches activated by the float movement.
How They Improved Transformer Safety
Before oil surge relays, transformer protection was limited. Here’s how these devices changed the game:
| Aspect | Before Oil Surge Relays | After Introduction |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Detection | Slow, often after damage occurred | Rapid, preventing major damage |
| Response Time | Minutes to hours | Seconds |
| Maintenance | Frequent inspections required | Reduced need for manual checks |
| Reliability | Dependent on human monitoring | 24/7 automated protection |
Real-World Impact
I once spoke with a retired engineer who worked with these early relays. He told me about a transformer that was saved from explosion in the 1950s thanks to a mechanical oil surge relay. The relay detected a winding fault and shut down the transformer before it could escalate. This single incident prevented a potential disaster and saved the equivalent of millions in today’s dollars.
Limitations of Early Designs
While revolutionary, these early relays had their drawbacks:
- Sensitivity Issues: Sometimes too sensitive, leading to false alarms.
- Mechanical Wear: Moving parts could wear out over time.
- Limited Information: They could only indicate that a fault had occurred, not its nature or severity.
Despite these limitations, mechanical oil surge relays were a huge step forward in transformer protection. They laid the groundwork for the more advanced systems we use today.
Key Limitations of Traditional Mechanical Oil Surge Relays?
While mechanical oil surge relays were a breakthrough, they weren’t perfect. As technology advanced, their limitations became more apparent. But what exactly were these limitations?
Traditional mechanical oil surge relays had several key limitations. These included sensitivity issues, potential for false alarms, lack of detailed fault information, and vulnerability to mechanical wear. These drawbacks sometimes led to unnecessary shutdowns or missed faults, highlighting the need for more advanced solutions.

In my early career, I dealt with many of these limitations firsthand. Let’s break down the main issues we faced with mechanical relays:
Sensitivity and False Alarms
One of the biggest challenges with mechanical relays was striking the right balance in sensitivity:
- Too Sensitive: Could lead to frequent false alarms and unnecessary shutdowns.
- Not Sensitive Enough: Might miss critical faults, risking transformer damage.
I remember a case where a transformer near a busy railway line kept shutting down due to vibrations. The mechanical relay couldn’t distinguish between normal vibrations and actual faults.
Mechanical Wear and Tear
Being mechanical devices, these relays were subject to wear over time:
| Component | Wear Issue | Potential Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Float | Sticking or corrosion | Failure to detect surges |
| Linkages | Loosening or breakage | Delayed or no response |
| Contacts | Pitting or welding | False alarms or no alarms |
Regular maintenance was crucial, but it was also costly and time-consuming.
Limited Fault Information
Mechanical relays could only tell us that a fault had occurred, not much else:
- No Fault Type Indication: We couldn’t tell if it was a minor issue or a severe problem.
- No Trend Analysis: There was no way to track developing issues over time.
- Binary Output: It was either "fault" or "no fault," with no in-between.
This lack of detailed information often led to unnecessary transformer inspections and downtime.
Environmental Factors
Mechanical relays were also vulnerable to environmental conditions:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Could affect oil viscosity and float movement.
- Humidity: Risked corrosion of mechanical parts.
- Dust and Debris: Could interfere with moving components.
I once worked on a transformer in a desert environment. The extreme heat and sand caused frequent issues with the mechanical relay, requiring constant maintenance.
Integration Limitations
As power systems became more complex, mechanical relays struggled to keep up:
- No Remote Monitoring: All checks had to be done on-site.
- Difficult Data Collection: No easy way to gather and analyze performance data.
- Limited Automation: Couldn’t easily integrate with modern control systems.
These limitations became more pronounced as the power industry moved towards smarter, more interconnected grids.
While mechanical oil surge relays were a significant improvement over having no protection at all, their limitations paved the way for the development of more advanced, digital solutions. The industry needed a more reliable, informative, and flexible approach to transformer protection.
The Digital Transformation: Introduction of Electronic Oil Surge Relays?
As technology advanced, so did our approach to transformer protection. The introduction of electronic oil surge relays marked a significant leap forward. But what exactly changed with this digital transformation?
Electronic oil surge relays revolutionized transformer protection by introducing digital sensors and microprocessor-based analysis. These new relays offered improved accuracy, real-time monitoring, and the ability to provide detailed fault information. They also enabled remote monitoring and integration with broader control systems.
I remember the excitement when we first installed electronic relays in our substation. The difference was night and day. Let’s explore the key aspects of this digital transformation:
Key Features of Electronic Oil Surge Relays
The shift to electronic relays brought several significant improvements:
- Digital Sensors: More accurate and reliable than mechanical floats.
- Microprocessor Analysis: Ability to process complex data in real-time.
- Adjustable Settings: Easy to fine-tune sensitivity without physical adjustments.
- Data Logging: Continuous recording of transformer conditions.
Comparison with Mechanical Relays
To understand the impact, let’s compare electronic relays to their mechanical predecessors:
| Aspect | Mechanical Relays | Electronic Relays |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Limited by mechanical tolerances | High precision digital measurements |
| Response Time | Seconds | Milliseconds |
| Fault Information | Binary (fault/no fault) | Detailed fault type and severity |
| Adjustability | Physical adjustments required | Software-based settings |
| Data Collection | Manual readings | Automatic data logging |
| Remote Monitoring | Not possible | Easily integrated |
Real-World Benefits
I recall a project where we upgraded a critical transformer with an electronic relay. Within the first month, it detected a developing fault that the old mechanical relay would have missed. We were able to schedule maintenance during a planned outage, avoiding a potential emergency shutdown that could have cost millions.
Challenges in Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, the transition wasn’t without challenges:
- Initial Cost: Electronic relays were more expensive upfront.
- Training Needs: Staff needed to learn new digital systems.
- Compatibility: Integrating with older transformer designs.
- Cybersecurity: New concerns about digital vulnerabilities.
We had to carefully plan the rollout, ensuring our team was well-trained and our systems were secure.
Impact on Maintenance Practices
The introduction of electronic relays also changed how we approached maintenance:
- Predictive Maintenance: Data trends allowed us to anticipate issues.
- Remote Diagnostics: Many problems could be assessed without site visits.
- Firmware Updates: Relays could be improved over time with software updates.
This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance was a game-changer for reliability and cost-efficiency.
The digital transformation of oil surge relays was more than just a technological upgrade. It represented a fundamental shift in how we approach transformer protection and maintenance. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with digital technology, the role of these relays in ensuring a stable and reliable power supply becomes ever more critical.
How Modern Digital Oil Surge Relays Enhance Transformer Protection?
The evolution from mechanical to digital oil surge relays was just the beginning. Today’s modern digital relays are pushing the boundaries of transformer protection. But what makes them so much better?
Modern digital oil surge relays enhance transformer protection through advanced algorithms, real-time data analysis, and predictive capabilities. They offer unprecedented accuracy in fault detection, provide detailed diagnostics, and integrate seamlessly with smart grid systems. This results in improved reliability, reduced downtime, and optimized transformer performance.
In my recent projects, I’ve been amazed by the capabilities of these new systems. Let’s dive into how they’re revolutionizing transformer protection:
Advanced Features of Modern Digital Relays
Today’s digital relays are a far cry from their early electronic predecessors:
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Adapt to specific transformer characteristics.
- Multi-Parameter Analysis: Consider various factors beyond just oil movement.
- Predictive Maintenance: Forecast potential issues before they become critical.
- High-Speed Communication: Rapid data exchange with control systems.
Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis
One of the most significant advantages is the ability to monitor and analyze transformer conditions in real-time:
| Aspect | Benefit | Impact on Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Data Streaming | Instant awareness of changes | Faster response to developing issues |
| Trend Analysis | Identification of slow-developing faults | Prevention of long-term degradation |
| Dynamic Thresholds | Adapts to changing operating conditions | Reduces false alarms while maintaining sensitivity |
| Waveform Capture | Detailed analysis of fault events | Better understanding of fault causes and effects |
I recently worked on a project where we installed these advanced relays across a network of transformers. The system detected a pattern of minor disturbances that, individually, wouldn’t have raised alarms. But the cumulative analysis revealed a developing issue that we were able to address during scheduled maintenance, avoiding a potential major failure.
Integration with Smart Grid Systems
Modern digital relays don’t operate in isolation. They’re part of a broader, interconnected system:
- SCADA Integration: Seamless communication with supervisory control systems.
- Asset Management: Contributes to overall equipment health monitoring.
- Grid Stability Analysis: Provides data for wider power system stability assessments.
- Automated Response: Can trigger automated protective actions across the grid.
This integration allows for a more holistic approach to power system management. In one case, our relay system detected a fault and automatically rerouted power, preventing a widespread outage.
Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
The level of detail provided by modern relays is unprecedented:
- Fault Type Classification: Accurately identifies the nature of the fault.
- Severity Assessment: Quantifies the impact and urgency of detected issues.
- Historical Comparison: Compares current events with past incidents for context.
- Recommended Actions: Suggests appropriate responses based on fault analysis.
This wealth of information allows for more informed decision-making. I’ve seen cases where this detailed diagnostics helped us pinpoint issues that would have been nearly impossible to identify with older systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, implementing these advanced systems comes with its own set of challenges:
- Data Management: Handling the vast amount of data generated.
- Cybersecurity: Ensuring the security of interconnected digital systems.
- Training and Expertise: Requiring specialized skills for operation and maintenance.
- Cost Justification: Balancing the higher upfront costs with long-term benefits.
In my experience, addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, involving not just technical solutions but also organizational changes and ongoing training.
The enhancements offered by modern digital oil surge relays represent a significant leap forward in transformer protection. They’re not just reacting to faults; they’re actively predicting and preventing them. As we continue to rely more heavily on our power infrastructure, these advanced protection systems will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Comparing Mechanical vs. Digital Oil Surge Relays: Pros and Cons?
When it comes to choosing between mechanical and digital oil surge relays, it’s not always a clear-cut decision. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. So, how do they stack up against each other?
Mechanical oil surge relays offer simplicity and reliability but lack advanced features. Digital relays provide superior accuracy, data analysis, and integration capabilities but are more complex and costly. The choice depends on factors like transformer criticality, budget, and existing infrastructure.
Having worked with both types extensively, I’ve seen their pros and cons in action. Let’s break down the comparison:
Mechanical Oil Surge Relays
Pros:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and troubleshoot.
- Reliability: Proven track record over many decades.
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment.
- No Power Required: Operates without external power source.
Cons:
- Limited Information: Only provides basic fault detection.
- Slower Response: Mechanical action takes more time than electronic.
- Maintenance Intensive: Regular checks and adjustments needed.
- No Remote Monitoring: Requires on-site inspection.
Digital Oil Surge Relays
Pros:
- High Accuracy: Precise fault detection and analysis.
- Advanced Features: Real-time monitoring, trend analysis, predictive maintenance.
- Integration Capabilities: Easily connects with SCADA and smart grid systems.
- Customizable Settings: Can be fine-tuned for specific transformer characteristics.
Cons:
- Higher Initial Cost: More expensive upfront investment.
- Complexity: Requires specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance.
- Power Dependency: Needs a reliable power source to function.
- Potential for Cybersecurity Risks: As with any digital system.
Comparative Analysis
Let’s look at a side-by-side comparison of key factors:
| Factor | Mechanical Relays | Digital Relays |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Response Time | Seconds | Milliseconds |
| Data Analysis | None | Extensive |
| Maintenance Needs | High | Low |
| Remote Monitoring | Not Available | Available |
| Initial Cost | Low | High |
| Long-term Cost | Variable (due to maintenance) | Generally Lower |
| Lifespan | 20-30 years | 10-15 years (but updateable) |
Real-World Considerations
In my experience, the choice between mechanical and digital relays often depends on specific circumstances:
- Critical Infrastructure: For crucial transformers, digital relays are usually preferred due to their advanced protection capabilities.
- Budget Constraints: Smaller utilities or less critical applications might opt for mechanical relays to save costs.
- Existing Systems: The choice may be influenced by compatibility with current infrastructure.
- Expertise Available: Some organizations may stick with mechanical relays if they lack personnel trained in digital systems.
I once worked on a project where we decided to keep mechanical relays on older, less critical transformers while upgrading to digital for the main transmission units. This hybrid approach balanced cost, performance, and risk management.
Future Trends
As we look to the future, the trend is clearly moving towards digital systems. However, mechanical relays are far from obsolete:
- Digital Dominance: New installations predominantly use digital relays.
- Hybrid Solutions: Some manufacturers are developing relays that combine mechanical and digital elements.
- Retrofit Options: Digital systems that can be easily installed in place of old mechanical relays are becoming popular.
- AI Integration: The next generation of digital relays may incorporate artificial intelligence for even more advanced protection.
The choice between mechanical and digital oil surge relays isn’t always straightforward. It requires careful consideration of the specific needs, resources, and future plans of each power system. While digital relays offer superior capabilities, mechanical relays still have their place in certain applications. The key is to make an informed decision based on a thorough analysis of your particular situation.
Integration with Smart Grid Systems: The Future of Oil Surge Relay Technology?
As our power grids become smarter, how do oil surge relays fit into this evolving landscape? The integration of these relays with smart grid systems is opening up exciting new possibilities. But what does this integration really mean for the future of transformer protection?
The integration of oil surge relays with smart grid systems represents a significant leap in transformer protection and grid management. It enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and coordinated responses across the entire power network. This integration enhances grid reliability, efficiency, and resilience against widespread outages.
In my recent projects, I’ve seen firsthand how this integration is transforming our approach to power system management. Let’s explore the key aspects of this technological convergence:
Key Features of Smart Grid Integration
The integration of oil surge relays with smart grids brings several advanced capabilities:
- Real-Time Data Exchange: Continuous communication between relays and central systems.
- Coordinated Protection Schemes: Relays work in harmony with other grid protection devices.
- Adaptive Grid Management: Dynamic adjustments based on overall grid conditions.
- Big Data Analytics: Leveraging vast amounts of data for system-wide insights.
Benefits of Integration
This integration offers numerous advantages:
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Grid Stability | Coordinated responses to disturbances | Reduced risk of cascading failures |
| Improved Asset Management | Comprehensive health monitoring of transformers | Optimized maintenance schedules |
| Faster Fault Location | Precise identification of fault locations | Quicker restoration of power |
| Demand Response Integration | Balancing transformer loads with grid demands | Improved energy efficiency |
I recently worked on a project where integrated oil surge relays helped prevent a potential blackout. The system detected a developing fault in a key transformer and automatically redistributed the load, avoiding a critical failure.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits are clear, implementing this integration comes with challenges:
- Interoperability: Ensuring different systems and devices can communicate effectively.
- Data Management: Handling and analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting the integrated system from cyber threats.
- Legacy System Integration: Incorporating older equipment into the smart grid.
Addressing these challenges often requires a multi-faceted approach. In one case, we had to develop custom interfaces to integrate older relays with the new smart grid system.
Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, several exciting developments are on the horizon:
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms for predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source for faster responses.
- Blockchain Technology: Enhancing security and enabling decentralized grid management.
- 5G Integration: Utilizing high-speed, low-latency communication for even more responsive systems.
I’m particularly excited about the potential of AI in this field. Imagine a system that can learn from grid-wide data to predict and prevent faults before they occur, or even self-optimize the entire network for maximum efficiency.
Impact on Grid Resilience
One of the most significant benefits of this integration is improved grid resilience:
- Faster Recovery: Quicker identification and isolation of faults.
- Proactive Maintenance: Addressing issues before they cause outages.
- Adaptive Load Management: Dynamically adjusting to prevent overloads.
- Improved Situational Awareness: Comprehensive view of grid health for operators.
In a recent project, we implemented an integrated system that reduced our average outage response time by 40%, significantly improving our overall grid reliability.
The integration of oil surge relays with smart grid systems is more than just a technological upgrade. It represents a fundamental shift in how we approach power system management. As this integration continues to evolve, it will play a crucial role in building more resilient, efficient, and sustainable power grids for the future.
Maintenance and Testing: Ensuring Reliability in Both Mechanical and Digital Relays?
Regardless of whether you’re using mechanical or digital oil surge relays, proper maintenance and testing are crucial for ensuring their reliability. But how do these processes differ between the two types, and what are the best practices for each?
Maintenance and testing are essential for both mechanical and digital oil surge relays, but the approaches differ. Mechanical relays require regular physical inspections and adjustments, while digital relays focus more on software updates and electronic diagnostics. Both types need periodic testing to ensure they respond correctly to simulated fault conditions.
Having overseen maintenance programs for both types of relays, I can attest to the importance of a well-planned maintenance strategy. Let’s dive into the specifics for each type:
Maintenance for Mechanical Oil Surge Relays
Mechanical relays require more frequent hands-on maintenance:
- Visual Inspections: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or oil leaks.
- Mechanical Adjustments: Ensure proper alignment and movement of components.
- Lubrication: Apply lubricants to moving parts as needed.
- Oil Level Checks: Verify and adjust oil levels in the relay.
Typical maintenance schedule:
| Task | Frequency | Time Required |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | 30 minutes |
| Mechanical Check | Quarterly | 1-2 hours |
| Full Service | Annually | 4-6 hours |
| Oil Replacement | Every 3-5 years | 2-3 hours |
Maintenance for Digital Oil Surge Relays
Digital relays have different maintenance needs:
- Software Updates: Install latest firmware and security patches.
- Electronic Diagnostics: Run built-in self-test routines.
- Calibration Checks: Verify sensor accuracy and adjust if necessary.
- Battery Replacement: Change backup batteries as recommended.
Typical maintenance schedule:
| Task | Frequency | Time Required |
|---|---|---|
| Software Update | As released | 1-2 hours |
| Diagnostic Check | Monthly | 30 minutes |
| Calibration | Annually | 2-3 hours |
| Battery Replacement | Every 3-5 years | 30 minutes |
Testing Procedures
Testing is crucial for both types of relays to ensure they will respond correctly in fault conditions:
- Simulated Fault Tests: Apply controlled oil surges to verify relay operation.
- Timing Tests: Measure response time to ensure it meets specifications.
- Insulation Resistance Tests: Check electrical integrity of the relay.
- Functional Tests: Verify all features and settings are working correctly.
I remember a case where routine testing revealed a mechanical relay that had become sluggish due to oil contamination. If left unchecked, it could have failed to protect the transformer during a real fault.
Challenges in Maintenance and Testing
Each type of relay presents unique challenges:
Mechanical Relays:
- Wear and tear of moving parts
- Sensitivity to environmental conditions
- Difficulty in fine-tuning settings
Digital Relays:
- Complexity of software-based systems
- Need for specialized testing equipment
- Potential for cyber vulnerabilities
To address these challenges, we’ve developed comprehensive training programs for our maintenance teams, ensuring they’re equipped to handle both types of relays effectively.
Best Practices for Reliability
Based on my experience, here are some key best practices for maintaining relay reliability:
- Develop a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan: Tailor it to your specific relay types and operating conditions.
- Keep Detailed Records: Document all maintenance activities and test results for trend analysis.
- Use Proper Test Equipment: Invest in high-quality, calibrated testing tools.
- Stay Updated on Manufacturer Recommendations: Relay designs and best practices evolve over time.
- Implement Predictive Maintenance: Use data trends to anticipate maintenance needs.
In one of our substations, implementing these best practices led to a 30% reduction in relay-related issues over a two-year period.
The Future of Maintenance and Testing
As technology advances, we’re seeing new trends in maintenance and testing:
- Remote Diagnostics: Ability to perform some tests and diagnostics from afar.
- AI-Assisted Maintenance: Using artificial intelligence to predict maintenance needs.
- Augmented Reality: Utilizing AR tools for guided maintenance procedures.
- Automated Testing Systems: Developing more sophisticated, automated testing equipment.
I’m particularly excited about the potential of AI in predictive maintenance. It could revolutionize how we approach relay upkeep, making it more proactive and efficient.
Proper maintenance and testing are the unsung heroes of relay reliability. Whether dealing with mechanical or digital relays, a well-executed maintenance program is crucial for ensuring the continued protection of our transformers and the stability of our power systems.
Case Study: Real-World Impact of Upgrading to Digital Oil Surge Relays?
Theory is one thing, but real-world results speak volumes. Let’s look at a case study that demonstrates the tangible benefits of upgrading from mechanical to digital oil surge relays. What kind of improvements can we actually expect to see?
A major utility company upgraded its transformer protection system from mechanical to digital oil surge relays across 50 substations. The results were significant: a 40% reduction in transformer-related outages, 60% decrease in maintenance costs, and improved grid stability. The upgrade also enabled predictive maintenance, further enhancing reliability.

I was fortunate to be part of this upgrade project, and the results were truly eye-opening. Let’s dive into the details of this case study:
Project Overview
- Utility: MidWest Power Distribution (name changed for privacy)
- Scope: 50 substations, 150 large power transformers
- Timeline: 18 months for full implementation
- Investment: $5 million for equipment and installation
Pre-Upgrade Situation
Before the upgrade, MidWest Power was facing several challenges:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many transformers were protected by 30+ year old mechanical relays.
- Frequent False Alarms: Leading to unnecessary outages and inspections.
- Limited Fault Data: Making it difficult to analyze and prevent recurring issues.
- High Maintenance Costs: Regular adjustments and replacements were needed.
Upgrade Process
The upgrade was carried out in phases:
- Pilot Phase: 5 critical substations were upgraded first.
- Assessment: Results were analyzed and processes refined.
- Full Rollout: Remaining substations were upgraded over 15 months.
- Training: Extensive training provided to operations and maintenance staff.
Key Results
The impact of the upgrade was substantial:
| Metric | Before Upgrade | After Upgrade | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Outages | 25 | 15 | 40% reduction |
| False Alarms | 40 per year | 5 per year | 87.5% reduction |
| Maintenance Costs | $1.5 million/year | $600,000/year | 60% reduction |
| Fault Response Time | 45 minutes | 10 minutes | 78% faster |
Specific Improvements
-
Enhanced Fault Detection:
- The digital relays could distinguish between true faults and harmless disturbances.
- Example: A transformer near a railway line that previously experienced frequent false alarms now operates without interruption.
-
Predictive Maintenance:
- Data trends allowed for early identification of developing issues.
- Case in Point: A gradual increase in oil movement patterns led to the discovery of a minor winding fault, which was repaired during scheduled maintenance, avoiding a potential major failure.
-
Improved Grid Stability:
- Faster and more accurate responses to faults prevented cascading failures.
- Real-world Impact: During a severe storm, the system isolated a fault in one substation, preventing a widespread blackout that could have affected 100,000 customers.
-
Cost Savings:
- Reduced need for physical inspections and emergency repairs.
- Long-term Benefit: The utility estimates a return on investment within 4 years, with ongoing savings thereafter.
-
Enhanced Data Analysis:
- Comprehensive fault data allowed for in-depth analysis and system improvements.
- Outcome: Identified a design flaw in certain transformer models, leading to proactive replacements and preventing future failures.
Challenges Faced
The upgrade wasn’t without its hurdles:
- Initial Resistance: Some staff were hesitant to move away from familiar mechanical systems.
- Integration Issues: Compatibility challenges with older SCADA systems required additional work.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: New protocols had to be implemented to secure the digital systems.
- Training Requirements: Significant time and resources were invested in staff training.
Lessons Learned
This project provided valuable insights:
- Phased Implementation: Starting with a pilot phase allowed for refinement of processes.
- Comprehensive Training: Investing in staff training was crucial for successful adoption.
- Data Management: Developing robust systems to handle the increased data flow was essential.
- Customization: Fine-tuning relay settings for each transformer’s characteristics maximized benefits.
Future Plans
Based on the success of this upgrade, MidWest Power is now:
- Expanding the digital relay network to all remaining substations.
- Exploring AI integration for even more advanced predictive maintenance.
- Developing a centralized asset health monitoring system.
- Planning to share their experience with other utilities to promote industry-wide improvements.
This case study clearly demonstrates the significant real-world benefits of upgrading to digital oil surge relays. While the initial investment was substantial, the improvements in reliability, efficiency, and cost savings have proven to be well worth it. It’s a powerful example of how embracing new technology can transform the performance and management of our critical power infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Oil Surge Relay: Factors to Consider in the Digital Age?
With the rapid advancement of oil surge relay technology, choosing the right system for your needs can be challenging. What factors should you consider when making this crucial decision in the digital age?
Choosing the right oil surge relay involves considering factors such as transformer criticality, budget, existing infrastructure, and future expansion plans. Key considerations include relay accuracy, response time, data analysis capabilities, integration with existing systems, maintenance requirements, and long-term cost-effectiveness.

Having advised numerous utilities and industrial clients on relay selection, I’ve learned that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Let’s explore the key factors to consider:
Critical Factors in Relay Selection
-
Transformer Criticality
The importance of the transformer in your network is a primary consideration:Transformer Role Recommended Relay Type Critical transmission Advanced digital with redundancy Distribution substation Standard digital Industrial application Digital or high-quality mechanical -
Budget Constraints
While digital relays offer advanced features, they come at a higher initial cost:- Mechanical Relays: Lower upfront cost, higher long-term maintenance
- Digital Relays: Higher initial investment, lower ongoing costs
-
Existing Infrastructure
Consider compatibility with your current systems:- SCADA Integration: Digital relays offer easier integration
- Legacy Equipment: Some mechanical relays might be more compatible with older systems
-
Future Expansion Plans
Think about your long-term goals:- Smart Grid Initiatives: Digital relays are essential for future smart grid integration
- Gradual Upgrades: Consider relays that allow for phased implementation
Technical Specifications to Evaluate
When comparing different relay options, pay close attention to these specifications:
- Accuracy: Digital relays generally offer higher accuracy (typically ±1% vs ±5% for mechanical)
- Response Time: Digital relays can respond in milliseconds compared to seconds for mechanical
- Sensitivity Range: Look for adjustable settings to match specific transformer characteristics
- Data Logging Capabilities: Important for trend analysis and predictive maintenance
- Communication Protocols: Ensure compatibility with your network (e.g., IEC 61850, DNP3)
Real-World Considerations
From my experience, here are some practical aspects to keep in mind:
-
Maintenance Requirements
- Mechanical: Regular physical inspections and adjustments
- Digital: Software updates and electronic diagnostics
-
Reliability Track Record
Research the performance history of different relay models. I once worked with a utility that chose a relay based solely on features, only to discover it had a high failure rate in similar environments. -
Vendor Support
Consider the manufacturer’s reputation for customer support and spare parts availability. This can be crucial during emergencies or for long-term maintenance. -
Environmental Factors
- Temperature Range: Ensure the relay can operate in your climate conditions
- Electromagnetic Interference: Digital relays may need additional shielding in some environments
-
Training and Expertise
Assess your team’s capabilities:- Do you have the expertise to maintain digital systems?
- What training will be required for your staff?
Case-Specific Examples
To illustrate how these factors play out in real-world scenarios, let’s look at two contrasting examples:
-
Large Urban Utility
- Scenario: Upgrading a critical substation serving 500,000 customers
- Choice: Advanced digital relay with redundancy
- Reasoning: High reliability needs, integration with smart grid initiatives, long-term cost savings
-
Small Rural Cooperative
- Scenario: Replacing relays on older distribution transformers
- Choice: Mix of basic digital and high-quality mechanical relays
- Reasoning: Budget constraints, simpler infrastructure, varied criticality of different transformers
Decision-Making Process
When helping clients choose the right relay, I recommend this step-by-step approach:
- Assess Current Needs: Evaluate your existing system’s performance and pain points
- Define Future Goals: Consider your long-term plans for grid modernization
- Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis: Look at both initial and long-term costs
- Evaluate Technical Fit: Ensure the relay meets your specific technical requirements
- Consider Operational Impact: Think about how the choice will affect your day-to-day operations
- Seek Expert Opinions: Consult with manufacturers, peers, and independent experts
- Plan for Implementation: Consider how you’ll manage the transition and any required training
Emerging Trends to Watch
As you make your decision, keep an eye on these emerging trends in relay technology:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: For more advanced predictive capabilities
- IoT Connectivity: Enabling broader integration with smart grid systems
- Cybersecurity Features: As digital systems become more prevalent, security becomes crucial
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Relays with lower environmental impact and energy consumption
Choosing the right oil surge relay in the digital age requires careful consideration of multiple factors. While the trend is clearly moving towards digital systems, the best choice depends on your specific circumstances, needs, and future plans. By thoroughly evaluating these factors and following a structured decision-making process, you can select a relay system that not only meets your current needs but also positions you well for the future of power distribution.
Conclusion
The evolution of oil surge relays from mechanical to digital systems represents a significant leap in transformer protection technology. While mechanical relays have served us well for decades, digital relays offer enhanced accuracy, advanced features, and integration capabilities that are becoming increasingly crucial in our modern, interconnected power grids. The choice between mechanical and digital relays depends on various factors including transformer criticality, budget, existing infrastructure, and future plans. Proper maintenance and testing remain essential for both types to ensure reliability. As we move forward, the integration of these relays with smart grid systems promises even greater improvements in grid stability, efficiency, and resilience. Ultimately, the right choice of oil surge relay can significantly impact the reliability and performance of our power systems, making it a critical decision for power professionals in the digital age.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group