Box Type Transformer vs Pad Mounted Transformer: What’s the Difference?
Are you struggling to decide between a box type and a pad mounted transformer for your power distribution project? You’re not alone. Many engineers and project managers find this choice challenging. But what if you could easily understand the key differences and make an informed decision?
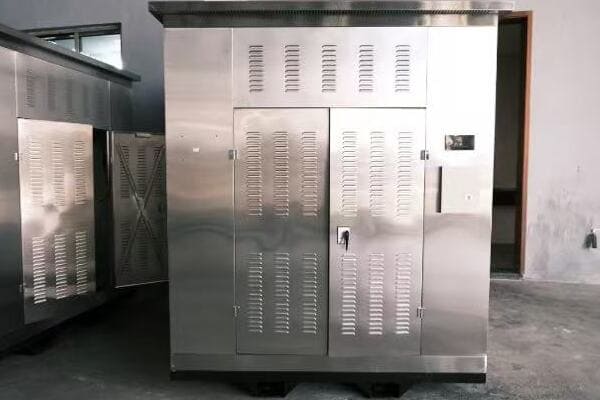
A box type transformer is an integrated power distribution unit combining a transformer, switchgear, and protective devices in one enclosure. A pad mounted transformer is a standalone oil-immersed transformer on a concrete base with enclosed terminals. Box types are ideal for urban grids and industrial zones, offering all-in-one solutions. Pad mounted transformers suit residential areas and underground networks, providing a compact, tamper-resistant design. The choice depends on installation requirements, space constraints, and specific project needs.

In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through the essential differences between box type and pad mounted transformers. We’ll explore their structures, applications, advantages, and limitations. Whether you’re designing a new residential development, upgrading an industrial facility, or planning a commercial complex, this article will provide valuable insights to help you make the right choice for your specific needs.
What Is a Box Type Transformer?
Have you ever noticed those large metal cabinets in industrial areas or near commercial buildings and wondered what they are? These are often box type transformers, but what exactly are they, and why are they becoming increasingly popular in urban power distribution?
A box type transformer, also known as a compact substation or kiosk substation, is an integrated power distribution unit that combines a transformer, high-voltage switchgear, low-voltage switchboard, and protective devices within a single enclosure. It typically features a three-compartment layout: high-voltage, transformer, and low-voltage sections. Box type transformers are commonly used in urban power grids, industrial zones, and commercial complexes, offering a compact, all-in-one solution for medium-voltage power distribution, usually at 11kV or 22kV levels.

Key Features of Box Type Transformers
Let’s break down the main characteristics:
- Integrated Design
- Compartmentalized Structure
- Versatile Installation Options
- Safety and Accessibility
- Customization Possibilities
Integrated Design
All-in-one power distribution solution:
- Transformer, switchgear, and protection in one unit
- Factory-assembled and tested before delivery
- Reduced on-site work and installation time
I recently managed a project for a new shopping mall where we chose box type transformers. Their integrated design allowed us to significantly reduce the substation footprint and streamline the installation process, saving both space and time.
Compartmentalized Structure
Enhancing safety and functionality:
- High-voltage compartment: Houses incoming switchgear
- Transformer compartment: Contains the main transformer
- Low-voltage compartment: Includes outgoing distribution panels
During a recent factory tour, I observed the assembly of a box type transformer. The clear separation of compartments impressed me, showcasing how this design enhances safety and ease of maintenance.
Versatile Installation Options
Adapting to various environments:
- Above-ground installation in urban areas
- Suitable for outdoor placement with proper enclosure ratings
- Can be customized for indoor installations in some cases
Here’s a quick overview of installation options:
| Installation Type | Typical Application | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Standalone | Industrial zones | Easy access, robust |
| Indoor Substation | Commercial buildings | Space-saving, noise reduction |
| Rooftop Installation | Urban areas | Utilizes unused space |
Safety and Accessibility
Ensuring protection and ease of maintenance:
- Interlocked compartments for operator safety
- External operation of switchgear possible
- Designed for easy access during maintenance
Customization Possibilities
Meeting specific project needs:
- Scalable capacity (typically from 100 kVA to 2500 kVA)
- Various cooling options (oil-immersed or dry-type)
- Integration of smart grid technologies possible
Key points about box type transformers:
- They offer an integrated solution for power distribution
- Feature a compartmentalized structure for safety and functionality
- Provide versatile installation options for different environments
- Ensure safety while maintaining accessibility for maintenance
- Allow for customization to meet specific project requirements
In my experience, box type transformers have been game-changers for urban power distribution projects. I recall a case where we needed to upgrade the power supply for a growing industrial park. The compact, all-in-one nature of box type transformers allowed us to increase capacity without significantly expanding the substation footprint, a crucial factor in the space-constrained environment.
For example, in a recent smart city project, we utilized box type transformers with integrated smart grid capabilities. Their ability to house advanced monitoring and control systems within the same enclosure as the transformer and switchgear was crucial in implementing a responsive, efficient power distribution network.
As we move on to discuss pad mounted transformers, keep these features of box type transformers in mind. Understanding the unique advantages of each type will help you make a more informed choice for your specific project requirements.
What Is a Pad Mounted Transformer?
Have you ever noticed those green metal boxes in residential areas and wondered about their purpose? These are often pad mounted transformers, but what exactly are they, and why are they a common sight in many neighborhoods?
A pad mounted transformer is a ground-mounted, oil-filled distribution transformer enclosed in a locked steel cabinet. It’s designed to step down medium voltage electricity (typically 11kV or 22kV) to low voltage (400V/230V) for residential and light commercial use. Unlike box type transformers, pad mounted units contain only the transformer itself, with separate termination points for high and low voltage connections. They are commonly used in underground distribution networks, residential subdivisions, and areas where aesthetics and safety are primary concerns.
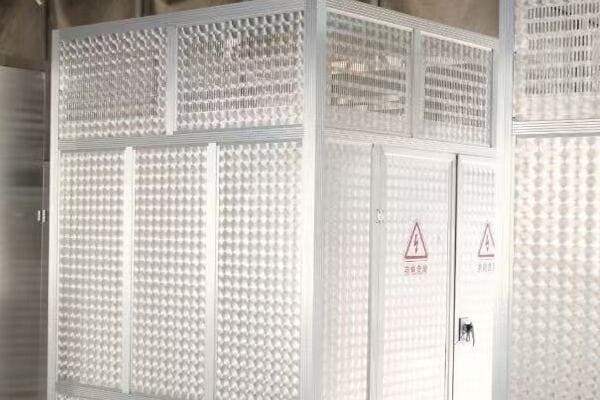
Key Characteristics of Pad Mounted Transformers
Let’s examine the main features:
- Compact and Self-Contained Design
- Ground-Level Installation
- Safety and Aesthetic Considerations
- Flexibility in Power Distribution
- Maintenance and Accessibility
Compact and Self-Contained Design
Focused transformer solution:
- Houses only the transformer and necessary connections
- Oil-immersed for efficient cooling and insulation
- Tamper-resistant enclosure for public safety
I recently worked on a project upgrading a suburban power distribution system. We chose pad mounted transformers for their compact design, which allowed us to place them strategically throughout the neighborhood without disrupting the landscape.
Ground-Level Installation
Simplifying access and maintenance:
- Mounted on concrete pads at ground level
- Eliminates need for pole-mounted equipment
- Suitable for areas with underground power lines
During a recent residential development project, the ease of installing pad mounted transformers significantly reduced our construction timeline compared to traditional pole-mounted solutions.
Safety and Aesthetic Considerations
Blending function with form:
- Locked, tamper-resistant enclosures
- Low profile design minimizes visual impact
- Can be painted or landscaped around to match surroundings
Here’s a quick comparison of safety features:
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Locked Enclosure | Prevent unauthorized access | Enhanced public safety |
| Dead-front Design | Minimize exposure to live parts | Safer for technicians |
| Low Profile | Reduce visual impact | Better neighborhood aesthetics |
Flexibility in Power Distribution
Adapting to various needs:
- Available in single-phase or three-phase configurations
- Typical capacities range from 25 kVA to 2500 kVA
- Can be customized for specific voltage requirements
Maintenance and Accessibility
Ensuring long-term reliability:
- Easy ground-level access for maintenance
- Designed for quick replacement if necessary
- Often equipped with oil level and temperature indicators
Key points about pad mounted transformers:
- They offer a compact, self-contained transformer solution
- Designed for ground-level installation, ideal for underground networks
- Prioritize safety and aesthetic integration in residential areas
- Provide flexibility in power distribution configurations
- Allow for easy maintenance and accessibility
In my experience, pad mounted transformers have revolutionized residential power distribution. I recall a project where we retrofitted an older neighborhood with pad mounted units, replacing aging pole-mounted transformers. Not only did this improve the area’s visual appeal, but it also increased power reliability and simplified maintenance procedures.
For example, in a recent smart community development project, we utilized pad mounted transformers with integrated smart metering capabilities. Their ground-level installation made it easy to incorporate advanced monitoring systems, enabling efficient power management across the residential area.
As we move on to compare box type and pad mounted transformers directly, keep these characteristics in mind. Understanding the strengths and applications of each type will help you make a more informed decision for your specific project needs.
Box Type vs Pad Mounted: Key Differences in Structure and Installation?
Are you finding it challenging to decide between box type and pad mounted transformers for your project? You’re not alone. Many engineers and project managers struggle with this choice. But what are the fundamental differences in structure and installation that set these two transformer types apart?
Box type transformers are integrated units containing the transformer, switchgear, and low-voltage distribution in one enclosure. They typically have a three-compartment structure: high-voltage, transformer, and low-voltage sections. Pad mounted transformers, conversely, house only the transformer with external connections for high and low voltage. Box types are usually larger, offering a complete substation solution, while pad mounted units are more compact, focusing solely on voltage transformation. Installation methods differ significantly, with box types often requiring more substantial site preparation compared to the simpler concrete pad needed for pad mounted units.
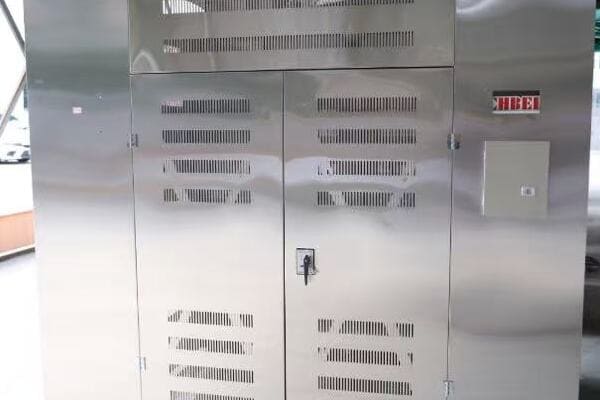

Key Structural and Installation Differences
Let’s examine the main distinctions:
- Component Integration
- Size and Footprint
- Installation Requirements
- Accessibility and Maintenance
- Customization and Scalability
Component Integration
Differing approaches to power distribution:
- Box Type: All-in-one solution with integrated switchgear and distribution
- Pad Mounted: Transformer-only, requiring separate switchgear and distribution panels
I recently managed two similar capacity projects – one using a box type and another using a pad mounted transformer. The box type installation was completed in half the time due to its integrated design, while the pad mounted setup required additional time for connecting external switchgear.
Size and Footprint
Space considerations:
- Box Type: Larger overall footprint, but consolidates multiple components
- Pad Mounted: Smaller individual footprint, but may require additional space for separate components
During a recent urban substation upgrade, the compact nature of pad mounted transformers allowed us to fit more units in a limited space, crucial for meeting the growing power demands of the area.
Installation Requirements
Site preparation and mounting:
- Box Type: Often requires a larger concrete foundation and more complex site preparation
- Pad Mounted: Simpler installation on a basic concrete pad
Here’s a comparison of typical installation requirements:
| Aspect | Box Type Transformer | Pad Mounted Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Large, engineered concrete base | Simple concrete pad |
| Crane Requirement | Usually needed for placement | May be placed with a forklift |
| Cable Entry | Multiple options, often bottom entry | Typically underground entry |
| Site Preparation | More extensive, may need fencing | Minimal, often just landscaping |
Accessibility and Maintenance
Ease of servicing and repairs:
- Box Type: Compartmentalized access, potentially easier for routine checks
- Pad Mounted: Simple access to transformer, but may require opening in public areas
Customization and Scalability
Adapting to project needs:
- Box Type: Highly customizable with various internal configurations
- Pad Mounted: Standardized designs with limited customization options
Key points about structural and installation differences:
- Box type transformers offer integrated solutions, while pad mounted focus on transformation only
- Size and footprint vary significantly between the two types
- Installation requirements differ in complexity and site preparation needs
- Accessibility and maintenance approaches vary based on design
- Customization options are generally more extensive for box type units
In my experience, these structural and installation differences can significantly impact project timelines and costs. I recall a project where we initially planned to use box type transformers for a new commercial development. However, after assessing the site constraints and installation timeline, we switched to pad mounted units. This decision allowed for a more flexible layout and faster installation, crucial for meeting the project’s tight deadline.
For example, in a recent industrial park expansion, we used a combination of box type and pad mounted transformers. Box types were installed at main distribution points, leveraging their integrated design for efficient power management. Pad mounted units were used for individual lots, providing flexibility for future changes in tenant power needs.
As we move on to discuss when to choose between box type and pad mounted transformers, keep these structural and installation differences in mind. Understanding these practical aspects will help you make a more informed decision based on your specific project requirements and constraints.
When to Choose Box Type vs Pad Mounted Transformer?
Are you grappling with the decision between a box type and a pad mounted transformer for your project? You’re not alone. This choice can significantly impact your project’s timeline, budget, and long-term functionality. But how can you determine which option is best suited for your specific needs?
Choose a box type transformer when you need an all-in-one power distribution solution, especially in industrial or commercial settings with limited space for separate components. Opt for a pad mounted transformer in residential areas, underground distribution networks, or where aesthetics and public safety are primary concerns. Box types are ideal for projects requiring integrated switchgear and higher capacities, while pad mounted units excel in scenarios needing compact, standalone transformation. Consider factors like installation space, maintenance accessibility, future expandability, and local regulations when making your decision.

Key Factors in Transformer Selection
Let’s examine the main considerations:
- Application and Environment
- Space and Installation Constraints
- Power Capacity and Scalability
- Safety and Aesthetic Requirements
- Maintenance and Accessibility Needs
Application and Environment
Matching transformer type to project needs:
- Box Type: Ideal for industrial zones, commercial complexes, urban substations
- Pad Mounted: Suitable for residential areas, underground networks, public spaces
I recently worked on a project for a new shopping mall where we chose box type transformers. Their integrated design was perfect for the mall’s centralized power distribution needs, allowing us to efficiently manage the complex’s varied power requirements from a single point.
Space and Installation Constraints
Considering available area and site conditions:
- Box Type: Requires larger installation area but consolidates multiple components
- Pad Mounted: Needs less individual space but may require additional area for separate switchgear
During a recent residential development project, we opted for pad mounted transformers due to space limitations and the need to distribute them throughout the neighborhood discreetly.
Power Capacity and Scalability
Planning for current and future needs:
- Box Type: Generally available in higher capacities, easier to upgrade internal components
- Pad Mounted: Typically lower capacity range, may require full unit replacement for significant upgrades
Here’s a quick comparison of typical capacities:
| Transformer Type | Common Capacity Range | Scalability |
|---|---|---|
| Box Type | 100 kVA – 2500 kVA | High (modular internals) |
| Pad Mounted | 25 kVA – 2500 kVA | Limited (fixed design) |
Safety and Aesthetic Requirements
Meeting regulatory and community standards:
- Box Type: Fully enclosed, suitable for restricted access areas
- Pad Mounted: Tamper-resistant design, blends with residential landscapes
Maintenance and Accessibility Needs
Ensuring long-term serviceability:
- Box Type: Compartmentalized access, potentially easier for routine maintenance
- Pad Mounted: Simple access, but may require special considerations in public areas
Key points for choosing between box type and pad mounted transformers:
- Consider the specific application and environmental context
- Evaluate available space and installation constraints carefully
- Assess both current power needs and future scalability requirements
- Factor in safety regulations and aesthetic considerations
- Think about long-term maintenance and accessibility needs
In my experience, the choice between box type and pad mounted transformers often involves balancing multiple factors. I recall a case where a client initially leaned towards box type transformers for a new office park development. However, after considering the project’s phased construction plan and the need for distributed power sources, we opted for strategically placed pad mounted units. This decision provided greater flexibility for the project’s evolving needs and simplified the installation process for each phase.
For example, in a recent smart city project, we used a combination of both transformer types. Box type units were installed at main distribution hubs, leveraging their integrated design for efficient power management and smart grid integration. Pad mounted transformers were used throughout residential areas, providing a safer, more aesthetically pleasing solution for neighborhood power distribution.
As we move on to discuss the cost-effectiveness of each transformer type, keep these selection criteria in mind. Understanding when to choose each type will help you better evaluate the overall value proposition of box type versus pad mounted transformers for your specific project requirements.
Which Transformer Is More Cost-Effective for Your Project?
Are you struggling to determine whether a box type or pad mounted transformer will be more economical for your project? You’re not alone. Many project managers find it challenging to weigh the upfront costs against long-term benefits. But how can you accurately assess which option offers the best value for your specific situation?
The cost-effectiveness of box type versus pad mounted transformers depends on various factors including initial purchase price, installation costs, long-term maintenance, and project-specific requirements. Box type transformers generally have a higher upfront cost but offer integrated solutions that can reduce overall installation expenses. Pad mounted transformers are typically less expensive initially but may require additional costs for separate switchgear and protective equipment. Long-term considerations like maintenance accessibility, energy efficiency, and future expandability also play crucial roles in determining the most cost-effective choice for your project.

Key Cost Factors to Consider
Let’s examine the main elements affecting cost-effectiveness:
- Initial Purchase and Installation Costs
- Operational Efficiency and Energy Savings
- Maintenance and Repair Expenses
- Lifespan and Replacement Considerations
- Regulatory Compliance and Safety Measures
Initial Purchase and Installation Costs
Upfront investment comparison:
- Box Type: Higher unit cost but includes integrated components
- Pad Mounted: Lower individual cost but may require additional equipment purchases
I recently managed two similar capacity projects – one using a box type and another using pad mounted transformers. While the box type units were more expensive initially, the total installation cost ended up being comparable due to reduced labor and additional equipment needs.
Operational Efficiency and Energy Savings
Long-term performance factors:
- Box Type: Potentially higher efficiency due to optimized integrated design
- Pad Mounted: Efficiency can vary based on the quality of connections and external components
During a recent industrial facility upgrade, we found that the box type transformers offered slightly better overall efficiency, leading to noticeable energy savings over time.
Maintenance and Repair Expenses
Ongoing cost considerations:
- Box Type: Centralized maintenance, potentially lower long-term costs
- Pad Mounted: Simpler individual maintenance, but may require more frequent attention
Here’s a simplified comparison of maintenance aspects:
| Aspect | Box Type Transformer | Pad Mounted Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Checks | Consolidated, less frequent | More units to check, but simpler |
| Repair Complexity | Can be complex due to integration | Generally straightforward |
| Accessibility | May require specialized access | Easy ground-level access |
| Replacement Parts | Potentially more expensive | Standard parts often available |
Lifespan and Replacement Considerations
Long-term value assessment:
- Box Type: Longer potential lifespan due to protected components
- Pad Mounted: May require earlier replacement of individual units
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Measures
Meeting standards and regulations:
- Box Type: Often easier to comply with industrial safety standards
- Pad Mounted: May require additional safety measures in public areas
Key points for assessing cost-effectiveness:
- Consider both initial costs and long-term operational expenses
- Evaluate potential energy savings from improved efficiency
- Factor in ongoing maintenance and repair requirements
- Assess expected lifespan and future replacement needs
- Account for costs related to regulatory compliance and safety measures
In my experience, determining the most cost-effective option often requires a comprehensive, long-term view. I recall a project for a growing commercial district where we initially considered pad mounted transformers due to their lower upfront cost. However, after conducting a 20-year total cost of ownership analysis, including projected maintenance and energy costs, we found that box type transformers offered better long-term value. This decision proved beneficial as the district expanded, with the integrated design of the box type units accommodating increased power demands more efficiently.
For example, in a recent residential development project, we chose pad mounted transformers despite their potentially higher long-term maintenance costs. This decision was driven by the need for distributed power sources and the aesthetic requirements of the neighborhood. The lower initial cost and flexibility in placement allowed us to optimize the power distribution network within the project’s budget constraints.
As we move on to discuss top Chinese manufacturers offering both box and pad mounted transformers, keep these cost considerations in mind. Understanding the long-term financial implications will help you make a more informed decision when selecting a supplier and transformer type for your project.
Top Chinese Manufacturers Offering Box and Pad Mounted Transformers?
Are you finding it challenging to identify reliable manufacturers of box and pad mounted transformers in China? You’re not alone. With China’s vast industrial landscape, pinpointing trustworthy suppliers can be overwhelming. But which companies stand out for their quality, innovation, and export capabilities in both transformer types?
Leading Chinese manufacturers of box and pad mounted transformers include CHBEB, CHINT, TBEA, Sieyuan Electric, and Taikai Electric. These companies offer a range of products suitable for various applications, from urban power distribution to renewable energy projects. They are known for their adherence to international standards like IEC and IEEE, quality certifications such as ISO 9001 and CE marking, and their ability to provide customized solutions. These manufacturers have strong export presences in markets across Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and beyond, demonstrating their capability to meet diverse global requirements.

Leading Transformer Manufacturers in China
Let’s examine the top recommended suppliers:
- CHBEB (China Bei Er Bian)
- CHINT
- TBEA
- Sieyuan Electric
- Taikai Electric
CHBEB (China Bei Er Bian)
Specializing in customized solutions:
- Box Type: 630-2500kVA, CE certified
- Pad Mounted: 11kV/0.4kV, up to 1000kVA
- Key strengths: Export-oriented, strong in Middle East and African markets
- Certifications: ISO 9001, IEC, CE
I recently visited CHBEB’s manufacturing facility and was impressed by their advanced testing lab for both box and pad mounted transformers, ensuring high-quality products for international markets.
CHINT
Comprehensive power solution provider:
- Box Type: Rapid delivery models available
- Pad Mounted: Wide range of standard configurations
- Key strengths: Cost-effective solutions, strong presence in Southeast Asia and Africa
- Certifications: CE, ISO, IEC
During a recent project in Southeast Asia, we sourced pad mounted transformers from CHINT. Their ability to provide a large quantity of standardized units quickly was crucial for meeting our tight project timeline.
TBEA
High-end transformer solutions:
- Box Type: Customizable for large projects
- Pad Mounted: High voltage range available
- Key strengths: Experience in ultra-high voltage projects, strong domestic market
- Certifications: KEMA, CNAS
Here’s a quick overview of TBEA’s offerings:
| Product Type | Voltage Range | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Box Type | Up to 35kV | Highly customizable |
| Pad Mounted | Up to 35kV | Robust design for harsh environments |
Sieyuan Electric
Smart grid integration specialist:
- Box Type: GIS + CSS (Compact Substation) combinations
- Pad Mounted: Smart protection features
- Key strengths: Advanced monitoring and control systems integration
- Certifications: ISO, CE
Taikai Electric
Renewable energy focus:
- Box Type: Tailored for new energy projects
- Pad Mounted: Optimized for solar and wind farm applications
- Key strengths: Experience in renewable energy integration
- Certifications: ISO, IEC
Key points about top Chinese transformer manufacturers:
- They offer a wide range of both box and pad mounted transformers
- Many have strong capabilities in customization and R&D
- Adherence to international standards and certifications is a common feature
- Several specialize in specific applications like renewable energy or smart grids
- Most have significant experience in both domestic and export markets
In my experience, these top manufacturers have consistently demonstrated their ability to meet diverse project requirements. I recall a large-scale urban redevelopment project where we sourced both box and pad mounted transformers from multiple Chinese manufacturers on this list. By leveraging the specific strengths of each company – such as CHBEB’s customization capabilities for unique installation requirements and CHINT’s cost-effective standard units for widespread distribution – we were able to optimize the overall power distribution system while managing costs effectively.
For example, in a recent renewable energy project involving both solar and wind power integration, we utilized box type transformers from Taikai Electric for the main power collection points and pad mounted units from Sieyuan Electric for individual turbine connections. This combination allowed us to balance the need for integrated solutions at key nodes with distributed transformation across the renewable energy site.
As we conclude our exploration of box and pad mounted transformers, remember that choosing the right manufacturer is as crucial as selecting the appropriate transformer type. Consider factors like the manufacturer’s experience in your specific application area, their ability to provide technical support, and their track record in international projects when making your final decision.
Conclusion: Choose Based on Function, Layout, and Cost
Selecting between box type and pad mounted transformers depends on your project’s specific needs. Box types excel in integrated solutions for industrial and commercial settings, while pad mounted units are ideal for residential areas and underground networks. Consider factors like space constraints, power requirements, aesthetic needs, and long-term costs. Both types have their strengths, and the right choice will optimize your power distribution system’s efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Remember, at chbeb-ele, we’re not just sharing information – we’re empowering you to be part of the solution in creating a secure, clean, and efficient energy future. Let’s continue this journey together.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group


