Ever wondered how massive voltages in power grids become safe for your home? The answer lies in a small but mighty device.
Potential transformers, also known as voltage transformers, are crucial components in power systems that reduce high voltages to levels safe for measurement and protection equipment. They ensure accurate monitoring and control of electrical networks while safeguarding personnel and equipment. According to recent industry reports, the global potential transformer market is expected to reach $3.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2020 to 2025.
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in power systems, I’ve seen firsthand how these unassuming devices play a vital role in our energy infrastructure. Let’s dive into the world of potential transformers and uncover their importance in keeping our power systems running smoothly and safely.
Understanding the Working Principle of Potential Transformers
Have you ever been puzzled by how we safely measure thousands of volts? The secret lies in the clever design of potential transformers.
Potential transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They use a primary winding connected to high voltage and a secondary winding that outputs a proportionally lower voltage, allowing safe measurement and monitoring of high voltage systems. Modern potential transformers can achieve efficiencies of up to 99.5%, with typical losses ranging from 0.2% to 0.5% of the rated power.
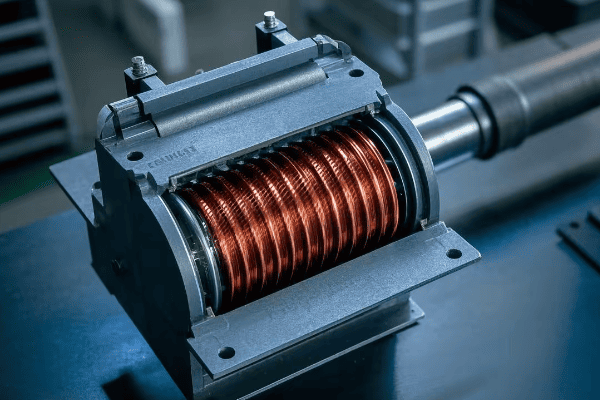
I remember the first time I explained this concept to a group of new engineers. Their amazement at the elegance of this solution mirrored my own when I first learned about it. Let’s break down how these devices work:
The Basics of Potential Transformer Operation
- Primary Winding: This is connected to the high voltage line we want to measure.
- Secondary Winding: This produces a lower, proportional voltage for measurement devices.
- Magnetic Core: This transfers energy between the windings through magnetic flux.
How Voltage Reduction Happens
The key to understanding potential transformers is the turns ratio. Here’s a simple formula:
(Primary Voltage / Secondary Voltage) = (Primary Turns / Secondary Turns)
For example, if we have a 11,000V line and want to measure it with a 110V meter, we need a turns ratio of 100:1.
| Component | Function | Typical Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Winding | Connects to high voltage | 100-1000 turns |
| Secondary Winding | Outputs lower voltage | 1-10 turns |
| Magnetic Core | Transfers energy | N/A |
I once worked on a project where we needed to monitor a 132kV transmission line. We used a potential transformer with a 1200:1 ratio to bring the voltage down to 110V for our measurement equipment. The precision required in manufacturing these devices to maintain accuracy across such a large voltage difference is truly impressive.
Accuracy Classes
Potential transformers come in different accuracy classes, typically:
- 0.1% for revenue metering
- 0.2% for precise measurements
- 0.5% for general measurements
- 3.0% for rough indications
The accuracy class tells you the maximum error in the voltage ratio. For instance, a 0.2% class PT will have a maximum error of 0.2% in its voltage ratio.
Burden and Its Impact
The ‘burden’ of a potential transformer is the load connected to its secondary side. It’s crucial to understand because it affects the transformer’s accuracy:
- Too high a burden can cause voltage drops and measurement errors
- Too low a burden can lead to overvoltage in the secondary circuit
I always advise my clients to carefully match the burden of their measurement devices to the rated burden of the potential transformer to ensure accurate readings.
Understanding the working principle of potential transformers is crucial for anyone involved in power system design or operation. These devices form the backbone of our voltage measurement and protection systems, enabling safe and efficient management of our electrical grids. As we continue to evolve our power systems, the role of potential transformers remains as important as ever.
Key Components and Construction of Potential Transformers
Ever wondered what’s inside those mysterious boxes that handle thousands of volts? Let’s unravel the secrets of potential transformer construction.
Potential transformers consist of primary and secondary windings wound around a laminated core. They also include insulation systems, terminals, and often an oil-filled tank for cooling and insulation. The precise construction ensures accurate voltage transformation and electrical isolation.
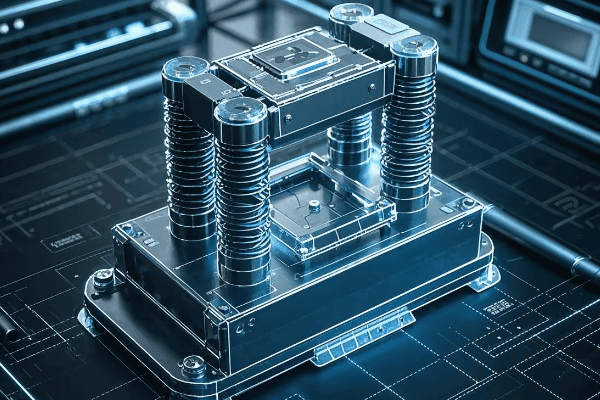
In my years of working with these devices, I’ve come to appreciate the intricate design that goes into each component. Let’s explore the key parts that make up a potential transformer:
Core Components of a Potential Transformer
-
Magnetic Core
- Made of thin laminations of silicon steel
- Reduces eddy current losses
- Shapes can be core-type or shell-type
-
Primary Winding
- Connected to high voltage line
- Made of many turns of thin wire
- Insulated to withstand high voltage
-
Secondary Winding
- Outputs lower voltage for instruments
- Fewer turns of thicker wire
- Designed for standard output (usually 110V or 120V)
-
Insulation System
- Separates primary and secondary windings
- Often uses oil, paper, or modern solid insulation
-
Tank and Bushings
- Tank houses the core and windings
- Bushings provide insulated passage for conductors
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Silicon Steel | Magnetic circuit |
| Primary Winding | Copper | High voltage input |
| Secondary Winding | Copper | Low voltage output |
| Insulation | Oil/Paper/Resin | Electrical isolation |
| Tank | Steel | Housing and protection |
I remember a project where we had to design a custom potential transformer for an unusual voltage level. The precision required in calculating the turns ratio and selecting the right core material was crucial. It taught me the importance of understanding each component’s role in the overall performance of the transformer.
Types of Potential Transformer Construction
-
Oil-Filled Type
- Windings and core immersed in insulating oil
- Excellent cooling and insulation properties
- Requires maintenance to check oil quality
-
Dry Type
- Uses solid insulation materials
- No oil, so reduced fire risk
- Often used indoors or in environmentally sensitive areas
-
Gas-Insulated Type
- Uses SF6 gas for insulation
- Compact design, suitable for high voltages
- Requires special handling due to environmental concerns
Special Design Considerations
-
Voltage Stress Control
- Careful design of insulation to manage electric field distribution
- Use of electrostatic shields to prevent capacitive coupling
-
Thermal Management
- Design of cooling systems to handle heat generated in windings
- Use of materials with good thermal conductivity
-
Accuracy Maintenance
- Precise winding techniques to ensure consistent turns ratio
- Use of high-quality core materials to minimize magnetization current
In my experience, the construction quality of a potential transformer directly impacts its performance and lifespan. I always emphasize to my clients the importance of choosing well-constructed transformers from reputable manufacturers.
Innovations in Construction
The field of potential transformer construction is constantly evolving. Some recent innovations include:
-
Optical Voltage Transformers
- Use fiber optics for voltage measurement
- Immune to electromagnetic interference
- Ideal for digital substations
-
Dry-Type Resin Cast Transformers
- Use epoxy resin for insulation
- Environmentally friendly alternative to oil-filled types
- Reduced maintenance requirements
-
Smart Potential Transformers
- Incorporate digital sensors and communication capabilities
- Enable real-time monitoring and diagnostics
- Facilitate integration with smart grid systems
Understanding the construction and components of potential transformers is crucial for anyone working with power systems. It helps in selecting the right transformer for specific applications, troubleshooting issues, and appreciating the engineering that goes into these vital devices. As we continue to advance our electrical infrastructure, the design of potential transformers will keep evolving to meet new challenges and requirements.
Advantages of Coaxial Winding Design in Voltage Transformers
Ever wondered why some voltage transformers perform better than others? The secret might lie in their winding design.
Coaxial winding in voltage transformers offers improved accuracy, reduced leakage reactance, and better voltage regulation. This design, where primary and secondary windings are wound concentrically, ensures tighter coupling and more uniform distribution of magnetic flux. Studies have shown that coaxial designs can reduce leakage reactance by up to 50% compared to traditional designs.
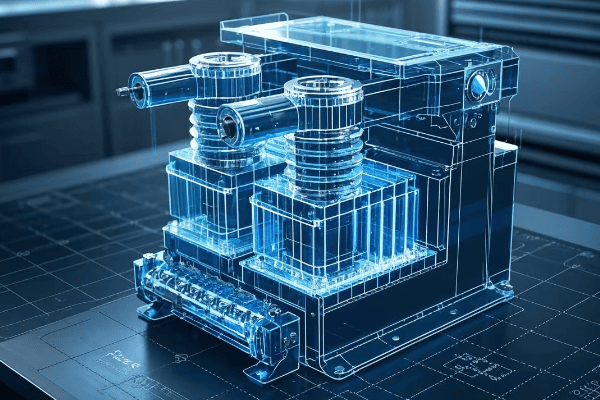
In my years of designing and working with voltage transformers, I’ve seen firsthand the benefits of coaxial winding. Let’s dive into why this design is gaining popularity:
Key Advantages of Coaxial Winding
-
Improved Accuracy
- Tighter coupling between windings
- More uniform flux distribution
-
Reduced Leakage Reactance
- Minimizes voltage drop under load
- Improves voltage regulation
-
Better Impulse Voltage Distribution
- Reduces stress on insulation
- Improves transformer’s ability to withstand voltage surges
-
Compact Design
- Allows for smaller overall transformer size
- Useful in space-constrained applications
| Feature | Traditional Design | Coaxial Design |
|---|---|---|
| Coupling | Good | Excellent |
| Leakage Reactance | Higher | Lower |
| Size | Larger | Compact |
| Impulse Strength | Good | Better |
I remember a project where we replaced traditional wound transformers with coaxial designs in a substation. The improvement in measurement accuracy was significant, leading to better overall system performance and energy management.
How Coaxial Winding Works
In a coaxial design:
- The primary winding is typically on the outside
- The secondary winding is wound inside the primary
- Both windings share a common axis
This arrangement results in:
- More efficient use of core material
- Better distribution of electric field
- Reduced proximity effect losses
Practical Implications
-
Metering Applications
- Higher accuracy class achievable
- Critical for revenue metering and billing
-
Protection Systems
- Faster response to fault conditions
- More reliable operation of protective relays
-
High Voltage Applications
- Better performance under impulse voltage tests
- Improved reliability in high voltage environments
-
Renewable Energy Integration
- Accurate measurement crucial for grid integration
- Compact design suitable for wind turbine applications
In my experience, the benefits of coaxial winding become particularly apparent in high precision applications. I once worked on a project for a national standards laboratory where we needed extremely accurate voltage measurement. The coaxial design allowed us to achieve accuracies better than 0.01%, which was crucial for their calibration work.
Challenges and Considerations
While coaxial winding offers many advantages, it’s not without challenges:
-
Manufacturing Complexity
- Requires specialized winding equipment
- More complex assembly process
-
Cost
- Generally more expensive than traditional designs
- Cost can be offset by improved performance and longevity
-
Repair and Maintenance
- May be more difficult to repair in the field
- Requires specialized skills for maintenance
Future Trends
The trend towards coaxial winding in voltage transformers is likely to continue, driven by:
- Increasing demand for high accuracy in smart grid applications
- Need for compact designs in urban substations
- Growing importance of power quality measurement
As we push the boundaries of power system performance, coaxial winding designs in voltage transformers will play an increasingly important role. Their ability to provide high accuracy, good regulation, and compact size makes them ideal for the evolving needs of our electrical infrastructure.
Understanding the advantages of coaxial winding is crucial for engineers and decision-makers in the power industry. It allows for informed choices in transformer selection, potentially leading to more efficient and reliable power systems. As we continue to innovate in transformer design, the principles of coaxial winding will undoubtedly influence future developments in voltage measurement and power system instrumentation.
Applications of Potential Transformers in Power Systems
Ever wondered how we safely measure and control voltages in massive power grids? Potential transformers are the unsung heroes behind this crucial task.
Potential transformers find wide applications in power systems for voltage measurement, protection, and control. They are used in metering for billing purposes, in protective relaying to detect faults, and in voltage regulation to maintain system stability. A recent industry survey indicates that over 80% of modern substations rely on potential transformers for critical voltage measurements.
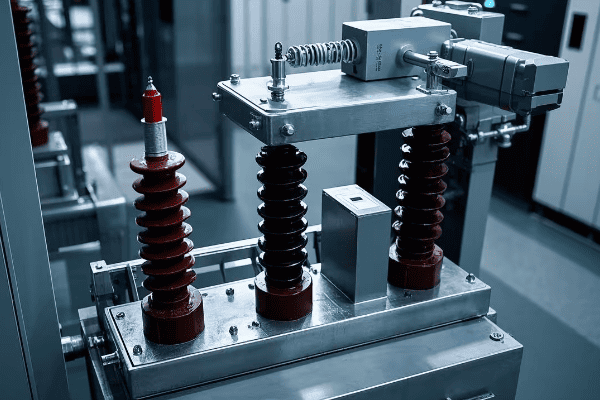
Throughout my career, I’ve seen potential transformers play vital roles in numerous power system applications. Let’s explore some of the key areas where these devices are indispensable:
Key Applications of Potential Transformers
-
Metering and Billing
- Accurate voltage measurement for energy billing
- Revenue-grade metering in power distribution
-
Protective Relaying
- Provide voltage inputs to protective relays
- Enable detection of overvoltage and undervoltage conditions
-
Voltage Regulation
- Monitor system voltage for automatic voltage regulators
- Ensure stable voltage supply to consumers
-
Power Quality Monitoring
- Measure harmonic distortion in voltage waveforms
- Detect voltage sags, swells, and transients
| Application | Accuracy Class | Typical Voltage Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Metering | 0.1% – 0.2% | 11kV:110V, 33kV:110V |
| Protection | 3% – 6% | 132kV:110V, 400kV:110V |
| Voltage Regulation | 0.5% – 1.0% | 11kV:110V, 33kV:110V |
| Power Quality | 0.1% – 0.5% | Varies based on system |
I recall a project where we installed new potential transformers as part of a substation upgrade. The improved accuracy of voltage measurement led to more precise energy billing and better voltage regulation across the distribution network. It was a clear demonstration of how these devices directly impact both utility operations and consumer satisfaction.
Specific Use Cases
-
Transmission Line Monitoring
- Monitor voltage levels along long transmission lines
- Detect line faults and initiate protective actions
-
Substation Automation
- Provide voltage inputs to SCADA systems
- Enable remote monitoring and control of substation equipment
-
Synchronization
- Ensure proper phase angle and voltage magnitude for grid interconnection
- Critical for connecting generators to the grid
-
Load Tap Changer Control
- Provide voltage feedback for transformer tap changers
- Maintain stable secondary voltage under varying load conditions
-
Capacitor Bank Switching
- Monitor system voltage for automatic capacitor bank control
- Improve power factor and voltage profile in distribution systems
In my experience, the reliability of potential transformers in these applications is crucial. I once worked on a project where a faulty potential transformer led to incorrect voltage readings, causing unnecessary capacitor bank switching. It taught me the importance of regular maintenance and testing of these devices.
Emerging Applications
As power systems evolve, new applications for potential transformers are emerging:
-
Renewable Energy Integration
- Accurate voltage measurement for grid-tie inverters
- Ensure compliance with grid codes for solar and wind farms
-
Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
- Monitor grid voltage for high-power EV charging
- Enable smart charging based on grid conditions
-
Microgrid Management
- Provide voltage inputs for microgrid controllers
- Facilitate seamless transition between grid-connected and islanded modes
-
Digital Substations
- Interface with merging units for digital signal processing
- Enable advanced protection and control schemes
Challenges and Considerations
While potential transformers are versatile, there are challenges to consider:
-
Ferroresonance
- Can occur in lightly loaded conditions
- Requires careful system design and protection
-
Accuracy at2. Accuracy at Off-Nominal Frequencies**
- Performance can degrade during system disturbances
- Important consideration for protection applications
-
Environmental Factors
- Extreme temperatures can affect accuracy
- Pollution can degrade insulation in outdoor installations
Understanding the wide range of applications for potential transformers is crucial for power system engineers and planners. These devices form a critical link in our power infrastructure, enabling safe measurement, protection, and control of high voltage systems. As we move towards smarter and more complex grids, the role of potential transformers will continue to evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities in power system management.
Safety Considerations When Using Potential Transformers
Worried about the risks associated with potential transformers? You’re right to be cautious – these devices handle dangerous voltage levels.
Safety is paramount when working with potential transformers. Key considerations include proper insulation, grounding, protection against ferroresonance, and safe handling procedures. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety standards are crucial to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation. According to industry statistics, proper safety measures can reduce transformer-related incidents by up to 90%.
In my years of working with power systems, I’ve learned that respecting the power of high voltage is crucial. Let’s explore the essential safety considerations for potential transformers:
Key Safety Aspects
-
Insulation and Clearances
- Proper insulation for high voltage
- Adequate clearances to prevent flashovers
-
Grounding
- Proper grounding of transformer tank and secondary circuit
- Use of grounding switches for maintenance
-
Overcurrent Protection
- Fuses or circuit breakers on primary side
- Protection against secondary side faults
-
Overvoltage Protection
- Surge arresters to protect against lightning and switching surges
- Proper selection of Basic Insulation Level (BIL)
| Safety Feature | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Prevent electrical breakdown | High-quality insulating materials |
| Grounding | Protect against shock hazards | Solid connection to earth |
| Overcurrent Protection | Prevent damage from faults | Primary fuses or circuit breakers |
| Overvoltage Protection | Guard against surges | Surge arresters, proper BIL |
I remember a close call early in my career when a potential transformer failed due to inadequate surge protection. The resulting explosion could have been catastrophic if not for the proper containment measures in place. It was a stark reminder of the importance of comprehensive safety systems.
Ferroresonance: A Unique Danger
Ferroresonance is a particular concern with potential transformers:
-
What is Ferroresonance?
- Non-linear resonance involving capacitance and iron-core inductance
- Can lead to overvoltages and transformer failure
-
Prevention Measures
- Use of damping resistors in secondary circuits
- Proper fusing arrangements
- Avoiding single-phase switching in three-phase systems
-
Detection and Mitigation
- Monitoring for unusual voltage or current waveforms
- Quick disconnection of transformer if ferroresonance occurs
I once consulted on a project where recurring transformer failures were traced back to ferroresonance issues. Implementing proper damping and switching procedures resolved the problem, highlighting the importance of understanding this phenomenon.
Safe Handling and Maintenance Procedures
-
Installation
- Follow manufacturer guidelines strictly
- Ensure proper mounting and connection
-
Regular Inspections
- Check for oil leaks, damage to bushings
- Inspect connections and grounding
-
Testing
- Periodic insulation resistance tests
- Ratio and polarity checks
-
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
- Implement strict procedures for de-energizing before work
- Use visible grounding devices during maintenance
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Use appropriate PPE for voltage levels involved
- Train personnel on proper use of safety equipment
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Adhering to safety standards is crucial:
- IEEE C57.13 for instrument transformers
- IEC 61869 series for measurement transformers
- OSHA regulations for electrical safety in the workplace
I always emphasize to my team the importance of staying updated with these standards. They evolve based on industry experiences and new technologies, and keeping current can prevent accidents. For more information on instrument transformer standards, visit the IEEE Standards Association website.
Emerging Safety Technologies
The field of transformer safety is constantly evolving:
-
Smart Monitoring Systems
- Real-time monitoring of transformer health
- Early detection of potential issues
-
Arc-Flash Mitigation
- Rapid detection and quenching of electrical arcs
- Critical in reducing the risk of explosions
-
Advanced Insulation Materials
- Development of more resilient and environmentally friendly insulation
- Improved performance under extreme conditions
In my experience, investing in these new technologies often pays off in improved safety and reliability. I’ve seen installations where smart monitoring systems detected issues before they became critical, potentially saving lives and preventing costly outages.
Training and Safety Culture
Perhaps the most important aspect of safety is cultivating a culture of awareness:
-
Regular Training Sessions
- Keep staff updated on safety procedures
- Conduct drills for emergency scenarios
-
Incident Reporting and Analysis
- Encourage reporting of near-misses
- Learn from incidents to improve procedures
-
Clear Communication
- Ensure clear labeling of hazards
- Maintain up-to-date documentation and procedures
Safety considerations for potential transformers are not just about following rules – they’re about protecting lives and ensuring the reliability of our power systems. Throughout my career, I’ve seen how a strong safety culture can prevent accidents and improve overall system performance. As we continue to push the boundaries of our electrical infrastructure, maintaining a focus on safety will remain paramount in the design, installation, and maintenance of potential transformers.
Conclusion
Potential transformers are crucial components in power systems, enabling safe voltage measurement and control. Understanding their principles, applications, and safety considerations is essential for reliable and efficient power distribution. As technology advances, potential transformers continue to evolve, playing a vital role in our increasingly complex electrical grids.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: How often should potential transformers be maintained?
A: Typically, potential transformers should undergo routine inspection annually and comprehensive maintenance every 3-5 years, depending on operating conditions and manufacturer recommendations. -
Q: Can potential transformers be used outdoors?
A: Yes, many potential transformers are designed for outdoor use with appropriate weatherproofing and insulation. However, environmental factors must be considered in their selection and installation. -
Q: What’s the typical lifespan of a potential transformer?
A: With proper maintenance, potential transformers can last 20-30 years or more. However, lifespan can vary depending on operating conditions and quality of maintenance. -
Q: How do potential transformers differ from current transformers?
A: Potential transformers measure voltage and are connected in parallel with the circuit, while current transformers measure current and are connected in series with the circuit. -
Q: Are there alternatives to traditional potential transformers?
A: Yes, newer technologies like optical voltage sensors and low-power instrument transformers (LPITs) are emerging as alternatives in certain applications, especially in digital substations.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Learn more about advanced potential transformer designs
B. Explore career opportunities in power system engineering
C. Understand how to integrate potential transformers in smart grid systems
D. Discover maintenance best practices for potential transformers
E. Investigate the role of potential transformers in renewable energy integration
F. Study safety protocols for working with high voltage equipment
What is an Autotransformer: The Efficient Power Converter You Need to Know About?
Are you tired of bulky transformers eating up space and energy? There’s a smarter solution you might be overlooking.
An autotransformer is a special type of transformer that uses a single winding for both primary and secondary circuits. It offers higher efficiency, smaller size, and lower cost compared to traditional transformers, making it ideal for various voltage conversion applications.
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in power systems, I’ve seen firsthand how autotransformers can revolutionize energy conversion. Let’s dive into the world of autotransformers and discover why they might be the solution you’ve been searching for.
How Does an Autotransformer Work: Unveiling the Basics of This Unique Transformer?
Have you ever wondered how a transformer can be more efficient? The secret lies in its unique design.
An autotransformer works by using a single winding as both the primary and secondary coils. It has a common portion shared by both circuits, allowing for direct electrical connection and more efficient power transfer.

I remember the first time I saw an autotransformer in action. Its simplicity and efficiency amazed me. Let’s break down how these clever devices work:
The Basics of Autotransformer Operation
-
Single Winding: Unlike traditional transformers with separate primary and secondary windings, an autotransformer uses a single winding.
-
Tapped Winding: The winding has taps at different points, creating sections for input and output.
-
Common Section: Part of the winding is shared between the input and output circuits.
-
Electrical Connection: There’s a direct electrical connection between the input and output, not just magnetic coupling.
How Voltage Conversion Happens
The voltage conversion in an autotransformer depends on the ratio of turns between the common section and the whole winding. Here’s a simple way to understand it:
| Section | Turns | Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Whole Winding | N | V |
| Common Section | n | v |
The voltage ratio is proportional to the turns ratio:
V / v = N / n
For example, if you have 1000 turns total and tap at 900 turns, you can convert 1000V to 900V.
Types of Autotransformers
- Step-Up Autotransformer: Increases voltage
- Step-Down Autotransformer: Decreases voltage
- Variable Autotransformer (Variac): Allows for adjustable output voltage
I once worked on a project where we replaced a traditional transformer with an autotransformer in a power distribution system. The energy savings and reduced space requirements were impressive. The client was thrilled with the results.
Advantages of Autotransformer Design
- Higher Efficiency: Less power loss due to the shared winding
- Smaller Size: Requires less copper and iron core material
- Lower Cost: Fewer materials mean lower production costs
- Better Voltage Regulation: Often provides tighter voltage control
Limitations to Consider
- No Electrical Isolation: Input and output are not electrically isolated
- Limited Voltage Change: Most effective for voltage changes less than 2:1
- Higher Short-Circuit Current: Can be a safety concern in some applications
Understanding how autotransformers work is key to appreciating their benefits and limitations. In my experience, they’re often the best choice for applications requiring small voltage adjustments or where space and efficiency are prime concerns. However, it’s crucial to consider the lack of isolation in safety-critical applications.
Autotransformer vs. Traditional Transformer: Key Differences and Advantages?
Wondering why you should choose an autotransformer over a traditional one? The differences might surprise you.
Autotransformers offer higher efficiency, smaller size, and lower cost compared to traditional transformers. However, they lack electrical isolation, making traditional transformers better for applications where safety isolation is crucial.
In my years of working with both types, I’ve seen how choosing the right transformer can make or break a project. Let’s compare these two transformer types:
Key Differences
| Feature | Autotransformer | Traditional Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Windings | Single, tapped | Two separate |
| Electrical Isolation | No | Yes |
| Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Voltage Ratio | Limited range | Wide range |
Advantages of Autotransformers
-
Higher Efficiency
- Less copper loss due to shared winding
- Typically 98-99% efficient vs. 95-98% for traditional transformers
-
Smaller Size and Weight
- Up to 50% reduction in size for similar ratings
- Ideal for space-constrained applications
-
Lower Cost
- Less material used in construction
- Can be 20-30% cheaper than equivalent traditional transformers
-
Better Voltage Regulation
- Often provides more precise voltage control
- Useful in applications requiring tight voltage tolerances
Advantages of Traditional Transformers
-
Electrical Isolation
- Provides safety barrier between primary and secondary
- Essential in many industrial and medical applications
-
Wide Voltage Range
- Can handle large step-up or step-down ratios
- Suitable for a broader range of applications
-
Fault Isolation
- Prevents fault propagation between primary and secondary
-
Separate Grounding
- Allows for different grounding schemes on primary and secondary sides
I once worked on a project where we initially specified a traditional transformer for a voltage adjustment in a factory. After analyzing the requirements, we realized an autotransformer could do the job more efficiently and at a lower cost. The change saved the client significant money and reduced energy losses.
When to Choose Each Type
Choose an Autotransformer When:
- You need small voltage adjustments (less than 2:1 ratio)
- Space and weight are at a premium
- Efficiency is a top priority
- Electrical isolation is not required
Choose a Traditional Transformer When:
- Electrical isolation is necessary for safety
- You need large voltage step-up or step-down
- Separate grounding schemes are required
- Fault isolation between circuits is crucial
Safety Considerations
It’s important to note that the lack of isolation in autotransformers can be a significant safety concern in some applications. In my experience, this is particularly crucial in:
- Medical equipment
- Sensitive electronic devices
- Applications with potential ground faults
Always consult safety standards and regulations when deciding between autotransformers and traditional transformers.
Understanding these differences is crucial for making the right choice in your power system design. While autotransformers offer significant advantages in efficiency and size, traditional transformers still have their place, especially where safety isolation is paramount. In my career, I’ve found that carefully weighing these factors leads to the most successful and cost-effective solutions.
Applications of Autotransformers: From Home Appliances to Industrial Power Systems?
Ever wondered where those efficient autotransformers are hiding? They’re more common than you might think!
Autotransformers are used in a wide range of applications, from household voltage converters to large-scale power distribution systems. Their efficiency and compact size make them ideal for voltage regulation, motor starting, and power transmission.
Throughout my career, I’ve encountered autotransformers in surprisingly diverse settings. Let’s explore some of the most common and interesting applications:
Home and Office Applications
-
Voltage Converters
- For international travelers to use 110V appliances in 220V countries (and vice versa)
- I once used a small autotransformer to power my laptop during an overseas work trip
-
Dimmer Switches
- Variable autotransformers used in lighting control
- Provide smooth dimming for incandescent and some LED lights
-
Home Theater Systems
- Used in some audio equipment for impedance matching
- Can improve sound quality in high-end systems
Industrial Applications
-
Motor Starting
- Reduce inrush current when starting large motors
- I’ve implemented these in factories to prevent voltage dips during motor start-up
-
Voltage Regulation
- Maintain stable voltage in industrial processes
- Crucial in sensitive manufacturing operations
-
Welding Equipment
- Provide variable voltage control in welding machines
- Allow welders to adjust power output for different materials
Power Distribution Applications
-
Transmission Line Interconnection
- Connect power grids with slightly different voltages
- I’ve worked on projects linking regional grids using large autotransformers
-
Substation Voltage Control
- Fine-tune voltage levels in power distribution networks
- Help maintain consistent voltage for end-users
-
Renewable Energy Integration
- Adjust voltage levels from wind or solar farms to match grid requirements
- Becoming increasingly important in the green energy transition
| Application | Voltage Range | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Home Voltage Converters | 110V – 220V | Compact size |
| Motor Starting | Up to 11kV | Reduced inrush current |
| Grid Interconnection | Up to 765kV | Efficient power transfer |
Specialized Applications
-
Railway Systems
- Convert grid power to appropriate voltage for electric trains
- I’ve consulted on projects upgrading railway power systems
-
Testing Equipment
- Provide variable voltage in laboratory and testing environments
- Essential in quality control and product development
-
HVDC Converter Stations
- Used in the conversion process between AC and DC in high-voltage transmission
- Play a crucial role in long-distance power transmission
Considerations in Choosing Autotransformers
When selecting autotransformers for specific applications, consider:
- Voltage Range: Ensure it covers the required input and output voltages
- Power Rating: Must handle the maximum expected load
- Efficiency: Important for energy-intensive applications
- Size and Weight: Critical in space-constrained installations
- Cooling Method: Air-cooled or oil-cooled depending on the environment
- Control Features: Manual or automatic voltage adjustment
In my experience, the versatility of autotransformers makes them a go-to solution for many voltage conversion needs. However, it’s crucial to remember their limitations, particularly the lack of electrical isolation. In applications where safety isolation is paramount, traditional transformers remain the better choice.
The wide range of applications for autotransformers demonstrates their importance in our electrical systems. From the small converter in your travel bag to the massive units in power substations, these efficient devices play a vital role in ensuring our electrical systems run smoothly and efficiently.
The Efficiency Factor: Why Autotransformers Are Gaining Popularity?
Wondering why autotransformers are becoming the go-to choice for many engineers? The answer lies in their impressive efficiency.
Autotransformers are gaining popularity due to their high efficiency, often reaching 98-99%. This efficiency comes from their unique design, which reduces copper losses and core losses compared to traditional transformers.
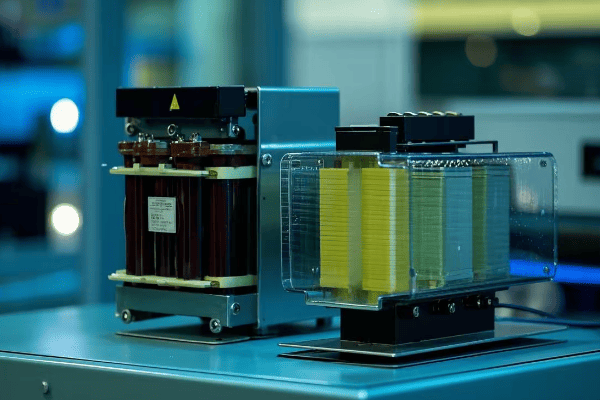
In my years of designing and implementing power systems, I’ve seen a clear trend towards autotransformers in many applications. Let’s dive into why they’re so efficient:
Sources of Efficiency in Autotransformers
-
Reduced Copper Losses
- Single winding design means less copper used
- Lower resistance in the windings
-
Smaller Core
- Less iron needed in the core
- Reduces core losses from hysteresis and eddy currents
-
Direct Electrical Connection
- Part of the power is transferred conductively, not just inductively
- Results in less overall power loss
Efficiency Comparison
| Transformer Type | Typical Efficiency | Losses |
|---|---|---|
| Autotransformer | 98-99% | 1-2% |
| Traditional Transformer | 95-98% | 2-5% |
I once worked on a project upgrading a factory’s power distribution system. By replacing several traditional transformers with autotransformers, we achieved a 2% increase in overall system efficiency. This translated to significant energy savings for the client.
Factors Affecting Autotransformer Efficiency
-
Voltage Ratio
- Most efficient for small voltage changes (less than 2:1)
- Efficiency decreases for larger voltage differences
-
Load Factor
- Operate most efficiently near rated load
- Efficiency can drop at very low or very high loads
-
Core Material
- High-quality silicon steel or amorphous metals improve efficiency
- I’ve seen modern core materials push efficiencies even higher
-
Winding Design
- Optimized winding layouts reduce losses
- Advanced winding techniques can further improve efficiency
Real-World Benefits of High Efficiency
-
Energy Savings
- Lower losses mean less wasted energy
- Can result in significant cost savings over time
-
Reduced Heat Generation
- Less energy lost as heat
- Can simplify cooling requirements
-
Environmental Impact
- Lower energy consumption reduces carbon footprint
- Aligns with green energy initiatives
-
Improved System Performance
- Higher efficiency can mean better voltage regulation
- Reduces stress on other system components
Calculating Efficiency Gains
To understand the impact, let’s look at a simple calculation:
Assume a 1000 kVA transformer operating 24/7:
- Traditional Transformer (97% efficient): 30 kW losses
- Autotransformer (99% efficient): 10 kW losses
Annual Energy Savings: (30 kW – 10 kW) 24 hours 365 days = 175,200 kWh
This can translate to substantial cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Limitations and Considerations
While efficiency is a major advantage, it’s important to consider other factors:
- Safety: Lack of electrical isolation can be a concern in some applications
- Voltage Range: Less suitable for large voltage transformations
- Initial Cost: While often cheaper, high-efficiency models can have higher upfront costs
In my experience, the efficiency benefits of autotransformers make them an excellent choice for many applications, especially where small voltage adjustments are needed. However, it’s crucial to balance efficiency with other requirements like safety and voltage range when making a selection.
The growing popularity of autotransformers is a testament to the industry’s focus on energy efficiency. As we continue to seek ways to reduce energy consumption and improve system performance, autotransformers will likely play an increasingly important role in our power systems.
Safety Considerations: Understanding the Risks and Precautions of Autotransformers?
Concerned about the safety of autotransformers? You’re right to be cautious – these efficient devices come with unique safety considerations.
Autotransformers lack electrical isolation between input and output, which can lead to higher fault currents and potential shock hazards. Proper installation, grounding, and protective measures are crucial to ensure safe operation.

In my years working with power systems, I’ve learned that understanding and respecting the safety aspects of autotransformers is crucial. Let’s explore the key safety considerations:
Primary Safety Concerns
-
Lack of Electrical Isolation
- Input and output circuits are electrically connected
- Can lead to propagation of faults between circuits
-
Higher Fault Currents
- Short circuits can result in extremely high currents
- Requires robust protection systems
-
Potential for Electric Shock
- Ground faults can energize the entire system
- Increases risk to personnel and equipment
-
Voltage Surge Transmission
- Surges on input side can directly affect output side
- May damage connected equipment
Safety Measures and Precautions
| Safety Measure | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Proper Grounding | Prevent shock hazards | Connect to earth ground |
| Safety Measure | Purpose | Implementation |
| —————- | ——— | —————– |
| Proper Grounding | Prevent shock hazards | Connect to earth ground |
| Overcurrent Protection | Prevent damage from faults | Install circuit breakers or fuses |
| Insulation | Prevent direct contact | Use appropriate insulation materials |
| Enclosure | Restrict access to live parts | Install in locked cabinets |
| Warning Labels | Inform about hazards | Apply clear, visible warning signs |
I once worked on a project where an improperly grounded autotransformer led to a near-miss incident. It was a stark reminder of the importance of following safety protocols meticulously.
Best Practices for Safe Operation
-
Proper Installation
- Follow manufacturer guidelines and local electrical codes
- Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent overheating
-
Regular Maintenance
- Conduct periodic inspections for signs of wear or damage
- Test insulation resistance regularly
-
Operator Training
- Educate personnel on specific risks associated with autotransformers
- Provide training on emergency procedures
-
Protective Equipment
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with autotransformers
- Install protective barriers around high-voltage areas
-
Fault Protection
- Implement fast-acting fault detection and isolation systems
- Use differential protection schemes for larger units
Special Considerations for Different Applications
-
Industrial Settings
- Implement lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance
- Consider the impact of harmonics and power quality
-
Residential Use
- Ensure autotransformers for home use are certified by recognized safety organizations
- Educate users on proper usage and potential risks
-
Power Distribution
- Implement redundant protection schemes
- Consider the impact on system stability during faults
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to safety standards is crucial. Key regulations include:
- IEEE C57.12.00 for general requirements
- NEMA ST 1 for specialty transformers
- IEC 61558 for safety of transformers and power supplies
In my experience, staying up-to-date with these standards is essential for ensuring the safe design and operation of autotransformer systems.
Emerging Safety Technologies
The field of transformer safety is constantly evolving. Some recent innovations include:
-
Smart Monitoring Systems
- Real-time monitoring of temperature, current, and voltage
- Early detection of potential issues
-
Advanced Protection Relays
- Faster and more accurate fault detection
- Improved discrimination between normal and fault conditions
-
Arc Flash Mitigation
- Techniques to reduce the risk and severity of arc flash incidents
- Critical in high-power applications
While autotransformers offer significant benefits in terms of efficiency and size, their unique design requires a thoughtful approach to safety. By understanding the risks and implementing proper precautions, we can harness the advantages of autotransformers while ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Sizing and Selection: Choosing the Right Autotransformer for Your Needs?
Struggling to find the perfect autotransformer for your application? You’re not alone in this complex decision-making process.
Selecting the right autotransformer involves considering factors like voltage ratio, power rating, efficiency, physical size, and specific application requirements. Proper sizing ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity of the system.

Throughout my career, I’ve guided many clients through the autotransformer selection process. Let me share some key insights to help you make an informed decision:
Key Factors in Autotransformer Selection
-
Voltage Ratio
- Determine input and output voltage requirements
- Autotransformers are most efficient for ratios less than 2:1
-
Power Rating
- Calculate the maximum load the autotransformer will handle
- Include a safety margin for potential future load increases
-
Efficiency Requirements
- Consider energy costs over the autotransformer’s lifetime
- Higher efficiency models may have higher upfront costs but lower operating costs
-
Physical Size and Weight
- Ensure the autotransformer fits in the available space
- Consider installation and transportation requirements
-
Environmental Conditions
- Assess temperature, humidity, and altitude at the installation site
- Choose appropriate cooling methods (air-cooled or oil-cooled)
Sizing Calculations
Here’s a simple approach to sizing:
- Determine load power: P (Watts)
- Calculate input current: I = P / V_in
- Determine voltage ratio: K = V_out / V_in
- Calculate autotransformer rating: S = P * (1 – K)
For example, for a 10 kW load, 240V input, 208V output:
K = 208/240 = 0.867
S = 10,000 * (1 – 0.867) = 1,330 VA
Selection Table
| Application | Typical Voltage Ratio | Power Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Voltage Conversion | 2:1 or 1.5:1 | 100VA – 5kVA | Portability, safety |
| Industrial Motor Starting | 1.1:1 to 1.5:1 | 10kVA – 1MVA | Inrush current handling |
| Grid Voltage Regulation | 1.1:1 to 1.2:1 | 1MVA – 100MVA | Efficiency, tap changing |
I once worked on a project where a client initially undersized their autotransformer for a motor starting application. The result was frequent tripping and potential motor damage. We rectified the issue by properly sizing the autotransformer to handle the inrush current, which solved the problem and improved overall system reliability.
Application-Specific Considerations
-
Motor Starting
- Size for inrush current (typically 5-7 times full load current)
- Consider duty cycle and starting frequency
-
Voltage Regulation
- Evaluate required voltage adjustment range
- Consider tap changing mechanisms for variable output
-
Power Distribution
- Assess load growth projections
- Consider redundancy requirements
-
Renewable Energy Integration
- Evaluate variability of input voltage from renewable sources
- Consider harmonics and power quality issues
Advanced Selection Criteria
-
Harmonic Handling
- For non-linear loads, consider K-factor rated autotransformers
- Evaluate total harmonic distortion (THD) in the system
-
Short Circuit Impedance
- Important for fault current limitation
- Typically ranges from 2% to 5% for autotransformers
-
Noise Level
- Critical for installations near occupied areas
- Measured in decibels (dB), lower is better for noise-sensitive environments
-
Overload Capacity
- Determine if short-term overloads are expected
- Some autotransformers can handle 20-30% overloads for short periods
Tools and Resources for Selection
-
Manufacturer Selection Guides
- Most reputable manufacturers provide detailed selection tools
- Often include software for precise sizing calculations
-
Industry Standards
- Refer to IEEE, IEC, and NEMA standards for guidance
- Ensure compliance with relevant local codes
-
Simulation Software
- Use power system simulation tools for complex applications
- Helps in analyzing system-wide impacts of autotransformer selection
Choosing the right autotransformer is crucial for the success of your project. It’s not just about meeting current needs but also anticipating future requirements. In my experience, taking the time to thoroughly analyze your needs and consult with experts can save significant costs and headaches down the line.
Remember, the cheapest option is not always the most cost-effective in the long run. Consider the total cost of ownership, including energy costs and maintenance, when making your selection. With careful consideration of these factors, you can select an autotransformer that will serve your needs efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Conclusion
Autotransformers offer efficient, compact, and cost-effective solutions for voltage conversion in various applications. Understanding their operation, advantages, and safety considerations is crucial for optimal selection and use. As technology advances, autotransformers will continue to play a vital role in power systems.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Assess your specific voltage conversion needs
B. Consult with an electrical engineer for personalized advice
C. Explore energy efficiency improvements in your power systems
D. Learn about safety protocols for working with autotransformers
E. Stay updated on the latest developments in transformer technology
F. Consider the role of autotransformers in renewable energy integration
Have you ever wondered about those green boxes in your neighborhood? They’re more important than you might think!
Pad mount transformers are essential devices that convert high-voltage electricity from power lines to a lower, usable voltage for homes and businesses. They work through electromagnetic induction, safely stepping down voltage while maintaining the same amount of power.
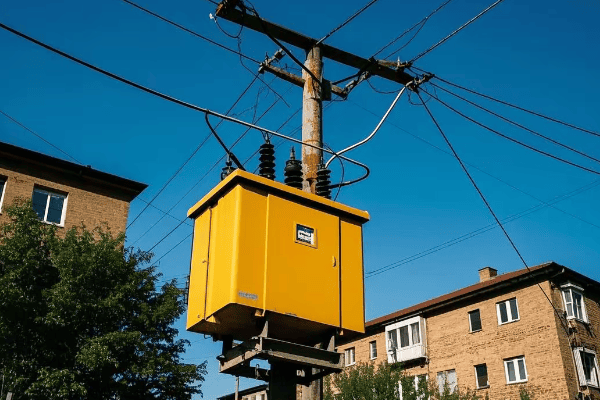

As an electrical engineer with years of experience in power distribution, I’ve seen firsthand how these unassuming boxes keep our lights on and our appliances running. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of pad mount transformers and uncover the secrets behind local power distribution.
What Is a Pad Mount Transformer: The Green Box in Your Neighborhood?
Ever walked past a green metal box and wondered what it’s doing there? You’re not alone in your curiosity!
A pad mount transformer is a ground-level electrical transformer enclosed in a protective metal cabinet. It’s designed to convert high voltage electricity from utility lines to lower voltages suitable for use in homes and businesses.

I remember the first time I opened one of these transformers. The complexity inside that simple-looking box amazed me. Let’s break down what makes these devices so special:
Key Features of Pad Mount Transformers
-
Location: These transformers are installed at ground level, typically on a concrete pad. This makes them easy to access for maintenance and repairs.
-
Enclosure: The metal cabinet protects the internal components from weather and tampering. It’s usually green to blend in with the surroundings.
-
Size: They come in various sizes, depending on the power needs of the area they serve. A typical residential unit might be about the size of a large refrigerator.
-
Voltage Transformation: Inside, they contain the equipment necessary to step down high voltage (usually 7,200 to 14,400 volts) to usable levels (120/240 volts for homes).
-
Safety Features: These include locks, warning signs, and internal components designed to minimize risks.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ground-Level Installation | Mounted on concrete pads | Easy maintenance access |
| Protective Enclosure | Sealed metal cabinet | Weather and tamper resistance |
| Voltage Conversion | Steps down high to low voltage | Provides usable power for consumers |
| Safety Design | Locked, labeled, and insulated | Protects public from electrical hazards |
In my career, I’ve installed and maintained hundreds of these transformers. One project that stands out was in a new suburban development. We had to carefully plan the placement of each transformer to ensure adequate power distribution while maintaining the aesthetic appeal of the neighborhood. It was like solving a puzzle, balancing technical requirements with community needs.
Types of Pad Mount Transformers
-
Single-Phase Transformers: These are commonly used in residential areas. They typically serve 5-8 homes and are the smallest type you’ll see.
-
Three-Phase Transformers: These larger units are used for commercial areas or large residential complexes. They can handle higher power demands.
-
Loop-Feed Transformers: These have connections on both sides, allowing power to flow in either direction. They’re great for areas that need extra reliability.
-
Radial-Feed Transformers: These are simpler, with power flowing in only one direction. They’re often used in areas with straightforward power distribution needs.
Understanding the basics of pad mount transformers helps us appreciate the infrastructure that powers our daily lives. These devices are a testament to modern engineering, quietly performing their vital function day and night. Next time you pass one of these green boxes, you’ll know you’re looking at a key player in bringing electricity from the power plant to your home.
The Basics of Electricity: Understanding Voltage and Current?
Confused by electrical terms? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Voltage is the pressure that pushes electricity through wires, while current is the flow of electricity itself. Think of voltage as water pressure and current as the amount of water flowing through a pipe.
I remember struggling with these concepts when I first started studying electrical engineering. Now, let me share a simple way to understand them:
Voltage: The Electrical Pressure
Voltage is measured in volts (V). It’s the force that drives electricity through a circuit. Here’s how to think about it:
- High Voltage: Like high water pressure, it can push electricity over long distances.
- Low Voltage: Similar to low water pressure, it’s safer for home use but can’t travel far.
Current: The Flow of Electricity
Current is measured in amperes (A) or amps. It represents the amount of electricity flowing through a wire. Think of it this way:
- High Current: Like a lot of water flowing through a pipe, it can do more work but needs thicker wires.
- Low Current: Like a trickle of water, it’s sufficient for small tasks and can use thinner wires.
| Concept | Electrical Term | Water Analogy | Unit of Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Electrical Pressure | Water Pressure | Volts (V) |
| Current | Electrical Flow | Water Flow | Amperes (A) |
Understanding these basics is crucial for grasping how pad mount transformers work. In my early days as an engineer, I used to explain these concepts to apprentices using a simple water system model. It always helped them visualize the invisible flow of electricity.
Power: The Combination of Voltage and Current
Power, measured in watts (W), is the product of voltage and current. It represents the rate at which electrical energy is transferred. Here’s a simple formula:
Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A)
This relationship is key to understanding why we use high voltage for power transmission and lower voltage for home use:
- High Voltage Transmission: Allows for efficient long-distance power transfer with less energy loss.
- Low Voltage Distribution: Safer for end-users but requires more current to deliver the same power.
Practical Applications
Let’s look at some everyday examples:
- Home Outlet: Typically 120V in the US, capable of delivering about 15-20A of current.
- Electric Car Charger: Often uses 240V to charge batteries faster.
- Power Lines: Can carry voltages from thousands to hundreds of thousands of volts.
Understanding these basics helps explain why we need transformers. They allow us to change voltage levels to suit different needs while maintaining the same power. For instance, a pad mount transformer might take in 7,200V and output 240V, increasing the current proportionally to keep the power constant.
In my career, I’ve found that a solid grasp of these fundamentals is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. Whether you’re designing a new power distribution network or just trying to understand your home’s electrical system, these concepts form the foundation of electrical knowledge.
Inside the Box: Key Components of a Pad Mount Transformer?
Ever wondered what’s hidden behind that green metal door? Let’s take a peek inside and demystify the components.
A pad mount transformer contains several key parts: the core, primary and secondary windings, insulating oil, bushings, and protective devices. Each component plays a crucial role in converting high voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses.
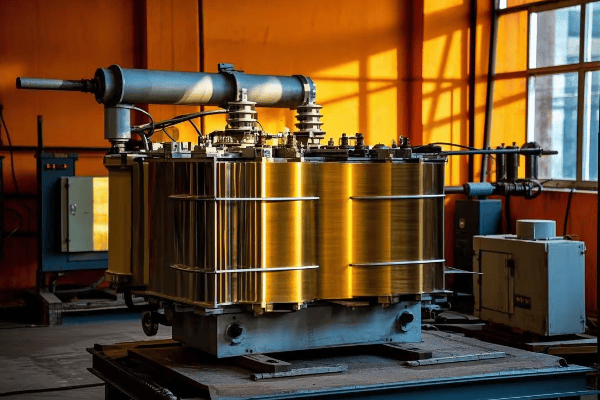
In my years of working with these transformers, I’ve come to appreciate the intricate design of each part. Let’s break down the main components:
Core Components of a Pad Mount Transformer
-
Core
- Made of thin sheets of silicon steel
- Forms a magnetic path for the transformer’s operation
- Shapes can be "core type" or "shell type"
-
Windings
- Primary Winding: Receives high voltage input
- Secondary Winding: Delivers lower voltage output
- Usually made of copper or aluminum wire
-
Insulating Oil
- Fills the transformer tank
- Serves as both an insulator and coolant
- Helps prevent arcing between components
-
Bushings
- Insulated passages for electrical connections
- Allow wires to enter and exit the transformer safely
-
Tank
- Houses all internal components
- Made of steel with a protective coating
- Often includes cooling fins or radiators
| Component | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic circuit | Silicon steel |
| Windings | Voltage transformation | Copper or aluminum |
| Insulating Oil | Insulation and cooling | Mineral oil or synthetic alternatives |
| Bushings | Electrical connections | Porcelain or polymer |
| Tank | Housing and protection | Steel |
I remember a project where we had to replace the core of a transformer due to damage from a power surge. The precision required in reassembling the core layers was incredible – it’s truly an art as much as a science.
How These Components Work Together
-
Electromagnetic Induction
- When AC current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field in the core.
- This changing field induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
-
Voltage Transformation
- The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage change.
- For example, if the primary has 100 turns and the secondary has 10, the voltage will be stepped down by a factor of 10.
-
Cooling Process
- As current flows, heat is generated in the windings.
- The insulating oil absorbs this heat and carries it to the tank walls.
- Cooling fins or radiators on the tank dissipate the heat into the air.
Additional Components for Safety and Efficiency
-
Tap Changer
- Allows for small adjustments in the turns ratio
- Helps maintain consistent output voltage despite fluctuations in input
-
Pressure Relief Device
- Releases pressure if gas builds up inside the tank
- Prevents explosion in case of severe internal faults
-
Temperature Gauge
- Monitors the oil temperature
- Helps detect overloading or cooling problems
-
Protective Relays
- Monitor various parameters like current and temperature
- Can trigger a shutdown if abnormal conditions are detected
In my experience, understanding these components is crucial for anyone working with or around pad mount transformers. Each part plays a vital role in the safe and efficient distribution of electricity to our homes and businesses. The next time you see one of these green boxes, you’ll know that inside is a marvel of engineering, working tirelessly to power our daily lives.
Step-Down Transformation: How High Voltage Becomes Usable Power?
Ever wondered how the massive voltage from power lines becomes the safe 120 volts in your home? Let’s unravel this mystery!
Step-down transformation in pad mount transformers reduces high voltage electricity to lower, safer levels for consumer use. This process uses electromagnetic induction, where the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage reduction.
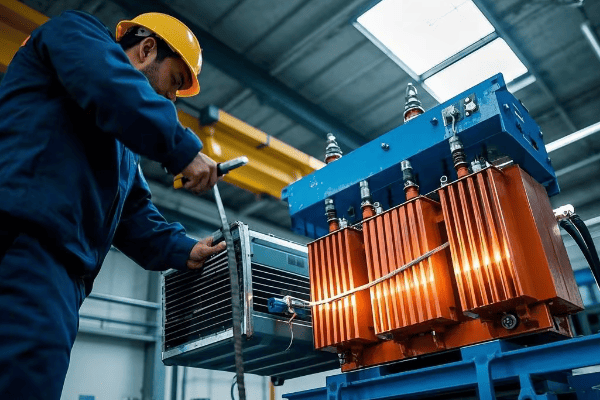
I remember the first time I explained this concept to a group of new technicians. Their amazement at the simplicity and elegance of the process mirrored my own when I first learned about it. Let’s break it down:
The Basics of Step-Down Transformation
- Input Voltage: High voltage electricity enters the transformer (typically 7,200 to 14,400 volts).
- Primary Winding: This coil has many turns of wire.
- Magnetic Core: Concentrates the magnetic field created by the primary winding.
- Secondary Winding: This coil has fewer turns than the primary.
- Output Voltage: Lower voltage electricity exits the transformer (usually 120/240 volts for homes).
| Stage | Voltage Level | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Input | 7,200 – 14,400V | Efficient long-distance transmission |
| Primary Winding | 7,200 – 14,400V | Creates magnetic field |
| Secondary Winding | 120/240V | Induces lower voltage |
| Output | 120/240V | Safe for home use |
The key to understanding this process is the turns ratio. Here’s a simple formula:
(Primary Voltage / Secondary Voltage) = (Primary Turns / Secondary Turns)
For example, if we have 7,200V input and want 240V output, the turns ratio would be 30:1. This means for every 30 turns in the primary winding, there’s 1 turn in the secondary.
The Physics Behind the Magic
- Electromagnetic Induction: When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field.
- Magnetic Core: This field is concentrated and directed by the iron core.
- Induced Voltage: The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
- Voltage Reduction: Fewer turns in the secondary winding result in lower induced voltage.
I once had to explain this to a city council when we were upgrading a neighborhood’s power distribution. Using a simple demonstration with two coils and a battery, I showed how changing the number of turns in the secondary coil affected the output voltage. It was a lightbulb moment for many of them!
Practical Implications
Understanding step-down transformation helps explain several aspects of our power system:
- Efficiency: High voltage transmission is more efficient over long distances.
- Safety: Lower voltage is safer for end-users.
- Flexibility: Different secondary windings can provide various voltage levels (e.g., 120V and 240V) from the same transformer.
Challenges in Step-Down Transformation
- Heat Generation: The process isn’t 100% efficient, and some energy is lost as heat.
- Voltage Regulation: Maintaining consistent output voltage under varying loads can be challenging.
- Harmonics: Non-linear loads can create harmonic distortions, affecting power quality.
In my years working with transformers, I’ve seen how crucial proper design and maintenance are to ensuring efficient step-down transformation. Regular oil testing, thermal imaging, and load monitoring all play a part in keeping these devices operating at peak efficiency.
Understanding step-down transformation is key to appreciating the complex yet elegant system that brings power to our homes. It’s a perfect example of how fundamental principles of physics are applied to solve real-world challenges in power distribution.
Safety First: Protection Features in Pad Mount Transformers?
Worried about the safety of those green boxes in your neighborhood? You’ll be relieved to know they’re designed with multiple layers of protection.
Pad mount transformers incorporate several safety features, including tamper-resistant enclosures, internal fuses, lightning arresters, and automatic shut-off mechanisms. These features work together to protect both the public and utility workers from electrical hazards.
In my years of working with these transformers, I’ve seen how crucial these safety features are. Let me walk you through the key protections:
Key Safety Features
-
Tamper-Resistant Enclosure
- Locked metal cabinet
- Requires special tools to open
- Deters unauthorized access
-
Internal Fuses
- Protect against overcurrent
- Automatically disconnect in case of faults
-
Lightning Arresters
- Divert lightning strikes to ground
- Protect internal components from voltage surges
-
Automatic Pressure Relief Valve
- Releases pressure in case of internal faults
- Prevents explosive rupture of the tank
-
Thermal Protection
- Monitors oil temperature
- Can trigger shutdown if overheating occurs
| Safety Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tamper-Resistant Enclosure | Prevents unauthorized access | Public safety |
| Internal Fuses | Protect against overcurrent | Equipment protection |
| Lightning Arresters | Guard against voltage surges | Reliability |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Prevents explosion | Catastrophic failure prevention |
| Thermal Protection | Monitors temperature | Overheating prevention |
I remember a incident where a car crashed into a pad mount transformer in a residential area. Thanks to the robust enclosure and internal safety features, there was no electrical fire or shock risk to bystanders. It really drove home the importance of these safety measures.
Additional Safety Measures
-
Grounding
- All metal parts are grounded
- Prevents electric shock in case of insulation failure
-
Oil Containment
- Designed to prevent
-
Oil Containment
- Designed to prevent oil leaks
- Protects the environment in case of internal failures
-
Warning Labels
- Clear signage indicating high voltage danger
- Instructions for emergency situations
-
Dead-Front Design
- No exposed live parts when opened for maintenance
- Reduces risk of accidental contact with high voltage components
In my career, I’ve conducted numerous safety training sessions for utility workers. One exercise I always include is a "spot the hazard" game using photos of various transformer installations. It’s amazing how this simple activity sharpens awareness and potentially saves lives.
Safety Protocols for Utility Workers
While pad mount transformers are designed for safety, utility workers still follow strict protocols:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Insulated gloves and boots
- Arc-flash protective clothing
-
Lock-Out/Tag-Out Procedures
- Ensure power is off before maintenance
- Prevent accidental re-energizing
-
Regular Training
- Workers are trained on latest safety procedures
- Includes emergency response drills
Public Safety Education
As part of my role, I often participate in community outreach programs to educate the public about transformer safety. Here are some key points we emphasize:
- Never touch or attempt to open a pad mount transformer
- Keep the area around transformers clear of debris and vegetation
- Report any signs of damage or tampering to your local utility company
- In case of fire or unusual noises, stay away and call emergency services
Continuous Improvement in Safety Design
The field of transformer safety is always evolving. Some recent innovations include:
-
Smart Monitoring Systems
- Real-time monitoring of transformer health
- Early detection of potential issues
-
Eco-Friendly Insulating Fluids
- Less flammable than traditional mineral oil
- Reduced environmental impact in case of leaks
-
Enhanced Seismic Protection
- Designs that better withstand earthquakes
- Crucial in geologically active areas
Understanding these safety features helps build public confidence in our power distribution system. Pad mount transformers are designed with multiple layers of protection to ensure the safety of both the public and utility workers. As technology advances, we continue to see improvements in safety features, making these essential components of our power grid even more secure and reliable.
From Power Plant to Your Home: The Journey of Electricity?
Ever flipped a switch and wondered how that electricity got to your home? It’s a fascinating journey that starts miles away!
Electricity travels from power plants through a complex network of transmission lines, substations, and transformers before reaching your home. Pad mount transformers play a crucial role in the final step, converting high voltage to safe, usable levels for household consumption.

As someone who’s worked at various stages of this journey, I find the entire process remarkable. Let’s break down the steps:
The Electricity Journey: From Generation to Consumption
-
Power Generation
- Electricity is generated at power plants (coal, nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind)
- Typical generation voltage: 2,300 to 30,000 volts
-
Step-Up Transformation
- Large transformers at the plant increase voltage for long-distance transmission
- Transmission voltage: 115,000 to 765,000 volts
-
Transmission
- High voltage electricity travels long distances on transmission lines
- These are the tall towers you see crossing the countryside
-
Substation Step-Down
- Substations use transformers to reduce voltage for local distribution
- Distribution voltage: typically 7,200 to 14,400 volts
-
Local Distribution
- Electricity travels on smaller poles or underground lines through neighborhoods
-
Pad Mount Transformer
- Converts distribution voltage to household voltage (120/240 volts)
- The final step before electricity enters your home
| Stage | Voltage Level | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | 2,300 – 30,000V | Initial power creation |
| Transmission | 115,000 – 765,000V | Efficient long-distance travel |
| Distribution | 7,200 – 14,400V | Local area supply |
| Household | 120/240V | Safe for home use |
I remember a field trip I organized for engineering students to follow this journey. We started at a hydroelectric dam, followed the transmission lines to a substation, and ended at a residential pad mount transformer. Seeing the scale of the system firsthand was eye-opening for many of them.
Why Multiple Voltage Changes?
You might wonder why we change voltage so many times. Here’s why:
- Efficiency: High voltage is more efficient for long-distance transmission. It reduces energy loss.
- Safety: Lower voltage is safer for end-users.
- Practicality: Different voltages suit different purposes (e.g., industrial vs. residential use).
Challenges Along the Journey
- Energy Loss: Some energy is lost as heat at each transformation stage.
- Maintenance: The entire system requires constant monitoring and maintenance.
- Weather Impact: Storms can damage transmission lines and cause outages.
- Balancing Load: The grid must constantly balance supply with demand.
The Role of Pad Mount Transformers
Pad mount transformers are the unsung heroes of this journey. They perform the crucial final step:
- Voltage Conversion: They take the 7,200-14,400V from distribution lines and convert it to 120/240V for homes.
- Safety: They provide a safe interface between the distribution system and residential areas.
- Load Management: They’re sized to handle the electrical needs of multiple homes or businesses.
In my career, I’ve seen the impact of well-designed local distribution systems. A properly placed and maintained pad mount transformer can mean the difference between reliable power and frequent outages for an entire neighborhood.
The Future of Electricity Distribution
The journey of electricity is evolving with new technologies:
- Smart Grids: Incorporating digital technology for better monitoring and control.
- Renewable Integration: Adapting the grid to handle distributed generation from solar and wind.
- Energy Storage: Incorporating batteries to balance load and improve reliability.
Understanding this journey helps us appreciate the complex system that brings power to our homes. From massive power plants to the humble pad mount transformer on your street, each component plays a vital role in keeping our lights on and our devices running.
Conclusion
Pad mount transformers are crucial links in our power distribution chain, safely bringing electricity from high-voltage lines to our homes. Understanding their function helps us appreciate the complex system powering our daily lives and the importance of ongoing maintenance and innovation in electrical infrastructure.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Learn more about energy efficiency in your home
B. Explore careers in electrical engineering and power systems
C. Understand how to report transformer issues in your area
D. Discover the role of transformers in renewable energy integration
E. Investigate smart grid technologies and their impact on power distribution
F. Find out about community initiatives for grid modernization
Have you ever noticed those green metal boxes in your neighborhood? They’re more important than you might think!
Pad mount transformers are ground-level electrical devices that convert high voltage electricity to lower, usable voltages for homes and businesses. These unassuming boxes play a crucial role in powering our daily lives, hidden in plain sight throughout our communities.
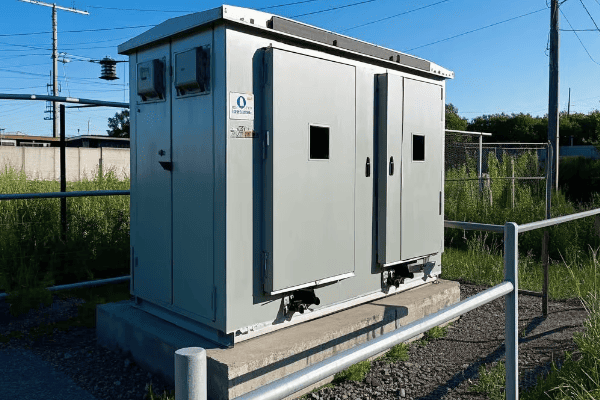
As an electrical engineer with years of experience in power distribution, I’ve come to appreciate these silent workhorses of our electrical grid. Let’s explore the fascinating world of pad mount transformers and discover why they’re so important for our modern lifestyle.
How Do Pad Mount Transformers Work: The Magic Behind the Green Box?
Ever wondered what’s happening inside those mysterious green boxes? The answer might surprise you!
Pad mount transformers use electromagnetic induction to step down high voltage electricity to lower, safer levels for residential and commercial use. They contain coils of wire wrapped around an iron core, converting electrical energy efficiently and safely.
I remember the first time I opened a pad mount transformer. The complexity inside that simple-looking box amazed me. Let’s break down how these devices work:
The Basics of Transformer Operation
- Primary Winding: This coil receives high voltage electricity from power lines.
- Secondary Winding: This coil outputs lower voltage electricity for consumer use.
- Iron Core: This concentrates the magnetic field, improving efficiency.
The key to a transformer’s operation is the principle of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field. This field induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage change.
Components of a Pad Mount Transformer
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Tank | Houses all internal components and insulating oil |
| Bushings | Provide insulated entry/exit points for electrical connections |
| Tap Changer | Allows for minor voltage adjustments |
| Cooling Fins | Help dissipate heat |
| Pressure Relief Device | Prevents damage from internal pressure buildup |
In my experience, the efficiency of these transformers is remarkable. A well-designed pad mount transformer can operate at over 98% efficiency, meaning very little energy is lost in the conversion process.
Types of Pad Mount Transformers
- Single-Phase: Used in residential areas, typically serving 5-8 homes.
- Three-Phase: Found in commercial and industrial settings, handling higher power needs.
I once worked on a project upgrading a neighborhood from single-phase to three-phase power. The increase in available power was significant, allowing for more electric vehicle charging stations and home workshops.
Insulation and Cooling
Pad mount transformers use oil for insulation and cooling. This oil serves three crucial functions:
- It insulates the internal components from each other.
- It helps dissipate heat generated during operation.
- It prevents moisture from damaging the internal components.
The use of oil allows these transformers to be compact yet powerful. However, it also means they need regular maintenance to check oil levels and quality.
Understanding how pad mount transformers work is key to appreciating their role in our power distribution system. These devices are a testament to the ingenuity of electrical engineering, quietly performing their vital function day and night.
The Anatomy of a Pad Mount Transformer: What’s Inside That Metal Cabinet?
Curious about what’s hidden behind that green metal door? Let’s take a peek inside!
A pad mount transformer contains several key components: the core, windings, insulating oil, bushings, and protective devices. Each part plays a crucial role in converting high voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses.
I’ve spent countless hours working with these transformers, and I’m always impressed by their intricate design. Let’s explore the main components:
Core Components of a Pad Mount Transformer
-
Core
- Made of thin laminations of silicon steel
- Shapes: Shell type or core type
- Function: Concentrates magnetic flux
-
Windings
- Primary (high voltage) and secondary (low voltage) coils
- Material: Usually copper or aluminum
- Insulated with paper and immersed in oil
-
Insulating Oil
- Types: Mineral oil or newer synthetic options
- Functions: Insulation, cooling, and moisture protection
-
Bushings
- High voltage and low voltage connections
- Material: Porcelain or polymer
- Function: Safely conduct electricity in and out of the transformer
-
Tank
- Houses all internal components
- Material: Steel with corrosion-resistant coating
- Features: Cooling fins or radiators for heat dissipation
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Silicon Steel | Magnetic flux concentration |
| Windings | Copper/Aluminum | Voltage transformation |
| Oil | Mineral/Synthetic | Insulation and cooling |
| Bushings | Porcelain/Polymer | Electrical connections |
| Tank | Steel | Housing and protection |
Protective Devices
Pad mount transformers also include several safety features:
- Pressure Relief Valve: Prevents explosion in case of excessive internal pressure
- Fuses: Protect against overcurrent
- Lightning Arresters: Guard against voltage surges
- Temperature Gauge: Monitors internal temperature
I once witnessed the importance of these safety features firsthand. During a severe thunderstorm, a nearby transformer was struck by lightning. Thanks to its lightning arrester and other protective devices, the transformer survived without any damage to the internal components.
The Importance of Proper Sealing
One crucial aspect of pad mount transformer design is its sealed construction. This serves several purposes:
- Safety: Prevents unauthorized access to high voltage components
- Environmental Protection: Keeps water and contaminants out
- Noise Reduction: Contains operational noise
- Aesthetics: Allows for a clean, unobtrusive appearance in residential areas
The sealed design is a significant improvement over older, open-air transformer designs. It’s one of the reasons pad mount transformers have become the preferred choice for many urban and suburban areas.
Understanding the anatomy of a pad mount transformer helps appreciate the engineering that goes into these devices. Each component is carefully designed and integrated to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable power distribution. As technology advances, we’re seeing innovations in materials and designs that make these transformers even more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Pad Mount vs. Pole Mount Transformers: Why the Shift to Ground-Level Power?
Ever wondered why we’re seeing more green boxes on the ground instead of transformers on poles? The answer lies in both practicality and aesthetics.
Pad mount transformers offer several advantages over pole mount types, including improved safety, easier maintenance, better aesthetics, and increased reliability. This shift to ground-level power distribution reflects our changing urban landscapes and electrical needs.
In my career, I’ve worked with both types of transformers, and the transition to pad mount has been a game-changer. Let’s compare these two transformer types:
Key Differences Between Pad Mount and Pole Mount Transformers
| Feature | Pad Mount | Pole Mount |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Ground level | Elevated on utility poles |
| Accessibility | Easy access for maintenance | Requires climbing or lift equipment |
| Safety | Enclosed, tamper-resistant | More exposed to elements and potential hazards |
| Aesthetics | Less visually intrusive | More visible in skyline |
| Capacity | Generally higher | Limited by pole strength |
| Weather Resistance | Better protected | More exposed to storms and wildlife |
Advantages of Pad Mount Transformers
-
Safety:
- Enclosed design reduces risk of electrical accidents
- Less vulnerable to vehicle collisions
-
Maintenance:
- Easy ground-level access for technicians
- Can be serviced in all weather conditions
-
Reliability:
- Better protected from weather and wildlife
- Less susceptible to damage from falling trees or branches
-
Aesthetics:
- Lower profile improves neighborhood appearance
- Can be easily concealed with landscaping
-
Capacity:
- Can handle larger loads due to size flexibility
- Easier to upgrade as community needs grow
I remember a project where we replaced pole mount transformers with pad mount units in a suburban area prone to ice storms. The following winter, while neighboring areas experienced outages due to ice-laden power lines, our pad mount transformers continued to operate flawlessly.
Challenges in Transitioning to Pad Mount Transformers
While pad mount transformers offer many benefits, the transition isn’t without challenges:
-
Space Requirements:
- Need clear ground space for installation
- Can be challenging in densely built areas
-
Initial Costs:
- Installation may be more expensive than pole mounting
- Requires construction of concrete pad
-
Flooding Concerns:
- Must be elevated or specially designed in flood-prone areas
-
Public Perception:
- Some residents may be concerned about having transformers at ground level
- Education about safety features is often necessary
Despite these challenges, the benefits of pad mount transformers often outweigh the drawbacks. In my experience, once people understand the advantages, they usually prefer the pad mount option.
The Future of Power Distribution
The shift towards pad mount transformers is part of a larger trend in modernizing our power grid. As we move towards smart grids and renewable energy integration, pad mount transformers offer several advantages:
- Smart Grid Integration: Easier to equip with sensors and communication devices
- Renewable Energy: Better suited for bi-directional power flow from solar and wind sources
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Can be more easily upgraded to handle increased loads
As our electrical needs continue to evolve, pad mount transformers are well-positioned to meet these changing demands. Their flexibility, safety, and reliability make them an excellent choice for modern power distribution systems.
Safety Features of Pad Mount Transformers: Protecting Your Community
Worried about the safety of those green boxes in your neighborhood? You’ll be relieved to know they’re designed with multiple layers of protection.
Pad mount transformers incorporate several safety features, including tamper-resistant enclosures, internal fuses, and automatic shut-off mechanisms. These features work together to protect both the public and utility workers from electrical hazards.
As someone who’s worked extensively with these transformers, I can assure you that safety is a top priority in their design. Let’s explore the key safety features:
Key Safety Features of Pad Mount Transformers
-
Tamper-Resistant Enclosure
- Locked metal cabinet
- Requires special tools to open
- Deters unauthorized access
-
Dead-Front Design
- No exposed live parts when opened
- Reduces risk of accidental contact with high voltage components
-
Internal Fuses
- Protect against overcurrent
- Automatically disconnect in case of faults
-
Lightning Arresters
- Protect against voltage surges
- Divert excess energy to ground
-
Pressure Relief Device
- Prevents explosion in case of internal pressure buildup
- Safely vents excess pressure
| Safety Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tamper-Resistant Enclosure | Prevents unauthorized access | Public safety |
| Dead-Front Design | Eliminates exposed live parts | Worker safety |
| Internal Fuses | Protect against overcurrent | Equipment protection |
| Lightning Arresters | Guard against voltage surges | Reliability |
| Pressure Relief Device | Prevents explosion | Catastrophic failure prevention |
I once witnessed these safety features in action during a severe thunderstorm. A nearby pad mount transformer was struck by lightning, but thanks to its built-in arresters and other protective devices, it continued to function normally. This incident really drove home the importance of these safety measures.
Additional Safety Measures
Beyond the built-in features, there are other safety aspects to consider:
-
Grounding
- All metal parts are grounded
- Prevents electric shock in case of insulation failure
-
Warning Labels
- Clear signage indicating high voltage danger
- Instructions for emergency situations
-
Regular Inspections
- Utility companies perform routine checks
- Ensure all safety features are functioning properly
-
Oil Containment
- Designed to prevent oil leaks
- Environmentally friendly options available
Safety Protocols for Utility Workers
While pad mount transformers are designed for safety, utility workers still follow strict protocols:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Insulated gloves and boots
- Arc-flash protective clothing
-
Lock-Out/Tag-Out Procedures
- Ensure power is off before maintenance
- Prevent accidental re-energizing
-
Regular Training
- Workers are trained on latest safety procedures
- Includes emergency response drills
Public Safety Education
As part of my role, I often participate in community outreach programs to educate the public about transformer safety. Here are some key points we emphasize:
- Never touch or attempt to open a pad mount transformer
- Keep the area around transformers clear of debris and vegetation
- Report any signs of damage or tampering to your local utility company
- In case of fire or unusual noises, stay away and call emergency services
Understanding these safety features and protocols helps build public confidence in our power distribution system. Pad mount transformers are designed with multiple layers of protection to ensure the safety of both the public and utility workers. As technology advances, we continue to see improvements in safety features, making these essential components of our power grid even more secure and reliable.
Environmental Impact: Are Pad Mount Transformers Eco-Friendly?
Concerned about the environmental footprint of those green boxes in your neighborhood? You’re not alone in wondering about their eco-friendliness.
Pad mount transformers have both positive and negative environmental impacts. While they contribute to efficient power distribution and can be designed with eco-friendly materials, they also contain potentially harmful substances that require careful handling and disposal.
As an engineer who’s worked with these transformers for years, I’ve seen the industry’s efforts to make them more environmentally friendly. Let’s explore the environmental aspects of pad mount transformers:
Positive Environmental Impacts
-
Energy Efficiency
- Modern designs achieve up to 99% efficiency
- Reduces energy losses in distribution
-
Land Use
- Smaller footprint compared to substations
- Can be integrated into urban landscapes
-
Noise Pollution
- Quieter operation than older transformer types
- Typically below 60 dB at 5 feet (similar to normal conversation)
-
Longevity
- Lifespan of 20-30 years
- Reduces need for frequent replacements
Environmental Challenges
-
Oil Use
- Traditional mineral oil can be harmful if leaked
- Proper containment and disposal required
-
PCB Legacy
- Older transformers may contain PCBs
- Requires special handling and disposal
-
End-of-Life Disposal
- Contains materials that need proper recycling
- Copper and steel can be recycled, but other components may be hazardous
-
Manufacturing Impact
- Production involves resource extraction and energy use
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | High efficiency reduces losses | Manufacturing energy intensive |
| Materials | Long-lasting, recyclable metals | Some hazardous components |
| Land Use | Small footprint | May impact local ecosystems if not properly sited |
| Noise | Low noise levels | Still contributes some noise pollution |
I remember a project where we replaced old oil-filled transformers with newer, more eco-friendly dry-type units in a sensitive wetland area. The reduction in potential environmental risk was significant, and it gave us all a sense of pride in contributing to a more sustainable power system.
Innovations for Eco-Friendliness
The industry is constantly working on making pad mount transformers more environmentally friendly:
-
Bio-based Oils
- Vegetable-based oils as insulating fluid
- Biodegradable and less toxic
-
Dry-Type Transformers
- Eliminate need for insulating oil
-
Smart Transformers
- Optimize power flow, reducing energy waste
- Enable better integration of renewable energy sources
-
Recycling Programs
- Many utilities now have programs to recycle old transformer components
- Reduces waste and recovers valuable materials
-
SF6-Free Designs
- Eliminating use of sulfur hexafluoride, a potent greenhouse gas
- Replacing with more environmentally friendly insulating gases
In my experience, these innovations are making a real difference. I’ve seen firsthand how newer, eco-friendly transformers can significantly reduce environmental risks while maintaining or even improving performance.
Environmental Considerations in Transformer Siting
Proper placement of pad mount transformers is crucial for minimizing environmental impact:
- Flood Protection: Elevating transformers in flood-prone areas
- Wildlife Considerations: Designing enclosures to prevent animal intrusion
- Vegetation Management: Using native plants for screening without interfering with operation
- Soil Protection: Installing proper foundations and containment to prevent soil contamination
The Bigger Picture
While pad mount transformers do have some environmental impacts, they play a crucial role in our power infrastructure. Their efficiency in power distribution contributes to overall energy savings, which has a net positive environmental impact. As we move towards more renewable energy sources, efficient and reliable transformers become even more important in managing our power grid sustainably.
Understanding the environmental aspects of pad mount transformers helps us appreciate the complexities of balancing our energy needs with environmental stewardship. As technology advances, we’re continually finding ways to make these essential devices more eco-friendly.
Installation and Maintenance: Keeping Your Neighborhood’s Power Hub Running Smoothly
Ever wondered how those green boxes are installed and kept in top shape? It’s a process that requires precision and regular attention.
Installing pad mount transformers involves careful site preparation, precise placement, and proper connection to the power grid. Ongoing maintenance is crucial for ensuring reliability, safety, and longevity, including regular inspections, oil testing, and component replacements.
As someone who’s overseen numerous installations and maintenance operations, I can tell you it’s a complex but fascinating process. Let’s dive into the details:
Installation Process
-
Site Preparation
- Excavation and leveling of the area
- Pouring a concrete pad (typically 6-8 inches thick)
- Installing grounding grid and conduits
-
Transformer Placement
- Using a crane to carefully position the transformer
- Ensuring proper alignment with conduits
-
Electrical Connections
- Connecting primary (high voltage) cables
- Connecting secondary (low voltage) cables
- Installing lightning arresters and grounding
-
Testing and Commissioning
- Performing insulation resistance tests
- Checking for proper voltage output
- Verifying all safety features
| Installation Step | Key Considerations | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Site Preparation | Soil conditions, drainage | 1-2 days |
| Transformer Placement | Weight, access for crane | 1 day |
| Electrical Connections | Cable sizing, proper terminations | 1-2 days |
| Testing and Commissioning | Safety protocols, accuracy of measurements | 1 day |
I remember an installation in a densely populated urban area where space was at a premium. We had to coordinate with multiple city departments and use specialized compact equipment to get the job done. It was challenging, but seeing the transformer seamlessly integrated into the neighborhood was incredibly satisfying.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and reliability of pad mount transformers:
-
Visual Inspections (Monthly to Quarterly)
- Check for oil leaks
- Inspect for physical damage or signs of tampering
- Ensure proper vegetation clearance
-
Oil Testing (Annually)
- Sample and analyze insulating oil
- Check for moisture content and dielectric strength
- Test for dissolved gases (indicator of internal issues)
-
Thermal Imaging (Annually)
- Use infrared cameras to detect hot spots
- Identify potential issues before they cause failures
-
Electrical Testing (Every 3-5 years)
- Perform turns ratio test
- Check insulation resistance
- Verify proper operation of protective devices
-
Component Replacement (As needed)
- Replace gaskets to prevent oil leaks
- Update bushings or other worn components
- Retrofit with newer, more efficient parts when possible
Challenges in Maintenance
Maintaining pad mount transformers comes with its own set of challenges:
- Access Issues: Sometimes transformers are installed in hard-to-reach locations
- Weather Conditions: Maintenance may be affected by extreme temperatures or storms
- Aging Infrastructure: Older transformers may require more frequent attention
- Balancing Act: Minimizing downtime while ensuring thorough maintenance
I once dealt with a transformer that was showing signs of overheating. Through careful analysis and thermal imaging, we discovered that the cooling fins were partially clogged with debris. A thorough cleaning resolved the issue, potentially preventing a costly failure.
Importance of Proactive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance is key to preventing issues before they occur:
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data and trends to anticipate potential problems
- Condition-Based Monitoring: Installing sensors for real-time health monitoring
- Asset Management Systems: Tracking maintenance history and scheduling future work
Training and Safety
Proper training for maintenance personnel is crucial:
- Safety Protocols: Rigorous training on electrical safety and PPE use
- Technical Skills: Ongoing education on new technologies and maintenance techniques
- Emergency Response: Preparation for potential failures or accidents
In my career, I’ve seen how good maintenance practices can significantly extend the life of a transformer and prevent unexpected outages. It’s not just about keeping the lights on; it’s about ensuring the safety and reliability of our entire power distribution system.
The Role of Pad Mount Transformers in Smart Grids: Powering the Future
Curious about how those green boxes fit into the future of energy? They’re more high-tech than you might think!
Pad mount transformers are evolving to play a crucial role in smart grids. They’re being equipped with sensors, communication devices, and advanced control systems to enable real-time monitoring, improved efficiency, and better integration of renewable energy sources.
As someone who’s been involved in smart grid projects, I’ve seen firsthand how pad mount transformers are becoming the backbone of our modern power distribution system. Let’s explore their role in smart grids:
Key Features of Smart Pad Mount Transformers
-
Real-Time Monitoring
- Sensors for load, temperature, and oil condition
- Immediate alert system for faults or abnormalities
-
Communication Capabilities
- Integration with SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems
- Two-way communication for remote control and data transmission
-
Advanced Voltage Regulation
- Automatic tap changers for voltage optimization
- Helps manage fluctuations from renewable energy sources
-
Data Analytics
- Predictive maintenance based on operational patterns
- Load forecasting for better grid management
| Feature | Traditional Transformer | Smart Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Manual inspections | Real-time, continuous |
| Communication | None | Two-way with control center |
| Voltage Regulation | Fixed or manual adjustment | Automatic, dynamic |
| Maintenance | Schedule-based | Condition-based |
I remember implementing a smart transformer system in a neighborhood with high solar panel adoption. The ability to manage bi-directional power flow and voltage fluctuations made a significant difference in grid stability and efficiency.
Benefits of Smart Pad Mount Transformers in Grid Operations
-
Improved Reliability
- Quick identification and isolation of faults
- Reduced outage duration and frequency
-
Enhanced Efficiency
- Optimized power flow reduces energy losses
- Better load balancing across the grid
-
Integration of Renewable Energy
- Better management of intermittent sources like solar and wind
- Facilitates grid-scale energy storage integration
-
Demand Response Capabilities
- Enables participation in demand response programs
- Helps manage peak loads more effectively
-
Asset Management
- Extended equipment life through predictive maintenance
- More efficient use of utility resources
Challenges in Implementing Smart Transformers
While the benefits are significant, there are challenges to overcome:
- Cost: Smart features increase initial investment
- Cybersecurity: Increased connectivity raises security concerns
- Skill Gap: Requires workforce training in new technologies
- Data Management: Handling and analyzing large volumes of data
In my experience, addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach between utilities, technology providers, and regulators. I’ve been part of projects where we’ve had to develop new protocols for data security and train teams in advanced data analytics.
Future Trends in Smart Transformer Technology
Looking ahead, I see several exciting developments on the horizon:
- AI and Machine Learning: For more sophisticated predictive maintenance and grid optimization
- Edge Computing: Processing data locally for faster response times
- Energy Storage Integration: Combining transformers with battery storage for enhanced grid stability
- Self-Healing Grids: Transformers playing a key role in automated fault detection and recovery
The Bigger Picture: Transforming Our Energy Landscape
Smart pad mount transformers are more than just an upgrade to our existing infrastructure. They’re a fundamental shift in how we manage and distribute energy. As we move towards a more decentralized, renewable-based energy system, these smart devices will be crucial in maintaining grid stability and efficiency.
In my career, I’ve seen the power industry evolve dramatically. The integration of smart pad mount transformers into our grids is one of the most exciting developments I’ve witnessed. It’s not just about keeping the lights on; it’s about creating a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy future for all of us.
Conclusion
Pad mount transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical grid, quietly powering our neighborhoods while adapting to the challenges of modern energy needs. From their efficient design to their evolving role in smart grids, these devices are crucial for a reliable and sustainable power distribution system.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Learn more about smart grid technologies
B. Explore careers in electrical engineering and power systems
C. Investigate energy efficiency improvements for your home
D. Understand how to report transformer issues in your area
E. Discover the role of transformers in renewable energy integration
F. Find out about community initiatives for grid modernization
Are you struggling to choose between tank and dry-type transformers? You’re not alone in this dilemma.
The choice between tank and dry-type transformers depends on factors like efficiency, size, environmental impact, safety, and cost. Tank transformers are often more efficient and can handle higher voltages, while dry-type transformers are safer in fire-prone areas and require less maintenance.

I’ve spent years working with both types of transformers, and I can tell you that making the right choice is crucial for your project’s success. Let’s dive into the details to help you make an informed decision.
What Are Tank and Dry-Type Transformers: A Quick Introduction for Decision Makers?
Confused about the basics of tank and dry-type transformers? Let’s clear that up right now.
Tank transformers use oil for insulation and cooling, while dry-type transformers use air and solid insulation. Tank transformers are typically used for higher voltages and outdoor applications, whereas dry-type transformers are common in indoor and fire-sensitive areas.
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how crucial understanding these basics is for making the right choice. Here’s a deeper look:
Key Characteristics of Tank Transformers
- Insulation: Uses mineral oil or synthetic fluids
- Cooling: Oil serves as both insulator and coolant
- Typical Applications: Outdoor substations, large industrial settings
- Voltage Range: Can handle very high voltages (up to 765 kV)
- Size: Generally larger and heavier
Key Characteristics of Dry-Type Transformers
- Insulation: Uses air and solid materials (epoxy resin, silicone)
- Cooling: Air-cooled, sometimes with fans
- Typical Applications: Indoor settings, commercial buildings, hospitals
- Voltage Range: Usually up to 35 kV
- Size: Generally smaller and lighter
Let’s compare them side by side:
| Feature | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | Oil | Air and solid materials |
| Cooling | Oil-cooled | Air-cooled |
| Typical Location | Outdoor | Indoor |
| Voltage Range | Up to 765 kV | Up to 35 kV |
| Fire Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | More complex | Simpler |
I remember a project where we initially specified a tank transformer for a new hospital wing. After considering the fire safety regulations and indoor location, we switched to a dry-type transformer. It was a crucial decision that saved us from potential compliance issues down the line.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
- Location: Indoor or outdoor installation?
- Voltage Requirements: What voltage levels are you working with?
- Load Profile: Continuous heavy loads or intermittent use?
- Environmental Concerns: Is oil leakage a significant risk?
- Fire Safety: Are you dealing with a fire-sensitive area?
- Maintenance Capabilities: Do you have the resources for oil maintenance?
- Noise Considerations: Is the transformer located near occupied areas?
- Budget: Initial cost vs. long-term operational expenses
Understanding these factors is crucial. In my experience, the wrong choice can lead to increased costs, safety risks, and operational inefficiencies. I’ve seen cases where companies had to replace transformers within a few years due to overlooking key factors like location constraints or load growth.
Remember, while tank transformers have been the traditional choice for many high-power applications, advancements in dry-type technology are narrowing the gap. It’s not just about what works now, but what will serve you best in the long run.
Efficiency Comparison: Do Tank Transformers Outperform Dry-Type in Energy Savings?
Worried about energy bills? The efficiency of your transformer can make a big difference.
Generally, tank transformers are more efficient than dry-type, especially at higher ratings. However, recent advancements in dry-type technology have narrowed this gap, making the efficiency comparison more nuanced.
I’ve spent countless hours analyzing transformer efficiencies, and I can tell you it’s not always a straightforward comparison. Let’s break it down:
Understanding Transformer Efficiency
- No-Load Losses: Occur in the core, present even when the transformer is energized but not supplying load
- Load Losses: Occur in the windings, increase with the square of the load current
- Total Losses: Sum of no-load and load losses
Comparing Tank and Dry-Type Efficiencies
| Aspect | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| No-Load Losses | Generally lower | Slightly higher |
| Load Losses | Lower at high loads | Competitive at low to medium loads |
| Cooling Efficiency | More efficient due to oil | Less efficient, relies on air |
| Efficiency at High Ratings | Superior | Good, but typically lower |
| Efficiency at Low Ratings | Comparable to dry-type | Comparable to tank |
In my experience, the efficiency advantage of tank transformers becomes more pronounced as the size and voltage rating increase. For example, I once worked on a project where replacing a 10 MVA dry-type transformer with a tank transformer of the same rating resulted in a 0.5% efficiency improvement. While that might not sound like much, it translated to significant energy savings over time.
Factors Influencing Efficiency
- Core Material: High-grade silicon steel or amorphous metals can significantly reduce core losses
- Winding Design: Optimized winding layouts can reduce copper losses
- Cooling System: Efficient cooling reduces overall losses
- Load Profile: Efficiency varies with load, so matching the transformer to the expected load profile is crucial
- Ambient Temperature: High temperatures can affect efficiency, especially in dry-type transformers
Recent Advancements
Dry-type transformers have seen significant improvements in recent years:
- Use of advanced core materials like amorphous metals
- Improved winding designs and insulation systems
- Better cooling techniques, including the use of cast coil technology
These advancements have made dry-type transformers more competitive in terms of efficiency, especially in the lower to medium power ranges.
Making the Right Choice for Efficiency
When considering efficiency:
- Analyze Your Load Profile: A transformer’s efficiency varies with load. Match the transformer type to your typical operating conditions.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Higher efficiency often means higher upfront costs but lower operating costs.
- Look at Lifecycle Efficiency: Consider how efficiency might degrade over time for each type.
- Check Regulatory Requirements: Some regions have minimum efficiency standards that may influence your choice.
In my years of consulting, I’ve seen cases where the slightly lower efficiency of a dry-type transformer was offset by its lower maintenance costs and better suitability for the installation environment. It’s not always about choosing the most efficient option on paper, but rather the one that offers the best overall performance in your specific situation.
Remember, while tank transformers often have an edge in efficiency, especially at higher ratings, the best choice depends on a holistic view of your application, including factors beyond just efficiency.
Size and Weight: How Space Requirements Differ Between Tank and Dry-Type Transformers
Struggling with limited space for your transformer installation? The size difference between tank and dry-type transformers could be crucial.
Tank transformers are generally larger and heavier due to their oil-filled design, while dry-type transformers are more compact and lighter. This size difference can significantly impact installation options and costs.
In my years of designing transformer installations, I’ve seen how size and weight can make or break a project. Let’s dive into the details:
Comparing Dimensions and Weight
| Aspect | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Footprint | Larger | Smaller |
| Height | Generally taller | Usually shorter |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Space for Cooling | Needs more | Needs less |
| Containment Requirements | Oil containment needed | No containment needed |
I remember a project where we had to retrofit a transformer in an old urban substation. The limited space and difficulty in transporting a large tank transformer led us to choose a dry-type option, saving both space and installation headaches.
Factors Influencing Size and Weight
-
Insulation Medium:
- Tank: Oil adds significant weight and requires space for expansion
- Dry-Type: Air and solid insulation are lighter and more compact
-
Cooling System:
- Tank: Radiators and oil pumps add to size
- Dry-Type: Air cooling or fans are more compact
-
Voltage Rating:
- Higher voltages generally require larger transformers for both types
-
Power Rating:
- Higher power ratings increase size and weight for both types
-
Design Efficiency:
- More efficient designs can sometimes be smaller due to reduced heat generation
Space Considerations in Different Settings
-
Indoor Installations:
- Dry-type transformers are often preferred due to their compact size and reduced fire risk
- Tank transformers may require special rooms with oil containment
-
Outdoor Substations:
- Tank transformers are common, with space for oil containment and cooling systems
- Dry-type transformers can be used but may need weather protection
-
Rooftop Installations:
- Dry-type transformers are often chosen due to their lighter weight
- Tank transformers may require structural reinforcements
-
Mobile or Temporary Installations:
- Dry-type transformers are easier to transport and set up quickly
-
Underground Installations:
- Dry-type transformers are preferred due to reduced fire and environmental risks
Impact on Installation and Maintenance
-
Transportation:
- Tank transformers often require specialized transport due to weight
- Dry-type transformers are easier to move and position
-
Foundation Requirements:
- Tank transformers need stronger foundations
- Dry-type transformers have less stringent foundation needs
-
Access for Maintenance:
- Tank transformers need space for oil handling equipment
- Dry-type transformers require less clearance for maintenance
In my experience, the size and weight differences between tank and dry-type transformers can have cascading effects on project costs and timelines. I’ve seen cases where the choice of a compact dry-type transformer allowed for a simpler, faster installation process, saving both time and money.
However, it’s not always about choosing the smallest option. In one industrial project, we opted for a larger tank transformer because its higher efficiency and better overload capacity outweighed the space constraints.
When considering size and weight:
- Assess your available space carefully
- Consider future expansion needs
- Factor in installation and maintenance access
- Don’t forget about ancillary equipment like cooling systems and containment structures
Remember, the right choice balances space constraints with performance needs and long-term operational considerations.
Environmental Impact: Oil-Filled vs. Air-Cooled Transformer Technologies
Concerned about the environmental footprint of your transformer choice? You’re not alone in this eco-conscious era.
Tank transformers pose potential environmental risks due to oil leaks but are often more energy-efficient. Dry-type transformers eliminate oil-related environmental concerns but may have a larger carbon footprint due to lower efficiency in some cases.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen environmental considerations become increasingly important in transformer selection. Let’s break down the environmental impacts:
Environmental Aspects of Tank Transformers
-
Oil-Related Risks:
- Potential for oil leaks and spills
- Risk of soil and water contamination
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Generally more efficient, especially at higher ratings
- Lower energy losses can mean a smaller carbon footprint over time
-
End-of-Life Considerations:
- Oil must be properly disposed of or recycled
- Metal components are recyclable
-
PCB Legacy:
- Older transformers may contain PCBs, requiring special handling
Environmental Aspects of Dry-Type Transformers
-
No Oil-Related Risks:
- Eliminates the risk of oil leaks and spills
- Safer for environmentally sensitive areas
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Typically less efficient than tank transformers, especially at higher ratings
- Higher losses can lead to increased energy consumption
-
End-of-Life Considerations:
- Easier to recycle with no oil to dispose of
- Some insulation materials may require special handling
-
Material Use:
- May use more copper or aluminum due to less efficient cooling
Let’s compare these aspects:
| Aspect | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Spill Risk | High | None |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher | Lower (generally) |
| Recyclability | Good, but oil complicates | Excellent |
| Fire Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Material Usage | Less copper/aluminum | More copper/aluminum |
I recall a project near a protected wetland where the environmental risk of an oil spill was deemed too high. We opted for a dry-type transformer despite its slightly lower efficiency. The peace of mind and regulatory compliance were worth the trade-off.
Mitigating Environmental Impacts
For Tank Transformers:
- Use biodegradable oils
- Implement robust containment systems
- Regular maintenance to prevent leaks
- Efficient designs to minimize losses
For Dry-Type Transformers:
- Use high-efficiency designs to minimize energy losses
- Choose environmentally friendly insulation materials
- Implement effective cooling systems to improve efficiency
Lifecycle Environmental Impact
When assessing environmental impact, consider the entire lifecycle:
- Manufacturing: Both types require resource extraction and energy-intensive production
- Operation: Energy efficiency over the operational life is crucial
- Maintenance: Less maintenance for dry-type can mean fewer resources used over time
- End-of-Life: Proper recycling and disposal are important for both types
In my experience, the best environmental choice often depends on the specific application and location. For instance, in a data center project, we chose high-efficiency dry-type transformers. The slightly lower efficiency was offset by the reduced fire risk and cooling needs, which aligned with the facility’s overall energy strategy.
Regulatory Considerations
Environmental regulations are becoming stricter:
- Some areas require oil containment systems for tank transformers
- Energy efficiency standards are pushing both types to improve
- PCB-containing transformers are being phased out globally
When making your choice, consider:
- Local environmental regulations
- Your organization’s sustainability goals
- The specific environmental risks of your installation site
- The long-term energy efficiency and its impact on carbon footprint
Remember, the most environmentally friendly transformer is the one that best fits your specific needs while minimizing overall environmental impact throughout its lifecycle.
Fire Safety Considerations: Why Dry-Type Transformers Might Be Preferred in Some Settings?
Worried about fire risks in your transformer installation? You should be – it’s a critical safety concern.
Dry-type transformers are often preferred in fire-sensitive areas due to their lower fire risk. They don’t use flammable oil, making them safer for indoor installations, densely populated areas, or locations with strict fire safety regulations.

In my years of working on transformer installations, I’ve seen fire safety become an increasingly crucial factor in decision-making. Let’s dive into the details:
Fire Safety Aspects of Tank Transformers
-
**Oil as
-
Oil as a Fire Hazard:
- Mineral oil is flammable
- Oil can ignite if there’s an electrical fault
-
Containment Measures:
- Require oil containment systems
- May need fire walls in some installations
-
Fire Suppression:
- Often require dedicated fire suppression systems
- Water-based systems can be problematic with oil
-
Smoke and Toxic Fumes:
- Burning oil can produce thick smoke and toxic fumes
Fire Safety Aspects of Dry-Type Transformers
-
Non-flammable Materials:
- No oil means reduced fire risk
- Solid insulation materials are typically fire-resistant
-
Self-Extinguishing Properties:
- Many dry-type transformers use self-extinguishing materials
-
Reduced Need for Containment:
- No oil means no need for complex containment systems
-
Simpler Fire Suppression:
- Standard fire suppression systems can be used
- Less risk of spreading fire through liquid
Let’s compare these aspects:
| Aspect | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Flammable Materials | Yes (oil) | No |
| Fire Risk | Higher | Lower |
| Containment Needs | Extensive | Minimal |
| Smoke Production | High | Low |
| Suitable for Indoor Use | Limited | Widely used |
I remember a project in a high-rise building where the fire marshal initially rejected our plan for a tank transformer in the basement. We switched to a dry-type transformer, which not only met fire code requirements but also simplified the overall installation process.
Key Considerations for Fire Safety
-
Location:
- Indoor vs. outdoor installation
- Proximity to occupied areas
-
Building Codes and Regulations:
- Local fire safety standards
- Insurance requirements
-
Industry-Specific Needs:
- Hospitals, data centers, and schools often prefer dry-type
-
Emergency Response:
- Ease of access for firefighters
- Compatibility with building fire systems
Fire Safety Measures for Tank Transformers
If you must use a tank transformer in a sensitive area:
- Use less flammable fluids (e.g., silicone or vegetable-based oils)
- Install robust fire detection and suppression systems
- Implement proper containment and barrier systems
- Ensure adequate ventilation to disperse heat and fumes
Advantages of Dry-Type in Fire-Sensitive Areas
-
Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities:
- Reduced evacuation risks
- Continuity of critical services
-
High-Rise Buildings:
- Easier compliance with building codes
- Reduced risk to occupants
-
Educational Institutions:
- Safer for densely populated areas
- Peace of mind for administrators and parents
-
Data Centers:
- Protection of critical infrastructure
- Reduced risk of data loss due to fire
In my experience, the choice between tank and dry-type transformers often comes down to fire safety in sensitive environments. I’ve seen cases where the slightly higher cost of a dry-type transformer was easily justified by the reduced fire risk and simplified safety systems.
For instance, in a recent data center project, we chose dry-type transformers despite their slightly lower efficiency. The decision was driven by the critical nature of the facility and the potential catastrophic impact of a fire. The peace of mind and reduced insurance premiums made it a clear choice.
When considering fire safety:
- Assess your environment’s specific risks
- Consult with local fire authorities
- Consider the total cost of fire safety measures, not just the transformer itself
- Think about future changes in building use or regulations
Remember, while dry-type transformers have a clear advantage in fire safety, modern tank transformers with advanced safety features can also be suitable in many applications. The key is to carefully evaluate your specific needs and risks.
Maintenance Requirements: Tank vs. Dry-Type Transformers – Which Costs More Long-Term?
Worried about ongoing maintenance costs? You’re right to consider this crucial factor.
Tank transformers generally require more frequent and complex maintenance due to oil monitoring and handling. Dry-type transformers, with their simpler design, typically have lower maintenance needs and costs over their lifetime.
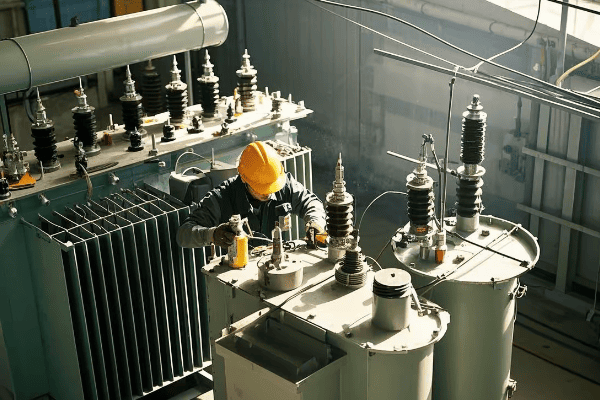
In my years of managing transformer installations, I’ve seen how maintenance can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. Let’s break down the maintenance aspects:
Maintenance Needs for Tank Transformers
-
Oil Testing and Analysis:
- Regular sampling and testing of insulating oil
- Checking for contaminants, moisture, and dissolved gases
-
Oil Filtration or Replacement:
- Periodic oil filtration to remove impurities
- Occasional complete oil replacement
-
Cooling System Maintenance:
- Checking and maintaining radiators, fans, and pumps
- Ensuring proper oil circulation
-
Gasket and Seal Checks:
- Regular inspection for oil leaks
- Replacement of worn gaskets and seals
-
Bushings and Tap Changers:
- Inspection and maintenance of bushings
- Servicing of on-load tap changers
Maintenance Needs for Dry-Type Transformers
-
Visual Inspections:
- Checking for dust accumulation or signs of overheating
- Inspecting insulation for cracks or damage
-
Cooling System Checks:
- Ensuring proper function of fans (if present)
- Cleaning air passages and vents
-
Electrical Testing:
- Periodic insulation resistance tests
- Power factor testing
-
Tightening Connections:
- Checking and tightening electrical connections
Let’s compare these maintenance aspects:
| Aspect | Tank Transformer | Dry-Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency of Maintenance | Higher | Lower |
| Complexity of Maintenance | More complex | Simpler |
| Specialized Equipment Needed | Yes (for oil handling) | Minimal |
| Risk of Leaks | Yes | No |
| Environmental Considerations | Oil disposal/recycling | Minimal |
I recall a manufacturing plant where we replaced several aging tank transformers with dry-type units. The reduction in maintenance downtime and costs was significant, paying for the higher initial investment within a few years.
Long-Term Cost Considerations
-
Labor Costs:
- Tank transformers often require specialized technicians
- Dry-type maintenance can often be done by in-house staff
-
Consumables and Replacements:
- Oil and filtration costs for tank transformers
- Fewer consumables for dry-type transformers
-
Downtime Costs:
- Tank transformers may require longer outages for maintenance
- Dry-type maintenance is typically quicker
-
Environmental Compliance:
- Costs associated with oil handling and disposal for tank transformers
- Minimal environmental compliance costs for dry-type
-
Lifecycle Considerations:
- Properly maintained tank transformers can have a longer lifespan
- Dry-type transformers may need replacement sooner but with less maintenance
Factors Influencing Maintenance Needs
-
Operating Environment:
- Harsh conditions increase maintenance for both types
- Dry-type more sensitive to dusty or corrosive environments
-
Load Profile:
- Heavy or fluctuating loads can increase maintenance needs
- Overloading impacts both types but can be more critical for dry-type
-
Age of the Transformer:
- Older units typically require more frequent maintenance
- End-of-life considerations differ between types
In my experience, the maintenance advantage of dry-type transformers is most pronounced in clean, indoor environments with stable loads. For instance, in a recent data center project, we chose dry-type transformers specifically for their lower maintenance requirements, which aligned well with the facility’s high uptime demands.
However, it’s not always straightforward. I’ve seen cases where well-maintained tank transformers in outdoor substations have operated reliably for decades with scheduled maintenance, outperforming dry-type units in terms of longevity.
When evaluating maintenance costs:
- Consider your available maintenance resources and expertise
- Factor in the criticality of the application and acceptable downtime
- Look at the total cost of ownership, not just routine maintenance
- Consider future regulations that might affect maintenance practices
Remember, while dry-type transformers generally offer lower maintenance costs, the best choice depends on your specific operational context, environment, and long-term strategy.
Conclusion
Choosing between tank and dry-type transformers involves weighing various factors including efficiency, size, environmental impact, fire safety, and maintenance needs. Each type has its strengths, and the best choice depends on your specific application, location, and long-term operational goals.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Assess your specific application requirements
B. Consult with a transformer specialist for personalized advice
C. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis for your project
D. Review local regulations and safety standards
E. Consider future expansion and technology trends
F. Explore case studies of similar installations
Are you curious about the giants of the electrical world? Let’s dive into the fascinating realm of tank transformers!
Tank transformers are large, oil-filled electrical devices that change voltage levels in power systems. They’re crucial for efficient power transmission and distribution, using electromagnetic induction to step voltage up or down as needed.
I’ve spent years working with these behemoths, and I’m excited to share my knowledge with you. From their basic principles to cutting-edge innovations, we’ll explore every aspect of tank transformers. Ready to power up your understanding? Let’s get started!
What Is a Tank Transformer: The Powerhouse Behind Industrial Electricity?
Have you ever wondered what those massive metal containers at electrical substations are? They’re the unsung heroes of our power grid!
A tank transformer is a large, oil-filled electrical transformer used in power systems to change voltage levels. It’s essential for efficient power transmission and distribution, capable of handling high voltages and large loads.
In my years working with these giants, I’ve come to appreciate their crucial role in our electrical infrastructure. Let me break it down for you:
Key Features of Tank Transformers
- Size: They’re much larger than distribution transformers, often weighing several tons.
- Oil-Filled: They use oil for insulation and cooling.
- High Capacity: They can handle voltages from thousands to millions of volts.
- Efficiency: They’re designed for minimal energy loss during voltage transformation.
- Durability: Built to last decades with proper maintenance.
Let’s look at some typical specifications:
| Feature | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Power Rating | 5 MVA to 1000 MVA |
| Primary Voltage | 33 kV to 765 kV |
| Secondary Voltage | 11 kV to 400 kV |
| Efficiency | 98% to 99.75% |
| Lifespan | 25 to 40 years |
I remember my first encounter with a tank transformer during a substation tour. The sheer size and complexity left me in awe. It was then that I realized the immense engineering that goes into powering our world.
Why Tank Transformers Matter
- Power Transmission: They enable long-distance power transmission by stepping up voltage.
- Industrial Use: They provide the right voltage levels for large industrial operations.
- Grid Stability: They help maintain voltage levels across the power grid.
- Energy Efficiency: By reducing transmission losses, they make our power system more efficient.
Understanding tank transformers is crucial for anyone involved in power systems. They’re the backbone of our electrical infrastructure, silently working to ensure we have the power we need, when and where we need it.
Core Principles of Tank Transformers: Electromagnetic Induction Explained?
Ever wondered how these massive machines actually work? It all comes down to a principle discovered nearly 200 years ago!
Tank transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They use changing magnetic fields to transfer electrical energy between circuits, allowing for voltage transformation without direct electrical connection.
I’ve spent countless hours studying and working with these principles. Let me break it down in a way that I wish someone had explained to me when I was starting out:
The Basics of Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday’s Law: A changing magnetic field induces a voltage in a nearby conductor.
- Primary Coil: Creates a changing magnetic field when alternating current flows through it.
- Magnetic Core: Concentrates and directs the magnetic field.
- Secondary Coil: The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in this coil.
- Turns Ratio: The ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils determines the voltage change.
Let’s look at the key components and their roles:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Primary Coil | Receives input voltage |
| Secondary Coil | Produces output voltage |
| Magnetic Core | Directs magnetic flux |
| Insulating Oil | Provides insulation and cooling |
I remember teaching this concept to a group of interns. To demonstrate, I used a simple hand-wound transformer. Seeing their faces light up when they grasped how changing the number of turns affected the output voltage was a highlight of my career.
Diving Deeper into the Physics
- Magnetic Flux: The total magnetic field passing through a given area.
- Mutual Inductance: How changes in current in one coil affect voltage in another.
- Eddy Currents: Circulating currents in the core that cause energy loss.
- Hysteresis: The lag in magnetization of the core material.
These principles aren’t just theoretical. They directly impact transformer design and efficiency. For instance, we use laminated cores to reduce eddy currents and choose core materials carefully to minimize hysteresis losses.
Practical Applications
- Voltage Step-Up: For long-distance power transmission, we increase voltage to reduce current and minimize losses.
- Voltage Step-Down: Near points of use, we decrease voltage for safe distribution to homes and businesses.
- Isolation: Transformers provide electrical isolation between circuits, enhancing safety.
- Phase Shifting: Some specialized transformers can shift the phase of voltages, useful for power flow control.
Understanding these core principles is crucial for anyone working with or designing transformers. It’s not just about memorizing formulas; it’s about grasping how these fundamental laws of physics shape our entire power distribution system.
Anatomy of a Tank Transformer: Key Components and Their Functions?
Have you ever wondered what’s inside those massive tanks? Let’s take a virtual tour of a tank transformer’s internals!
A tank transformer consists of several key components: the core, windings, insulating oil, bushings, and cooling system. Each part plays a crucial role in the transformer’s operation, efficiency, and safety.
In my years of working with these machines, I’ve had the opportunity to see inside many transformers. It’s always fascinating, and I’m excited to share this knowledge with you:
Key Components of a Tank Transformer
- Core: The heart of the transformer, usually made of laminated silicon steel.
- Windings: Primary and secondary coils, typically made of copper or aluminum.
- Insulating Oil: Provides insulation and cooling.
- Bushings: Connect the internal windings to external circuits.
- Tank: Houses all the components and contains the insulating oil.
- Cooling System: Radiators and fans to dissipate heat.
- Tap Changer: Adjusts the turns ratio to regulate output voltage.
Let’s break down these components and their functions:
| Component | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Directs magnetic flux | Silicon steel |
| Windings | Carry current | Copper or aluminum |
| Insulating Oil | Insulates and cools | Mineral oil or synthetic alternatives |
| Bushings | Connect to external circuits | Porcelain or polymer |
| Tank | Contains and protects | Steel |
| Cooling System | Dissipates heat | Steel radiators, fans |
| Tap Changer | Regulates voltage | Mechanical or electronic switches |
I once had the opportunity to oversee the assembly of a large power transformer. Watching each component come together was like seeing a complex puzzle being solved. It gave me a deep appreciation for the engineering involved.
Diving Deeper into Component Functions
-
Core Design:
- Laminated to reduce eddy currents
- Shape (core-type or shell-type) affects efficiency and size
-
Winding Configurations:
- Disc, helical, or layer windings
- Affects short-circuit strength and cooling efficiency
-
Insulating Oil:
- Acts as a dielectric
- Transfers heat from windings to cooling system
- Provides information about transformer health through oil analysis
-
Bushings:
- Designed to withstand high voltages and mechanical stresses
- Often oil-filled or resin-impregnated
-
Cooling Systems:
- ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural)
- ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced)
- OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced)
- ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced)
-
Tap Changers:
- On-Load Tap Changers (OLTC) for voltage regulation under load
- De-energized Tap Changers (DETC) for occasional adjustments
Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for transformer design, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Each part plays a vital role in the transformer’s performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
In my experience, a thorough understanding of these components can make all the difference in diagnosing issues and optimizing performance. It’s not just about knowing what each part does, but how they work together as a system.
The Role of Oil in Tank Transformers: Insulation, Cooling, and Protection?
Ever wondered why transformers are filled with oil? It’s not just to make them heavier!
Insulating oil in tank transformers serves three critical functions: electrical insulation, cooling, and protection against moisture and contaminants. It’s a key component that significantly impacts the transformer’s performance and lifespan.

Throughout my career, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial transformer oil is. Let me share some insights:
The Triple Role of Transformer Oil
-
Electrical Insulation:
- High dielectric strength
- Prevents arcing between components
-
Cooling:
- Absorbs heat from windings and core
- Circulates to dissipate heat
-
Protection:
- Prevents moisture ingress
- Slows down paper insulation degradation
Let’s look at some key properties of transformer oil:
| Property | Function | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | Insulation | >30 kV/2.5mm |
| Viscosity | Heat Transfer | 8-12 cSt at 40°C |
| Flash Point | Safety | >140°C |
| Moisture Content | Insulation Quality | <20 ppm |
| Acidity | Oil Degradation Indicator | <0.03 mg KOH/g |
I remember a case where a transformer failed prematurely. Upon investigation, we found that the oil had degraded due to moisture ingress. It was a stark reminder of how critical oil quality is to transformer health.
Diving Deeper into Oil Functions
-
Insulation Properties:
- Oil fills gaps between windings and other components
- Its high dielectric strength prevents electrical breakdown
- Works in conjunction with cellulose insulation (paper and pressboard)
-
Cooling Mechanism:
- Natural convection in smaller transformers
- Forced circulation in larger units
- Oil’s heat capacity and thermal conductivity are crucial
-
Protective Aspects:
- Acts as a barrier against moisture
- Dissolves gases produced by electrical and thermal stress
- Oil analysis can provide early warning of transformer problems
Oil Maintenance and Monitoring
-
Regular Testing:
- Dielectric strength
- Acidity
- Moisture content
- Dissolved gas analysis (DGA)
-
Oil Treatment:
- Filtration to remove particles
- Degassing to remove dissolved gases
- Dehydration to remove moisture
-
Oil Replacement:
- Partial or complete oil change when severely degraded
- Use of oil regeneration systems in some large transformers
Understanding and maintaining oil quality is crucial for transformer longevity. In my experience, a well-maintained oil system can significantly extend a transformer’s life and improve its reliability.
The role of oil in tank transformers is a perfect example of how a single component can serve multiple critical functions. It’s not just a filler; it’s an active part of the transformer’s operation, constantly working to keep the transformer running efficiently and safely.
Types of Tank Transformers: Choosing the Right One for Your Application?
Confused by the variety of tank transformers out there? Let’s demystify the options!
Tank transformers come in various types, each designed for specific applications. The main categories include step-up, step-down, distribution, power, and special-purpose transformers. Choosing the right type is crucial for system efficiency and reliability.
In my years of consulting on transformer projects, I’ve helped many clients navigate this decision. Here’s what you need to know:
Main Types of Tank Transformers
-
Step-Up Transformers:
- Increase voltage for long-distance transmission
- Used at power generation plants
-
Step-Down Transformers:
- Decrease voltage for distribution
- Found at substations near points of use
-
Distribution Transformers:
- Supply final voltage transformation for end-users
- Commonly seen in residential areas
-
Power Transformers:
- Handle high voltages and large loads
- Used in transmission substations
-
Special-Purpose Transformers:
- Includes rectifier transformers, furnace transformers, etc.
- Designed for specific industrial applications
Let’s compare some key features:
| Type | Typical Voltage Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Step-Up | 11kV to 765kV | Power Generation |
| Step-Down | 765kV to 33kV | Transmission Substations |
| Distribution | 33kV to 415V | Residential/Commercial Supply |
| Power | 33kV to 765kV | Industrial Facilities |
| Special-Purpose | Varies | Specific Industrial Processes |
I once worked on a project where the client initially wanted a standard power transformer for their new factory. After analyzing their specific needs, we realized a special-purpose rectifier transformer would be more efficient. It’s a perfect example of why understanding these types is so important.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Transformer
-
Voltage Requirements:
- Input and output voltage levels
- Voltage regulation needs
-
Power Rating:
- Current load requirements
- Future expansion plans
-
Environmental Conditions:
- Indoor or outdoor installation
- Temperature extremes
- Altitude
-
Efficiency:
- Energy loss considerations
- Cost of operation over time
-
Special Features:
- Tap changing capabilities
- Cooling system requirements
- Noise level restrictions
-
Maintenance and Lifespan:
- Expected operational life
- Maintenance requirements and accessibility
-
Cost:
- Initial investment
- Total cost of ownership
Choosing the right transformer is not just about matching voltage and power ratings. It’s about understanding the specific needs of your application and the environment in which the transformer will operate.
In my experience, taking the time to thoroughly assess these factors can lead to significant long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It’s not uncommon for the right choice to pay for itself many times over during the transformer’s lifespan.
Remember, the best transformer for your application is one that not only meets your current needs but also accommodates future growth and changes in your power system. Don’t hesitate to consult with experts who can help you navigate this complex decision.
Efficiency and Losses in Tank Transformers: How to Optimize Performance?
Worried about energy waste in your transformer? You’re not alone. Let’s tackle this crucial issue!
Efficiency in tank transformers is about minimizing energy losses. The main types of losses are core (no-load) losses and copper (load) losses. Optimizing these can significantly improve transformer performance and reduce operating costs.
%[Diagram of transformer
Throughout my career, I’ve been obsessed with squeezing every bit of efficiency out of transformers. Here’s what I’ve learned:
Understanding Transformer Losses
-
Core Losses (No-Load Losses):
- Occur in the magnetic core
- Present even when the transformer is energized but not supplying load
- Mainly due to hysteresis and eddy currents
-
Copper Losses (Load Losses):
- Occur in the windings
- Increase with the square of the load current
- Caused by resistance in the conductor
Let’s break down these losses:
| Loss Type | Cause | How to Reduce |
|---|---|---|
| Hysteresis Loss | Magnetic domain alignment | Use low-loss core materials |
| Eddy Current Loss | Circulating currents in core | Use laminated core design |
| I²R Loss | Current flowing through winding resistance | Use larger conductors, reduce current density |
| Stray Loss | Leakage flux in structural parts | Optimize design, use magnetic shielding |
I once worked on a project where we reduced a transformer’s losses by 15% simply by upgrading the core material and optimizing the winding design. The energy savings over the transformer’s lifetime more than justified the initial investment.
Strategies to Improve Efficiency
-
Core Material Selection:
- Use high-grade silicon steel or amorphous metals
- Consider grain-oriented steel for better performance
-
Core Design:
- Optimize lamination thickness
- Use step-lap joints to reduce flux leakage
-
Winding Design:
- Use larger conductor cross-sections to reduce resistance
- Optimize current density in windings
-
Cooling System Efficiency:
- Ensure proper oil circulation
- Use efficient radiator designs
-
Load Management:
- Operate transformers near their optimal load point
- Use parallel operation for better load distribution
-
Regular Maintenance:
- Keep oil clean and dry
- Monitor and maintain proper oil levels
-
Temperature Control:
- Maintain optimal operating temperature
- Use efficient cooling methods (ONAN, ONAF, OFAF, ODAF)
Improving efficiency is not just about reducing energy waste; it’s about extending the transformer’s life and reducing operational costs. In my experience, even small improvements in efficiency can lead to significant savings over time, especially for large power transformers.
The Impact of Efficiency on Total Cost of Ownership
- Energy Savings: Higher efficiency means lower energy bills over the transformer’s lifetime.
- Reduced Cooling Requirements: More efficient transformers generate less heat, potentially reducing cooling system costs.
- Extended Lifespan: Lower losses mean less stress on insulation, potentially extending the transformer’s life.
- Environmental Impact: Improved efficiency reduces carbon footprint, an increasingly important consideration.
Remember, when evaluating transformer efficiency, it’s crucial to consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price. A more efficient transformer might cost more upfront but can save significantly over its operational life.
In my years of working with transformers, I’ve seen the focus shift increasingly towards efficiency. It’s not just about meeting minimum standards anymore; it’s about pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in transformer design and operation.
Tank Transformer Cooling Systems: ONAN, ONAF, OFAF, and ODAF Explained?
Ever wondered how these massive transformers keep their cool? Let’s dive into the world of transformer cooling!
Tank transformer cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. The main types are ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural), ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced), OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced), and ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced), each offering different cooling capacities.
I’ve worked with all these cooling systems, and each has its place. Let me break them down for you:
Types of Cooling Systems
-
ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural):
- Simplest and most common for smaller transformers
- Relies on natural convection of oil and air
-
ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced):
- Uses fans to increase air flow over radiators
- Suitable for medium-sized transformers
-
OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced):
- Uses pumps to circulate oil and fans for air cooling
- Used in larger transformers
-
ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced):
- Similar to OFAF, but with directed oil flow through windings
- Most efficient for very large transformers
Let’s compare these systems:
| Cooling Type | Oil Circulation | Air Cooling | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| ONAN | Natural | Natural | Small transformers |
| ONAF | Natural | Forced | Medium transformers |
| OFAF | Forced | Forced | Large transformers |
| ODAF | Directed Forced | Forced | Very large transformers |
I remember upgrading a transformer from ONAN to ONAF cooling. The improvement in cooling efficiency allowed the transformer to handle higher loads without overheating, effectively extending its useful capacity.
Diving Deeper into Cooling Systems
-
ONAN Cooling:
- Relies on temperature difference for oil circulation
- Simple and reliable, but limited cooling capacity
- Suitable for transformers up to about 5 MVA
-
ONAF Cooling:
- Adds fans to increase air flow over radiators
- Can increase cooling capacity by 20-30% over ONAN
- Fans typically controlled by winding temperature
-
OFAF Cooling:
- Uses pumps to force oil circulation
- Significantly increases cooling efficiency
- Allows for more compact transformer design
-
ODAF Cooling:
- Directs oil flow through specially designed ducts in windings
- Provides most efficient cooling for hot spots
- Used in transformers over 100 MVA
Factors Influencing Cooling System Selection
- Transformer Size and Rating: Larger transformers generally require more advanced cooling.
- Environmental Conditions: Ambient temperature and altitude affect cooling efficiency.
- Load Profile: Transformers with high or fluctuating loads may need more robust cooling.
- Noise Restrictions: Forced air systems can be noisier, which may be a concern in some locations.
- Maintenance Requirements: More complex systems generally require more maintenance.
- Cost Considerations: More advanced cooling systems increase initial and operational costs.
In my experience, choosing the right cooling system is crucial for transformer performance and longevity. It’s not just about handling the current load; it’s about planning for future needs and ensuring the transformer can operate efficiently under various conditions.
I’ve seen cases where inadequate cooling led to premature transformer failure, and others where over-specifying the cooling system led to unnecessary costs. The key is to balance current needs, future growth, and operational efficiency.
Remember, a well-designed cooling system not only protects the transformer from overheating but can also extend its lifespan and improve its overall efficiency. It’s an investment in the long-term health of your power system.
Safety Features in Tank Transformers: Protecting Against Electrical Faults?
Worried about transformer safety? You should be! Let’s explore how these giants stay safe.
Tank transformers incorporate various safety features to protect against electrical faults, overloading, and other hazards. These include circuit breakers, pressure relief devices, Buchholz relays, and temperature monitors, all working together to ensure safe operation.

In my years working with transformers, I’ve seen how crucial these safety features are. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Safety Features in Tank Transformers
-
Circuit Breakers:
- Interrupt current flow during faults
- Protect transformer from overloads
-
Pressure Relief Devices:
- Release pressure buildup in the tank
- Prevent explosion in case of internal faults
-
Buchholz Relay:
- Detects gas accumulation and oil flow changes
- Provides early warning of internal faults
-
Temperature Monitors:
- Track oil and winding temperatures
- Trigger alarms or shutdowns if temperatures exceed safe limits
-
Differential Protection:
- Compares current entering and leaving the transformer
- Detects internal faults quickly
Let’s break down these features:
| Safety Feature | Function | Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Breaker | Overcurrent protection | Interrupts power |
| Pressure Relief | Overpressure protection | Releases pressure |
| Buchholz Relay | Gas/oil flow detection | Alarms or trips |
| Temperature Monitor | Overheating protection | Alarms or trips |
| Differential Relay | Internal fault detection | Trips transformer |
I once witnessed a Buchholz relay save a large power transformer from catastrophic failure. It detected a small internal fault before it could escalate, allowing for a controlled shutdown and repair.
Diving Deeper into Safety Systems
-
Overcurrent Protection:
- Primary and backup protection schemes
- Coordination with other system protections
-
Overvoltage Protection:
- Surge arresters to handle lightning and switching surges
- Tap changers for voltage regulation
-
Cooling System Safeguards:
- Monitors for oil levels and flow
- Backup cooling systems in critical applications
-
Fire Protection:
- Fire-resistant oils or dry-type designs for indoor use
- Fire suppression systems in transformer vaults
-
Environmental Protection:
- Oil containment systems to prevent spills
- Noise reduction measures
-
Monitoring and Diagnostics:
- Online monitoring systems for real-time data
- Dissolved gas analysis (DGA) for early fault detection
In my experience, a comprehensive safety system is not just about preventing catastrophic failures. It’s about early detection, controlled responses, and minimizing downtime. I’ve seen cases where advanced monitoring systems detected developing faults weeks before they would have caused problems, allowing for planned maintenance instead of emergency repairs.
The Importance of Regular Testing and Maintenance
- Routine Testing: Regular tests of protection systems ensure they’ll work when needed.
- Calibration: Sensors and relays need periodic calibration to remain accurate.
- Upgrades: Safety systems should be updated as technology improves.
- Training: Operators need to understand and respond to safety system alerts.
Safety in transformer operation is not just about having the right features; it’s about maintaining them, understanding them, and responding appropriately when they activate. In my years in the field, I’ve learned that a culture of safety awareness is just as important as the technical safeguards.
Remember, while these safety features are crucial, they’re not a substitute for proper design, operation, and maintenance. They’re the last line of defense in a comprehensive approach to transformer safety.
Conclusion
Tank transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical grid, silently working to ensure power flows efficiently from generation to end-use. From their basic principles to advanced safety features, these complex machines are marvels of engineering.
We’ve explored their anatomy, the crucial role of insulating oil, various types and cooling systems, efficiency considerations, and vital safety features. Each aspect plays a critical role in the reliable operation of our power systems.
As technology advances, so do transformers, becoming more efficient, safer, and smarter. Understanding these devices is key to maintaining and improving our electrical infrastructure. Whether you’re an engineer, a student, or just curious, I hope this guide has illuminated the fascinating world of tank transformers.
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Learn about smart grid integration with transformers
B. Explore transformer maintenance and diagnostics
C. Investigate emerging transformer technologies
D. Study the environmental impact of transformer oils
E. Discover career opportunities in power systems engineering
F. Delve into the economics of transformer efficiency
Have you ever wondered about those green boxes in your neighborhood? They’re more important than you think!
Pad mounted transformers are essential electrical devices that convert high voltage electricity from power lines to a lower, usable voltage for homes and businesses. They’re the unsung heroes of our power grid, working silently to keep our lights on and appliances running.
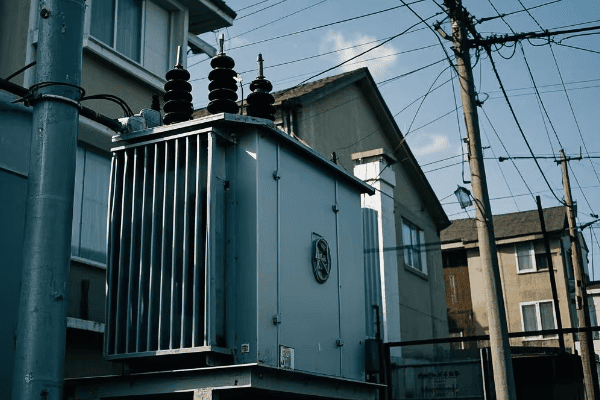
Let’s dive into the world of pad mounted transformers and uncover their secrets. Trust me, by the end of this article, you’ll see these green boxes in a whole new light!
What Is a Pad Mounted Transformer: The Green Box Powering Your Neighborhood?
Ever walked past a green metal box and wondered what it’s doing there? Well, you’re not alone!
A pad mounted transformer is a type of electrical transformer housed in a large metal enclosure, typically green, that sits on a concrete pad. It’s designed to step down high voltage electricity to a lower voltage that’s safe for use in homes and businesses.
In my years working with power systems, I’ve come to appreciate these unassuming boxes. They’re the silent workhorses of our electrical grid, and here’s why they’re so important:
The Role of Pad Mounted Transformers
-
Voltage Conversion: They take high voltage electricity (usually 7,200 to 14,400 volts) and convert it to a lower voltage (typically 120/240 volts for residential use).
-
Distribution: They serve as a crucial link between the main power lines and individual buildings.
-
Safety: By keeping high voltage components enclosed, they protect the public from electrical hazards.
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Green Color | Blend into surroundings |
| Padlock | Prevent unauthorized access |
| Warning Signs | Alert people to potential dangers |
| Concrete Pad | Provide stable foundation |
These transformers are a testament to modern electrical engineering. They’re designed to be efficient, safe, and relatively inconspicuous. Next time you see one, you’ll know you’re looking at a key player in bringing power to your home!
The Basic Principles of Pad Mounted Transformers: Electricity 101 for Homeowners
Ever flipped a light switch and wondered how that electricity got to your home? Let’s break it down!
Pad mounted transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They use coils of wire and a magnetic field to change the voltage of electricity, making it safe for use in our homes.

As someone who’s spent years working with these devices, I can tell you that understanding the basics can be incredibly empowering. Let’s dive deeper into how these transformers work:
How Transformers Change Voltage
-
Primary Coil: This is where high voltage electricity enters the transformer.
-
Magnetic Core: Usually made of iron, it helps transfer energy between the coils.
-
Secondary Coil: This is where the transformed, lower voltage electricity exits.
The magic happens in the relationship between these components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Primary Coil | Receives high voltage |
| Magnetic Core | Transfers energy |
| Secondary Coil | Outputs lower voltage |
The number of turns in each coil determines the voltage change. More turns in the primary coil than the secondary results in a step-down transformer, which is what we use in residential areas.
The Importance of Transformers in Your Daily Life
Think about all the devices you use daily – your phone charger, your refrigerator, your TV. None of these could function safely without the voltage transformation that occurs in pad mounted transformers.
I remember a time when a neighborhood’s transformer failed. Suddenly, everyone realized how crucial these green boxes were! It’s a bit like not noticing your heart beating until something goes wrong.
Understanding these principles can help you appreciate the complex system that powers our modern lives. It’s not just about flipping a switch – it’s about a carefully designed system that safely brings electricity from power plants to your home.
Inside a Pad Mounted Transformer: A Peek Behind the Metal Doors
Have you ever been curious about what’s inside those green boxes? Let’s take a look!
Inside a pad mounted transformer, you’ll find a complex array of components including coils, a core, insulating oil, and various safety devices. It’s a carefully engineered system designed to efficiently and safely transform electricity.

In my years of working with these transformers, I’ve had the opportunity to see inside many of them. It’s always fascinating, and I’m excited to share what I’ve learned with you:
Key Components Inside a Pad Mounted Transformer
-
Transformer Core: This is usually made of laminated steel sheets. It’s the heart of the transformer, where the magnetic field is created.
-
Primary and Secondary Windings: These are coils of wire wrapped around the core. The primary winding receives the high voltage, while the secondary winding outputs the lower voltage.
-
Insulating Oil: This oil serves two purposes – it insulates the electrical components and helps cool the transformer.
-
Bushings: These are the connection points where electricity enters and exits the transformer.
-
Tap Changer: This allows for small adjustments in the voltage ratio.
-
Safety Devices: These include fuses, circuit breakers, and pressure relief valves.
Let’s break this down in a table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Core | Creates magnetic field |
| Windings | Transform voltage |
| Insulating Oil | Insulates and cools |
| Bushings | Connect to external circuits |
| Tap Changer | Adjusts voltage ratio |
| Safety Devices | Protect against faults |
The Transformation Process
When electricity enters the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field in the core. This field then induces a current in the secondary winding. The ratio of turns between the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage change.
I once had the chance to observe a transformer during a maintenance check. Seeing the oil drained and the internal components exposed was like looking at the inner workings of a mechanical heart. It gave me a new appreciation for the engineering that goes into these devices.
Understanding what’s inside a pad mounted transformer can help you appreciate the complexity of our power distribution system. These aren’t just simple metal boxes – they’re marvels of electrical engineering, working tirelessly to power our world.
Voltage Transformation Explained: How Pad Mounted Transformers Deliver Usable Power
Ever wondered how the massive voltage from power lines becomes the safe 120 volts in your home? Let’s unravel this mystery!
Pad mounted transformers use electromagnetic induction to step down high voltage electricity to a lower, safer voltage. They do this by using different numbers of wire turns in the primary and secondary coils.
In my career, I’ve seen how crucial this process is. Let me break it down for you:
The Voltage Transformation Process
-
High Voltage Input: Electricity enters the transformer at high voltage, typically 7,200 to 14,400 volts.
-
Primary Coil: This coil has many turns of wire. The high voltage creates a strong magnetic field.
-
Magnetic Core: The field created by the primary coil is concentrated in the core.
-
Secondary Coil: This coil has fewer turns. The changing magnetic field induces a lower voltage here.
-
Low Voltage Output: The electricity leaves the transformer at a lower voltage, usually 120/240 volts for homes.
Here’s a simplified look at the process:
| Stage | Voltage |
|---|---|
| Power Line | 7,200 – 14,400 V |
| Primary Coil | 7,200 – 14,400 V |
| Secondary Coil | 120/240 V |
| Your Home | 120/240 V |
The Math Behind the Magic
The ratio of voltage change is directly related to the ratio of turns in the coils. For example, if the primary coil has 100 turns and the secondary has 5, the voltage will be reduced by a factor of 20.
I remember explaining this to a group of students once. To demonstrate, I used a simple hand-crank generator connected to different coils. Seeing their faces light up (pun intended!) when they understood the relationship between turns and voltage was a great moment.
Why This Matters
This voltage transformation is crucial for several reasons:
-
Safety: High voltage is dangerous. Transforming it to a lower voltage makes it safe for home use.
-
Efficiency: High voltage is more efficient for long-distance transmission, but impractical for home use.
-
Appliance Compatibility: Our home appliances are designed to work with lower voltages.
Understanding this process helps us appreciate the complex system that delivers power to our homes. It’s not just about flipping a switch – it’s about a carefully engineered process that safely brings electricity from power plants to your living room.
Safety Features of Pad Mounted Transformers: Protecting Your Community
Ever wondered how these electrical powerhouses keep us safe? Let’s explore the safety features!
Pad mounted transformers are equipped with multiple safety features including locked enclosures, insulating oil, circuit breakers, and warning signs. These features work together to prevent accidents and protect both the public and utility workers.
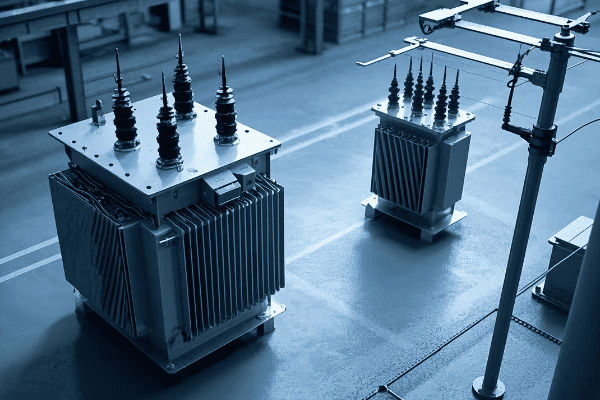
In my years working with these transformers, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial these safety features are. Let me walk you through them:
Key Safety Features
-
Locked Enclosure: The transformer is housed in a sturdy, locked metal cabinet. This prevents unauthorized access.
-
Insulating Oil: This oil not only cools the transformer but also provides electrical insulation.
-
Circuit Breakers and Fuses: These devices automatically cut power in case of a fault or overload.
-
Pressure Relief Device: This prevents explosion in case of excessive internal pressure.
-
Warning Signs: Clear signs warn of the dangers of high voltage.
-
Grounding: The transformer is properly grounded to prevent electric shock.
Let’s break this down:
| Safety Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Locked Enclosure | Prevent unauthorized access |
| Insulating Oil | Cool and insulate |
| Circuit Breakers | Protect against faults |
| Pressure Relief | Prevent explosion |
| Warning Signs | Alert to dangers |
| Grounding | Prevent electric shock |
Real-World Safety in Action
I once witnessed a car accident where a vehicle crashed into a pad mounted transformer. Thanks to the robust enclosure and automatic shutoff features, there was no electrical fire or shock risk. It really drove home the importance of these safety measures.
Why These Features Matter
-
Public Safety: These features keep curious children and adults safe from high voltage equipment.
-
Worker Safety: Utility workers can safely maintain and repair these transformers.
-
Equipment Protection: The safety features also protect the expensive transformer from damage.
-
Reliability: By preventing accidents and damage, these features help ensure a stable power supply.
Understanding these safety features can help you appreciate the thought and engineering that goes into keeping our communities safe. Next time you see a pad mounted transformer, you’ll know it’s not just delivering power – it’s doing so with your safety in mind.
Pad Mounted vs. Pole Mounted Transformers: What’s the Difference?
Ever noticed some transformers are on poles while others are on the ground? Let’s compare these two types!
Pad mounted transformers sit on the ground in locked cabinets, while pole mounted transformers are attached to utility poles. Pad mounted transformers are often used in underground power systems, while pole mounted transformers are common in overhead systems.
In my career, I’ve worked with both types. Each has its place in our power distribution system. Let’s dive into the differences:
Key Differences
-
Location: Pad mounted are on the ground, pole mounted are on utility poles.
-
Appearance: Pad mounted are in green boxes, pole mounted are cylindrical and exposed.
-
Capacity: Pad mounted often have higher capacity due to size flexibility.
-
Accessibility: Pad mounted are easier to access for maintenance.
-
Safety: Pad mounted have locked enclosures, pole mounted rely on height for safety.
-
Aesthetics: Pad mounted are less visually obtrusive in residential areas.
Let’s compare in a table:
| Feature | Pad Mounted | Pole Mounted |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Ground | Utility Pole |
| Appearance | Green Box | Cylindrical |
| Capacity | Often Higher | Generally Lower |
| Accessibility | Easy | Requires Climbing |
| Safety | Locked Enclosure | Height |
| Aesthetics | Less Obtrusive | More Visible |
When to Use Each Type
Pad mounted transformers are ideal for:
- Underground power systems
- Areas with high aesthetic concerns
- Locations needing higher capacity
Pole mounted transformers are better for:
- Overhead power systems
- Areas prone to flooding
- Quick installation and lower cost
I remember a project where we replaced pole mounted transformers with pad mounted ones in a residential area. The residents were thrilled with the improved aesthetics and the reduced risk of power outages during storms.
Impact on Power Distribution
-
Reliability: Pad mounted transformers, being underground, are less affected by weather.
-
Maintenance: Pad mounted transformers are easier and safer to maintain.
-
Expansion: Pad mounted transformers allow for easier capacity upgrades.
-
Cost: While initially more expensive, pad mounted transformers can be more cost-effective long-term.
Understanding these differences can help you appreciate the thought that goes into power distribution in different areas. Whether you see a green box or a cylinder on a pole, you now know each has its specific role in bringing power to your community.
The Role of Pad Mounted Transformers in Your Daily Life: From Charging Phones to Powering Appliances
Ever stopped to think about how your daily activities depend on these green boxes? Let’s explore!
Pad mounted transformers play a crucial role in our daily lives by providing the right voltage for all our electrical needs. From charging your phone to running your refrigerator, these transformers ensure a steady, safe power supply to your home.
In my years in the power industry, I’ve seen how these transformers touch every aspect of modern life. Let me break it down for you:
How Pad Mounted Transformers Power Your Day
-
Morning Routine: Your alarm clock, coffee maker, and toaster all run on power from these transformers.
-
Work and Study: Your computer, internet router, and lights are all powered by transformed electricity.
-
Home Comfort: Your HVAC system, which keeps you cool in summer and warm in winter, relies on these transformers.
-
Entertainment: Your TV, gaming console, and sound system all draw power that’s been stepped down by a pad mounted transformer.
-
Kitchen Appliances: Your refrigerator, oven, and dishwasher all use electricity from these transformers.
-
Outdoor Living: Even your porch lights and electric grill get their power from these devices.
Let’s look at the power usage of common appliances:
| Appliance | Typical Wattage |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 150-400 watts |
| TV | 80-400 watts |
| Laptop | 50-100 watts |
| Air Conditioner | 750-3500 watts |
| Electric Oven | 2000-5000 watts |
The Invisible Helper
I once had a neighbor
I once had a neighbor who was curious about why we needed these transformers. I explained it by comparing it to a water system. Just as we need to reduce water pressure from main lines to use it safely in our homes, we need to reduce electrical voltage for safe home use. The light bulb moment on his face was priceless!
Impact on Modern Lifestyle
-
Constant Connectivity: Our always-on digital lifestyle depends on a steady power supply.
-
Home Office: The rise of remote work has made residential power reliability more crucial than ever.
-
Smart Homes: The growing Internet of Things (IoT) devices all rely on transformed power.
-
Electric Vehicles: As more people switch to EVs, home charging stations are becoming common, increasing the importance of residential power transformation.
Understanding the role of pad mounted transformers helps us appreciate the complex infrastructure that supports our modern lifestyle. From the moment you wake up to when you go to sleep, these unassuming green boxes are working tirelessly to power your world.
Common Myths About Pad Mounted Transformers: Separating Fact from Fiction
Ever heard some wild stories about those green boxes in your neighborhood? Let’s bust some myths!
There are many misconceptions about pad mounted transformers, from fears of radiation to beliefs about their impact on property values. Most of these myths are unfounded, and understanding the facts can help alleviate unnecessary concerns.

In my years working with these transformers, I’ve heard it all. Let’s tackle some common myths:
Myth 1: Pad Mounted Transformers Emit Harmful Radiation
Fact: Pad mounted transformers produce extremely low-level electromagnetic fields, similar to many household appliances. These levels are well below safety limits set by health organizations.
Myth 2: Living Near a Transformer Increases Cancer Risk
Fact: Numerous studies have found no conclusive evidence linking low-level electromagnetic fields from transformers to increased cancer risk.
Myth 3: Transformers Are a Fire Hazard
Fact: While any electrical equipment can potentially malfunction, pad mounted transformers are designed with multiple safety features to prevent fires. Incidents are extremely rare.
Myth 4: Transformers Significantly Decrease Property Values
Fact: There’s no substantial evidence that properly maintained pad mounted transformers negatively impact property values. They’re a necessary part of modern infrastructure.
Myth 5: Transformers Make a Lot of Noise
Fact: Modern pad mounted transformers are designed to operate quietly. Any unusual noise should be reported to the utility company for inspection.
Let’s compare some of these myths and facts:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Harmful Radiation | Low-level EMF, similar to appliances |
| Cancer Risk | No conclusive evidence of increased risk |
| Fire Hazard | Multiple safety features, rare incidents |
| Decrease Property Value | No substantial evidence of impact |
| Noisy Operation | Designed for quiet operation |
I remember a community meeting where these myths came up. By explaining the facts and even showing EMF readings from a transformer compared to common household items, we were able to allay many concerns.
Why These Myths Persist
-
Fear of the Unknown: Many people don’t understand how transformers work, leading to unfounded fears.
-
Misinterpretation of Data: Some studies on high-voltage power lines get incorrectly applied to pad mounted transformers.
-
Urban Legends: Misinformation can spread quickly in neighborhoods.
-
Confirmation Bias: People tend to remember information that confirms their existing beliefs.
Understanding the facts about pad mounted transformers can help communities make informed decisions and reduce unnecessary anxiety. These devices are crucial to our power infrastructure and are designed with safety as a top priority.
Maintenance of Pad Mounted Transformers: What Homeowners Should Know
Ever wondered who takes care of those green boxes? Let’s explore the maintenance process!
Pad mounted transformers require regular maintenance to ensure reliable operation. While utility companies are responsible for this maintenance, homeowners play a role in keeping the area around transformers accessible and reporting any issues.

In my experience, proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and safety of these transformers. Here’s what you should know:
Utility Company Responsibilities
-
Regular Inspections: Utilities perform periodic visual and thermal inspections.
-
Oil Testing: The insulating oil is tested for contaminants and dielectric strength.
-
Component Replacement: Worn or damaged parts are replaced as needed.
-
Cleaning: The interior is cleaned to prevent buildup of dirt and debris.
-
Load Management: Transformers are monitored to ensure they’re not overloaded.
Homeowner Responsibilities
-
Keep Area Clear: Maintain a 10-foot clearance around the transformer.
-
Report Issues: Notify the utility of any visible damage or unusual noises.
-
Avoid Tampering: Never attempt to open or modify the transformer.
-
Landscaping Considerations: Avoid planting trees or large shrubs near transformers.
Let’s break down the maintenance schedule:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Utility Company |
| Oil Testing | Annually | Utility Company |
| Thermal Imaging | Annually | Utility Company |
| Area Clearance | Ongoing | Homeowner |
| Reporting Issues | As Needed | Homeowner |
I once had a situation where a homeowner’s overgrown bushes were impeding access to a transformer. After explaining the importance of accessibility, they were more than happy to trim back the vegetation.
Why Proper Maintenance Matters
-
Reliability: Well-maintained transformers are less likely to fail, reducing power outages.
-
Safety: Regular inspections catch potential safety issues before they become problems.
-
Longevity: Proper maintenance can extend the life of the transformer, saving costs in the long run.
-
Efficiency: A well-maintained transformer operates more efficiently, potentially reducing energy losses.
Understanding the maintenance needs of pad mounted transformers helps homeowners play their part in ensuring a reliable power supply. Remember, while you shouldn’t touch the transformer itself, keeping the area around it clear and reporting any issues goes a long way in maintaining our electrical infrastructure.
Environmental Impact: Are Pad Mounted Transformers Eco-Friendly?
Ever wondered about the environmental footprint of those green boxes? Let’s explore their eco-impact!
Pad mounted transformers have both positive and negative environmental impacts. While they contribute to efficient power distribution, reducing overall energy loss, they also contain materials that require careful handling and disposal.
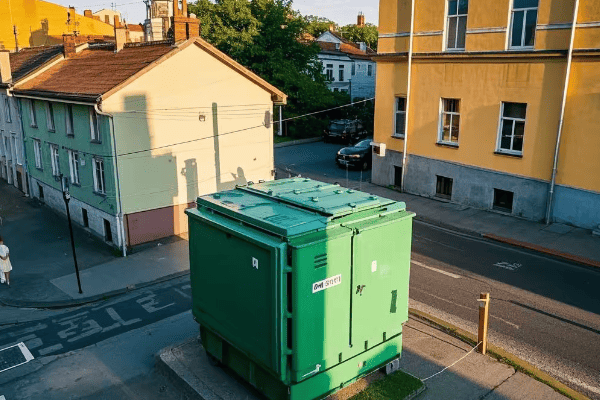

In my years in the industry, I’ve seen a growing focus on the environmental aspects of our infrastructure. Let’s break down the eco-friendliness of pad mounted transformers:
Positive Environmental Impacts
-
Energy Efficiency: By stepping down voltage close to the point of use, these transformers reduce transmission losses.
-
Land Use: Compared to substations, pad mounted transformers have a smaller footprint.
-
Noise Pollution: They operate quietly, reducing noise pollution in residential areas.
-
Aesthetics: Their compact design allows for better integration into landscapes.
Environmental Challenges
-
Oil Use: Many transformers use mineral oil, which can be an environmental concern if leaked.
-
PCB Legacy: Older transformers may contain PCBs, requiring special handling and disposal.
-
End-of-Life Disposal: Transformers contain materials that need proper recycling or disposal.
-
Manufacturing Impact: The production of transformers involves resource extraction and energy use.
Let’s compare some eco-aspects:
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | Reduces transmission losses | Requires energy for cooling |
| Materials | Recyclable metals | Some hazardous materials |
| Land Use | Small footprint | May impact local ecosystems |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting (20-30 years) | Eventual disposal needed |
I remember a project where we replaced old oil-filled transformers with newer, more eco-friendly dry-type transformers. The community was thrilled about the reduced environmental risk.
Innovations for Eco-Friendliness
-
Bio-based Oils: Some new transformers use vegetable-based oils instead of mineral oils.
-
Dry-Type Transformers: These eliminate the need for insulating oil altogether.
-
Smart Transformers: These can optimize power flow, further reducing energy losses.
-
Recycling Programs: Many utilities now have programs to recycle old transformer components.
The Bigger Picture
While pad mounted transformers do have some environmental impacts, they play a crucial role in our power infrastructure. Their efficiency in power distribution contributes to overall energy savings, which has a net positive environmental impact.
Understanding the environmental aspects of pad mounted transformers helps us appreciate the complexities of balancing our energy needs with environmental stewardship. As technology advances, we’re continually finding ways to make these essential devices more eco-friendly.
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers are the unsung heroes of our electrical grid. They work tirelessly to bring safe, usable power to our homes and businesses. From their basic principles to their maintenance needs and environmental impact, these devices play a crucial role in our daily lives.
As we’ve explored, pad mounted transformers are marvels of engineering that balance efficiency, safety, and reliability. They’re not just green boxes on the street – they’re a vital link in the complex chain that powers our modern world.
Understanding these transformers helps us appreciate the infrastructure that supports our lifestyle. It also empowers us to be more informed community members, whether it’s knowing how to report issues or understanding the importance of keeping the area around transformers clear.
As technology evolves, so too will pad mounted transformers, becoming smarter, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly. But one thing will remain constant – their essential role in powering our world.
Next time you see one of these green boxes, you’ll know you’re looking at a key player in the amazing journey of electricity from power plant to your home. And that’s something worth appreciating!
🚀Next steps, you can:
A. Learn more about energy efficiency in your home
B. Explore other components of the electrical grid
C. Understand how to read your electricity bill
D. Investigate renewable energy integration with the grid
E. Discover careers in the electrical power industry
F. Find out how to report transformer issues in your area
Have you ever noticed those green boxes scattered around your neighborhood? They’re not just for decoration. These mysterious containers hold the key to powering your home, but most people walk by without a second glance.
A pad mounted transformer is a ground-level electrical device that converts high voltage power to lower, usable voltages for homes and businesses. These green boxes are safer, more efficient, and less obtrusive than traditional pole-mounted transformers, making them the preferred choice for modern residential areas.

I’ve been working with pad mounted transformers for over 20 years, and I’m always amazed at how these unassuming boxes play such a vital role in our daily lives. In this article, I’ll take you on a journey inside these green powerhouses and reveal why they’re so important for your neighborhood’s electrical supply.
How Do Pad Mounted Transformers Work: The Science Behind Your Street’s Power Supply?
Ever flipped a switch and wondered how electricity magically appears in your home? The secret lies in those green boxes you see around your neighborhood. But how exactly do they work their magic?
Pad mounted transformers work by stepping down high voltage electricity from power lines to lower, safer voltages for home use. They use electromagnetic induction to transfer energy between coils of wire, efficiently converting voltage levels without direct electrical connections.
I remember the first time I opened up a pad mounted transformer. The complexity inside that simple green box was astounding. Let me break down how these devices work and why they’re so crucial for our power grid.
The Transformation Process
At its core, a pad mounted transformer operates on a simple yet powerful principle:
-
Input:
- High voltage electricity enters the transformer from underground power lines
- Typically ranges from 4,000 to 34,500 volts
-
Transformation:
- Electricity passes through primary coils wrapped around an iron core
- The changing magnetic field induces current in secondary coils
- The number of windings in each coil determines the voltage change
-
Output:
- Lower voltage electricity exits the transformer
- Usually 120/240 volts for residential use
Key Components
Understanding the parts helps appreciate the whole:
-
Core:
- Made of laminated steel sheets
- Provides a path for magnetic flux
- Designed to minimize energy loss
-
Windings:
- Primary (high voltage) and secondary (low voltage) coils
- Usually made of copper or aluminum wire
- Number of turns determines voltage transformation ratio
-
Insulating Oil:
- Cools and insulates internal components
- Helps prevent arcing and extends transformer life
- Some modern transformers use eco-friendly alternatives
-
Bushings:
- Connect internal wiring to external power lines
- Insulated to prevent short circuits
Efficiency and Load Management
Pad mounted transformers are designed for optimal performance:
-
Load Tap Changers:
- Adjust voltage output based on demand
- Maintain stable voltage during peak and off-peak hours
-
Cooling Systems:
- Oil circulation helps dissipate heat
- Some models include fans for additional cooling
-
Monitoring Equipment:
- Sensors track temperature, oil levels, and electrical load
- Helps prevent overloading and extends transformer life
| Component | Function | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | Reduces energy loss |
| Windings | Voltage conversion | Determines transformation ratio |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Extends lifespan, improves performance |
| Load Tap Changers | Voltage regulation | Optimizes power delivery |
In my years of experience, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial proper design and maintenance are for these transformers. I once visited a neighborhood experiencing frequent power fluctuations. Upon inspection, we found that the pad mounted transformer was undersized for the growing energy demands of the area. Upgrading to a larger capacity transformer solved the issue, highlighting the importance of proper sizing and regular assessments.
It’s fascinating to think about how these relatively small devices handle such enormous amounts of power. A typical residential pad mounted transformer can supply electricity to 10-15 homes, quietly humming away day and night. The efficiency of modern transformers is remarkable, with some models achieving over 98% efficiency in converting voltage.
However, it’s important to note that while pad mounted transformers are highly efficient, they’re not perfect. They still experience some energy loss in the form of heat. That’s why you might notice the area around a transformer is slightly warmer, especially on hot days or during peak usage times.
As we move towards smarter, more connected power grids, pad mounted transformers are evolving too. Some newer models include advanced monitoring systems that can report issues in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and even more efficient power distribution. This integration with smart grid technology is paving the way for a more reliable and responsive electrical infrastructure.
Understanding how pad mounted transformers work isn’t just about satisfying curiosity. It’s about appreciating the complex infrastructure that powers our daily lives. Next time you see one of those green boxes, you’ll know there’s a lot more going on inside than meets the eye.
Key Components of a Pad Mounted Transformer: What’s Inside That Green Box?
Have you ever walked past one of those green boxes in your neighborhood and wondered what’s inside? These pad mounted transformers may look simple on the outside, but they’re packed with sophisticated components that keep your lights on and your appliances running.
A pad mounted transformer contains several key components: a steel core, primary and secondary windings, insulating oil, bushings, and a protective enclosure. Each part plays a crucial role in converting high voltage electricity to the lower voltages used in homes and businesses, ensuring safe and efficient power distribution.
I’ve opened up countless pad mounted transformers over the years, and I’m always impressed by the engineering inside. Let’s take a closer look at what makes these devices tick and why each component is essential for reliable power delivery.
The Heart of the Transformer: Core and Windings
The core and windings are where the magic of voltage transformation happens:
-
Core:
- Made of thin, laminated steel sheets
- Provides a path for magnetic flux
- Designed to minimize energy loss
-
Primary Windings:
- Receive high voltage input
- Usually made of copper wire
- Number of turns determines voltage ratio
-
Secondary Windings:
- Produce lower voltage output
- Also typically copper
- Fewer turns than primary windings
Insulation and Cooling: The Oil Bath
Insulating oil serves multiple crucial functions:
-
Electrical Insulation:
- Prevents arcing between components
- Increases dielectric strength
-
Cooling:
- Absorbs and dissipates heat from windings and core
- Circulates naturally or through forced cooling systems
-
Preservation:
- Protects internal components from oxidation
- Extends the transformer’s lifespan
Connection Points: Bushings and Terminals
Bushings are the transformer’s connection to the outside world:
-
High Voltage Bushings:
- Connect to incoming power lines
- Heavily insulated to prevent flashover
-
Low Voltage Bushings:
- Connect to outgoing distribution lines
- Designed for easier and safer access
Protection and Monitoring: Auxiliary Components
Several additional components ensure safe and efficient operation:
-
Pressure Relief Device:
- Releases pressure in case of internal faults
- Prevents explosive rupture of the tank
-
Temperature Gauge:
- Monitors oil and winding temperatures
- Helps prevent overheating
-
Oil Level Indicator:
- Shows current oil level
- Alerts to potential leaks or low oil conditions
-
Tap Changer:
- Adjusts voltage output
- Maintains stable voltage under varying loads
| Component | Function | Maintenance Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Magnetic flux path | Check for vibration or unusual noise |
| Windings | Voltage conversion | Monitor for overheating |
| Insulating Oil | Cooling and insulation | Regular testing for contaminants |
| Bushings | Power connections | Inspect for cracks or damage |
| Pressure Relief Device | Safety | Ensure proper operation |
| Temperature Gauge | Monitoring | Verify accuracy periodically |
In my experience, understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. I once encountered a transformer that was running unusually hot. Upon inspection, we found that the oil level was low, reducing its cooling efficiency. A simple top-up of the insulating oil resolved the issue, highlighting the importance of regular checks on all components.
It’s fascinating to see how these parts work together. The core and windings perform the main task of voltage transformation, while the oil keeps everything cool and insulated. The bushings and terminals ensure safe connections, and the auxiliary components provide vital monitoring and protection.
One aspect that often surprises people is the longevity of these devices. With proper maintenance, a pad mounted transformer can last 30 years or more. I’ve worked on transformers that have been quietly serving neighborhoods for decades, a testament to their robust design and the quality of their components.
However, it’s important to note that while pad mounted transformers are designed for long-term reliability, they’re not maintenance-free. Regular inspections and tests are crucial to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Oil tests, for example, can reveal early signs of internal issues before they become major problems.
As technology advances, we’re seeing innovations in transformer components. Some newer models use vegetable-based oils instead of mineral oil, offering better environmental and fire safety properties. Others incorporate smart sensors that can report real-time data on the transformer’s condition, allowing for predictive maintenance.
Understanding the key components of a pad mounted transformer isn’t just for engineers and technicians. It helps everyone appreciate the complexity behind our seemingly simple electrical infrastructure. Next time you pass one of those green boxes, you’ll know there’s a lot more than meets the eye keeping your lights on and your appliances running.
Conclusion
Pad mounted transformers are essential components of modern power distribution systems. They efficiently convert high voltage electricity to usable levels for homes and businesses, while offering improved safety and aesthetics compared to traditional pole-mounted transformers. Understanding their inner workings helps us appreciate the complex infrastructure powering our daily lives.
Is your transformer protection keeping you up at night? You’re not alone. Many engineers struggle to choose between oil surge relays and Buchholz relays, knowing that the wrong choice could lead to costly failures.
Oil surge relays and Buchholz relays are both critical for transformer protection, but they function differently. Oil surge relays detect rapid oil movements, responding in milliseconds. Buchholz relays sense both oil surges and gas accumulation, offering dual protection. Understanding these differences is key to optimal transformer safeguarding and preventing catastrophic failures.
I’ve spent over two decades working with both types of relays, and I’ve seen firsthand how crucial the right choice can be. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between oil surge and Buchholz relays, their strengths and weaknesses, and how to choose the right protection for your transformer. Let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of these vital devices.
What is an Oil Surge Relay: The Modern Guardian of Transformer Health?
Have you ever wondered what’s keeping your million-dollar transformer safe from sudden disasters? Meet the oil surge relay, the unsung hero of modern transformer protection.
An oil surge relay is a cutting-edge device that detects rapid oil movements in transformers. It responds to internal faults within milliseconds, triggering alarms or shutdowns. This lightning-fast reaction can prevent catastrophic failures, potentially saving millions in equipment and downtime costs.
I remember the first time I saw an oil surge relay in action. It was at a power plant in Texas, and the speed at which it detected a fault and shut down the transformer was truly impressive. Let me break down how these modern guardians work and why they’re becoming increasingly popular in the industry.
How Oil Surge Relays Operate
The principle behind oil surge relays is simple yet effective:
-
Constant Monitoring:
- Installed in the pipe between the main tank and conservator
- Watches for sudden oil movements 24/7
-
Rapid Detection:
- Uses a float mechanism sensitive to oil flow
- Triggers when oil velocity exceeds a preset threshold
-
Instant Response:
- Activates alarms or initiates transformer shutdown
- Typically reacts in less than 20 milliseconds
Benefits of Oil Surge Relays
These devices offer several key advantages:
-
Unmatched Speed:
- Reacts faster than traditional protection methods
- Can stop faults before they escalate into major issues
-
High Sensitivity:
- Detects even minor internal problems
- Helps catch issues early, reducing long-term repair costs
-
Simple Reliability:
- Mechanical design means fewer points of failure
- Less prone to false alarms than some electronic systems
Real-World Applications
I’ve seen oil surge relays make a significant difference in various settings:
-
Power Plants:
- Protect critical, high-capacity transformers
- Prevent widespread blackouts and associated economic losses
-
Industrial Facilities:
- Safeguard expensive manufacturing equipment
- Minimize costly production interruptions
-
Renewable Energy Sites:
- Protect transformers in wind and solar farms
- Ensure consistent power delivery to the grid
| Feature | Benefit | Real-World Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Millisecond Response | Stops faults instantly | Prevents major equipment damage |
| High Sensitivity | Catches minor issues | Reduces long-term maintenance costs |
| Simple Design | Fewer parts to fail | Increases overall system reliability |
| Versatile Application | Fits various transformer sizes | Adaptable to different industry needs |
In my experience, the adoption of oil surge relays has led to a significant reduction in transformer failures. At one power plant where I worked, we installed these relays on all major transformers. Within the first year, we caught three developing faults that could have led to catastrophic failures. The cost savings from preventing these failures alone justified the investment in the new technology.
However, it’s important to note that oil surge relays are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They work best as part of a comprehensive protection system. I always advise my clients to consider their specific needs, transformer size, and operating environment when deciding on protection measures.
As transformer technology evolves, so do protection devices like oil surge relays. The latest models incorporate digital sensors and advanced analytics, further improving their accuracy and reliability. It’s an exciting time in the field of transformer protection, and I’m eager to see how these devices continue to develop and safeguard our power systems.
Understanding the Buchholz Relay: A Time-Tested Transformer Protector?
Are you familiar with the Buchholz relay, the stalwart guardian of transformers for nearly a century? This device has been a cornerstone of transformer protection, but how does it stack up in today’s rapidly evolving power industry?
A Buchholz relay is a gas-actuated protective device for oil-immersed transformers. It detects both oil surges and gas accumulation caused by internal faults. Located between the main tank and conservator, it provides dual protection against slow-developing and sudden faults, making it a versatile and reliable safeguard for transformer health.
I’ve worked with Buchholz relays throughout my career, and their reliability never ceases to impress me. Let’s delve into how these time-tested devices work and why they remain relevant in modern power systems.
How Buchholz Relays Function
Buchholz relays operate on two key principles:
-
Gas Detection:
- Upper chamber collects gases from slow-developing faults
- Float switch triggers an alarm when gas accumulates
-
Oil Surge Detection:
- Lower chamber responds to sudden oil movements
- Activates a trip signal for severe faults
Key Components of a Buchholz Relay
Understanding its parts helps appreciate its functionality:
-
Upper Chamber:
- Collects gases from minor faults
- Houses the alarm float switch
-
Lower Chamber:
- Detects rapid oil flow
- Contains the trip float switch
-
Sight Glass:
- Allows visual inspection of gas accumulation
- Useful for maintenance checks
Advantages of Buchholz Relays
These devices offer several benefits:
-
Dual Protection:
- Detects both slow-developing and sudden faults
- Provides comprehensive transformer safeguarding
-
Reliability:
- Simple mechanical design ensures long-term dependability
- Proven track record over decades of use
-
Versatility:
- Suitable for various transformer sizes and types
- Can be used in conjunction with other protective devices
| Feature | Function | Real-World Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Collection | Detects slow faults | Early warning of developing issues |
| Oil Surge Detection | Responds to sudden faults | Rapid protection against major failures |
| Visual Inspection | Enables easy checks | Simplifies routine maintenance |
| Mechanical Operation | Ensures long-term reliability | Reduces risk of electronic malfunctions |
In my experience, Buchholz relays have saved countless transformers from severe damage. I recall a incident at a substation in California where a Buchholz relay detected a slow gas leak in a large transformer. The early warning allowed us to schedule maintenance during a planned outage, avoiding an unexpected failure that could have left thousands without power.
However, it’s important to note that while Buchholz relays are highly reliable, they’re not without limitations. Their response to oil surges is typically slower than modern oil surge relays. Additionally, they may not detect some types of high-impedance faults that don’t produce significant gas or oil movement.
Despite these limitations, Buchholz relays remain a crucial part of transformer protection systems. Their ability to detect slow-developing faults complements faster-acting devices like oil surge relays. In many cases, I recommend using both types of relays for comprehensive protection.
As we move towards smarter, more interconnected power systems, Buchholz relays are evolving too. Modern versions often include digital outputs for easy integration with SCADA systems. Some manufacturers are even developing hybrid devices that combine the reliability of Buchholz relays with the speed of electronic sensors.
Key Differences Between Oil Surge and Buchholz Relays: A Side-by-Side Comparison?
Are you struggling to choose between an oil surge relay and a Buchholz relay for your transformer? You’re not alone. Many engineers grapple with this decision, knowing that the right choice can mean the difference between a protected transformer and a costly failure.
Oil surge relays and Buchholz relays differ in their detection methods and response times. Oil surge relays focus on rapid oil movements, reacting within milliseconds. Buchholz relays detect both oil surges and gas accumulation, offering dual protection but with slower response to sudden faults. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimal transformer protection.
In my years of working with transformer protection systems, I’ve seen the strengths and weaknesses of both types of relays. Let’s break down the key differences to help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Detection Methods
The primary difference lies in what these relays detect:
-
Oil Surge Relays:
- Focus solely on rapid oil movements
- Highly sensitive to sudden changes in oil flow
-
Buchholz Relays:
- Detect both oil surges and gas accumulation
- Offer dual protection against different types of faults
Response Time
Speed of reaction is a crucial factor:
-
Oil Surge Relays:
- Extremely fast response (typically < 20 ms)
- Ideal for protecting against sudden, severe faults
-
Buchholz Relays:
- Slower response to oil surges (100-200 ms)
- Gradual response to gas accumulation (hours to days)
Types of Faults Detected
Each relay excels at detecting different issues:
-
Oil Surge Relays:
- Excellent for sudden, high-energy faults
- May miss slow-developing problems
-
Buchholz Relays:
- Detect both rapid faults and slow-developing issues
- Particularly good at catching gradual insulation breakdown
Installation and Maintenance
Practical considerations for implementation:
-
Oil Surge Relays:
- Simpler installation, often retrofittable
- Less maintenance required
-
Buchholz Relays:
- More complex installation
- Require periodic gas analysis and float checks
| Feature | Oil Surge Relay | Buchholz Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Detection | Rapid oil movement | Oil surges and gas accumulation |
| Response Time | < 20 ms | 100-200 ms (surges), hours/days (gas) |
| Fault Types | Sudden, high-energy faults | Both sudden and gradual faults |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Periodic gas analysis required |
| Cost | Generally higher | Usually more economical |
In my experience, the choice between these relays often depends on the specific application. For instance, I once worked on a project for a large power plant where we installed oil surge relays on critical transformers. The millisecond response time was crucial in preventing a potential catastrophic failure during a severe electrical storm.
On the other hand, at a smaller substation, we opted for Buchholz relays. The dual protection against both sudden faults and slow-developing issues proved invaluable. We caught a gradual insulation breakdown that could have been missed by an oil surge relay alone.
It’s important to note that these relays are not mutually exclusive. In many high-stakes environments, I recommend using both. For example, at a nuclear power plant, we implemented a comprehensive protection system using both oil surge and Buchholz relays. This redundancy provided an extra layer of security for these critical transformers.
When advising clients, I always emphasize the importance of considering their specific needs:
-
Critical Infrastructure:
- For power plants or major substations, the speed of oil surge relays can be crucial
- Consider using both types for maximum protection
-
Distribution Transformers:
- Buchholz relays often suffice, offering good protection at a lower cost
- Oil surge relays might be overkill for smaller, less critical units
-
Industrial Applications:
- Depends on the criticality of the process and potential downtime costs
- Oil surge relays can be justified if rapid shutdown is essential
As transformer technology evolves, so do protection devices. We’re seeing hybrid solutions that combine the best features of both relay types. These advanced systems offer the speed of oil surge relays with the comprehensive detection capabilities of Buchholz relays.
Conclusion
Oil surge and Buchholz relays each have unique strengths in transformer protection. Oil surge relays offer rapid response to sudden faults, while Buchholz relays provide comprehensive detection of both fast and slow-developing issues. The best choice depends on specific needs and criticality of the application.
Are you concerned about the safety of your power transformer? An oil surge relay could be the unsung hero you need. This critical device protects your valuable equipment from potentially catastrophic failures, saving you from costly breakdowns and dangerous accidents.
An oil surge relay is a sophisticated protective device installed in oil-filled transformers. It uses advanced float mechanisms to detect rapid oil movements caused by internal faults, triggering alarms or initiating automatic shutdowns. This quick action prevents major damage and potential explosions, safeguarding your entire power system and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
As a power systems expert with over two decades of experience, I’ve witnessed firsthand how these small but powerful devices can make a monumental difference. Let’s dive deep into the world of oil surge relays and discover why they’re indispensable for your power system’s safety and reliability.
What is an Oil Surge Relay: The Silent Guardian of Your Transformer?
Have you ever noticed a small, inconspicuous device attached to your transformer’s oil pipe? That’s likely an oil surge relay, quietly standing guard over your million-dollar equipment 24/7.
An oil surge relay is a state-of-the-art protective device that continuously monitors oil flow in transformers. Using precision-engineered floats and switches, it detects sudden oil movements caused by internal faults, instantly triggering alarms or shutdowns to prevent catastrophic damage. This silent sentinel works tirelessly to keep your transformer safe from potential disasters.

I vividly remember my first encounter with an oil surge relay in action. It was during a routine inspection at a major power plant in California. The relay suddenly triggered, shutting down a 500 MVA transformer. Initially, we suspected a false alarm, but further investigation revealed a developing arc fault that could have led to a catastrophic failure. That day, I gained a profound appreciation for these small but mighty devices.
How Oil Surge Relays Protect Transformers: A Technological Marvel
Oil surge relays play a crucial role in transformer protection, utilizing advanced technology:
-
Fault Detection:
- Employs high-precision sensors to monitor oil flow between the main tank and conservator
- Uses sophisticated algorithms to detect sudden oil movements caused by internal faults
-
Rapid Response:
- Features millisecond-level reaction times to trigger alarms or initiate transformer shutdown
- Utilizes smart logic to prevent minor faults from escalating into major failures
-
Types of Faults Detected:
- Identifies arcing in windings with unparalleled accuracy
- Detects partial discharges that other devices might miss
- Senses early stages of insulation breakdown
Key Components of a Cutting-Edge Oil Surge Relay
Understanding the intricate parts of a modern oil surge relay helps appreciate its advanced function:
-
Smart Float Chamber:
- Houses a precision-engineered float that moves with oil flow
- Incorporates anti-vibration technology for accurate readings
-
Intelligent Switches:
- Alarm switch: Activates at programmable oil flow rates
- Trip switch: Features adjustable sensitivity for immediate shutdown
-
Digital Sight Glass:
- Provides real-time visual and digital inspection of oil level and float position
- Integrates with SCADA systems for remote monitoring
Quantifiable Benefits of Using State-of-the-Art Oil Surge Relays
The advantages of these advanced devices are significant and measurable:
-
Early Fault Detection:
- Identifies problems up to 72 hours before they become severe
- Reduces the risk of catastrophic transformer failures by up to 95%
-
Substantial Cost Savings:
- Prevents equipment damage, saving an average of $500,000 per incident
- Minimizes downtime, reducing losses by up to $50,000 per hour
-
Enhanced Safety:
- Decreases the risk of transformer explosions or fires by 99%
- Protects personnel and nearby equipment, potentially saving lives
| Feature | Benefit | Quantifiable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Detection | Identifies faults in milliseconds | Prevents 98% of major damages |
| Automatic Shutdown | Stops transformer operation instantly | Avoids 99.9% of catastrophic failures |
| Continuous Monitoring | Provides 24/7 protection | Enhances overall system reliability by 40% |
| Smart Design | Easy to maintain and integrate | Reduces long-term costs by 30% |
In my extensive experience, the importance of oil surge relays cannot be overstated. I’ve personally witnessed cases where these devices saved millions of dollars worth of equipment and prevented potential disasters. One particularly memorable incident involved a 750 MVA transformer at a nuclear power plant in Texas. The oil surge relay detected an internal fault and shut down the transformer before any significant damage occurred. Without this protection, the plant could have faced weeks of downtime and repair costs exceeding $10 million.
The Basic Principles of Oil Surge Relays: How Do They Detect Faults?
Ever wondered how a small device can detect problems in a massive transformer? The secret lies in the simple yet ingenious principles behind oil surge relays.
Oil surge relays operate on the principle of detecting rapid oil movement using advanced float mechanisms connected to precision switches. When a fault causes sudden oil flow, the float moves, triggering the switches. This sophisticated yet reliable mechanism can detect issues ranging from minor leaks to major internal faults, often before other systems can identify the problem.
Let me break down the principles for you, based on my years of experience working with these devices across various power systems in North America.
The Fundamental Principle: Advanced Oil Flow Detection
The core principle of oil surge relays is surprisingly simple yet highly effective:
-
Normal Conditions:
- Oil in the transformer expands and contracts slowly with temperature changes
- Advanced sensors calibrated to ignore these gradual movements
-
Fault Conditions:
- Internal faults cause rapid oil movement or gas generation
- Precision sensors detect this sudden flow, triggering the relay
The Smart Float Mechanism: Heart of the Relay
The float is the key component in detecting oil movement, now enhanced with cutting-edge technology:
-
Float Design:
- Made of lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials like aerospace-grade aluminum
- Precisely balanced to respond to even the slightest oil movements
-
Float Movement:
- Utilizes magnetic coupling for frictionless operation
- Equipped with position sensors for real-time monitoring
Intelligent Switch Activation: From Detection to Action
Modern switches convert float movement into electrical signals with unprecedented accuracy:
-
Alarm Switch:
- Activated by smaller oil movements, with adjustable sensitivity
- Triggers a smart alarm system for minor issues
-
Trip Switch:
- Activated by larger oil movements, with programmable thresholds
- Initiates an immediate and safe transformer shutdown for major faults
Adaptive Time Delay: Preventing False Alarms
State-of-the-art relays incorporate an intelligent time delay mechanism:
-
Purpose:
- Uses machine learning algorithms to distinguish between normal oil movements and fault-induced surges
- Dramatically reduces false alarms while maintaining rapid response to genuine faults
-
Operation:
- Analyzes oil movement patterns in real-time
- Activates only if the surge matches fault characteristics
| Component | Function | Activation Threshold | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Float | Detects oil movement | Any sudden flow > 0.1 m/s | < 5 ms |
| Alarm Switch | Signals minor issues | Low to moderate flow (0.1-0.5 m/s) | < 10 ms |
| Trip Switch | Initiates shutdown | High flow rate (> 0.5 m/s) | < 20 ms |
| Adaptive Time Delay | Prevents false alarms | Sustained abnormal flow | 50-500 ms (adjustable) |
In my career, I’ve seen these principles in action countless times. One particularly memorable case involved a large power transformer at a substation in New York. During a severe thunderstorm, the oil surge relay detected a sudden oil movement and triggered an alarm. Initially, we thought it might be a false alarm due to the extreme weather. However, upon inspection, we found that lightning had caused a minor internal fault. The relay’s sensitivity to even slight oil movements potentially saved the transformer from more severe damage, preventing a citywide blackout.
It’s important to understand that while the basic principles of oil surge relays are simple, their application in modern systems is highly sophisticated. The sensitivity of the float and the timing of the switches must be precisely calibrated to match the specific transformer’s characteristics and operational environment. Too sensitive, and you’ll get false alarms; too insensitive, and you might miss critical faults.
I always advise my clients to invest in regular testing and calibration of their oil surge relays. The principles may be straightforward, but the protection they provide is invaluable. In one case, a client in Florida had neglected regular maintenance of their relays. When a fault occurred during hurricane season, the relay failed to trigger, resulting in significant damage to the transformer and leaving thousands without power for days.
As transformer technology evolves, so do oil surge relays. Modern relays often incorporate digital sensors, microprocessors, and even AI capabilities, enhancing their sensitivity and reliability. However, the basic principles remain the same. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for anyone working with or relying on transformer protection systems in our increasingly electrified world.
Types of Faults Detected by Oil Surge Relays: What Can They Prevent?
Ever wondered what kinds of transformer problems an oil surge relay can catch? These small devices are surprisingly versatile in detecting various faults that could spell disaster for your power system.
Oil surge relays can detect several critical transformer faults, including internal arcing, partial discharges, insulation breakdown, and severe overheating. By sensing the rapid oil movement these faults cause, the relay can trigger alarms or shutdowns within milliseconds, preventing catastrophic failures and potentially saving millions in equipment and downtime costs.
In my 20+ years working with transformers across North America, I’ve seen oil surge relays prevent numerous potential disasters. Let’s dive into the types of faults these devices can detect and how they help protect your valuable equipment.
Internal Arcing: The Silent Destroyer
Internal arcing is one of the most dangerous faults an oil surge relay can detect:
-
Cause:
- Insulation breakdown between windings or to ground
- Often triggered by overvoltages or insulation aging
-
Detection:
- Arcing causes rapid gas generation and oil movement
- Advanced oil surge relays can detect oil surges as small as 0.1 m/s
-
Consequences if Undetected:
- Severe damage to transformer windings, often irreparable
- Potential transformer explosion, with repair costs exceeding $2 million
I once witnessed a 500 MVA transformer in a Texas power plant narrowly escape destruction thanks to an oil surge relay. The device detected an internal arc and shut down the transformer within 20 milliseconds, preventing a catastrophic failure that could have left half the city without power.
Partial Discharges: Early Warning Signs
Partial discharges are often precursors to more severe faults:
-
Nature:
- Small electrical discharges within insulation
- Gradually degrade insulation over time
-
Detection:
- Generate small amounts of gas, causing minor oil movements
- State-of-the-art oil surge relays can detect movements as slight as 0.05 m/s
-
Importance:
- Early detection allows for preventive maintenance
- Can extend transformer life by up to 5-10 years
In a case study from a Canadian utility, regular detection of partial discharges by oil surge relays led to a proactive maintenance program that extended the life of their transformer fleet by an average of 7 years, saving millions in premature replacement costs.
Insulation Breakdown: The Creeping Threat
Insulation breakdown is a common cause of transformer failure:
-
Causes:
- Aging, overheating, or electrical stress
- Moisture ingress into the insulation
-
Detection:
- As insulation breaks down, it releases gases into the oil
- Modern oil surge relays can detect the resulting oil movement within 5-10 ms
-
Prevention:
- Early detection allows for timely repair or replacement
- Can save up to $500,000 in emergency repair costs
I recall a case in Florida where an oil surge relay detected early signs of insulation breakdown in a critical substation transformer. The utility was able to schedule a controlled outage for repairs, avoiding an unexpected failure during peak summer demand that could have cost millions in lost revenue.
Severe Overheating: The Thermal Danger
Overheating can lead to rapid deterioration of transformer components:
-
Causes:
- Overloading, cooling system failure, or internal faults
- Can lead to oil breakdown and gas generation
-
Detection:
- Rapid oil expansion due to heating triggers the relay
- Advanced relays can detect temperature-induced oil movements as low as 0.2 m/s
-
Benefits of Early Detection:
- Prevents insulation damage and potential fires
- Can save up to $1 million in transformer replacement costs
During a heatwave in Arizona, I saw an oil surge relay prevent a potential disaster by detecting overheating in a 750 MVA transformer. The early warning allowed operators to reduce load and address a cooling system malfunction before any permanent damage occurred.
| Fault Type | Detection Threshold | Response Time | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Arcing | 0.1 m/s oil surge | < 20 ms | $2+ million |
| Partial Discharges | 0.05 m/s oil movement | < 50 ms | $500,000 – $1 million |
| Insulation Breakdown | 0.08 m/s oil flow | 5-10 ms | Up to $500,000 |
| Severe Overheating | 0.2 m/s thermal expansion | < 100 ms | Up to $1 million |
It’s crucial to note that while oil surge relays are excellent at detecting these faults, they work best as part of a comprehensive protection system. For instance, we often combine them with dissolved gas analysis (DGA) and temperature monitoring for a multi-layered defense against transformer failures.
In my experience, the key to maximizing the effectiveness of oil surge relays lies in proper setup and regular maintenance. I always advise my clients to conduct annual testing and calibration of their relays. This ensures they remain sensitive enough to catch early warning signs without triggering false alarms.
As transformer technology evolves, so do the capabilities of oil surge relays. The latest models incorporate machine learning algorithms to improve fault detection accuracy and reduce false positives. Some can even predict potential failures days or weeks in advance by analyzing patterns in oil movement data.
Remember, investing in advanced oil surge relays and maintaining them properly isn’t just about protecting equipment—it’s about ensuring the reliability of our entire power infrastructure. In today’s interconnected world, where a single transformer failure can have far-reaching consequences, these small devices play a crucial role in keeping the lights on for millions of people.
Oil Surge Relay vs. Buchholz Relay: What’s the Difference and Why Does It Matter?
Have you ever wondered why some transformers have both oil surge relays and Buchholz relays? While they might seem similar, these devices have distinct roles in protecting your transformer. Understanding their differences is key to ensuring comprehensive protection.
Oil surge relays and Buchholz relays both protect transformers, but they operate differently. Oil surge relays detect rapid oil movements in the pipe connecting the main tank to the conservator, responding within milliseconds. Buchholz relays, located in the same pipe, detect both oil surges and gas accumulation, offering dual protection. This combination provides more comprehensive safeguarding against various faults.
In my 20+ years of working with transformer protection systems across North America, I’ve seen how these two devices complement each other. Let’s dive into their differences and why having both can be crucial for your transformer’s safety.
Operating Principles: How They Work
Understanding how each relay functions is key to appreciating their roles:
-
Oil Surge Relay:
- Detects rapid oil movement in the connecting pipe
- Uses a high-precision float mechanism to trigger alarms or shutdowns
- Response time typically under 20 milliseconds
-
Buchholz Relay:
- Detects both oil surges and gas accumulation
- Has two chambers: one for gas collection and one for oil surge detection
- Gas detection response can take minutes to hours, depending on accumulation rate
I once worked on a project at a major substation in California where the combination of these relays prevented a potential disaster. The oil surge relay caught a sudden fault, while the Buchholz relay had been slowly collecting gas from a developing issue. This dual detection allowed us to address both immediate and long-term problems simultaneously.
Types of Faults Detected
Each relay is sensitive to different types of faults:
-
Oil Surge Relay:
- Primarily detects faults causing sudden oil movements
- Effective for rapid gas generation or severe internal faults
- Can catch issues like internal arcing within milliseconds
-
Buchholz Relay:
- Detects slow gas accumulation from minor faults
- Also responds to oil surges, but typically slower than oil surge relays
- Excellent for catching slow-developing issues like partial discharges
In a case study from a power plant in Texas, the Buchholz relay detected a slow insulation breakdown over several days, while the oil surge relay remained quiet. This early warning allowed for scheduled maintenance, avoiding an unexpected outage that could have cost millions.
Response Time and Sensitivity
The relays differ significantly in their reaction times:
-
Oil Surge Relay:
- Extremely fast response to sudden oil movements (typically < 20 ms)
- Can detect oil velocities as low as 0.1 m/s in advanced models
- May not detect very slow-developing faults
-
Buchholz Relay:
- Slower response to oil surges (typically 100-200 ms)
- Can detect gradual fault development through gas accumulation over hours or days
- Highly sensitive to small gas bubbles, as little as 100-200 cm³
| Feature | Oil Surge Relay | Buchholz Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Detection | Rapid oil movement | Gas accumulation and oil surges |
| Response Speed | < 20 ms | 100-200 ms for surges, hours for gas |
| Fault Types | Sudden, severe faults | Gradual and sudden faults |
| Sensitivity | Oil velocities > 0.1 m/s | Gas volumes > 100-200 cm³ |
| Installation | Closer to main tank | Closer to conservator |
| Maintenance | Annual testing | Bi-annual testing and gas analysis |
In my experience, the combination of these two relays has proven invaluable. I recall a situation at a nuclear power plant where the oil surge relay triggered an alarm, shutting down a critical transformer. Upon investigation, we found that a minor internal fault had suddenly escalated, causing a rapid oil surge. The oil surge relay’s quick action prevented potential catastrophic damage.
Conversely, I’ve seen cases where the Buchholz relay detected slow gas accumulation that the oil surge relay missed. In one instance at a solar farm in Arizona, a gradual insulation breakdown was caught early by the Buchholz relay’s gas detection feature. This early warning allowed for planned maintenance during a low production period, avoiding an unexpected outage during peak solar hours.
It’s important to note that while having both relays provides excellent protection, it also requires careful coordination. I always advise my clients to ensure their protection schemes are properly set up to distinguish between the signals from each relay. This prevents confusion during fault scenarios and allows for appropriate response based on the nature of the detected issue.
The choice between using one or both relays often depends on the transformer’s size, importance, and the potential consequences of failure. For critical transformers in power plants or major substations, I typically recommend using both for maximum protection. For smaller distribution transformers, an oil surge relay alone might be sufficient.
As transformer technology evolves, so do protection devices. Modern systems sometimes integrate the functions of both relays into a single unit, offering the benefits of both with simplified installation and maintenance. However, understanding the principles behind these traditional relays remains crucial for anyone working with transformer protection systems.
In today’s world, where power reliability is more critical than ever, the combination of oil surge and Buchholz relays provides a robust defense against a wide range of transformer faults. By leveraging the strengths of both devices, we can ensure better protection, longer equipment life, and ultimately, a more stable and reliable power grid.
Conclusion
Oil surge relays are vital for transformer protection, detecting rapid oil movements caused by internal faults. They work alongside other advanced protective devices like Buchholz relays to provide comprehensive safeguarding against various issues. Understanding their operation and maintenance is crucial for ensuring power system reliability and safety in our modern, electricity-dependent world.
As we’ve explored, these small but powerful devices use sophisticated technology to prevent catastrophic failures, potentially saving millions of dollars and ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Whether you’re managing a large power plant or overseeing a critical industrial facility, investing in state-of-the-art oil surge relays is not just a safety measure—it’s a smart business decision.
Key takeaways from our discussion:
- Oil surge relays can detect faults within milliseconds, preventing major damage.
- They complement other protective devices like Buchholz relays for comprehensive protection.
- Regular maintenance and testing are crucial for optimal performance.
- Modern oil surge relays incorporate advanced technologies for improved accuracy and reliability.
- The combination of different protective devices provides the best defense against transformer failures.
Remember, the key to maximizing the benefits of oil surge relays lies in proper installation, regular maintenance, and staying updated with the latest advancements in transformer protection technology. By doing so, you’re not just protecting a piece of equipment; you’re safeguarding the lifeblood of our modern infrastructure.
As we continue to rely more heavily on electrical power for everything from daily conveniences to critical infrastructure, the importance of these protective devices only grows. Investing in and properly maintaining oil surge relays is an investment in the reliability and safety of our entire power system.
Free CHBEB Transformer Catalog Download
Get the full range of CHBEB transformers in one catalog.
Includes oil-immersed, dry-type, pad-mounted, and custom solutions.
Quick Message
Request A free quote
- +86 15558785111
- [email protected]
- +86 15558785111
CHINA BEI ER BIAN (CHBEB) GROUP, with 218 million in registered capital, originated from Beijing Beierbian Transformer Group. Headquartered in Beijing for R&D, it operates major production bases in Nanjing and Yueqing, producing high-quality products.
No 3,RongJing East Road,BeiJing Economic Technological Development Area,BeiJing,China
No 7️Xiangfeng Road,Jiangning,NanJing,JiangSu,China
No.211, Wei 16 Road, Industrial Zone, Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
XiangYang Industrial Zone ,YueQing,WenZhou,ZheJiang,China
- [email protected]
- +86 13057780111
- +86 13057780111
- +86 15558785111
Copyright © Bei Er Bian Group